Please play the leading role: event mechanism in Spring
Yes, this section mainly talks about the event mechanism in Spring: ApplicationEventPublisher, which monitors ApplicationEvent, and finally uses event notification to realize asynchronous operation
1. Why implement asynchronous operations
- In the case of microservices, multiple services call each other, which is time-consuming. When we don't need this operation to return, we can execute asynchronously and call the interface. The interface returns quickly to reduce the response time of the interface.
- The logic of the code is clear. For those requiring multiple asynchronous operations, the unified management of events can be realized without creating a thread pool to reduce the consumption of resources
2. What can be executed asynchronously in the programming process
- All time-consuming functions that do not need to return
- For example, log recording, email sending, SMS and other operations
Code display (first actual combat, then principle)
If we have a demand now, buy member operation! Let's first analyze the specific steps:
1. Add the user in the member user list (representing that the user already has a member ID)
2. Send interests of specific members
3. Add points to users
4. Send SMS notification
If there are the above four steps, we can send SMS notification as an asynchronous operation.
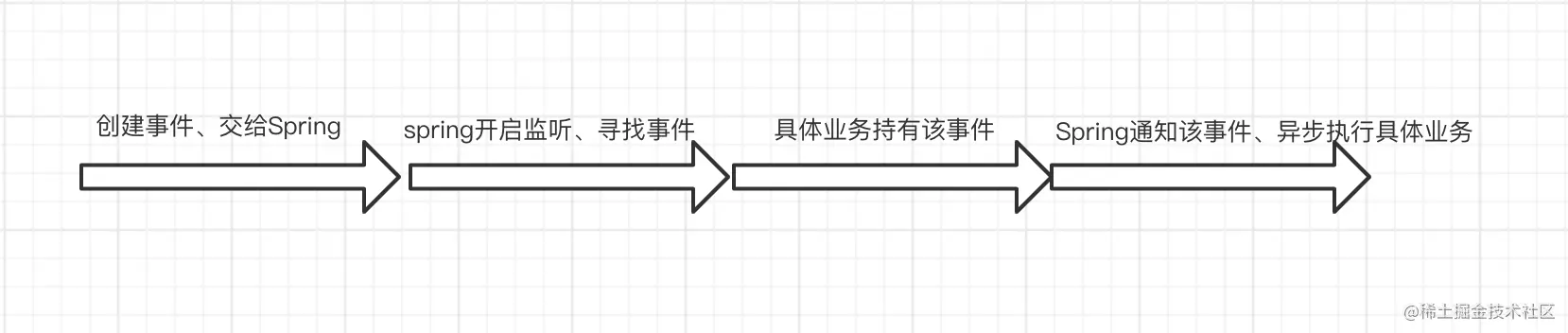
The first step is to create an event
public class SendMessageEvent extends ApplicationEvent { private SendMessageEventDto sendMessageEventDto; public SendMessageEvent(Object source) { super(source); } public SendMessageEvent(Object source,SendMessageEventDto dto){ super(source); this.sendMessageEventDto = dto; } public SendMessageEventDto getDto(){ return sendMessageEventDto; } public void setDto(SendMessageEventDto dto){ this.sendMessageEventDto = dto; } public class SendMessageEventDto{ /** * cell-phone number */ private Integer userId; /** * cell-phone number */ private String mobile; /** * SMS template parameter data body */ private String data; public String getMobile() { return mobile; } public void setMobile(String mobile) { this.mobile = mobile; } public String getData() { return data; } public void setData(String data) { this.data = data; } public Integer getUserId() { return userId; } public void setUserId(Integer userId) { this.userId = userId; } } }
In the above code, first define an entity for sending SMS (SendMessageEventDto), and hand this entity to the defined event management (SendMessageEvent), which inherits the ApplicationEvent of spring
Step 2: publish the event through spring, and spring will listen to the event
@Autowired private ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher; /** * Assemble data body and send SMS asynchronously * @param mobile cell-phone number * @param userId User ID * @param jsonObject Parameters required for SMS */ public void publishMessage(String mobile,Integer userId,JSONObject jsonObject){ SendMessageEvent event = new SendMessageEvent(this); SendMessageEvent.SendMessageEventDto dto = event.new SendMessageEventDto(); dto.setData(jsonObject.toString()); //Data body of specific business dto.setMobile(mobile); dto.setUserId(userId); event.setDto(dto); //Hand over the event to spring monitor applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(event); }
Step 3: let the specific business hold the event and set the monitored status
public interface SendMessageEventListener { //Send SMS void sendMessage(SendMessageEvent sendMessageEvent); }
@Component public class SendMessageEventListenerImpl implements SendMessageEventListener { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SendMessageEventListenerImpl.class); @Autowired private MiniProgramClient miniProgramClient; @Override @Async @EventListener public void sendMessage(SendMessageEvent sendMessageEvent) { try { SendMessageEvent.SendMessageEventDto dto = sendMessageEvent.getDto(); logger.error("Send SMS notification start -> The data body is -> "+ JSON.toJSONString(dto)); MarketMessageDto messageDto = new MarketMessageDto(); messageDto.setUserId(dto.getUserId()); messageDto.setData(dto.getData()); messageDto.setMobile(dto.getMobile()); //Call SMS service and send SMS miniProgramClient.sendMarketMsg(messageDto); }catch (Exception e){ e.getMessage(); e.printStackTrace(); } } }
Special attention should be paid here that @ EventListener must be added to the method to be monitored, and then asynchronous @ Async must be enabled
Demo call, done
public static void main(String[] args) { //Create member logic start //1,Create member user //2,Send membership benefits //3,Add points to users //4 Send SMS publishMessage("176********",7465388,Of specific business parameters json) //Return results return "Successfully opened member"; }
OK, you're done here. The whole process is like this. In this way, when you add points to the user, you can directly return success without waiting for the operation of sending SMS.
Special note: if it is used in the springBoot project, the annotation @ EnableAsync needs to be added to the startup class
Reprint of self digging gold blog:
https://juejin.cn/post/6985049438540529694