[experimental principle]
1. Eight digital problems
Judging whether there is a solution or not: directly judge whether there is a solution according to the reverse order number. For an eight digit number, after the sequence is arranged, each time the empty bit and the adjacent bit are exchanged. After research, it will be found that each exchange, the increase of the reverse order number is even, that is, it does not change the parity, so the parity of the reverse order number in the initial and target states is the same.
2. State chart search
(1) Search tree: the nodes and edges in the search process form a tree type digraph according to the connection relationship of the original graph, which is called search tree.
(2) Search method: tree search - record all nodes and edges in the search process
(3) Path acquisition: tree search reverse solution
(4) CLOSED table and OPEN table: CLOSED table stores a growing search tree for tree search, and a growing broken line for line search, which is the desired path. The OPEN table stores the current nodes to be examined.
3. A algorithm
(1) Heuristic function: a function used to estimate the proximity of node X to the target node Sg on the search tree. It is recorded as h(x)
(2) Evaluation function: f(x)=g(x)+h(x)f(x)=g(x)+h(x)f(x)=g(x)+h(x); where g(x)g(x)g(x) is the cost function and h(x)h(x)h(x) H (x) is the heuristic function. Or defined as: F (x) = D (x) + H (x) f (x) = D (x) + H (x) f (x) = D (x) + H (x); D (x) d (x) d (x) is the depth of xxx
(3) Algorithm steps
Step1Step1Step1: add S0 to the OPEN table
Step2Step2Step2: if the OPEN table is empty, the search fails and exits
Step3Step3Step3: move the first node N from the OPEN table to the CLOSED table
Step4Step4Step4: if N is the target node, the search is successful
Step5Step5Step5: if it is not extensible, turn to Step2Step2Step2
Step6Step6Step6: handle the extended word nodes accordingly:
① Generate whether there are existing points in the OPEN table or CLOSED table in the child node; if there are any, then consider whether there are predecessor nodes of N, and delete them; if there are other nodes, delete them, and modify their f(x) value;
② Modify the pointer of the parent node, add the remaining child nodes to OPEN, sort the OPEN table, and turn to Step2Step2Step2
[experiment content]
1. requirements
(1) The cost function G(x)G(x)G(x) and heuristic function H(X)H(X)H(X) H (x) are defined and solved by algorithm A.
(2) Enter the initial and target states.
(3) Outputs the route from the initial state to the target state.
2. Code list
#include <iostream> #include <type_traits> #include<stdlib.h> #include <windows.h> #include <time.h> using namespace std; #define MAXNUM 100 #define OK 1 #define ERROR 0 int ss0[9] = { 0 }; // Initial node, to be input int ssg[9] = { 0 }; // Target node, to be input class Table; class Node { // Node class public: Node(); // Default constructor Node(int s[]); // Constructor initialized with array Node &operator=(const Node ss); //Operator overload for assignment void showStatus(); // Display node status bool operator==(Node &N); // Operator overload, used to determine whether it is equal int Ancestors(Node ss); // Ancestor node int gx(); // Cost function int hx(); // Heuristic function int fx(); // Valuation function int expand( Node kid[]); // Expand child nodes friend class Table; // Friend class Table friend int A(Node S0, Node Sg); // Algorithm of friend function A private: int *status = new int[9]; // node state int steps; // Node depth int f; // Node fx value ֵ Node *father; // ָ parent node pointer }; Node deleted; // Represents the deleted node for comparison and assignment Node::Node() // Default constructor { for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { status[i] = 0; } f = steps = 0; father = NULL; } Node::Node(int s[])// Constructor initialized with array { for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { status[i] = s[i]; } steps = 0; f = fx(); father = NULL; } Node& Node::operator=(const Node ss)//Operator overload for assignment { for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { status[i] = ss.status[i]; } steps = ss.steps; f = ss.f; father = ss.father; return *this; } void Node::showStatus()// Display node status { cout << "┏━━━━━━━━━━┓" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { cout << "┃"; for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { if (status[i * 3 + j] == 0) { cout << " "; } else { cout << " " << status[i * 3 + j]; } } cout << " ┃" << endl; } cout << "┗━━━━━━━━━━┛" << endl; } bool Node::operator==(Node &N) { for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { if (status[i] != N.status[i]) { return false; } } return true; } int Node::Ancestors(Node ss) // If ss is the ancestor node, if yes, it will return a high number of generations { int generation = 1; Node *p = father; while (p != NULL) { if (*p == ss) { return generation; } p = p->father; generation++; } return 0; } int Node::gx() { return steps;// Cost function value is node depth } int Node::hx() { int h = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { if (status[i] != ssg[i]) { h++; // If each bit is inconsistent with the target node, the heuristic function value is increased by one } } return h; } int Node::fx() { return (gx() + hx()); } int Node::expand(Node kid[]) { int point, i, j; for (i = 0; i < 9; i++) { if (status[i] == 0) { point = i; } } i = 0; if (point - 3 >= 0) { // Prevent upward expansion across borders for (j = 0; j < 9; j++) { kid[i].status[j] = status[j]; } swap(kid[i].status[point], kid[i].status[point - 3]); kid[i].steps = steps + 1; kid[i].f = kid[i].fx(); i++; } if (point + 3 <= 8) { // Prevent downward expansion out of bounds for (j = 0; j < 9; j++) { kid[i].status[j] = status[j]; } swap(kid[i].status[point], kid[i].status[point + 3]); kid[i].steps = steps + 1; kid[i].f = kid[i].fx(); i++; } if (point % 3 != 0) { // Prevent left extend out of bounds for (j = 0; j < 9; j++) { kid[i].status[j] = status[j]; } swap(kid[i].status[point], kid[i].status[point - 1]); kid[i].steps = steps + 1; kid[i].f = kid[i].fx(); i++; } if ((point + 1) % 3 != 0) { // Prevent right expansion out of bounds for (j = 0; j < 9; j++) { kid[i].status[j] = status[j]; } swap(kid[i].status[point], kid[i].status[point + 1]); kid[i].steps = steps + 1; kid[i].f = kid[i].fx(); i++; } if (i == 0) { return ERROR; } else { return i; } } class Table { public: Table(); // Constructor int Add(Node S); // Add node to table int Delete(int i); // Delete node bool isEmpty(); // Judgement of surface space int Search(Node NS); // Find NS node in table int Sort(); // Sort tables in fx ascending order void showNode(); // Print table friend int A(Node S0, Node Sg); // A algorithm private: Node node[MAXNUM]; // Node in table int length; // Table length }; Table::Table() {// Constructor for (int i = 0; i < MAXNUM; i++) { // Initialization table length is 0 length = 0; } } int Table::Add(Node S) { if (length < MAXNUM) { // Determine if it is full node[length] = S; length++; return OK; } else { return ERROR; } } int Table::Delete(int i) { if (i > 0 && i < length) { // Judge whether the table is empty for (int j = i - 1; j < length - 1; j++) { node[j] = node[j + 1]; } length--; return OK; } else if (i == length) { node[i - 1]=deleted; length--; return OK; } else { // Error prompt cout << "Input illegal in delete function!" << endl; return ERROR; } } bool Table::isEmpty() { if (length > 0) { // Not empty return false; } else {// Empty return true; } } int Table::Search(Node NS) { for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { if (NS == node[i]) { return i + 1; // Return the sequence number of NS in the table } } return 0; } int Table::Sort() { // Sort in fx ascending order if (isEmpty()) { return ERROR; } else { Node temp; for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < length - 1 - i; j++) { if (node[j].f > node[j + 1].f) { temp = node[j]; node[j]=node[j + 1]; node[j + 1] = temp; } } } return OK; } } void Table::showNode() { // Print table if (length == 0) { cout << "Empty!" << endl; } else { for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) { node[i].showStatus(); cout << " ↓ " << endl; } node[length - 1].showStatus(); } } Table Path; // Record solution path int inversions(int S[]) // Calculating the reverse number of s array { int i = 0, point; int ss[8] = { 0 }; int s_inversions = 0; //Inverse number for (i = 0; i < 9; i++) { if (S[i]==0){ point = S[i]; } else { ss[i] = S[i]; } } for (i = point; i < 9; i++) { ss[point] = S[point + 1]; } for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) { for (int j = i; j < 8; j++) { if (ss[i] > ss[j]) s_inversions++; } } return s_inversions; } int A(Node S0, Node Sg) { // A algorithm if ((inversions(S0.status) + inversions(Sg.status)) % 2 != 0) { return ERROR; } Table OPEN, CLOSED; // OPEN and CLOSED tables int &m = OPEN.length; // OPEN table long alias int &n = CLOSED.length; // CLOSED table long alias int time = 0; Node *kid = new Node[4]; cout << "Original status: " << endl; S0.showStatus(); cout << "Goal status: " << endl; Sg.showStatus(); cout << endl << "========================" << endl; OPEN.Add(S0); // Step 1: add S0 to the OPEN table while (true) { if (OPEN.isEmpty()) { // Step 2: if the OPEN table is empty, the search fails and exits return ERROR; } CLOSED.Add(OPEN.node[0]); // Step 3: move the first node N from the OPEN table to the CLOSED table Node &N = CLOSED.node[n - 1]; // OPEN.Delete(1); if (N==Sg) { // Step4: if N is the target node, the search is successful cout << "Find succeed!" << endl; cout << "========================" << endl; system("pause"); return OK; } int kid_num = N.expand(kid); int flag = 4; for (int i = 0; i < kid_num; i++) { if ((OPEN.Search(kid[i]) != 0) || (CLOSED.Search(kid[i]) != 0)) { flag--; } } if (flag == ERROR) { // Step5: if it is not extensible, turn to Step2 continue; } for (int i = 0; i < kid_num; i++) { //Step 6: handle the extended word nodes accordingly int exOPEN = OPEN.Search(kid[i]);// Generate whether there are existing points in the OPEN table in the child node int exCLOSED = CLOSED.Search(kid[i]);// Generate whether there are existing points in the CLOSED table in the child node if (exOPEN > 0) { if (N.Ancestors(kid[i])) {// If there is, then consider whether there is a predecessor node of N, and delete if there is kid[i] = deleted; } else { // For other nodes, delete them, and modify their f(x) values if (OPEN.node[exOPEN - 1].f > kid[i].f) { OPEN.node[exOPEN - 1].father = &N; OPEN.node[exOPEN - 1].f = kid[i].f; } kid[i] = deleted; } } // if exOPEN>0 else if (exCLOSED>0) { if (N.Ancestors(kid[i])!=0) {// If there is, then consider whether there is a predecessor node of N, and delete if there is kid[i] = deleted; } else { // For other nodes, delete them, and modify their f(x) values if (CLOSED.node[exCLOSED - 1].f > kid[i].f) { CLOSED.node[exCLOSED - 1].father = &N; CLOSED.node[exCLOSED - 1].f = kid[i].f; } kid[i] = deleted; } } // else if else { kid[i].father = &N; // Modify parent node pointer } if (!(kid[i] == deleted)) { OPEN.Add(kid[i]); // The remaining child nodes are added to OPEN } } OPEN.Sort(); //OPEN table sort if ((Path.node[Path.length - 1] == *OPEN.node[0].father)&&!OPEN.isEmpty()) { Path.Add(OPEN.node[0]); } cout << "==========open============" << endl; OPEN.showNode(); cout << endl; cout << "==========closed==========" << endl; CLOSED.showNode(); cout << endl; cout << "==========path============" << endl; Path.showNode(); cout << endl; system("pause"); system("cls"); }// while delete kid; return ERROR; } int main() { cout << "Input the original status: "; // Input initial state for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { cin >> ss0[i]; } Node S0(ss0); Path.Add(S0); cout << "Input the goal status: ";// Enter target status for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { cin >> ssg[i]; } Node Sg(ssg); cout << endl; if (A(S0, Sg) == OK) { //Search success cout << endl << endl; cout << "The find process is: " << endl; Path.showNode();// Print solution path } else { // Prompt search failed cout << "Search failed! This status have no solution!" << endl; } system("pause"); return 0; }
3. Operation results
(1) Manual entry of initial and target states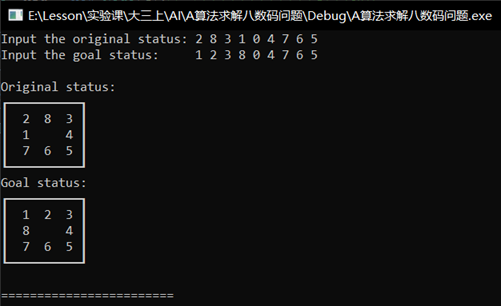
(2) Show OPEN and CLOSED tables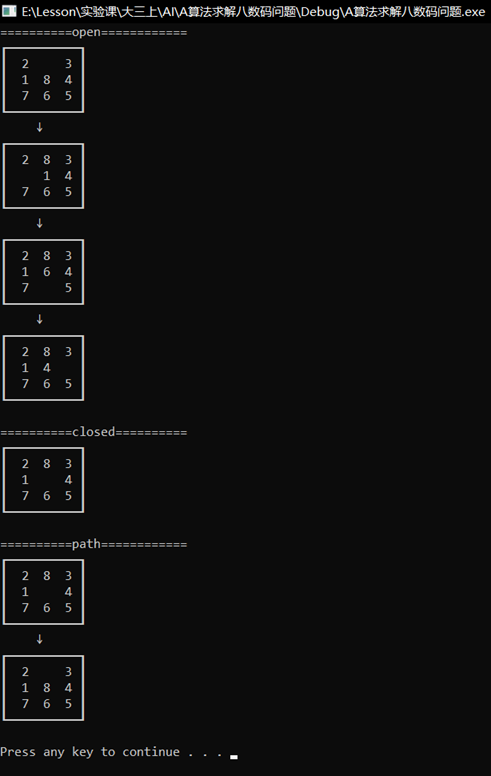
(3) Press enter to refresh the interface, the second sub node expansion: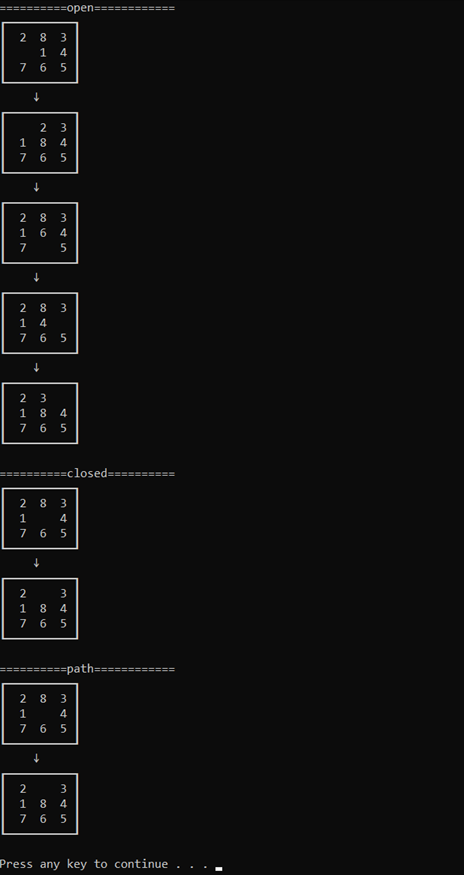
(4) Search succeeded, print search path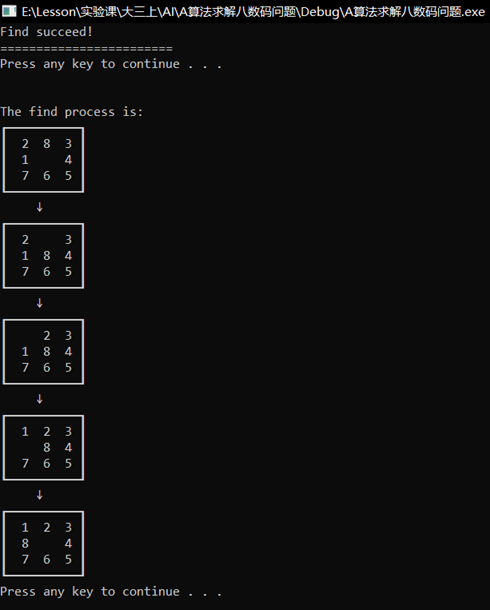
[summary or discussion]
In this experiment, I directly followed the textbook (Introduction to artificial intelligence technology (Third Edition) during the 11th Five Year Plan
Mr. Lian / November 2018/ In step 6, judge whether there are existing points in the OPEN table or CLOSED table in the generated sub node; if there are, consider whether there are N predecessor nodes in the generated sub node; if there are, delete them; if there are other nodes, modify their f(x) value. Here, I delete the generated sub node 2 and modify the CLOSED table There are no duplicate nodes in table D, but these nodes are not added to the OPEN table for re expansion, resulting in a life and death cycle in the case of many steps. In addition, it is discussed with a student that setting a clever heuristic function can improve the search efficiency, which can still be modified here.

