Ask questions
Through previous research on parsing excel in java, it was found that the parsing of Excel in some complex formats could not be satisfied, such as
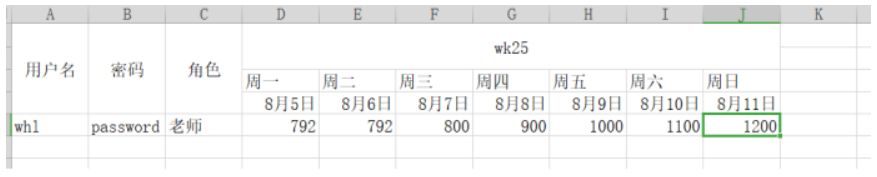
The excel of this format cannot be parsed using the previous method, so how should we parse Excel for this complex format?
Analytical problems
We studied the relationship of this complex format row through the debug test and found that although the first four rows were merged like user name, password, and role.But when parsing, they are placed in the first line by default, like wk25, which is also the default in the first line, but like Monday and Tuesday, you might think it should be the default in the second line, but not because wk25 combines the results of the first two lines, so Monday and Tuesday are the default in the third line.When it comes to this, you should understand his rules, so we've used improvements to the configuration file and modifications to the partial parsing code to solve this problem.
Solve the problem
First let's see what changes have been made to the configuration file

Detailed comments in the picture are not explained here, but the generic version of the resolveEntity tag is the corresponding generic version of the entity tag, which is renamed here to distinguish between parsing and exporting
Let's still look directly at the code, which has detailed comments
/**
* Resolve excel
*
* @param multipartFile File Stream
* @param savePath Path where files are stored in the project
* @param t Refers to the type of entity in the returned collection
* @param jsonResult Result Information
* @return Parse Set
*/
private List<T> resolveExcel(MultipartFile multipartFile, String savePath, T t, JsonResult jsonResult) throws Exception {
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
//1. Create Reader Objects
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
//2. Load xml
Document document=reader.read(Objects.requireNonNull(ExcelUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResource("ExcelUtils.xml")).getPath());
//Get the root element, entitys
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
//Get the child element of the root element, entity
List<Element> elements = rootElement.elements();
Class classes = t.getClass();
for (Element element : elements) {
if ("resolveEntity".equals(element.getName()) && classes.getSimpleName().equals(element.attributeValue("value"))) {
//Get the child element column of entity
List<Element> elementList = element.elements();
//Create local test file
File file = new File("E:\\user.xls");
//The following notes describe how to use the Utils using the MultipartFile file received in the actual project
// String[] split = multipartFile.getName().split("\\.");
String[] split = file.getName().split("\\.");
Workbook wb = null;
if ("xls".equals(split[1])) {
//The following notes describe how to use the Utils using the MultipartFile file received in the actual project
// InputStream fis = multipartFile.getInputStream();
InputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
wb = new HSSFWorkbook(fis);
} else if ("xlsx".endsWith(file.getName())) {
//The following notes describe how to use the Utils using the MultipartFile file received in the actual project
// wb = new XSSFWorkbook((File) multipartFile);
wb = new XSSFWorkbook(file);
} else {
jsonResult.setFailReason("File format error");
}
Sheet sheet = wb.getSheetAt(0);
//The first line here is the startRow we configured in the resolveEntity tag
int fistRowNumber = Integer.parseInt(element.attributeValue("startRow"));
//Get the last line
int lastRowNumber = sheet.getLastRowNum();
//Traverse all rows
for (int rIndex = fistRowNumber; rIndex <= lastRowNumber; rIndex++) {
//Instantiate an entity to store data obtained by traversing excel
t = (T) classes.newInstance();
//Get Rows
Row row = sheet.getRow(rIndex);
int rowCount = 0;
//Create a map to temporarily store data and assign it to the map field in entity
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
Field mapFiled = null;
if (row != null) {
//Start from the first column by default
int cel = 0;
while (true) {
//Determine whether the data in rows and columns is empty
if (row.getCell(cel) != null) {
//Traversing labels in column in xml
for (Element element1 : elementList) {
//If the corresponding cel is equal to the column currently being parsed and the number of rows is greater than or equal to the startRow we configured in the column tag in the configuration file, that is, when the current number of rows is greater than or equal to the number of starting rows from which the field begins to be assigned
if ("column".equals(element1.getName()) && Integer.parseInt(element1.attributeValue("cel")) - 1 == cel && Integer.parseInt(element1.attributeValue("startRow"))-1 <= rIndex) {
//Get all the properties of this class
Field[] fields = classes.getDeclaredFields();
//traversal attributes
for (Field field : fields) {
//Assign a value if the cel corresponding value exists in the entity
if (element1.attributeValue("value").equals(field.getName()) ) {
field.setAccessible(true);
//Assign a value to entity, if it is a date type get the corresponding date format
conversionType(field,row.getCell(cel).toString(),t,element.attributeValue("dateForMate"));
rowCount++;
}
}
//Get the parent of the incoming entity
Class clazz = classes.getSuperclass();
//If there is a parent
while(clazz != null){
//Get all the attributes of the parent class
Field[] supFiles = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : supFiles) {
//Assign a value if the cel corresponding value exists in the entity
if (element1.attributeValue("value").equals(field.getName())) {
field.setAccessible(true);
//Assigning values to entity
conversionType(field,row.getCell(cel).toString(),t, element.attributeValue("dateForMate"));
rowCount++;
break;
}
}
//Continue to get parent class
clazz = clazz.getSuperclass();
}
//If the current label is a map label
} else if ("map".equals(element1.getName())) {
//Get the corresponding property name in entity
String value = element1.attributeValue("name");
//Get the word label for the map label
List<Element> mapElements = element1.elements();
//Get this property by reflection
mapFiled = classes.getDeclaredField(value);
//If there are subtags
if(mapElements.size() > 0){
for (Element element2 : mapElements) {
if(element2.attributeValue("cel")!=null&&element2.attributeValue("startRow")!=null){
//Determines whether the current column is the same as the configured column and whether the current number of rows is greater than or equal to the configured starting number of rows
if("column".equals(element2.getName())&&Integer.parseInt(element2.attributeValue("cel")) - 1 == cel && Integer.parseInt(element2.attributeValue("startRow"))-1 <= rIndex) {
//Conditionally, values are built into map s
map.put(element2.attributeValue("value"), row.getCell(cel).toString());
rowCount++;
}
}
}
}
}
}
//Number of columns plus one
cel++;
//If the current column is empty and is larger than the last column, and rowCount > 0 represents an assignment of map
} else if (cel >= row.getLastCellNum() && rowCount > 0) {
if(map.size() > 0 && mapFiled != null){
mapFiled.setAccessible(true);
mapFiled.set(t, map);
}
//Add entity to list
list.add(t);
break;
//If the current column is empty and larger than the last column, and rowCount = 0 has no map assignment
}else if(cel >= row.getLastCellNum() && rowCount == 0){
break;
}
}
}
}
}
}
return list;
}
/**
* Determine what type entity attributes are (basic types can only be determined)
*
* @param field Current Properties
* @param value Value of current property
* @param t In entity
* @param dateFormat If there is a date format for the date type
*/
private void conversionType(Field field, String value, T t, String dateFormat) throws Exception {
//Or get the type of the property
Type genericType = field.getGenericType();
if (genericType.toString().endsWith("String")) {
field.set(t, value);
} else if (genericType.toString().endsWith("int") || "java.lang.Integer".equals(genericType.getTypeName())) {
field.set(t, Integer.parseInt(value));
} else if ("Long".endsWith(genericType.toString()) || "long".endsWith(genericType.toString())) {
field.set(t, new Long(value));
} else if ("char".endsWith(genericType.toString())) {
field.set(t, value.charAt(0));
} else if ("boolean".endsWith(genericType.toString()) || "java.lang.Boolean".equals(genericType.getTypeName())) {
field.set(t, Boolean.valueOf(value));
} else if ("double".endsWith(genericType.toString()) || "java.lang.Double".equals(genericType.getTypeName())) {
field.set(t, Double.valueOf(value));
} else if ("float".endsWith(genericType.toString()) || "java.lang.Float".equals(genericType.getTypeName())) {
field.set(t, Float.valueOf(value));
} else if ("java.util.Date".equals(genericType.getTypeName())) {
field.set(t, new SimpleDateFormat(dateFormat).parse(value));
}
}
Next let's take a look at the excel that was previously mentioned
Here is the test code
Here's the output from our console
Here we only configure Monday and Tuesday for testing, so you can configure them all for testing.
summary
1. Modify entity label to resolveEntity
2. Add map labels to map map map type fields in entity
3. Add the tag attribute startRow to determine which line to start parsing and assigning
Through the above answers, I believe you have clearly understood how we can use a general utils to resolve complex excel. Of course, there may still be some complex excels that can not be resolved. After the discovery of the small edition, it will continue to be studied and updated. If the text does not understand, please read the normal edition first and then come back to read it.The scale will be clear. Here we post a link to the normal version, http://www.lindasoft.com/view/article/details?articleId=603