catalogue
1 why look at this source code
1.1 since it is a thread class, let's see thread Find in C
1.2 since it is jvm, it is in jvm Line 2817 interrupted on CPP
5java_ Where is the start method? os_linux.cpp 806 OK, let's see what this method is doing
6 remember where the thread was created? jvm.cpp 2851, let's go down to 2884
1 why look at this source code
-
Be familiar with the source code and know the underlying friends. We usually write the start method, and we will call the run method anyway. Unreliable source code always feels vague and unreliable.
-
As a thread startup process, it is also a part of the main thread startup process, because main itself is also a thread. Last time, we talked about the main startup process. Combing the thread process again is also regarded as consolidating knowledge.
2. debug steps
1.1 since it is a thread class, let's see thread Find in C
1.2 since it is jvm, it is in jvm Line 2817 was interrupted on CPP
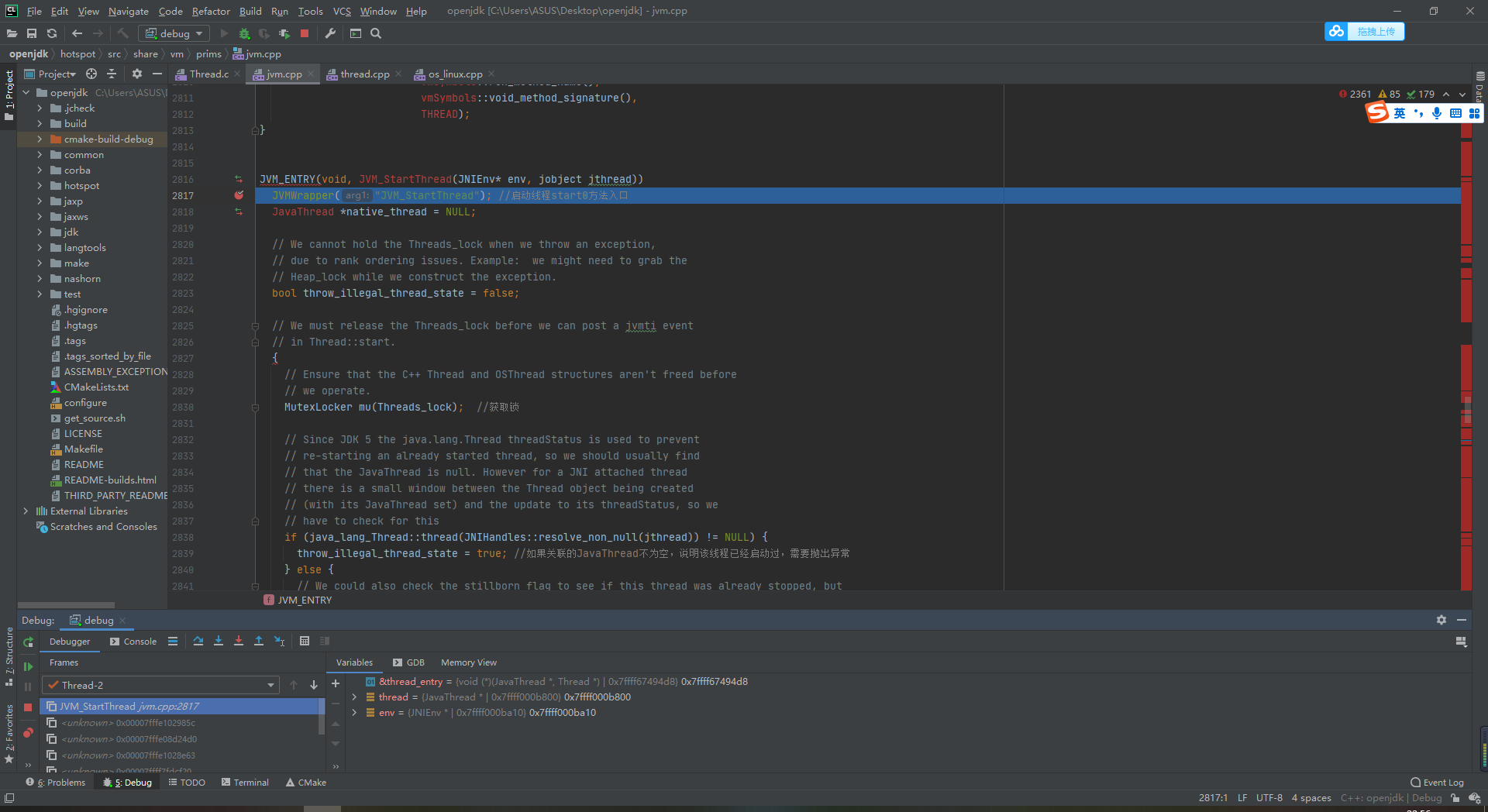
-
3 we jump to line 2851
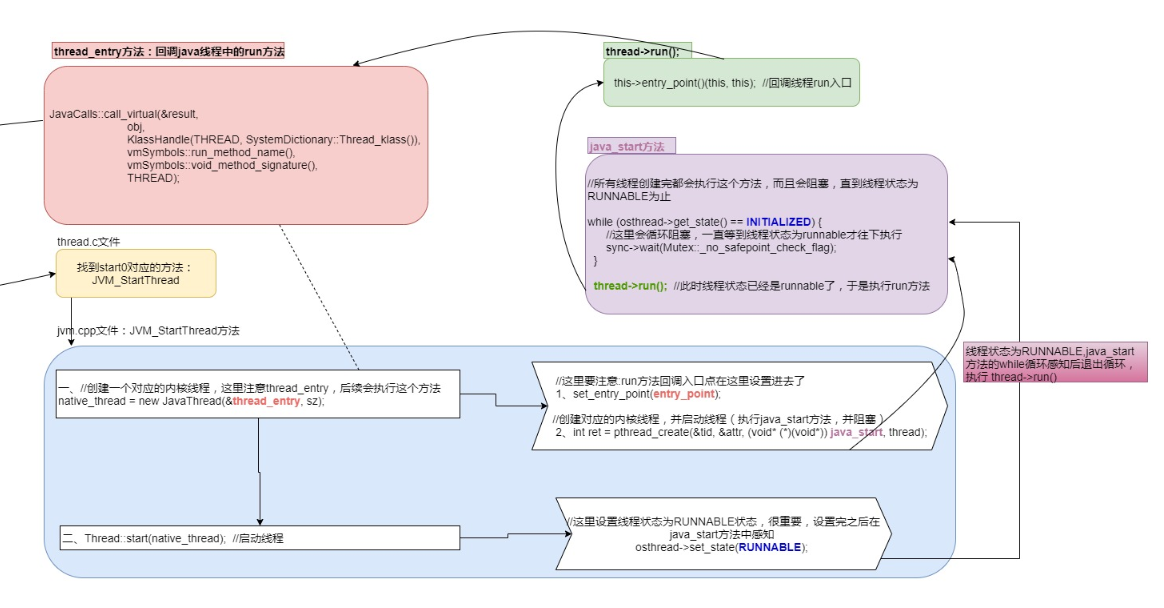
native_thread = new JavaThread(&thread_entry, sz); //Create a corresponding kernel thread. Note the thread here_ Entry, this method will be executed later
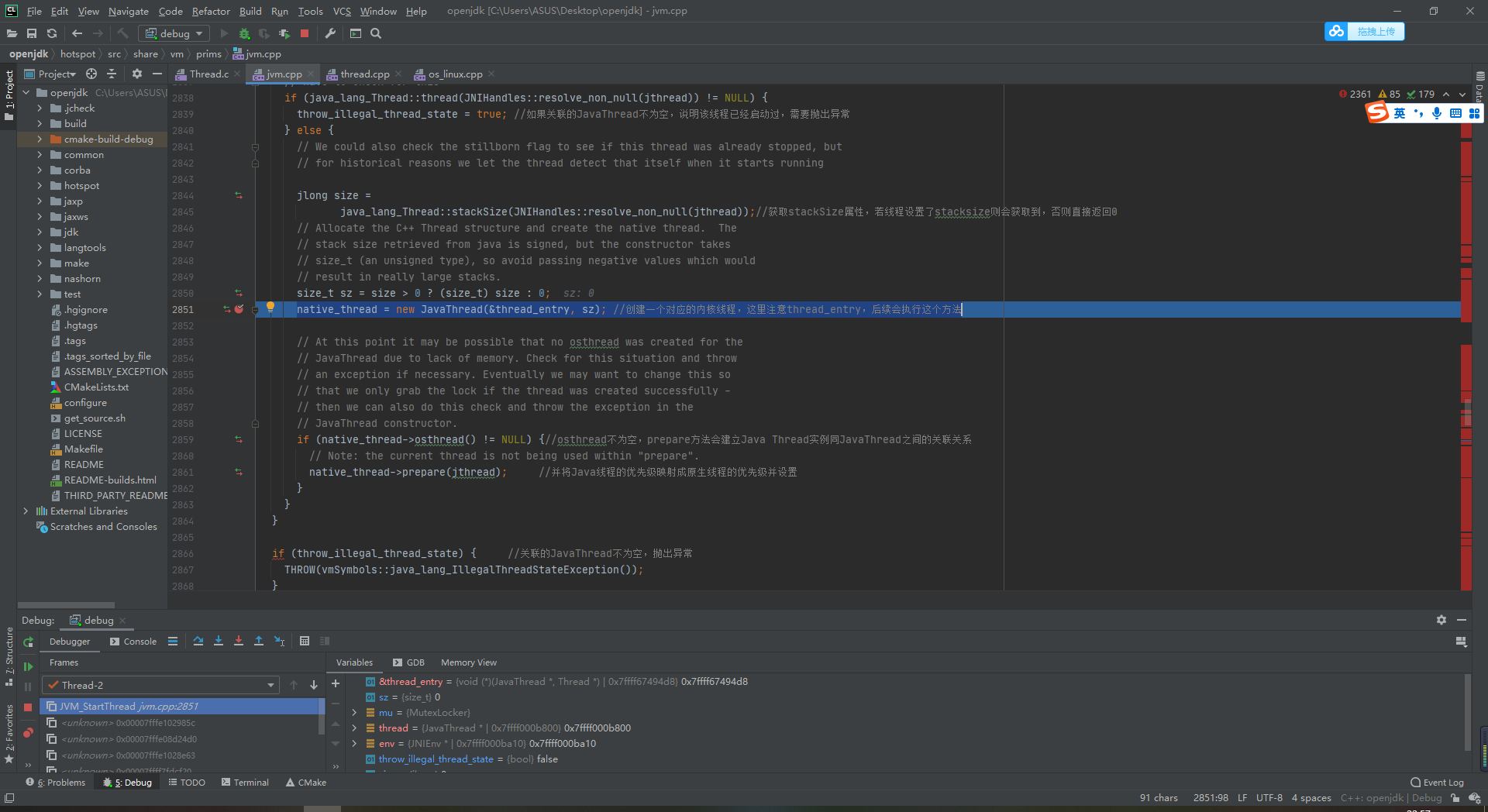
-
4. It can be seen that this is a construction method of javaThread. Let's go into thread CPP 1570 line
set_entry_point(entry_point); //Note here: the callback entry point of the run method is set here
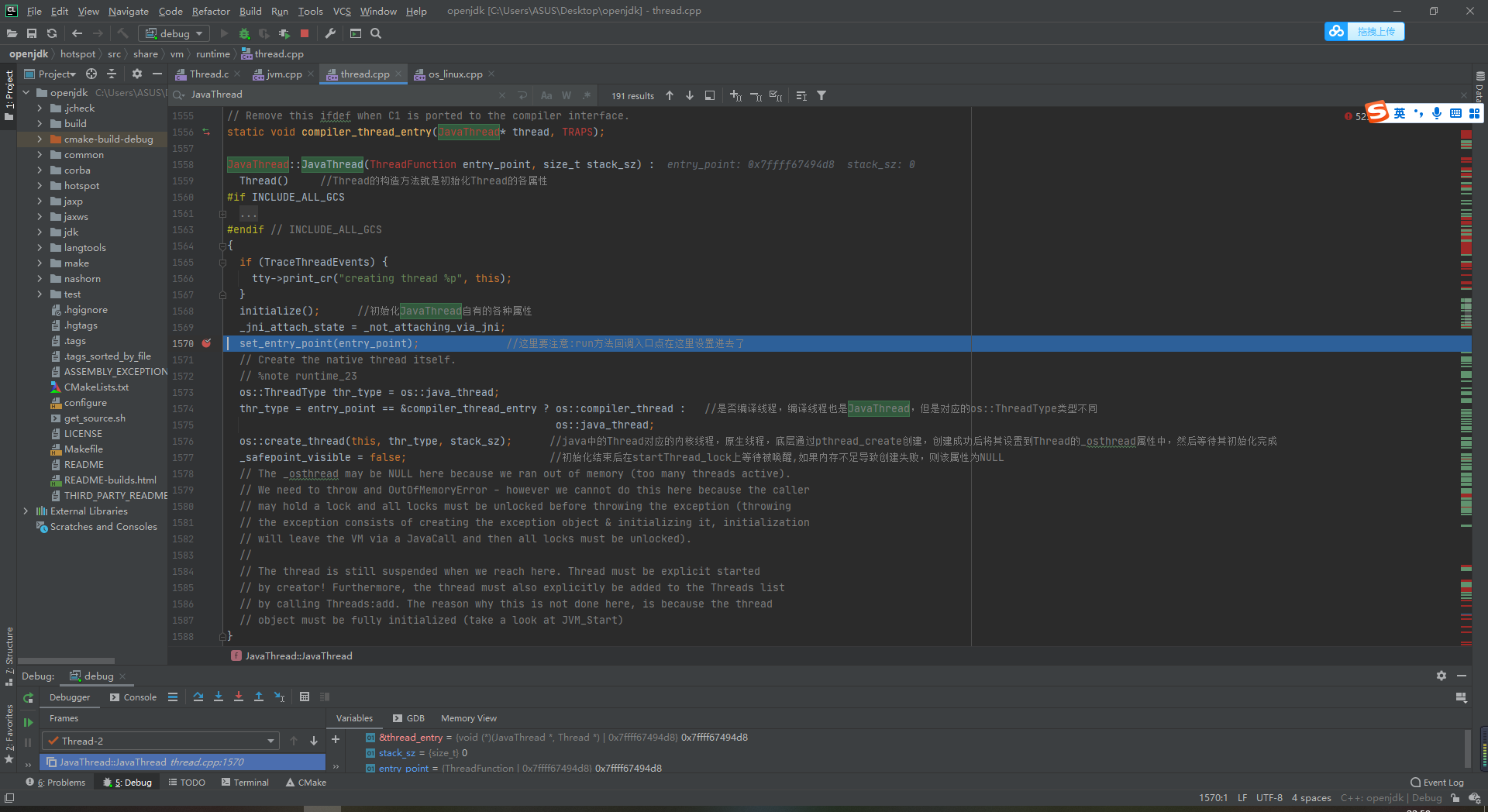
Line 1576, create native thread
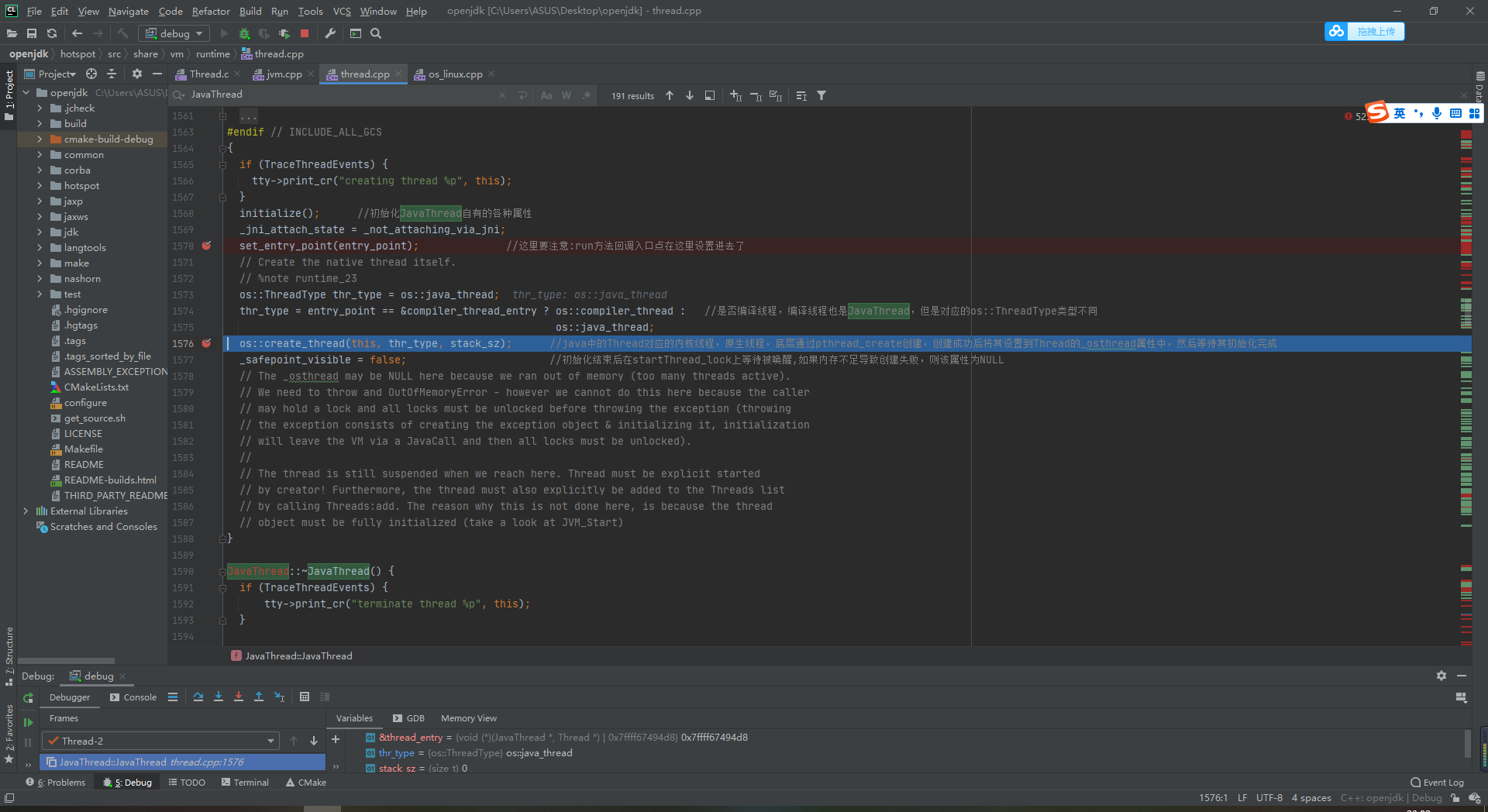
Let's go in and see what happened and jump into os_linux.cpp 865 line
// Allocate the OSThread object
OSThread* osthread = new OSThread(NULL, NULL); //OSThread is a direct bridge between java threads and kernel threads
if (osthread == NULL) {
return false;
}
// set the correct thread state
osthread->set_thread_type(thr_type);
// Initial state is ALLOCATED but not INITIALIZED
osthread->set_state(ALLOCATED);
thread->set_osthread(osthread); //First associate the osthread with the java thread
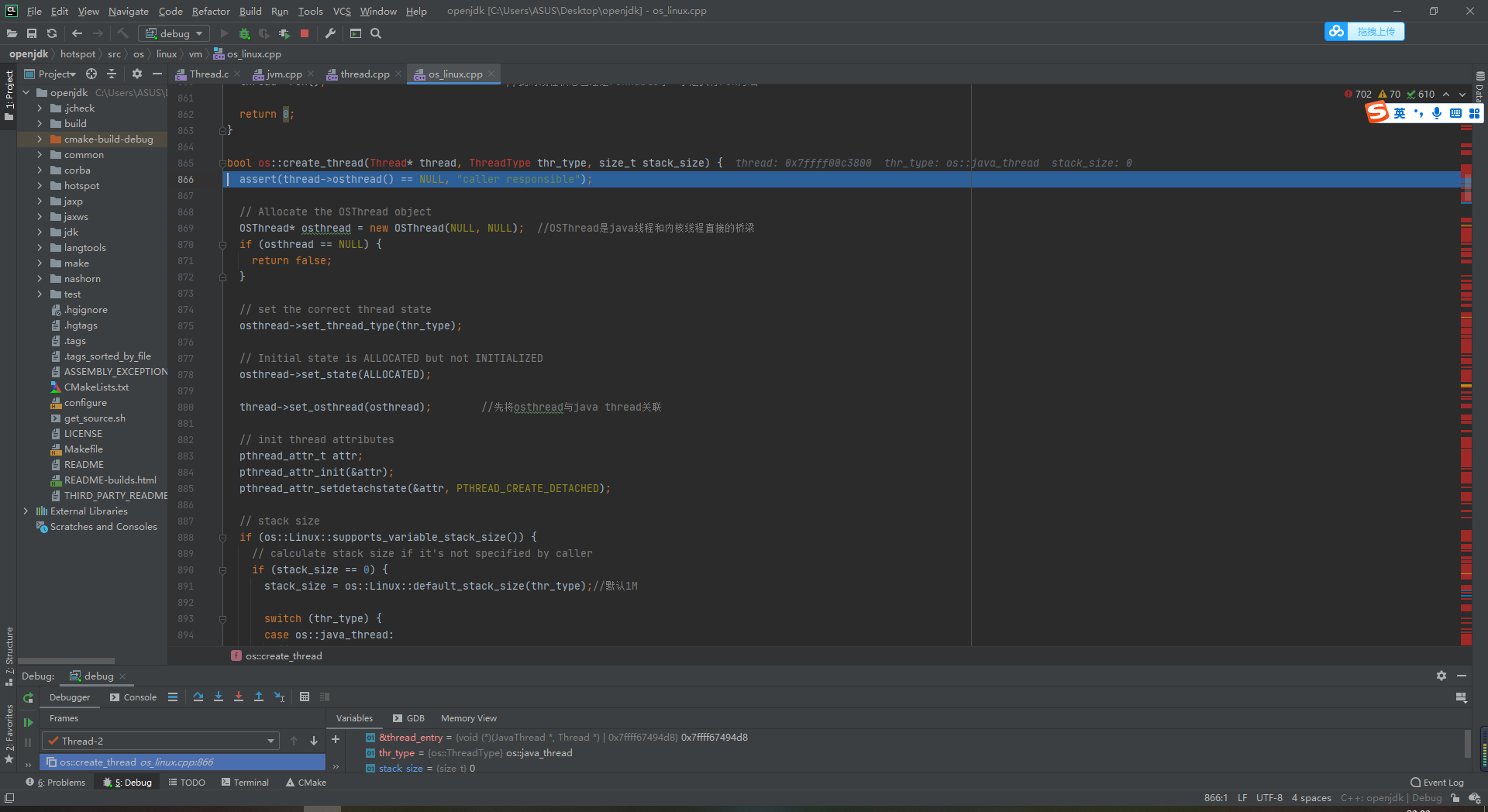
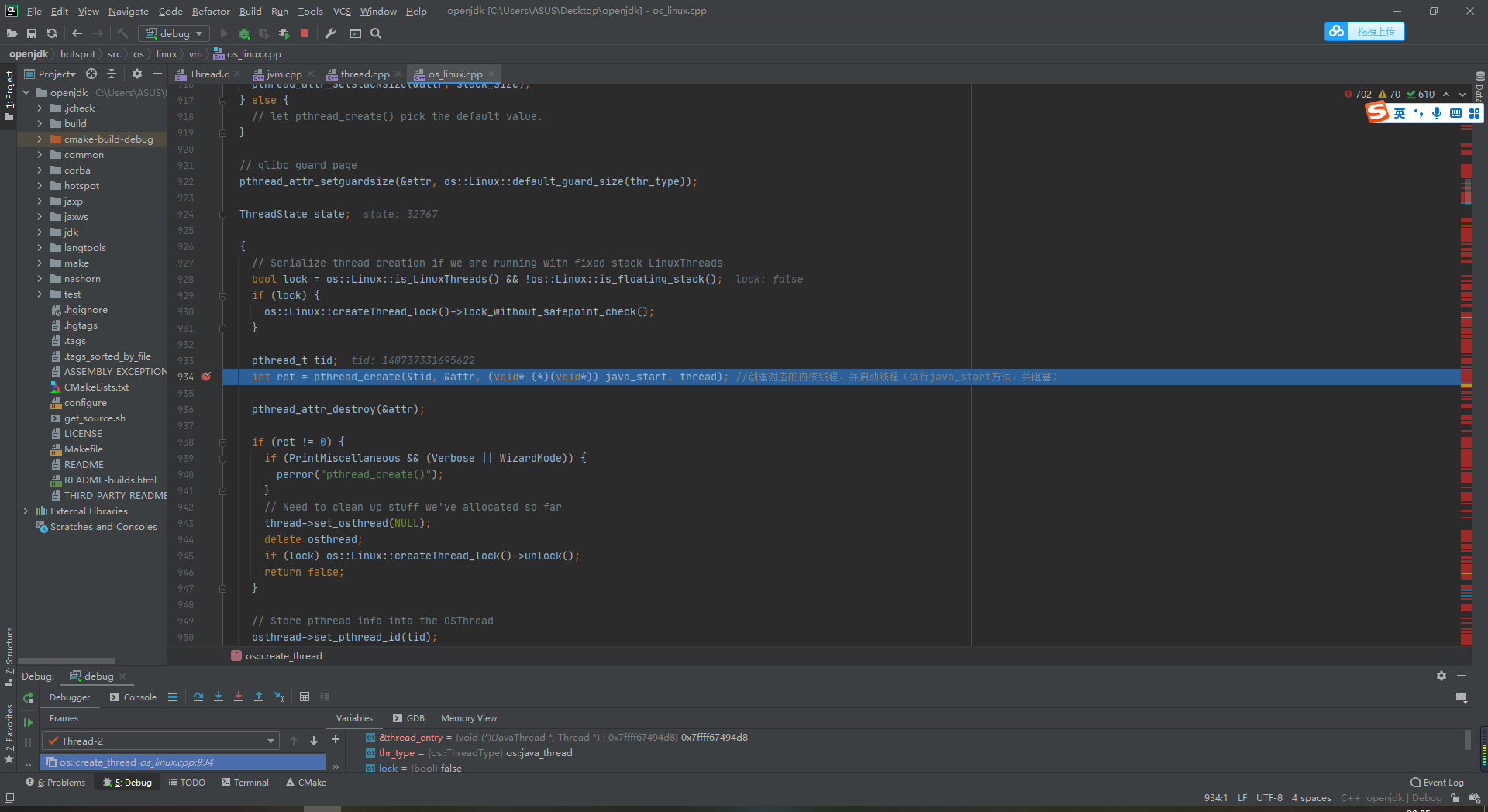
Jump to line 934, really create the kernel thread and wait for java_start method
int ret = pthread_create(&tid, &attr, (void* (*)(void*)) java_start, thread); //Create the corresponding kernel thread and start the thread (execute the java_start method and block it)
-
5java_ Where is the start method? os_linux.cpp 806 OK, let's see what this method is doing
Let's jump to line 854
// wait until os::start_thread()
while (osthread->get_state() == INITIALIZED) { //Here, the loop will be blocked until the thread state is runnable
sync->wait(Mutex::_no_safepoint_check_flag);
}
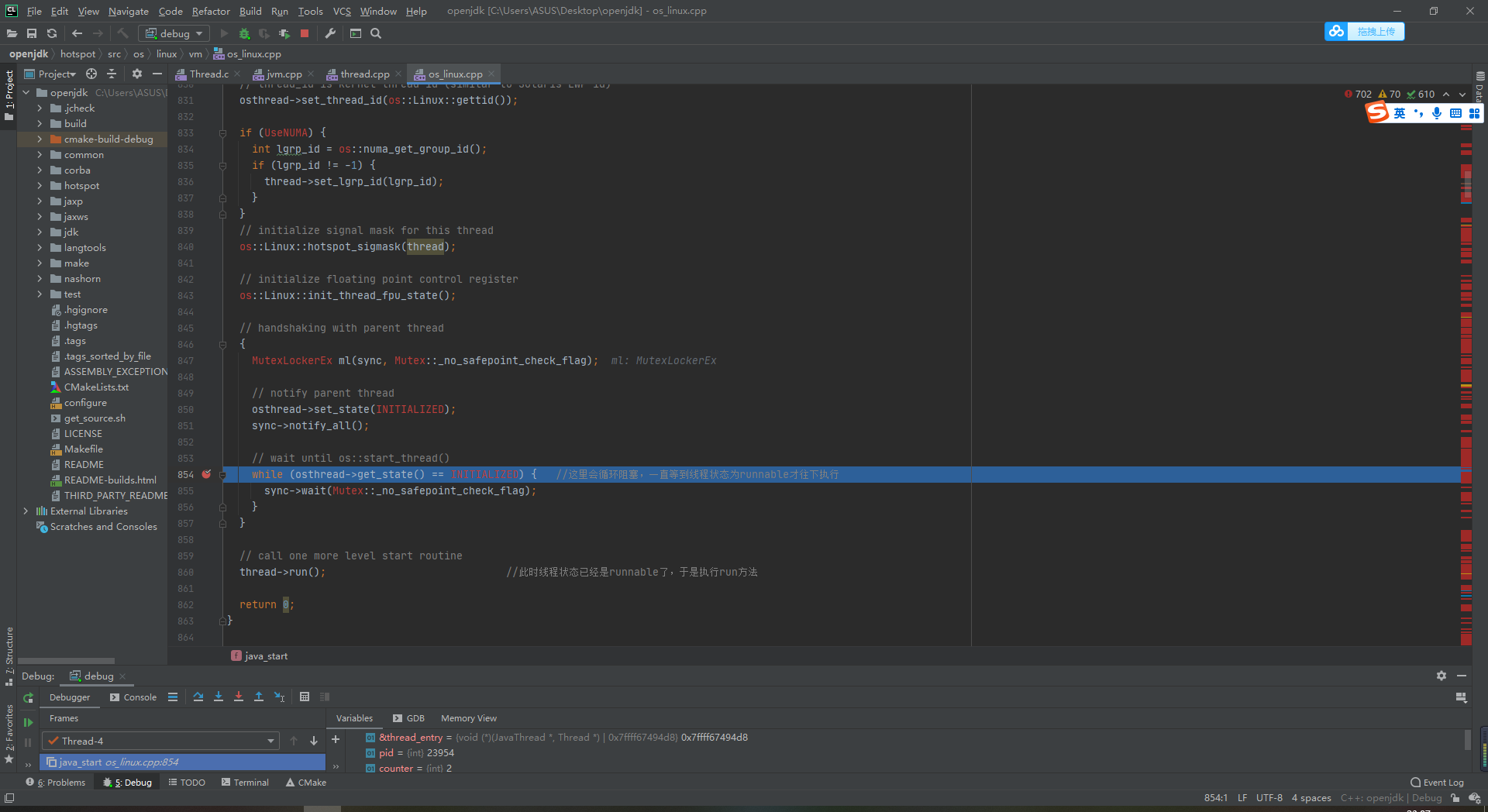
That is, Java_ The start method is always in the while loop. If the thread state is always INITIALIZED, the while loop will not be executed.
-
6 remember where the thread was created? jvm. Let's go down to line 2881, then go down to line 2854
Thread::start(native_thread); //Start the thread, mainly by setting the status to RUNNABLE (it will be perceived in the java_start method, and then the initialized status will be changed to RUNNABLE, and the process will continue to call the run method)
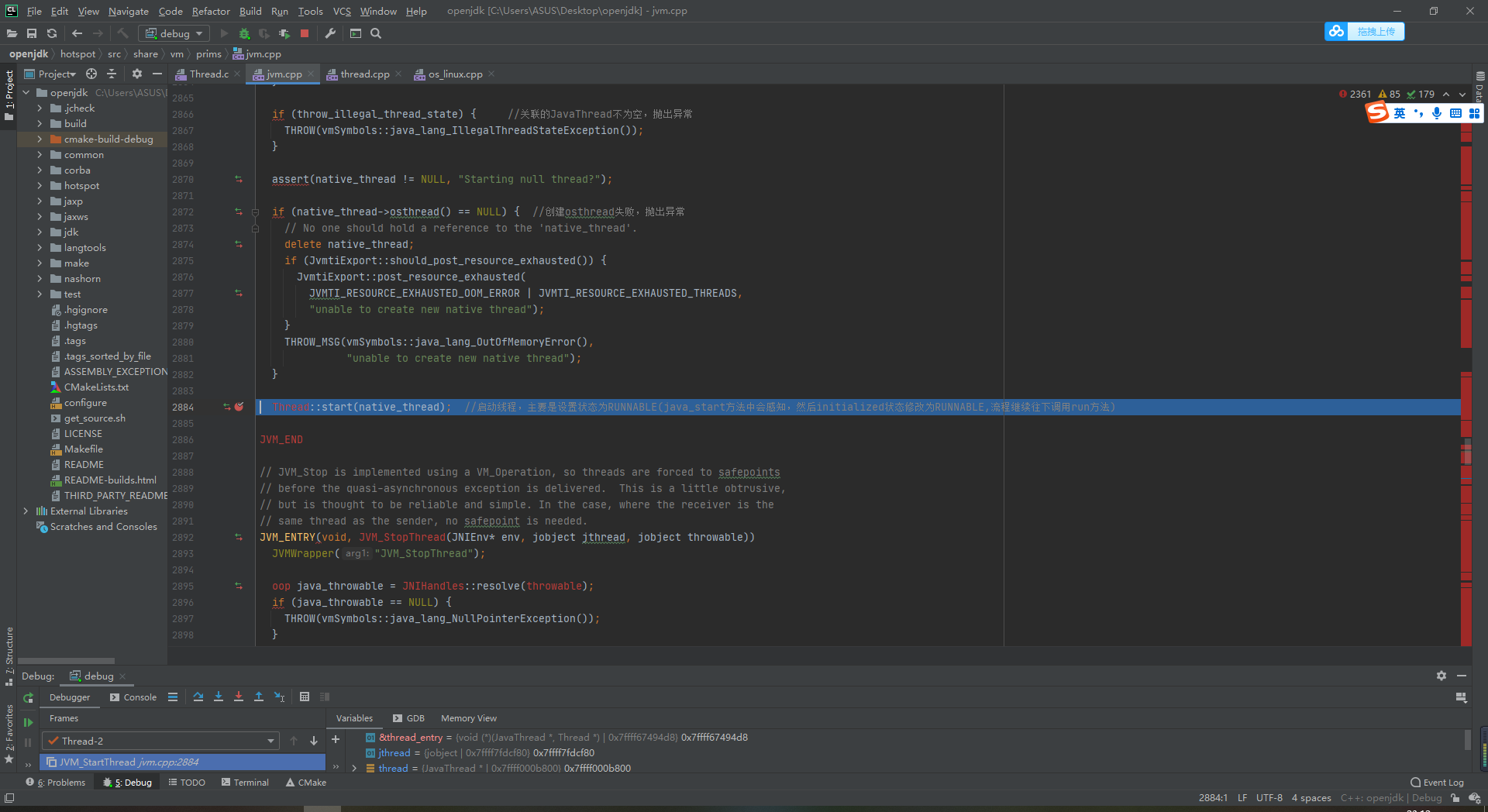
Point into thread CPP 464 line
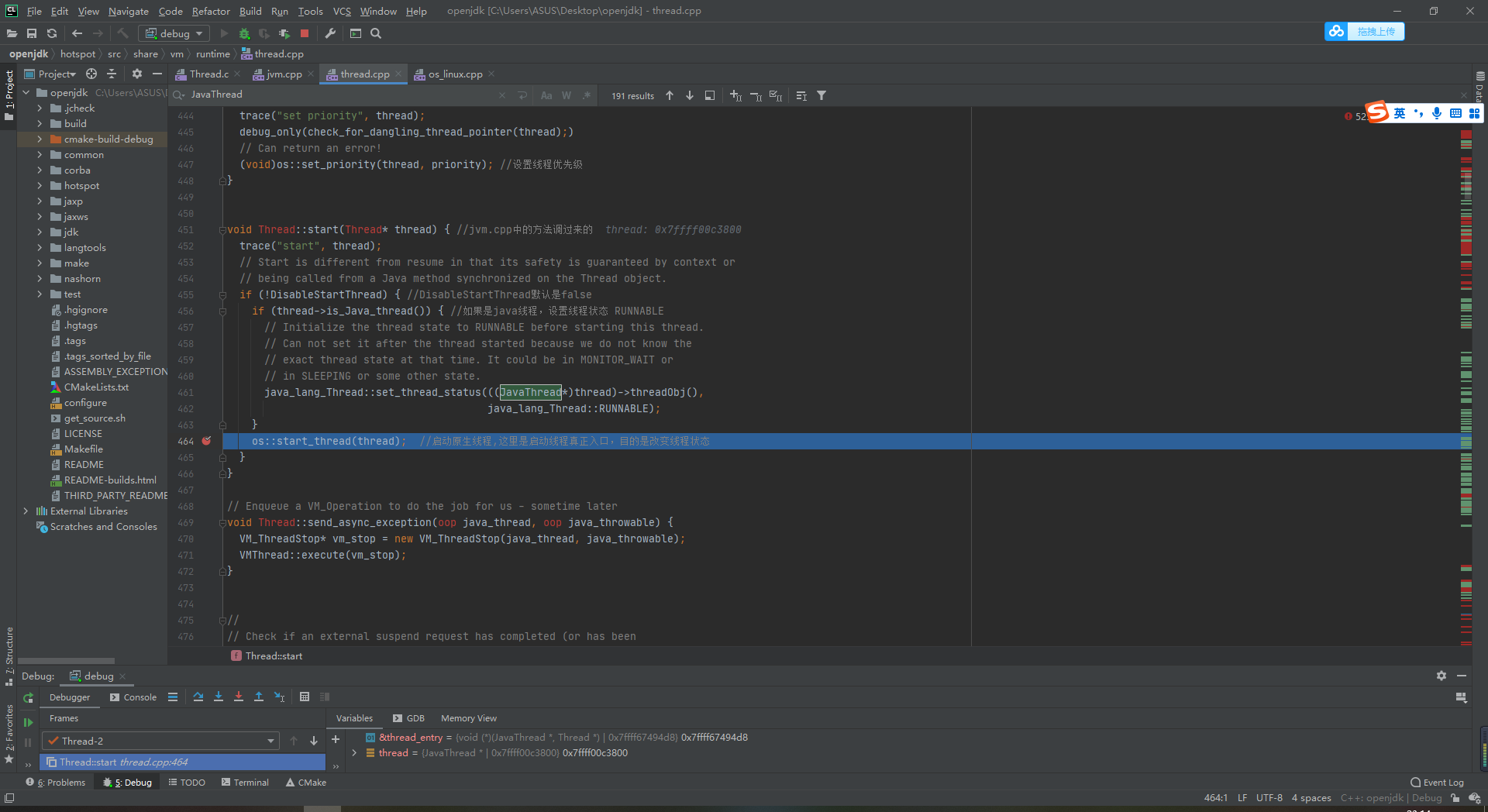
Follow up to os_linux.cpp 863
osthread->set_state(RUNNABLE); //It is very important to set the thread state to the RUNNABLE state here. After setting, it is in Java_ Perception in start method
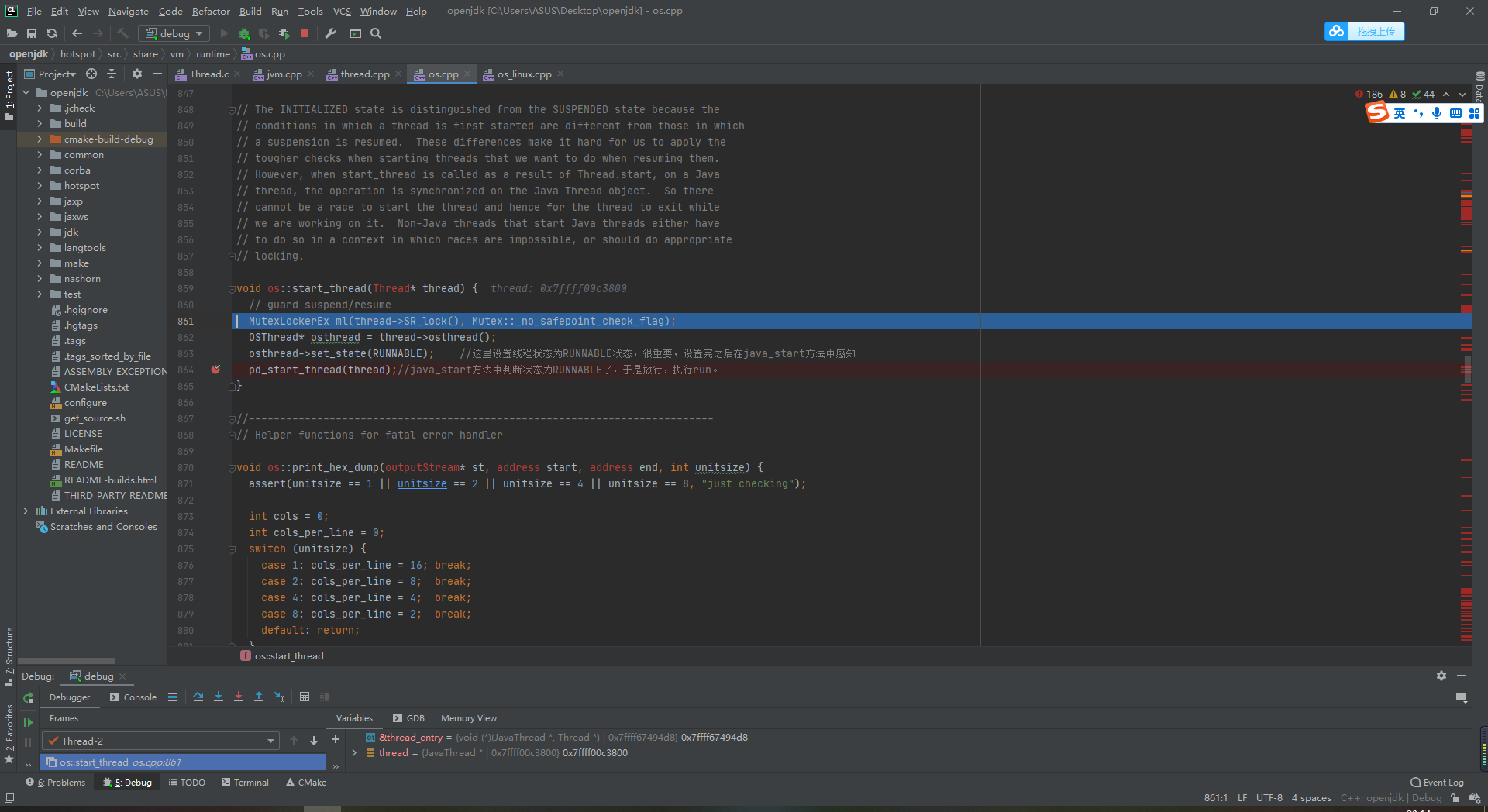
-
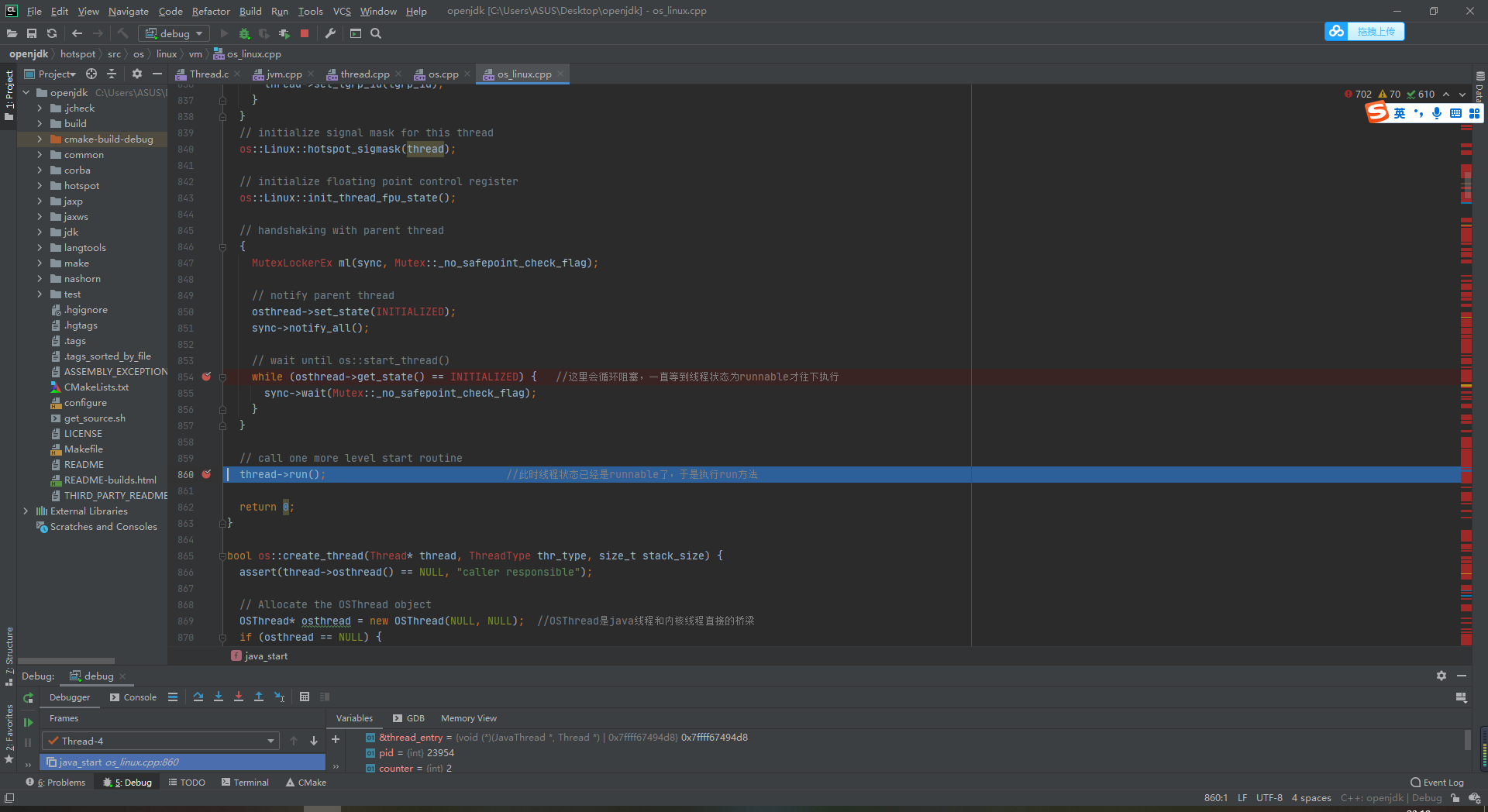
7 Java at this time_ The start method continues to execute os_linux.cpp determines that the thread state is running, so it is released. 860 lines
thread->run();
-
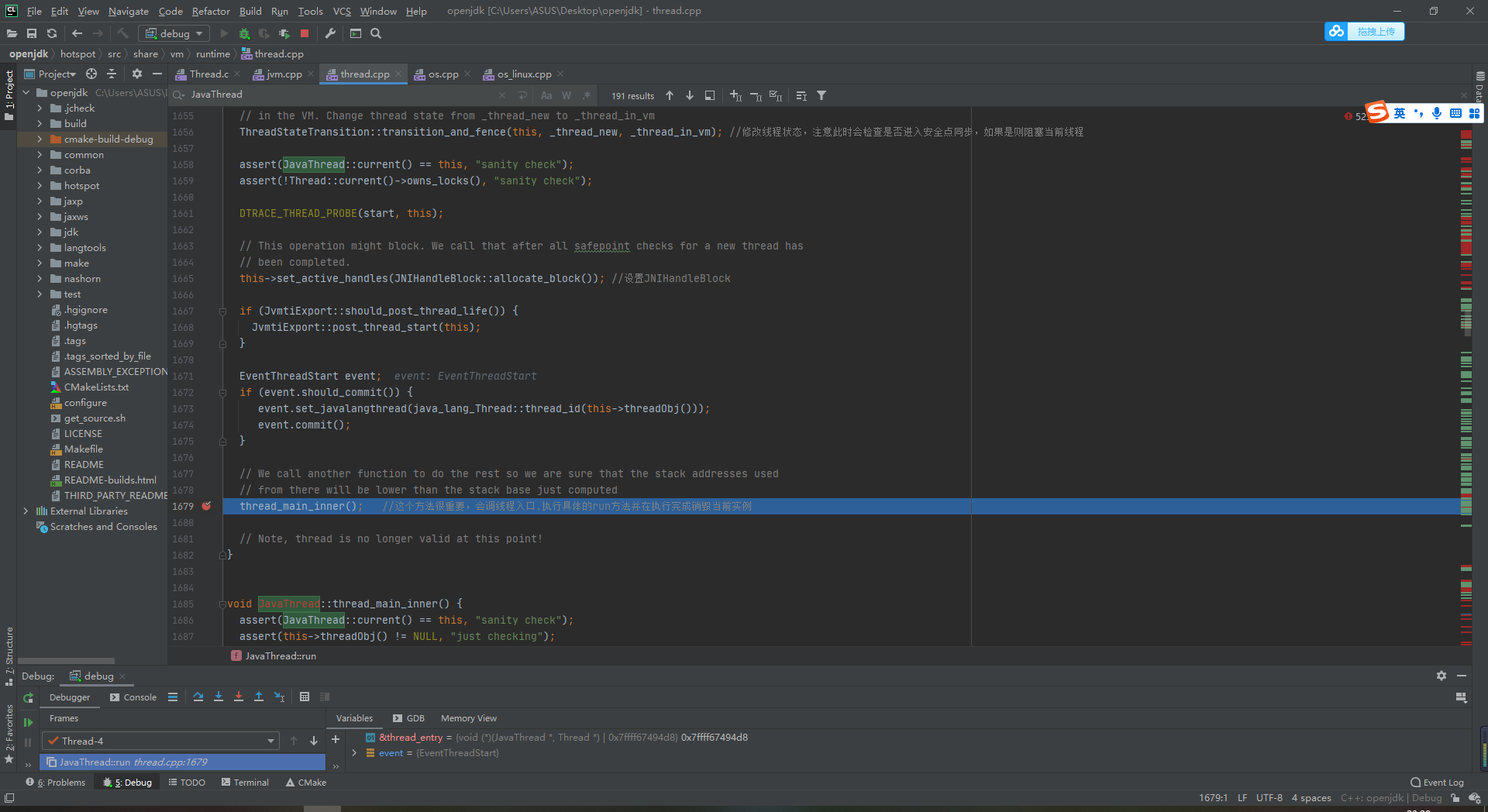
8 jump to thread CPP line 1679 actually executes the callback of the run method and thread destruction
thread_main_inner(); //This method is very important. It will adjust the thread entry Execute the specific run method and destroy the current instance after execution
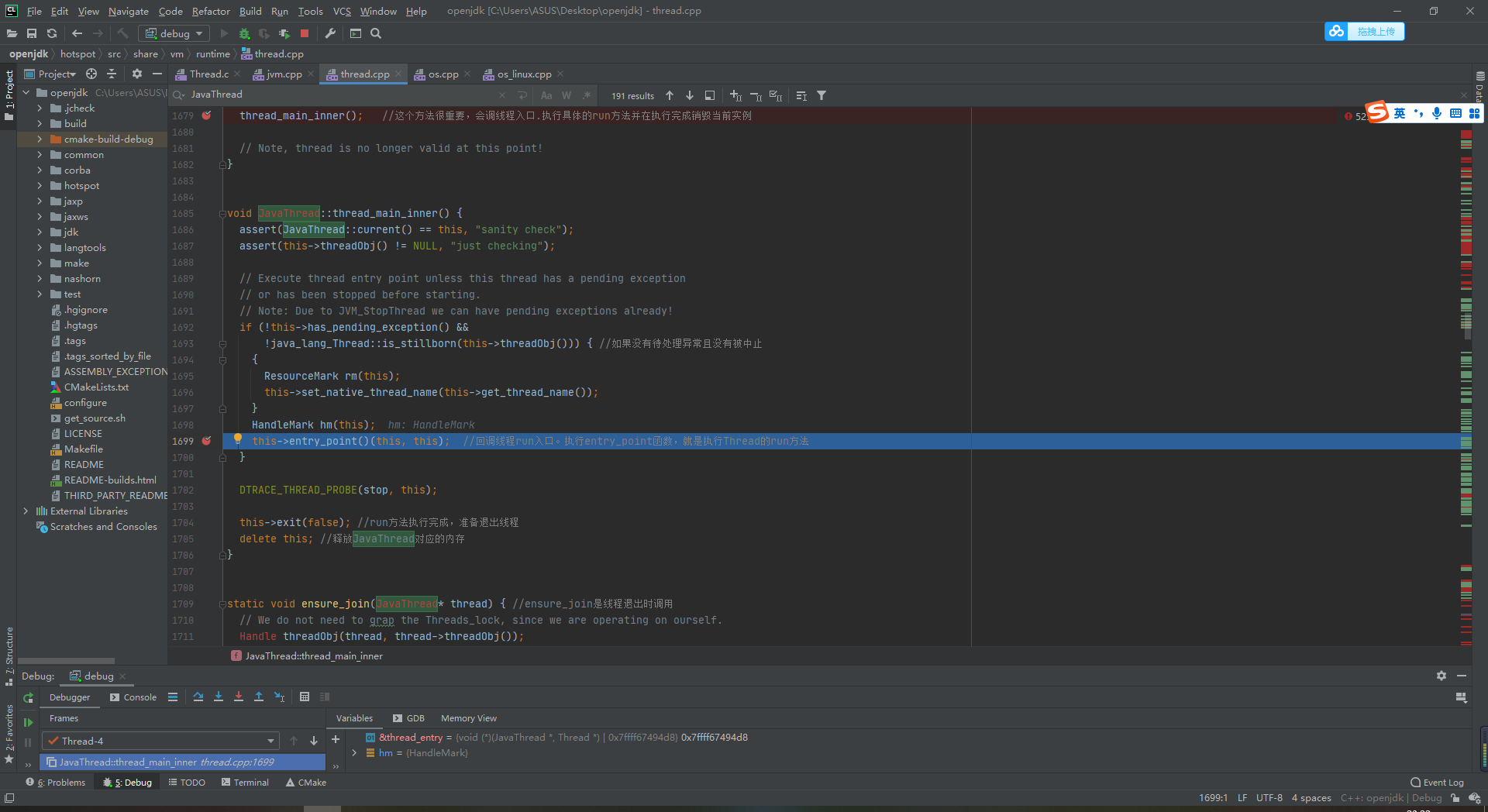
Continue to line 1699 to call back the run method
this->entry_point()(this, this); //Callback Thread run entry. Execute entry_ The point function is the run method that executes Thread
OK! At this point, the process has been completed. It's still relatively simple.
To sum up:
Create a thread, set the concurrent run callback entry, then create a kernel thread and wait for Java_ Completion of the start method, Java_ The start method determines the thread state. If it is initialized, it will continue the while loop until the thread state changes, and then continue to execute the last callback run method.