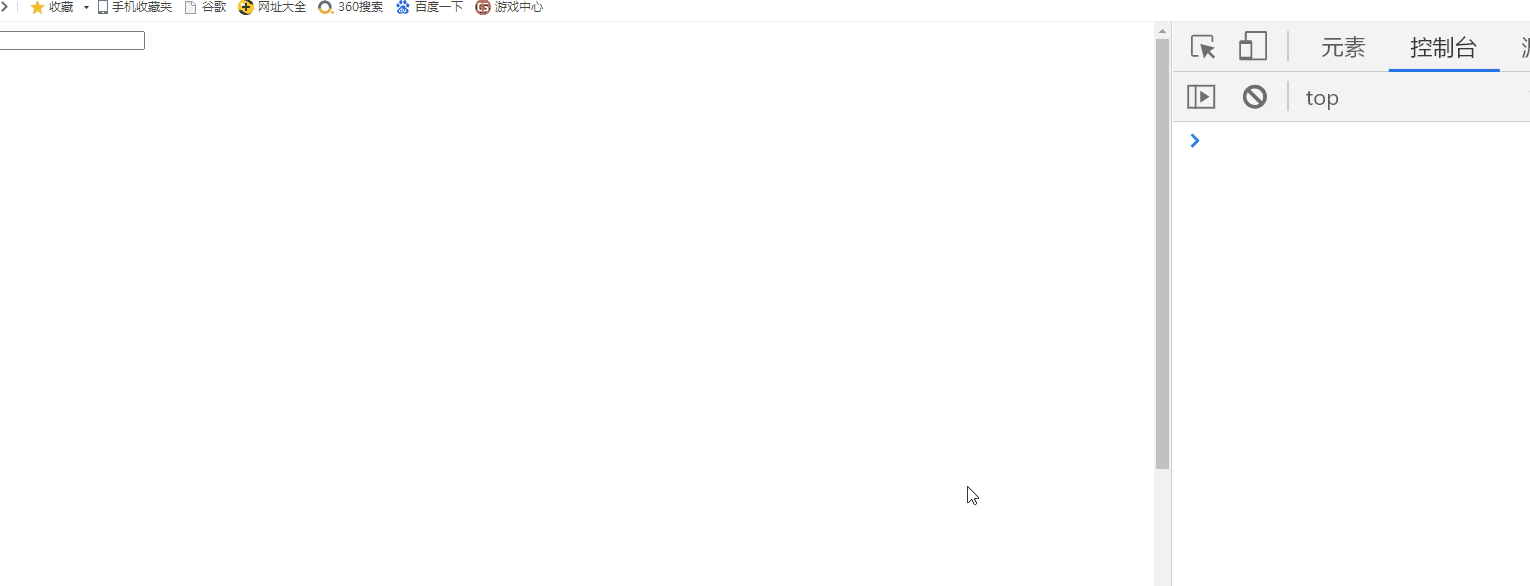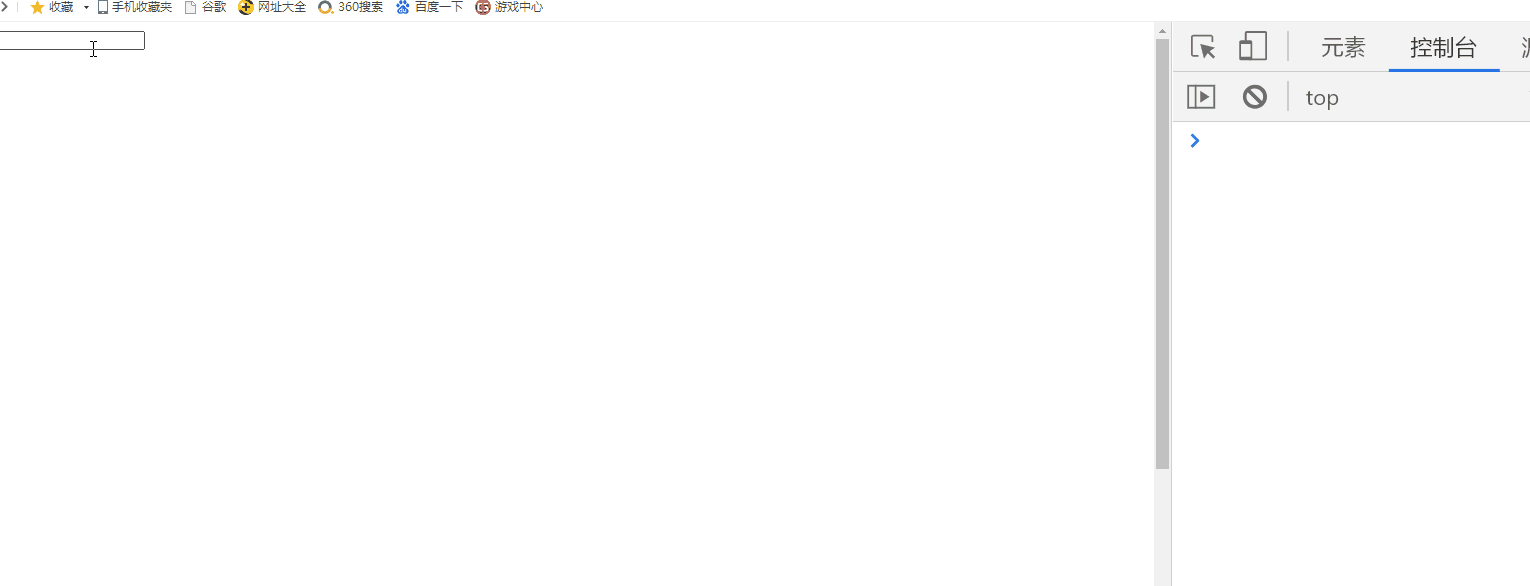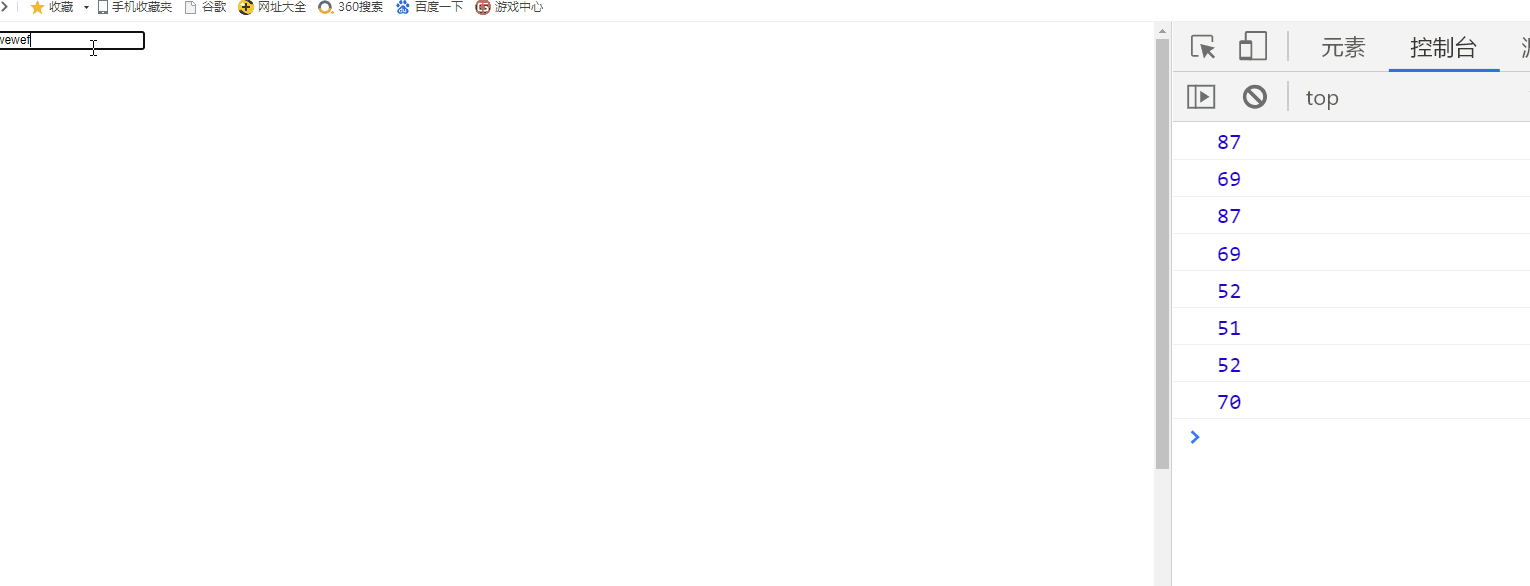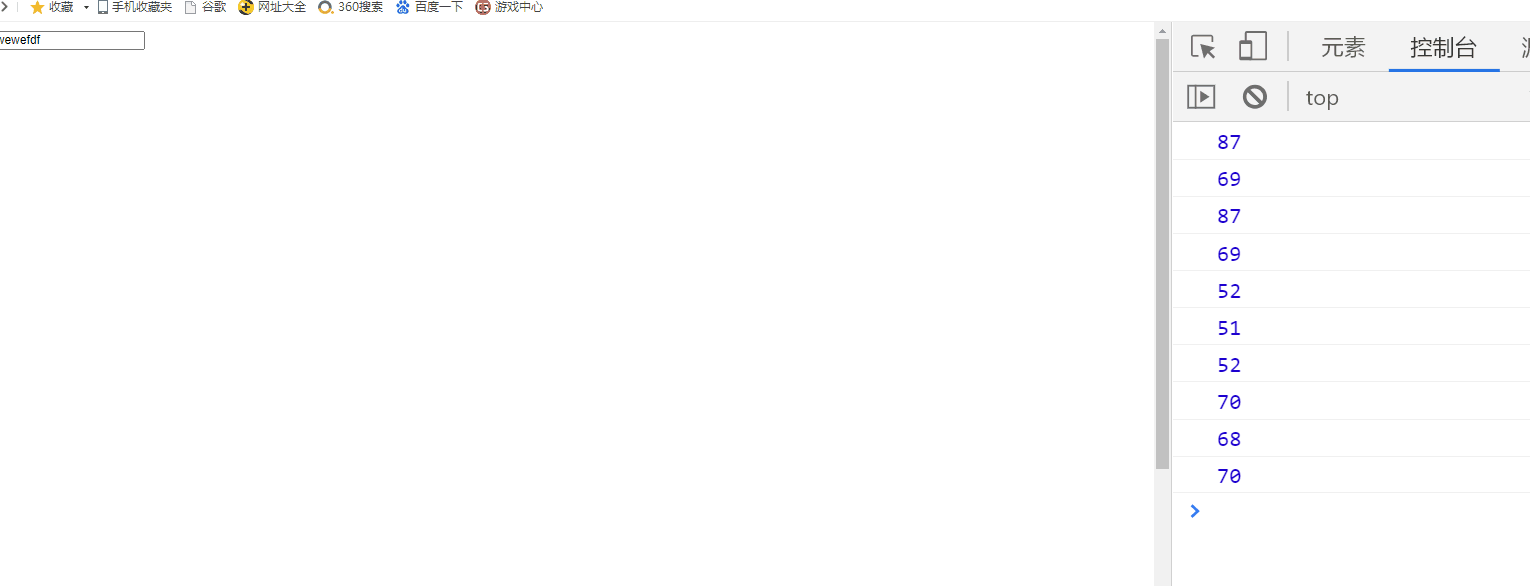1, Pulley rolling event
+++ Bind scroll event(Compatible with Google IE browser)
elem.onmousewheel=function(){ }
Bind scroll event
event.wheelDelta
Just look at the positive and negative, not the size. Roll up>0 . Roll down<0
(The value obtained by this property is a numeric value,The values obtained in different browsers are different.)
+++ Binding mouse scroll events(Compatible with Firefox browser,Unique to Firefox)
elem.addEventListener("DOMMouseSrolll",function(){})
Binding mouse scroll events(Compatible with Firefox browser,Unique writing method of Firefox)
event.detail
Just look at the positive and negative, not the size. Roll up < 0 . Roll down > 0
(The value obtained by this property is a numeric value,The values obtained in different browsers are different.)
+++ Rolling event compatibility handling
elem.onmousewheel=function(event){
event=event||widow.event;
if(event.wheelDelta>0 || event.detail<0){
console.log("scroll up")
}else{
console.log("Scroll down")
}
}
elem.addEventListener("DOMMouseSrolll",elem.onmousewheel)
1.1 binding pulley rolling event
1) Compatible with Google and IE browsers, binding pulley scrolling events
/**Bind scroll event*/
document.onmousewheel=function(event){
/** Compatibility handling of event objects*/
event=event || window.event;
if(event.wheelDelta>0){
console.log("Roll up")
}
if(event.wheelDelta<0){
console.log("Roll down")
}
}
2) Compatible with Firefox browser, binding pulley scrolling events
/**Bind scroll event*/
document.addEventListener("DOMMouseScroll",function(event){
event=event||window.event;
if(event.detail>0){
console.log("Roll down")
}else{
console.log("Roll up")
}
})
3) Binding event compatibility handling
<script>
/** Binding scrolling events, compatible with Google and Internet Explorer*/
document.onmousewheel=function(event){
event=event||window.event;
//event.wheelDelta is compatible with Google and Internet Explorer
//event.detail compatible with Firefox
if(event.wheelDelta >0 || event.detail<0){
console.log("Roll up")
}else{
console.log("Roll down")
}
}
/** Binding scrolling events, compatible with Firefox browser*/
document.addEventListener("DOMMouseScroll",document.onmousewheel)
</script>
1.2 event cases of binding mouse pulley
Implementation scenario: when the mouse scrolls up, the red div becomes longer. When the mouse moves down, the red div becomes shorter
1) Case 1
<body >
<div style="width:100px;height:100px;background-color: red;"></div>
</body>
<script>
var div=document.getElementsByTagName("div")[0];
/** Binding scrolling events, compatible with Google and Internet Explorer*/
document.onmousewheel=function(event){
event=event||window.event;
// Judge whether the mouse scrolls up
if(event.wheelDelta >0 || event.detail<0){
div.style.height=div.scrollHeight+10+"px";
}
//Judge whether the mouse scrolls down
if(event.wheelDelta <0 || event.detail >0){
div.style.height=div.scrollHeight-10+"px";
}
}
/** Binding scrolling events, compatible with Firefox browser*/
document.addEventListener("DOMMouseScroll",document.onmousewheel)
</script>
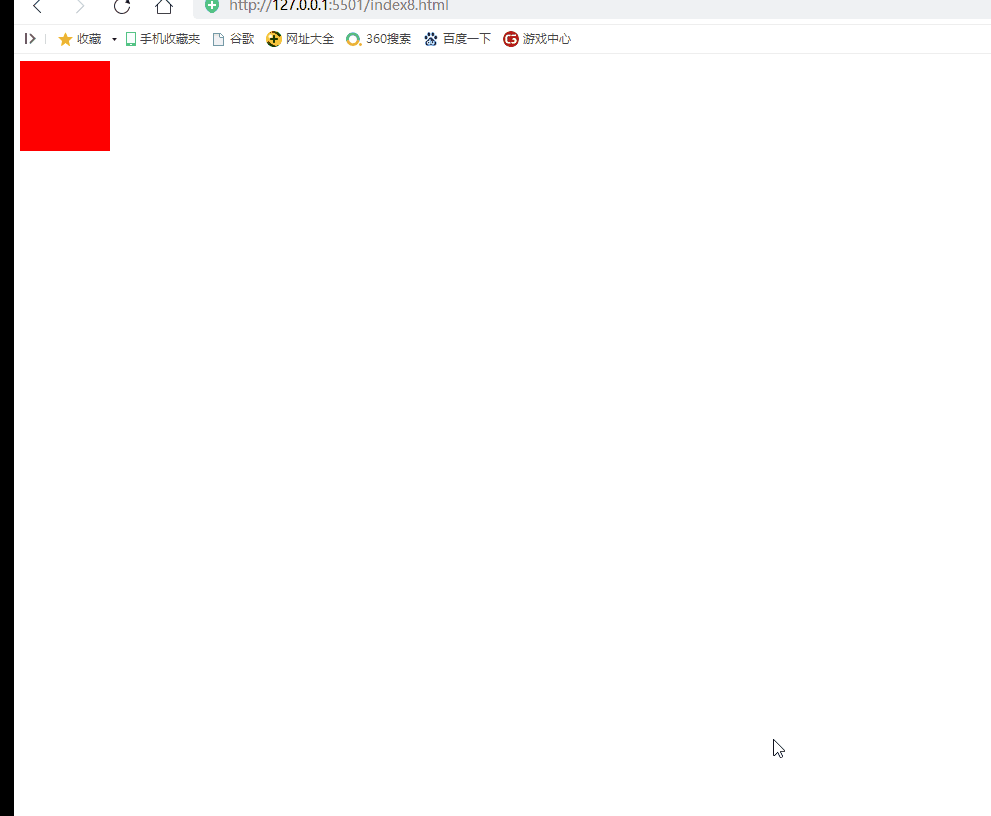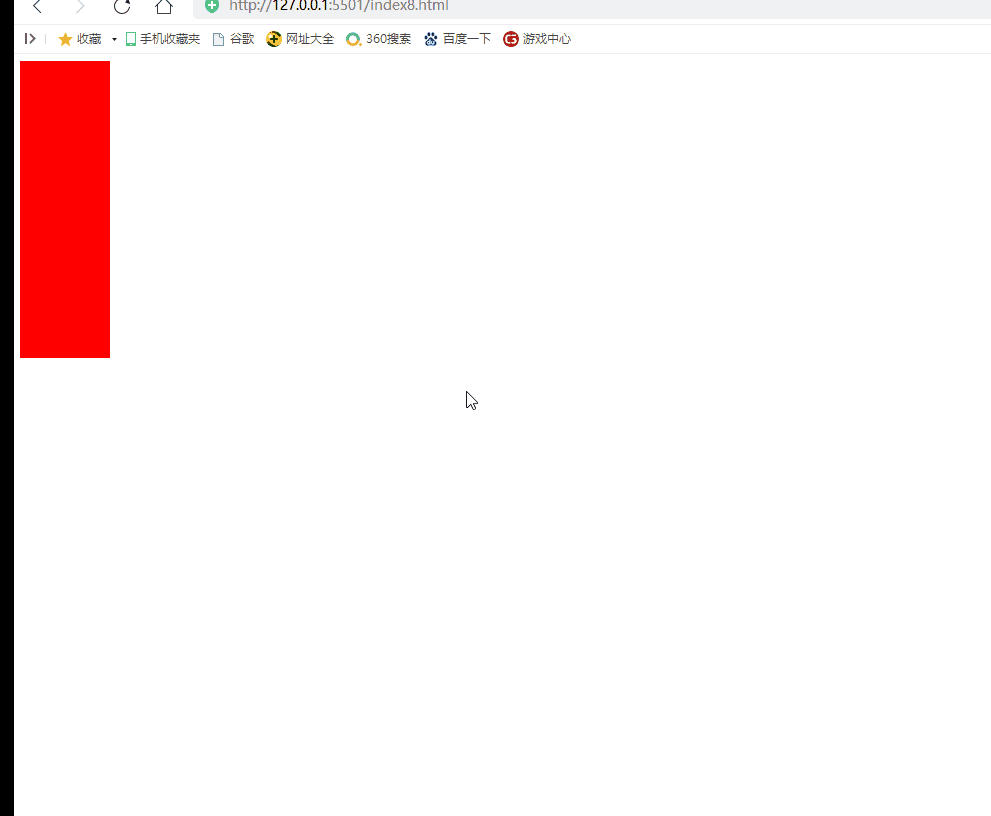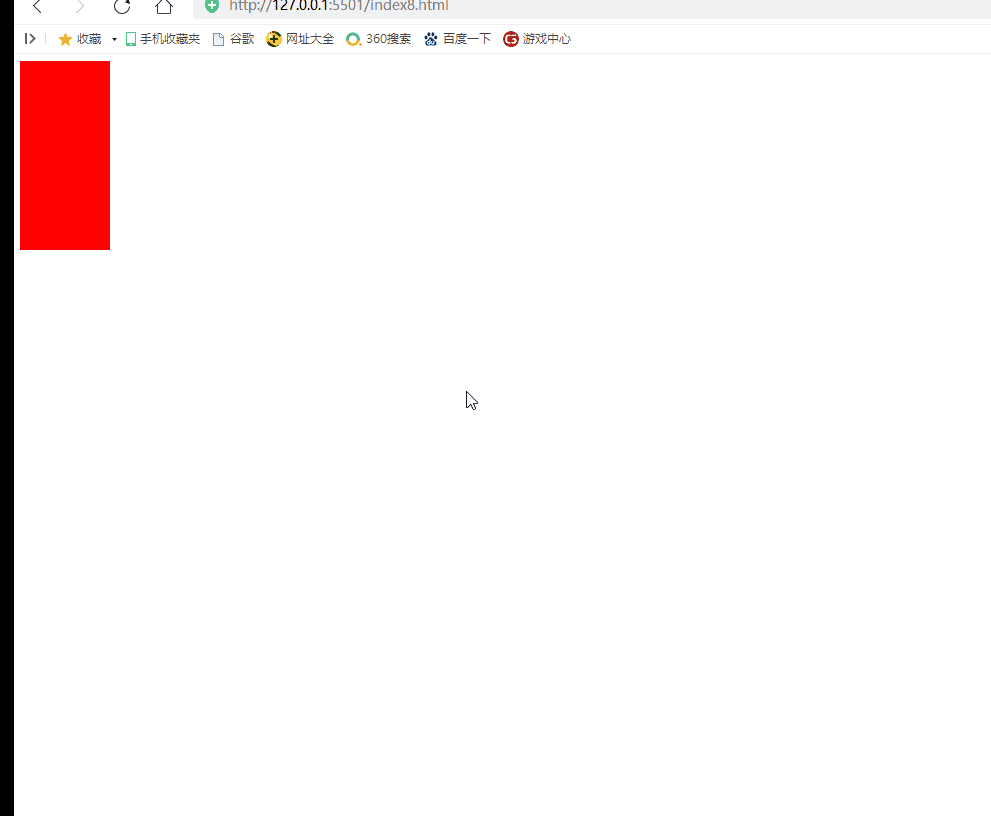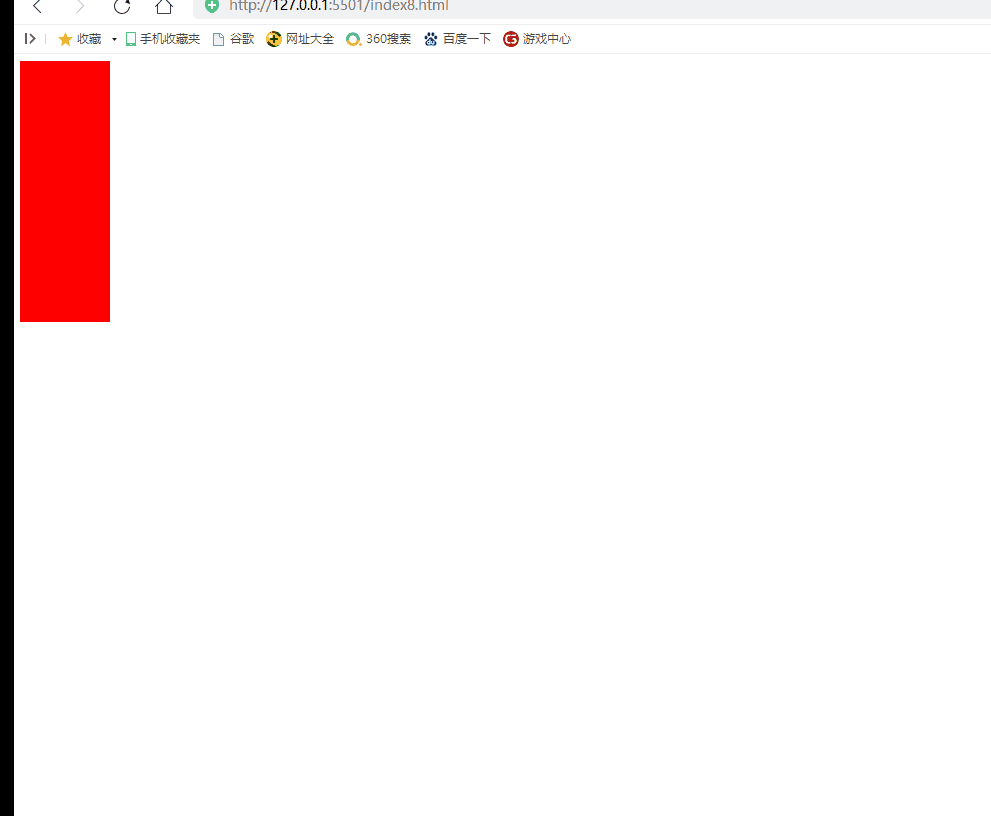
2) Case 2
>>>>>>Question
On the basis of case 1, when the scroll bar appears in the browser, the pulley will scroll and the scroll bar will move. The effect is very unfriendly
<body style="height:2000px">
<div style="width:100px;height:100px;background-color: red;"></div>
</body>
<script>
var div=document.getElementsByTagName("div")[0];
/** Binding scrolling events, compatible with Google and Internet Explorer*/
div.onmousewheel=function(event){
event=event||window.event;
// Judge whether the mouse scrolls up
if(event.wheelDelta >0 || event.detail<0){
div.style.height=div.scrollHeight+10+"px";
}
//Judge whether the mouse scrolls down
if(event.wheelDelta <0 || event.detail >0){
div.style.height=div.scrollHeight-10+"px";
}
}
/** Binding scrolling events, compatible with Firefox browser*/
div.addEventListener("DOMMouseScroll",document.onmousewheel)
</script>
>>>>>>Solution
When the scroll bar appears in the browser, the pulley scrolls div The height of the browser changes and the browser scrolls, This is due to the default behavior of the browser. We want to block the default behavior of the pulley.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body style="height:2000px">
<div style="width:100px;height:100px;background-color: red;"></div>
</body>
<script>
var div=document.getElementsByTagName("div")[0];
/** Binding scrolling events, compatible with Google and Internet Explorer*/
div.onmousewheel=function(event){
event=event||window.event;
// Judge whether the mouse scrolls up
if(event.wheelDelta >0 || event.detail<0){
div.style.height=div.scrollHeight+10+"px";
}
//Judge whether the mouse scrolls down
if(event.wheelDelta <0 || event.detail >0){
div.style.height=div.scrollHeight-10+"px";
}
/**
* When the scroll wheel scrolls, if the browser has a scroll bar, the scroll bar also scrolls. This is the default behavior of the browser.
* If you don't want this to happen, you can cancel the browser default behavior.
*/
/**
* Cancel browser default behavior
* 1,return false Cancels the default behavior of binding through JS events
* 2,event.preventDefault() Cancels the default behavior of binding through event listening
*/
event.preventDefault();
return false;
}
/** Binding scrolling events, compatible with Firefox browser*/
div.addEventListener("DOMMouseScroll",document.onmousewheel)
</script>
</html>
2, Keyboard events
+++ Keyboard events:Keyboard events are generally bound to objects or objects that can get focus document. (such as div Cannot get focus, so cannot bind keyboard events) onkeydown Indicates that the key is pressed 1,If you keep pressing a key and don't let go, the event will be triggered all the time. 2,When onkeydown When the event is triggered continuously,There will be a significant time interval between the first trigger and the second trigger, while others will be very fast. This design is for the occurrence of misoperation. onkeyup Indicates that the key is released +++ Keyboard event related properties keyCode Gets which key was pressed. Get key ASCII Code value altKey judge"ALT" Is the key pressed ctrlKey judge"CTRL" Is the key pressed shiftKey judge"SHIFT" Whether the key is pressed. metaKey Returns when the event is triggered,"meta" Whether the key is pressed.
2.1 keyboard events
1) onkeydown event, triggered when the key is pressed
document.onkeydown=function(){
console.log("The button was pressed")
}
2) onkeyup event, triggered when the key is lifted
document.onkeyup=function(){
console.log("The button was pressed and lifted")
}
3) Notes for keyboard events
>>>>>>For the onkeydown event, if you press the key without hands, it will be triggered all the time
document.onkeydown=function(){
console.log("The button was pressed")
}

>>>>>>Keyboard events are generally bound to objects that can get focus or document objects. If it is a div, it will not be triggered.
If the key event is bound to a div, the key event will not be triggered
<body>
<div style="width:100px;height:100px;background-color: red;"></div>
</body>
<script>
var div=document.getElementsByTagName("div")[0];
div.onkeydown=function(){
console.log("div Key event triggered")
}
</script>
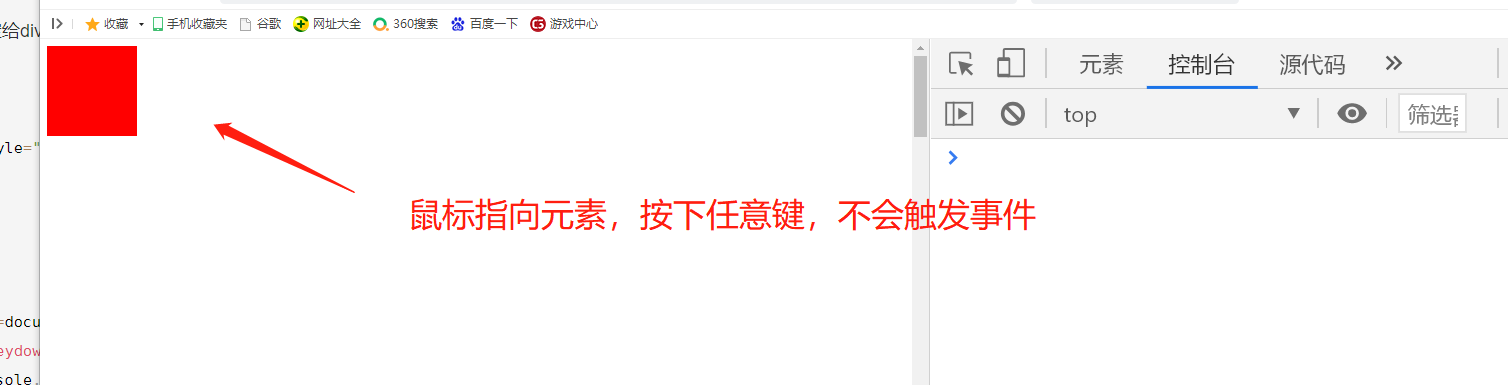
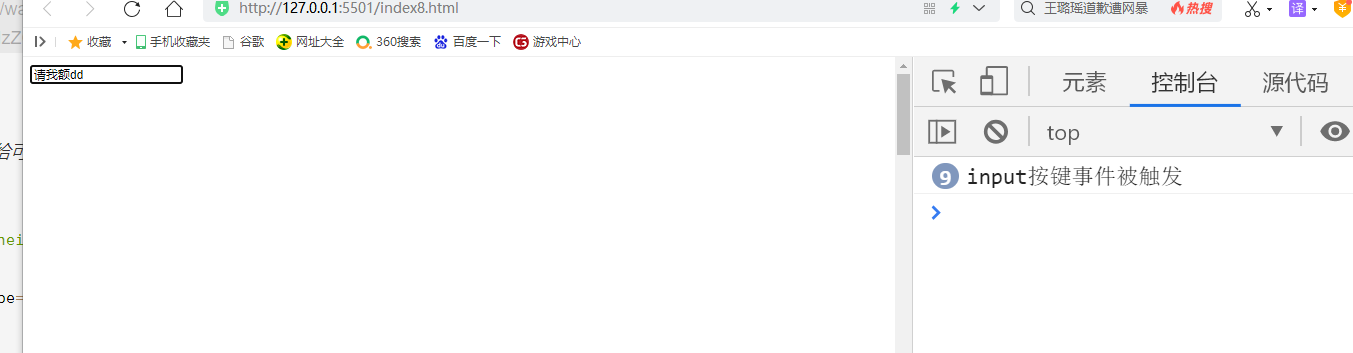
The key event can be triggered if it is bound to an object or document that can obtain focus
<body style="height:2000px">
<input type="text">
</body>
<script>
var input=document.getElementsByTagName("input")[0];
input.onkeydown=function(){
console.log("input Key event triggered")
}
</script>
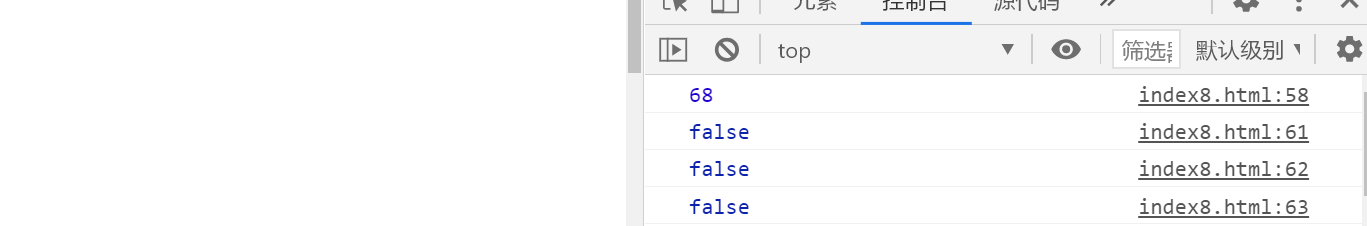
2.2 keyboard event related attributes
1) Gets which key was pressed
<script>
document.onkeydown=function(event){
event=event||window.event;
//Gets the ASCII value of the key
console.log(event.keyCode);
console.log(event.ctrlKey); //Judge whether the "CTRL" key is pressed
console.log(event.altKey); //Judge whether the "ALT" key is pressed
console.log(event.shiftKey);//Judge whether the "SHIFT" key is pressed.
}
</script>
2) Press and hold ctrl+A at the same time. If yes, it will be triggered
<script>
document.onkeydown=function(event){
event=event||window.event;
//Gets the ASCII value of the key
console.log(event.keyCode);
if(event.keyCode==65 && event.ctrlKey ){
console.log("ctrl+A Simultaneously pressed")
}
}
</script>

2.3 keyboard event cases
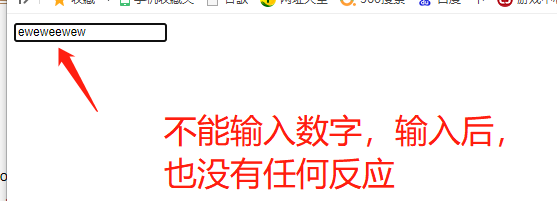
1) You cannot enter numbers in the text box
Principle: the input in the text box is the default behavior of onkeydown. Cancel the default behavior
<body>
<input type="text">
</body>
<script>
var input=document.getElementsByTagName("input")[0];
input.onkeydown=function(event){
event=event||window.event;
//The keycode of 0-9 is 48-57
if(event.keyCode>=48 && event.keyCode<=57){
//Cancels the default behavior of text boxes
return false;
}
}
</script>
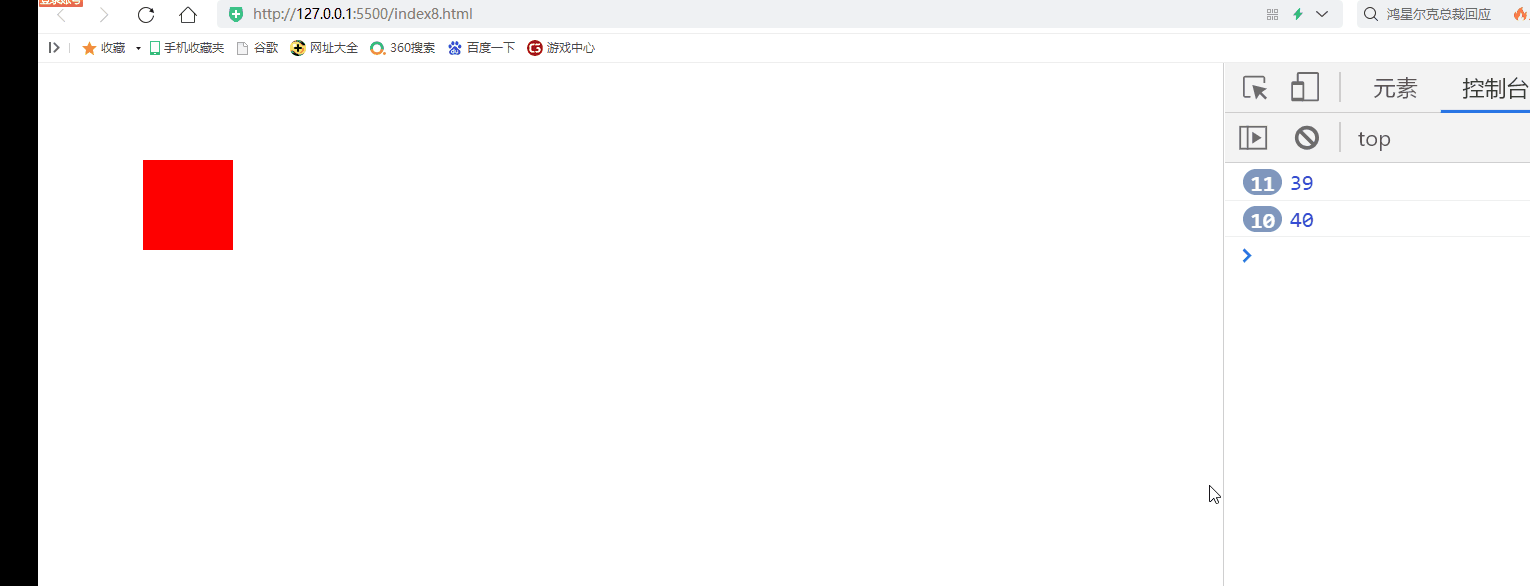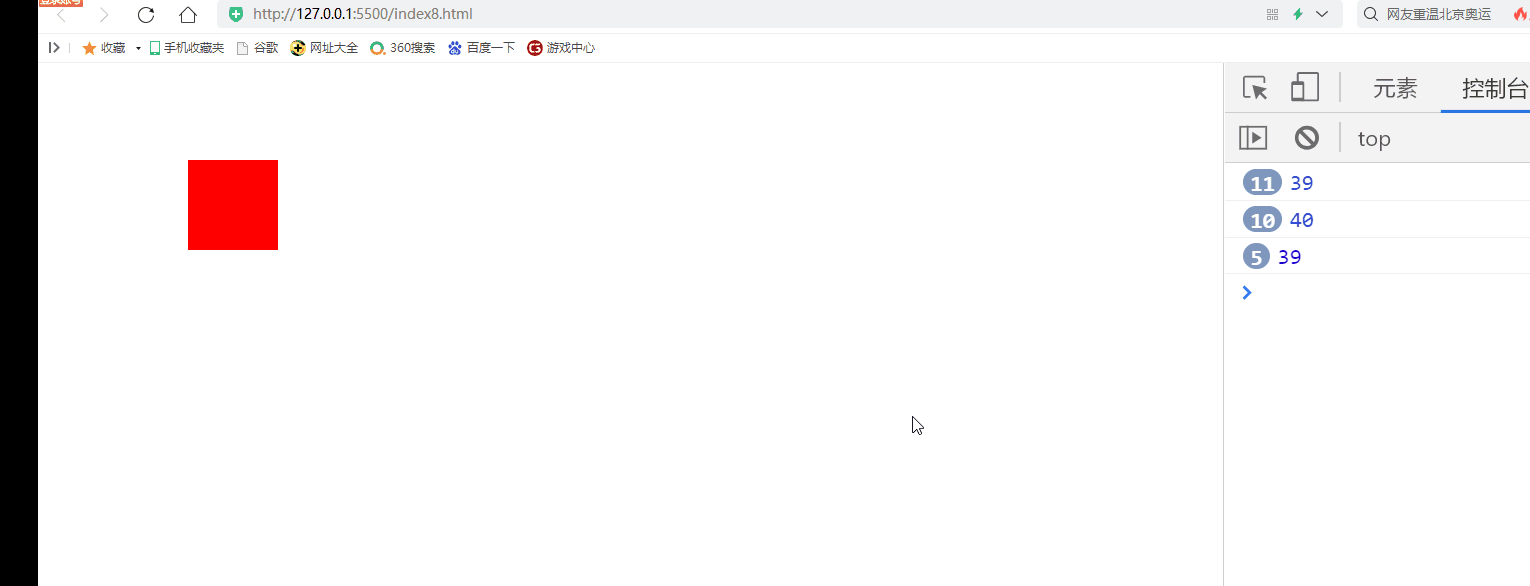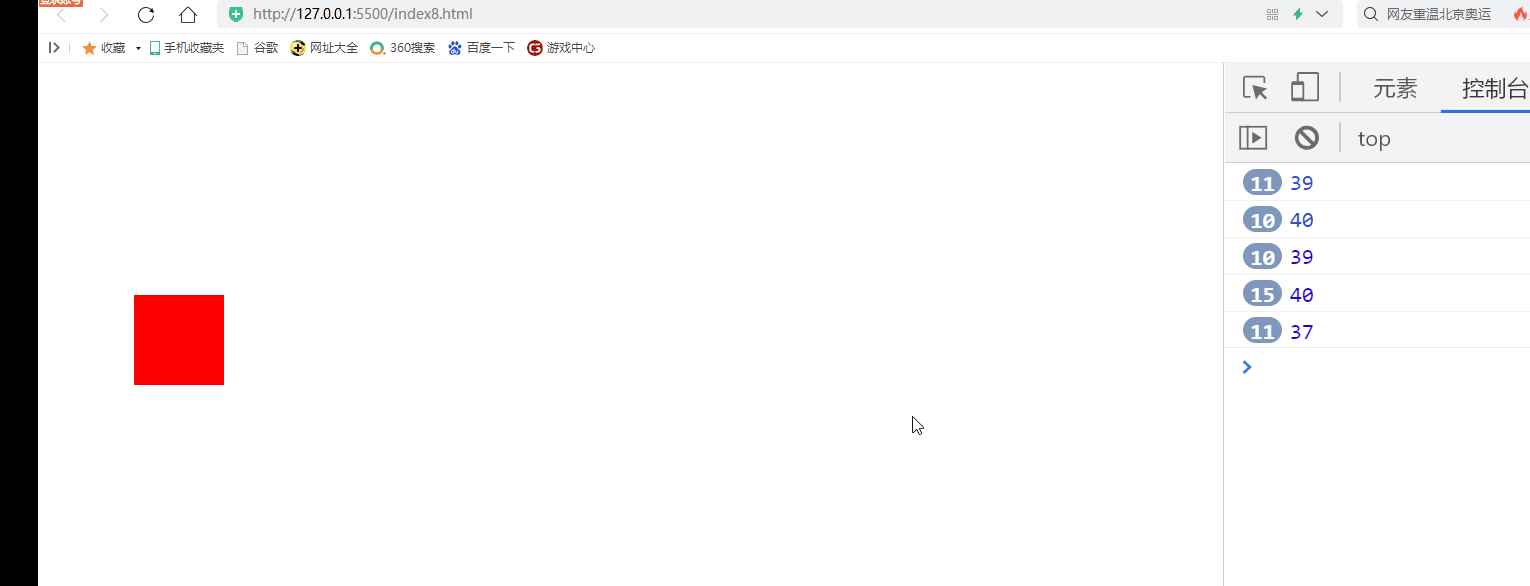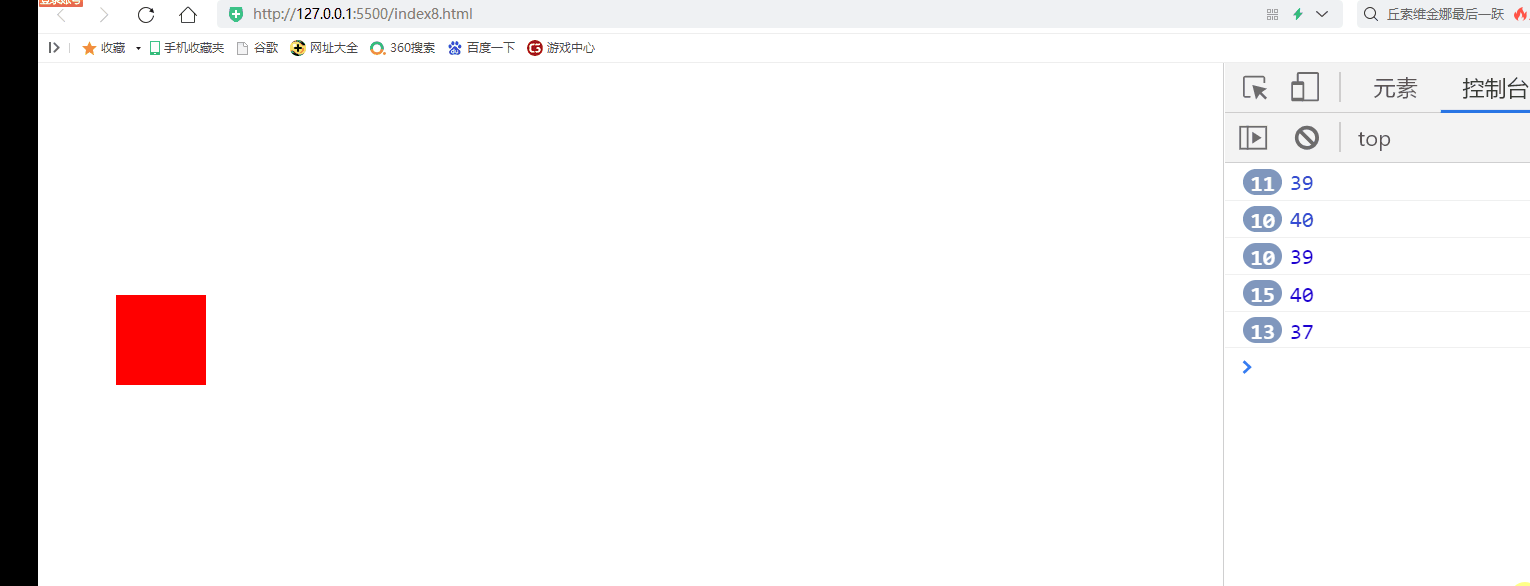
2) Keyboard keys control DIV movement
Disadvantages: when the key is pressed continuously, there is an obvious jam for the first time
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body >
<div style="width:100px;height: 100px;background-color: red; position: absolute;"></div>
</body>
<script>
var div=document.getElementsByTagName("div")[0];
document.onkeydown=function(event){
event=event||window.event;
//You can get up, down, left and right code values through keyCode
//Left: 37 upper: 38 right: 39 lower: 40
console.log(event.keyCode)
//Press the left key
if(event.keyCode==37){
div.style.left=(div.offsetLeft-10)+"px"
}
//Press the up key
if(event.keyCode==38){
div.style.top=(div.offsetTop-10)+"px"
}
//Press the right button
if(event.keyCode==39){
div.style.left=(div.offsetLeft+10)+"px"
}
//Press the next key
if(event.keyCode==40){
div.style.top=(div.offsetTop+10)+"px"
}
//Cancel browser default behavior
return false;
}
</script>
</html>
3, Browser default behavior
+++ Browser default behavior The browser's default behavior refers to the browser's own properties, such as 1,a Automatic jump of labels. a The automatic jump of the tag is a Tagged onclick Default behavior for events. 2,Pulley rolling,If the web page has a scroll bar, it will scroll automatically The scroll bar is the of the label onmousewheel Default behavior for events. 3,In the text box, enter what belongs to onkeydown Default behavior for events.
+++ Cancels the browser's default behavior
1) Cancels the default behavior of the browser, which is only applicable through addEventListener Event binding function.
elem.onclick=function(event){
//Call the preventDefault method to cancel the default behavior of the browser
event.preventDefault()
}
2) Cancels the default behavior of the browser, which is applicable through HTML Labels JS Bound event function
elem.onclick=function(event){
//Return false to cancel the default behavior of the browser
return false;
}
3) Cancel browser default behavior, compatibility processing
elem.onclick=function(event){
//Call the preventDefault method to cancel the default behavior of the browser
event.preventDefault()
//Return false to cancel the default behavior of the browser
return false;
}
2.1 cancel the default behavior of a tag
cancel a The default behavior of the tag, click a The tag will not jump.
Mode 1:
<a href="javascript:;">Baidu</a>
Mode II:
var aElem=document.getElementsByTagName("a")[0]
aElem.onclick=function(event){
event.preventDefault();
return false;
}
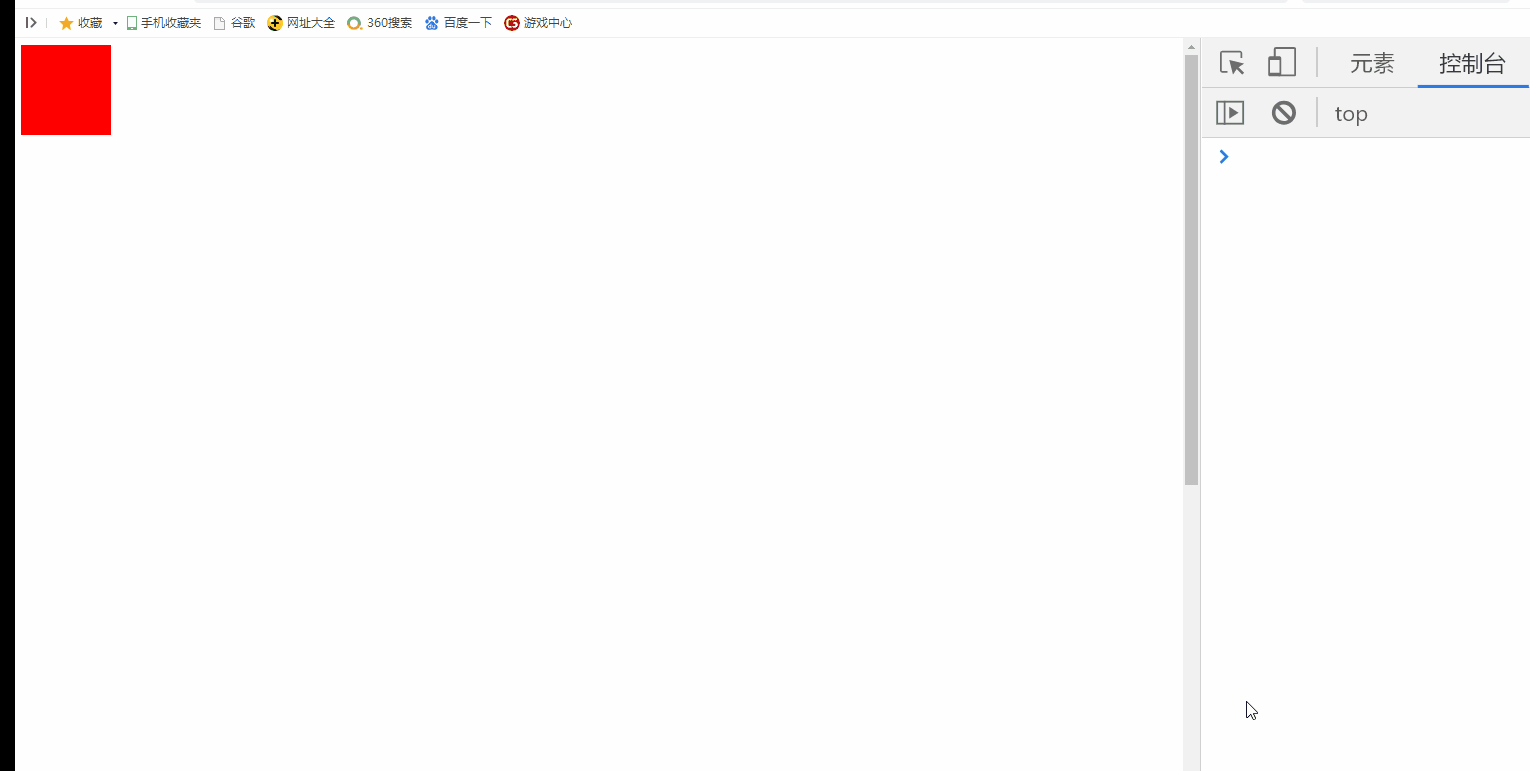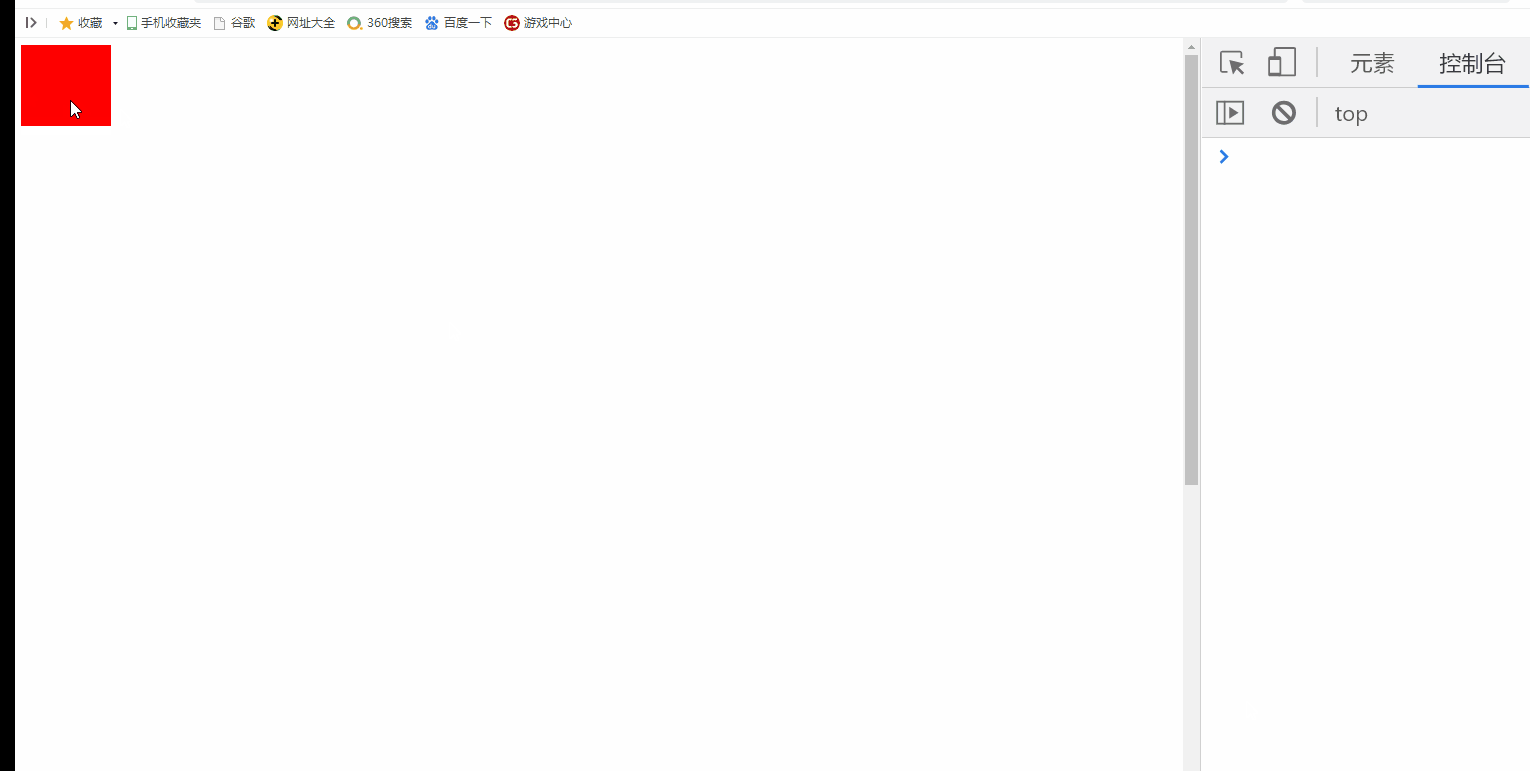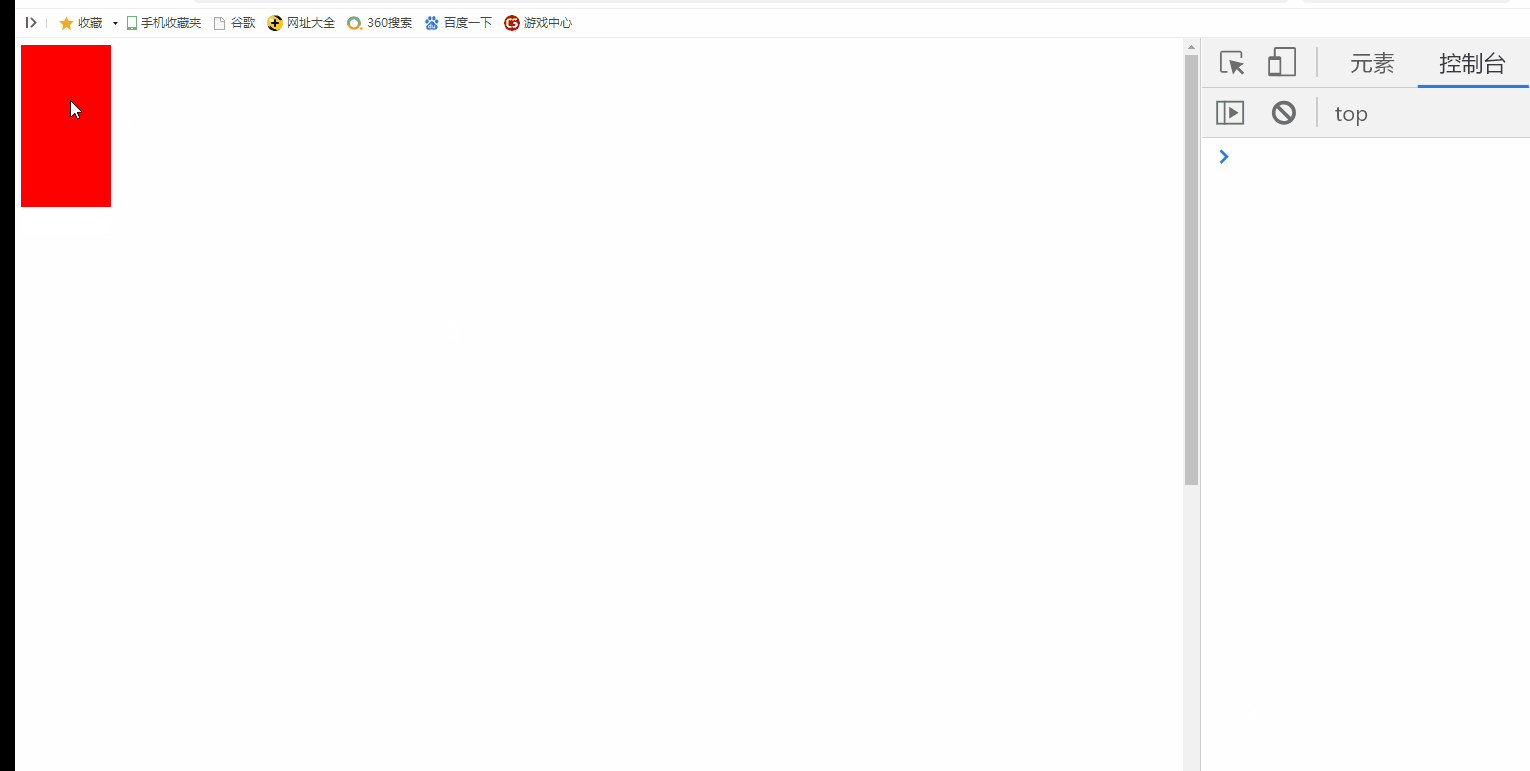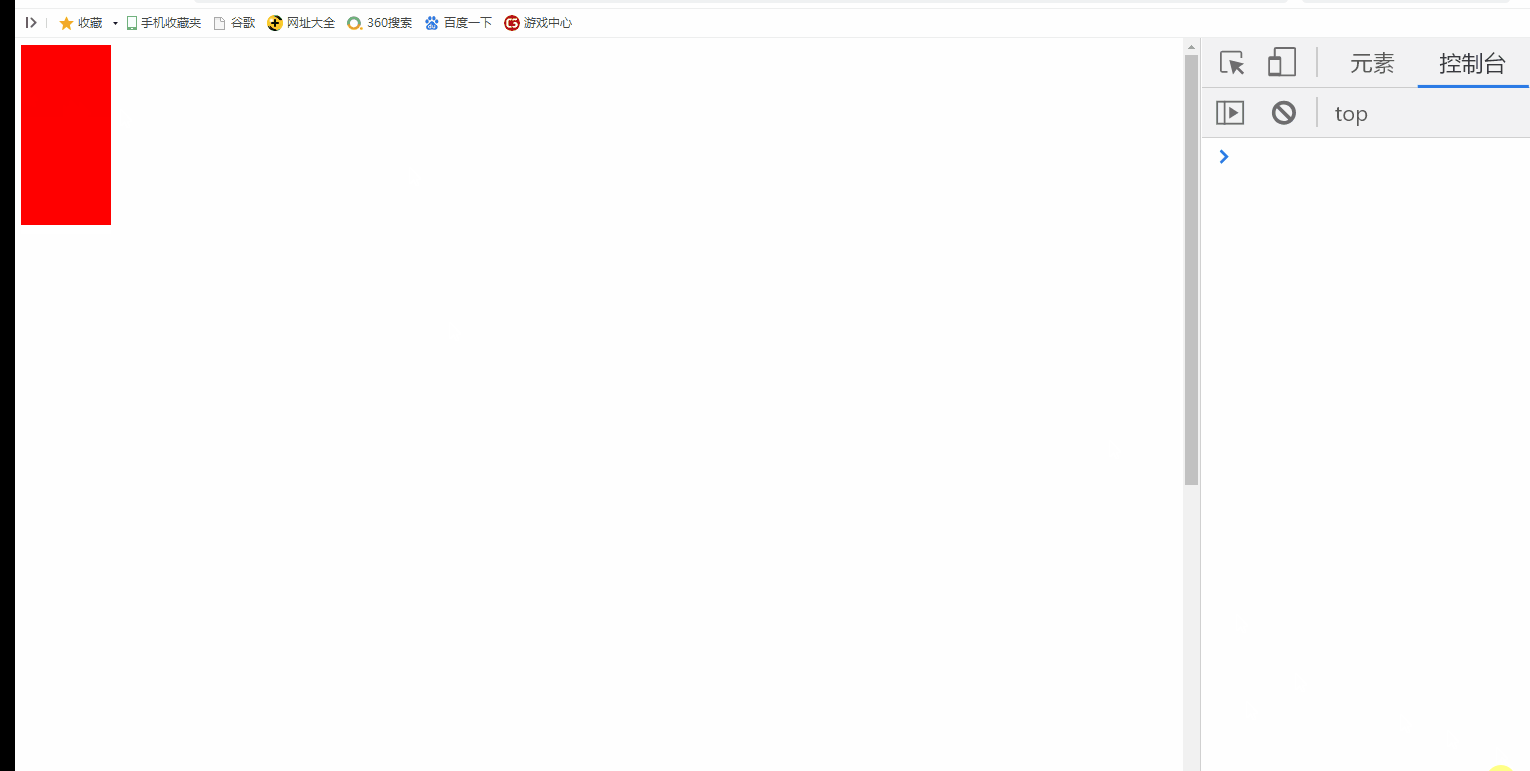
2.2 cancel the default behavior of pulley rolling
Cancel the default behavior of pulley rolling. At this time, if the browser has a scroll bar, it will not slide
var div=document.getElementsByTagName("div")[0]
div.onmouseWheel=function(event){
event.preventDefault();
return false;
}
>>>>>>Scroll wheel, the height of div changes, but the browser scroll bar does not scroll
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body style="height:2000px">
<div style="width:100px;height: 100px;background-color: red; position: absolute;"></div>
</body>
<script>
var div=document.getElementsByTagName("div")[0];
document.onmousewheel=function(event){
event=event||window.event;
//scroll up
if(event.wheelDelta>0){
div.style.height=(div.scrollHeight-10)+"px";
}
//Scroll down
if(event.wheelDelta<0){
div.style.height=(div.scrollHeight+10)+"px";
}
return false;
}
</script>
</html>
2.3 only English can be entered in the text box
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body style="height:2000px">
<input type="text">
</body>
<script>
var input=document.getElementsByTagName("input")[0];
input.onkeydown=function(event){
event=event||window.event;
console.log(event.keyCode)
if(event.keyCode < 65 || event.keyCode >90){
return false;
}
}
</script>
</html>