
In actual production projects, it is often necessary to encrypt and store sensitive data such as ID card information, mobile phone number, real name, etc. in the database, but manual encryption and decryption of sensitive information in the business code is not elegant, and there may even be wrong encryption, missing encryption, and business personnel need to know the actual encryption rules.
This article will introduce the detailed process of intercepting and encrypting sensitive data before storage in the form of springboot+mybatis interceptor + custom annotation.
1, What is Mybatis Plugin
In the official document of mybatis, the introduction of Mybatis plugin is as follows:
MyBatis allows you to intercept calls at some point during the execution of mapped statements. By default, MyBatis allows the use of plug-ins to intercept method calls, including:
//Statement execution interception Executor (update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed) // Intercept during parameter acquisition and setting ParameterHandler (getParameterObject, setParameters) // Intercept the returned results ResultSetHandler (handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters) //sql statement interception StatementHandler (prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query)
In short, in the whole cycle of executing sql, we can cut into a certain point to deal with the parameters of sql, the result set of sql execution, the sql statement itself and so on. Based on this feature, we can use it to uniformly encrypt the data we need to encrypt (this is how the paging plug-in pageHelper implements the database paging query).
2, Implement the encryption and decryption interceptor of sensitive information based on annotation
2.1 implementation ideas
For data encryption and decryption, there should be two interceptors to intercept the data
Refer to the official documents, so here we should use the ParameterHandler interceptor to encrypt the incoming parameters
Decrypt the output parameter using the ResultSetHandler interceptor.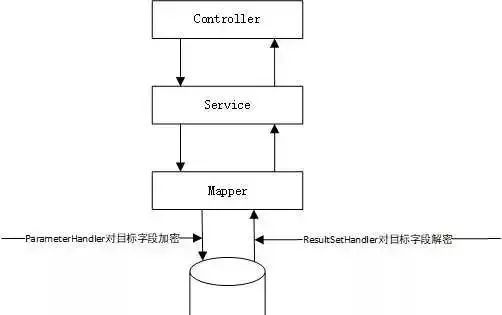 The fields to be encrypted and decrypted by the target may need to be changed flexibly. At this time, we define an annotation to annotate the fields to be encrypted, so we can cooperate with the interceptor to encrypt and decrypt the required data.
The fields to be encrypted and decrypted by the target may need to be changed flexibly. At this time, we define an annotation to annotate the fields to be encrypted, so we can cooperate with the interceptor to encrypt and decrypt the required data.
The interceptor interface of mybatis has the following methods to be implemented.
public interface Interceptor {
//Main parameters interception method
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
//mybatis plug-in chain
default Object plugin(Object target) {return Plugin.wrap(target, this);}
//Custom plug-in profile method
default void setProperties(Properties properties) {}
}
2.2 notes for defining sensitive information to be encrypted and decrypted
Define annotations for sensitive information classes (such as entity class POJOPO)
/**
* Annotation of sensitive information class
*/
@Inherited
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface SensitiveData {
}
Annotation for defining sensitive fields in sensitive information class
/**
* Annotation of sensitive fields in sensitive information class
*/
@Inherited
@Target({ ElementType.Field })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface SensitiveField {
}
2.3 define encryption interface and its implementation class
Define the encryption interface to facilitate the expansion of encryption methods in the future (for example, the expansion of AES encryption algorithm supports PBE algorithm, which only needs to be specified during injection)
public interface EncryptUtil {
/**
* encryption
*
* @param declaredFields paramsObject Declared fields
* @param paramsObject mapper Instance of paramtype in
* @return T
* @throws IllegalAccessException Field inaccessible exception
*/
<T> T encrypt(Field[] declaredFields, T paramsObject) throws IllegalAccessException;
}
EncryptUtil's AES encryption implementation class. Here AESUtil is a self encapsulated AES encryption tool, which can be encapsulated by small partners. It is not provided in this article. (search for official account number Java, reply, "2021", send you a Java interview question treasure).
@Component
public class AESEncrypt implements EncryptUtil {
@Autowired
AESUtil aesUtil;
/**
* encryption
*
* @param declaredFields paramsObject Declared fields
* @param paramsObject mapper Instance of paramtype in
* @return T
* @throws IllegalAccessException Field inaccessible exception
*/
@Override
public <T> T encrypt(Field[] declaredFields, T paramsObject) throws IllegalAccessException {
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
//Retrieve all fields annotated by EncryptDecryptField
SensitiveField sensitiveField = field.getAnnotation(SensitiveField.class);
if (!Objects.isNull(sensitiveField)) {
field.setAccessible(true);
Object object = field.get(paramsObject);
//For the time being, only String type encryption is implemented
if (object instanceof String) {
String value = (String) object;
//Encryption here I use the custom AES encryption tool
field.set(paramsObject, aesUtil.encrypt(value));
}
}
}
return paramsObject;
}
}
2.4 implementation of incoming secret interceptor
Org. In Myabtis package apache. ibatis. plugin. The interceptor interceptor interface requires us to implement the following three methods
public interface Interceptor {
//Core interception logic
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
//Interceptor chain
default Object plugin(Object target) {return Plugin.wrap(target, this);}
//Custom profile actions
default void setProperties(Properties properties) { }
}
Therefore, referring to the example in the official document, we customize an incoming secret interceptor.
@The Intercepts annotation enables the interceptor, and the @ Signature annotation defines the actual type of the interceptor.
@In Signature
The type attribute specifies that the current interceptor uses StatementHandler, ResultSetHandler and ParameterHandler. A method attribute of the Executor specifies the specific methods of the above four types (you can view their methods inside the class). The args attribute specifies the precompiled statement. Here we use ParameterHandler Setparamters() method, intercepting mapper Instance of paramsType in XML (that is, execute the interceptor in every mapper statement containing paramsType attribute to intercept the instance of paramsType)
/**
* Encryption interceptor
* Note that the @ Component annotation must be added
*
* @author : tanzj
* @date : 2020/1/19.
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = ParameterHandler.class, method = "setParameters", args = PreparedStatement.class),
})
public class EncryptInterceptor implements Interceptor {
private final EncryptDecryptUtil encryptUtil;
@Autowired
public EncryptInterceptor(EncryptDecryptUtil encryptUtil) {
this.encryptUtil = encryptUtil;
}
@Override
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
//@After type= parameterHandler is specified in the Signature, the invocation here Gettarget () is parameterHandler
//If ResultSetHandler is specified, it can be forcibly converted to ResultSetHandler here
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) invocation.getTarget();
// Get the parameter object, that is, the instance of paramsType in mapper
Field parameterField = parameterHandler.getClass().getDeclaredField("parameterObject");
parameterField.setAccessible(true);
//Take out the instance
Object parameterObject = parameterField.get(parameterHandler);
if (parameterObject != null) {
Class<?> parameterObjectClass = parameterObject.getClass();
//Verify whether the class of this instance is annotated by @ SensitiveData
SensitiveData sensitiveData = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(parameterObjectClass, SensitiveData.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(sensitiveData)) {
//Take out all fields of the current class and pass in the encryption method
Field[] declaredFields = parameterObjectClass.getDeclaredFields();
encryptUtil.encrypt(declaredFields, parameterObject);
}
}
return invocation.proceed();
}
/**
* Remember to configure, otherwise the current interceptor will not join the interceptor chain
*/
@Override
public Object plugin(Object o) {
return Plugin.wrap(o, this);
}
//Write custom configuration. If there is no custom configuration, this method can be directly blank
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
}
This completes the custom encryption interception encryption.
2.5 define decryption interface and its implementation class
Decrypt the interface, where result is mapper An instance of resultType in XML.
public interface DecryptUtil {
/**
* decrypt
*
* @param result resultType Examples of
* @return T
* @throws IllegalAccessException Field inaccessible exception
*/
<T> T decrypt(T result) throws IllegalAccessException;
}
Decryption interface AES tool decryption implementation class
public class AESDecrypt implements DecryptUtil {
@Autowired
AESUtil aesUtil;
/**
* decrypt
*
* @param result resultType Examples of
* @return T
* @throws IllegalAccessException Field inaccessible exception
*/
@Override
public <T> T decrypt(T result) throws IllegalAccessException {
//Get the class of resultType
Class<?> resultClass = result.getClass();
Field[] declaredFields = resultClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
//Retrieve all fields annotated by EncryptDecryptField
SensitiveField sensitiveField = field.getAnnotation(SensitiveField.class);
if (!Objects.isNull(sensitiveField)) {
field.setAccessible(true);
Object object = field.get(result);
//Only decryption of String is supported
if (object instanceof String) {
String value = (String) object;
//Decrypt the annotated fields one by one
field.set(result, aesUtil.decrypt(value));
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
2.6 define parameter decryption interceptor
@Slf4j
@Component
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = ResultSetHandler.class, method = "handleResultSets", args = {Statement.class})
})
public class DecryptInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Autowired
DecryptUtil aesDecrypt;
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
//Retrieve the results of the query
Object resultObject = invocation.proceed();
if (Objects.isNull(resultObject)) {
return null;
}
//selectList based
if (resultObject instanceof ArrayList) {
ArrayList resultList = (ArrayList) resultObject;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(resultList) && needToDecrypt(resultList.get(0))) {
for (Object result : resultList) {
//Decrypt one by one
aesDecrypt.decrypt(result);
}
}
//Based on selectOne
} else {
if (needToDecrypt(resultObject)) {
aesDecrypt.decrypt(resultObject);
}
}
return resultObject;
}
private boolean needToDecrypt(Object object) {
Class<?> objectClass = object.getClass();
SensitiveData sensitiveData = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(objectClass, SensitiveData.class);
return Objects.nonNull(sensitiveData);
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
}
So far, the configuration of decryption interceptor is completed.
3. Annotate the fields to be encrypted and decrypted in the entity class
 At this time, specify paramType=User resultType=User in mapper to realize the encryption and decryption operation based on mybatis interceptor.
At this time, specify paramType=User resultType=User in mapper to realize the encryption and decryption operation based on mybatis interceptor.
END

Previous recommendation
In the future, APP is all for one person
A programmer gets an offer and doubles his salary. Do you want to go? Netizen: programming for Yama
