A* algorithm (3) algorithm implementation
1. Array2D class
A generic class, Array2D, describes the width and height of a map and stores the data for the map
class Array2D: """ 1.The construction method requires two parameters, the width and height of a two-dimensional array 2.Member variables w and h Is the width and height of a two-dimensional array 3.Use:'object[x][y]'The corresponding values can be obtained directly 4.The default values for arrays are all 0 """ def __init__(self, w, h): self.w = w # Width of the map self.h = h # The height of the map self.data = [] # Stored data for maps self.data = [[0 for y in range(h)] for x in range(w)] # Data initialization assignment 0 def __getitem__(self, item): return self.data[item] # Set to get stored data
2. Point class
General class Point is used to describe coordinates of map nodes
And overload the equal sign operator to determine if two Point coordinates are equal
Finally formatted for printing
class Point: """ //Represents a node """ def __init__(self, x, y): self.x = x # The x-coordinate of a node self.y = y # y-coordinate of node def __eq__(self, other): # Determine if references are equal if self.x == other.x and self.y == other.y: return True return False def __str__(self): # Define the format for printing return "x:" + str(self.x) + ",y:" + str(self.y)
3. AStar class
AStar algorithm, heuristic function default Manhattan distance
class AStar: # Describing node data in AStar algorithm class Node: def __init__(self, point, goalPoint, g=0, hef='MD'): self.point = point # Own coordinates self.father = None # Parent node self.g = g # g value, the current cost incurred self.D = 10 # D-fold # h value, possible future cost if hef == 'DD': # Diagonal distance D2 = np.sqrt(2) * self.D h_diagonal = min(abs(point.x - goalPoint.x), abs(point.y - goalPoint.y)) h_straight = (abs(point.x - goalPoint.x) + abs(point.y - goalPoint.y)) self.h = D2 * h_diagonal + self.D * (h_straight - 2 * h_diagonal) elif hef == 'ED': # Euclidean Distance self.h = np.sqrt(pow(point.x - goalPoint.x, 2) + pow(point.y - goalPoint.y, 2)) else: # Manhattan Distance self.h = (abs(point.x - goalPoint.x) + abs(point.y - goalPoint.y)) * self.D def __init__(self, map2d, startPoint, goalPoint, passTag=0, hef='MD'): # Heuristic function if hef != 'MD' and hef != 'DD' and hef != 'ED': hef = 'MD' print("Error in heuristic function input, should be MD DD ED\n Default Manhattan Distance") self.hef = hef # Open the table to save nodes that have been generated but not accessed self.openList = [] # Close the table to save the visited nodes self.closeList = [] # Path finding map self.map2d = map2d # Starting point end point if isinstance(startPoint, Point) and isinstance(goalPoint, Point): self.startPoint = startPoint self.goalPoint = goalPoint else: self.startPoint = Point(*startPoint) self.goalPoint = Point(*goalPoint) # Walkable Marker self.passTag = passTag def getMinNode(self): currentNode = self.openList[0] for node in self.openList: if node.g + node.h < currentNode.g + currentNode.h: currentNode = node return currentNode def pointInCloseList(self, point): for node in self.closeList: if node.point == point: return True return False def pointInOpenList(self, point): for node in self.openList: if node.point == point: return node return None def goalPointeInCloseList(self): for node in self.closeList: if node.point == self.goalPoint: return node return None def searchNear(self, minF, offsetX, offsetY): # Cross-border detection if minF.point.x + offsetX < 0 or minF.point.x + offsetX > self.map2d.w - 1 or \ minF.point.y + offsetY < 0 or minF.point.y + offsetY > self.map2d.h - 1: return # If it's a barrier, ignore it if self.map2d[minF.point.x + offsetX][minF.point.y + offsetY] != self.passTag: return # Ignore if table is closed currentPoint = Point(minF.point.x + offsetX, minF.point.y + offsetY) if self.pointInCloseList(currentPoint): return # Set unit cost if offsetX == 0 or offsetY == 0: step = 10 else: step = 14 # If you no longer have an openList, add it to the openlist currentNode = self.pointInOpenList(currentPoint) if not currentNode: currentNode = AStar.Node(currentPoint, self.goalPoint, g=minF.g + step, hef=self.hef) currentNode.father = minF self.openList.append(currentNode) return # In openList, determine if the g value from minF to the current point is smaller if minF.g + step < currentNode.g: # If smaller, recalculate g and change the father currentNode.g = minF.g + step currentNode.father = minF def start(self): # Determine if the starting point is a barrier if self.map2d[self.startPoint.x][self.startPoint.y] != self.passTag: return None # Determine if the target point is an obstacle if self.map2d[self.goalPoint.x][self.goalPoint.y] != self.passTag: return None # 1. Put the starting point in the open list startNode = AStar.Node(self.startPoint, self.goalPoint, hef=self.hef) self.openList.append(startNode) # 2. Main Loop Logic while True: # Find the point with the lowest F value minF = self.getMinNode() # Add this point to the closeList and delete it in the openList self.closeList.append(minF) self.openList.remove(minF) # Determine the top, bottom, left, and right nodes of this target point. Diagonal motion is not allowed by default self.searchNear(minF, 0, -1) self.searchNear(minF, 0, 1) self.searchNear(minF, -1, 0) self.searchNear(minF, 1, 0) # Allow diagonal motion if heuristic function is not Manhattan distance if self.hef != 'MD': self.searchNear(minF, 1, 1) self.searchNear(minF, 1, -1) self.searchNear(minF, -1, 1) self.searchNear(minF, -1, -1) # Determine whether to terminate point = self.goalPointeInCloseList() if point: # If the end point is in the closed table, the result is returned cPoint = point pathList = [] while True: if cPoint.father: pathList.append(cPoint.point) cPoint = cPoint.father else: return list(reversed(pathList)) if len(self.openList) == 0: return None
Here's a more detailed look at the code:
3.1 Node Class
First, create a class Node that contains its own coordinate point, parent node father, g-value, h-value
Different heuristic functions, corresponding to different h-value operations
Default MD: Manhattan Distance, DD: Diagonal Distance, ED: Euclidean Distance
class Node: def __init__(self, point, goalPoint, g=0, hef='MD'): self.point = point # Own coordinates self.father = None # Parent node self.g = g # g value, the current cost incurred self.D = 10 # D-fold # h value, possible future cost if hef == 'DD': # Diagonal distance D2 = np.sqrt(2) * self.D h_diagonal = min(abs(point.x - goalPoint.x), abs(point.y - goalPoint.y)) h_straight = (abs(point.x - goalPoint.x) + abs(point.y - goalPoint.y)) self.h = D2 * h_diagonal + self.D * (h_straight - 2 * h_diagonal) elif hef == 'ED': # Euclidean Distance self.h = np.sqrt(pow(point.x - goalPoint.x, 2) + pow(point.y - goalPoint.y, 2)) else: # Manhattan Distance self.h = (abs(point.x - goalPoint.x) + abs(point.y - goalPoint.y)) * self.D
3.2 Initialization Processing
Then initialize the process
Make sure the hef boot function is correct first
Then create an open table openList to save the nodes that have been generated but not accessed
Then create a close table closeList to save the visited nodes
Initialize route finding map map2d, start point Point, end point goalPoint, feasible walk marker passTag
def __init__(self, map2d, startPoint, goalPoint, passTag=0, hef='MD'): # Heuristic function if hef != 'MD' and hef != 'DD' and hef != 'ED': hef = 'MD' print("Error in heuristic function input, should be MD DD ED\n Default Manhattan Distance") self.hef = hef # Open the table to save nodes that have been generated but not accessed self.openList = [] # Close the table to save the visited nodes self.closeList = [] # Path finding map self.map2d = map2d # Starting point end point if isinstance(startPoint, Point) and isinstance(goalPoint, Point): self.startPoint = startPoint self.goalPoint = goalPoint else: self.startPoint = Point(*startPoint) self.goalPoint = Point(*goalPoint) # Walkable Marker self.passTag = passTag
Define a function to get the node with the lowest F value in openlist
def getMinNode(self): currentNode = self.openList[0] for node in self.openList: if node.g + node.h < currentNode.g + currentNode.h: currentNode = node return currentNode
3.3 Judgment Function
Define some functions for judgment, which are literally easier to understand
pointInCloseList: Determines whether a node is in a CloseList, that is, whether the node has been visited
pointInOpenList: Determines whether a node is in OpenList, that is, whether a node is generated and not visited
goalPointeInCloseList: Determines whether the target point is in the CloseList, that is, whether the target point has been visited, and returns the target node if it exists
def pointInCloseList(self, point): for node in self.closeList: if node.point == point: return True return False def pointInOpenList(self, point): for node in self.openList: if node.point == point: return node return None def goalPointeInCloseList(self): for node in self.closeList: if node.point == self.goalPoint: return node return None
3.4 Search for points around nodes
Create a function to search for points around nodes
def searchNear(self, minF, offsetX, offsetY): # Cross-border detection if minF.point.x + offsetX < 0 or minF.point.x + offsetX > self.map2d.w - 1 or \ minF.point.y + offsetY < 0 or minF.point.y + offsetY > self.map2d.h - 1: return # If it's a barrier, ignore it if self.map2d[minF.point.x + offsetX][minF.point.y + offsetY] != self.passTag: return # Ignore if table is closed currentPoint = Point(minF.point.x + offsetX, minF.point.y + offsetY) if self.pointInCloseList(currentPoint): return # Set unit cost if offsetX == 0 or offsetY == 0: step = 10 else: step = 14 # If you no longer have an openList, add it to the openlist currentNode = self.pointInOpenList(currentPoint) if not currentNode: currentNode = AStar.Node(currentPoint, self.goalPoint, g=minF.g + step, hef=self.hef) currentNode.father = minF self.openList.append(currentNode) return # In openList, determine if the g value from minF to the current point is smaller if minF.g + step < currentNode.g: # If smaller, recalculate g and change the father currentNode.g = minF.g + step currentNode.father = minF
It is worth noting that:
Because searches are sequential, it is possible that the same batch of nodes exist when scattering searches for surrounding nodes
The parent of the surrounding node may not necessarily be the nearest node
If the node happens to be a routing path, it may result in extra paths
So if there is already an openlist around the point, you need to determine if the g value from minF to the current point is smaller
If smaller, the g-value is recalculated and the parent node father is changed
This eliminates the potential for parent nodes with non-minimum g values at the previous nodes and avoids generating redundant paths
Take a simple example: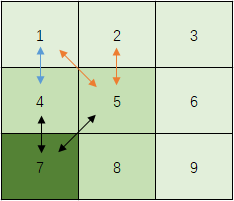
7 Search 8, 5, 4 in counterclockwise order, 9, 6, 3, 2, 1 in counterclockwise order if the f value of 5 is the smallest
If 5-way roads have obstacles and switch to 4 as routes, search counterclockwise for 2, 1, etc.
1 and 2 already exist in openlist
The parent node of 1 needs to be changed to 4 when searching again because 1 is shorter from 4 nodes
2 retains 5 as its parent because 2 is shorter from 5 nodes
3.5 Wayfinding
Create a function for routing
Start by determining whether the starting point startPoint and the target point goalPoint are reasonable
Then put the starting point startPoint in the open list openList
Then the main loop logic begins:
1. Find the point with the lowest F value in openlist
2. Add this point to the closeList and delete it in the openList
3. Search for surrounding nodes, default 4, 8 when diagonal motion is allowed
4. If the target point is in a closed table, abort the loop and return the result, otherwise return to the starting point of the loop
def start(self): # Determine if the starting point is a barrier if self.map2d[self.startPoint.x][self.startPoint.y] != self.passTag: return None # Determine if the target point is an obstacle if self.map2d[self.goalPoint.x][self.goalPoint.y] != self.passTag: return None # 1. Put the starting point in the open list startNode = AStar.Node(self.startPoint, self.goalPoint, hef=self.hef) self.openList.append(startNode) # 2. Main Loop Logic while True: # Find the point with the lowest F value minF = self.getMinNode() # Add this point to the closeList and delete it in the openList self.closeList.append(minF) self.openList.remove(minF) # Determine the top, bottom, left, and right nodes of this node. Diagonal motion is not allowed by default self.searchNear(minF, 0, -1) self.searchNear(minF, 0, 1) self.searchNear(minF, -1, 0) self.searchNear(minF, 1, 0) # Allow diagonal motion if heuristic function is not Manhattan distance if self.hef != 'MD': self.searchNear(minF, 1, 1) self.searchNear(minF, 1, -1) self.searchNear(minF, -1, 1) self.searchNear(minF, -1, -1) # Determine whether to terminate point = self.goalPointeInCloseList() if point: # Returns the result if the target point is in a closed table cPoint = point pathList = [] while True: if cPoint.father: pathList.append(cPoint.point) cPoint = cPoint.father else: return list(reversed(pathList)) if len(self.openList) == 0: return None
Here is a simple flowchart: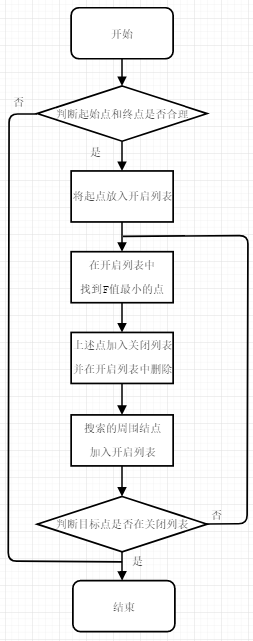
4. Map display
Tracks used to display A* algorithm calculations on the map
def Display_map(map, start=None, goal=None, title=None): plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # Set normal display Chinese plt.xlim(- 1, map.w) plt.ylim(- 1, map.h) plt.xticks(np.arange(0, map.w, 1)) plt.yticks(np.arange(0, map.h, 1)) plt.grid(lw=2) obstaclesX, obstaclesY = [], [] pathx, pathy = [], [] for x in range(map.w): for y in range(map.h): if map[x][y] == 1: obstaclesX.append(x) obstaclesY.append(y) elif map[x][y] == 'o': pathx.append(x) pathy.append(y) if obstaclesX != []: plt.plot(obstaclesX, obstaclesY, 'xr', markersize=10, label='obstacle') if pathx != []: plt.plot(pathx, pathy, 'og', markersize=10, label='Route') if start != None: plt.plot(start[0], start[1], 'or', markersize=10, label='Start') if goal != None: plt.plot(goal[0], goal[1], 'ob', markersize=10, label='target') if title != None: plt.title(title) # Set Title plt.legend() # Set Legend plt.show()
5. Computing tests
if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a 10*10 map mapw, maph = 10, 10 map2d = Array2D(mapw, maph) # obstruct obstacle = [[4, 9], [4, 8], [4, 7], [4, 6], [4, 5]] for i in obstacle: map2d[i[0]][i[1]] = 1 # Show what the map looks like when barriers are set Display_map(map2d, title="obstruct") # Set the starting point and ending point startx, starty = 0, 0 goalx, goaly = 9, 8 # Show what the map looks like when it sets the start and end points Display_map(map2d, [startx, starty], [goalx, goaly], title="Planning preparation") # Create an AStar object aStar = AStar(map2d, Point(startx, starty), Point(goalx, goaly), hef='MD') # Start to Find Way pathList = aStar.start() # Traverse path points, expressed as'o'on map2d for point in pathList: map2d[point.x][point.y] = 'o' # Show the map again Display_map(map2d, [startx, starty], [goalx, goaly], title="Track Planning")
Here's a more detailed look at the code:
5.1 Creating maps
Create a 10*10 map
mapw, maph = 10, 10 map2d = Array2D(mapw, maph)
5.2 Setting Barriers
Barriers are set at [4, 9], [4, 8], [4, 7], [4, 6], [4, 5] nodes
Then show the map with the barrier set at this time
obstacle = [[4, 9], [4, 8], [4, 7], [4, 6], [4, 5]] for i in obstacle: map2d[i[0]][i[1]] = 1 Display_map(map2d, title="obstruct")
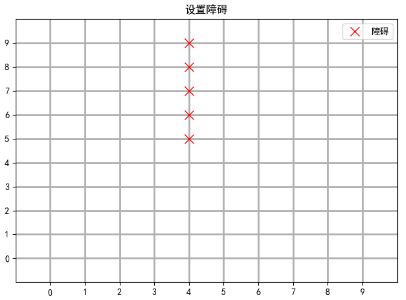
5.3 Setting the start and end points
Set the starting point (0, 0) and ending point (9, 8)
Then display the map after the start and end points are set at this time
startx, starty = 0, 0 goalx, goaly = 9, 8 Display_map(map2d, [startx, starty], [goalx, goaly], title="Planning preparation")
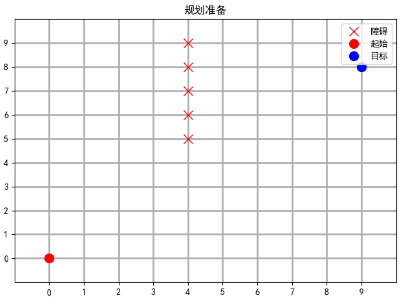
5.4 Manhattan Distance
The startup function uses Manhattan distance to start finding a way
# Create an AStar object aStar = AStar(map2d, Point(startx, starty), Point(goalx, goaly), hef='MD') # Start to Find Way pathList = aStar.start() # Traverse path points, expressed as'o'on map2d for point in pathList: map2d[point.x][point.y] = 'o' # Show the map again Display_map(map2d, [startx, starty], [goalx, goaly], title="Manhattan Distance Track Planning")
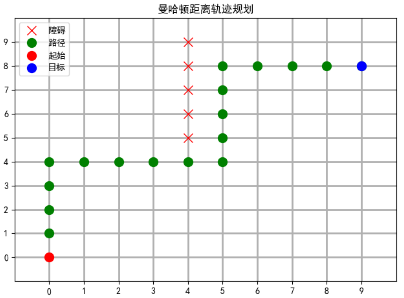
5.5 Diagonal Distance
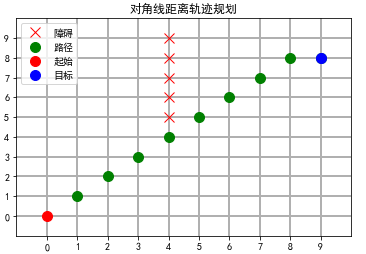
The startup function uses a diagonal distance to start finding a way
# Create an AStar object aStar = AStar(map2d, Point(startx, starty), Point(goalx, goaly), hef='DD') # Start to Find Way pathList = aStar.start() # Traverse path points, expressed as'o'on map2d for point in pathList: map2d[point.x][point.y] = 'o' # Show the map again Display_map(map2d, [startx, starty], [goalx, goaly], title="Diagonal Distance Track Planning")
5.6 Euclidean Distance
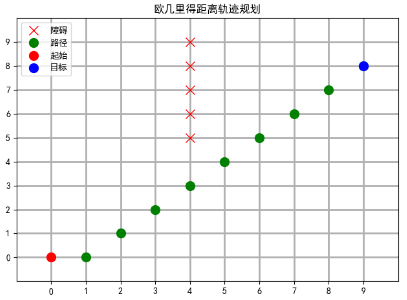
The startup function uses Euclidean distance to start finding a way
# Create an AStar object aStar = AStar(map2d, Point(startx, starty), Point(goalx, goaly), hef='ED') # Start to Find Way pathList = aStar.start() # Traverse path points, expressed as'o'on map2d for point in pathList: map2d[point.x][point.y] = 'o' # Show the map again Display_map(map2d, [startx, starty], [goalx, goaly], title="Euclidean Distance Trajectory Planning")
[1] Code address for python:
https://github.com/JoveH-H/A-simple-explanation/blob/master/A%20star.py
[2] Code address of jupyter notebook:
https://github.com/JoveH-H/A-simple-explanation/blob/master/ipynb/A%20star.ipynb
Recommendations:
A* algorithm (2) heuristic algorithm
A*Algorithms (1) Introduction to Algorithms
Thank you!