I. overview
1.1 definitions
Provide an interface for creating a set of related or interdependent objects without specifying their specific classes.
- Abstract factory pattern belongs to creation pattern
- The factory method pattern can only create one type of product per factory, while the abstract factory pattern can create multiple types of products
For example, the hard disk factory only produces hard disks, while the computer factory combines different hard disks, memory, CPU, etc. to produce computers
1.2 UML class diagram
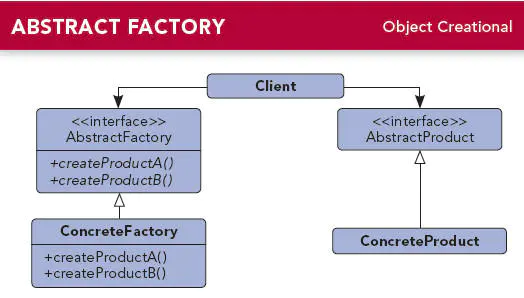
Role description:
- AbstractProduct (abstract product class): defines the public interface of the product
- Concrete product: defines the concrete object of the product and implements the interface in the abstract product class
- AbstractFactory (abstract factory class): defines the methods used to create different products in the factory
- ConcreteFactory (concrete factory class): implements the party that creates the product defined in the abstract factory
Second realization
2.1 creating abstract product classes
Define common interfaces:
// Abstract product class - CPU
public abstract class CPU {
public abstract void showCPU();
}
// Abstract product class - memory
public abstract class Memory {
public abstract void showMemory();
}
// Abstract product class - hard disk
public abstract class HD {
public abstract void showHD();
}
2.2 create specific product categories
Inherit Product class:
// Specific product category - Intet CPU
public class IntelCPU extends CPU {
@Override
public void showCPU() {
System.out.println("Intet CPU");
}
}
// Specific product category - AMD CPU
public class AmdCPU extends CPU {
@Override
public void showCPU() {
System.out.println("AMD CPU");
}
}
// Specific product category - Samsung memory
public class SamsungMemory extends Memory {
@Override
public void showMemory() {
System.out.println("Samsung memory");
}
}
// Specific product category -- Kingston memory
public class KingstonMemory extends Memory {
@Override
public void showMemory() {
System.out.println("Kingston memory");
}
}
// Specific product category -- Seagate hard disk
public class SeagateHD extends HD {
@Override
public void showHD() {
System.out.println("Seagate hard disk");
}
}
// Specific product category -- Western data hard disk
public class WdHD extends HD {
@Override
public void showHD() {
System.out.println("Western data hard disk");
}
}
2.3 creating abstract factory classes
Define the methods used in the factory to create different products:
// Abstract factory class
public abstract class ComputerFactory {
public abstract CPU createCPU();
public abstract Memory createMemory();
public abstract HD createHD();
}
2.4 create a specific factory class
Inherit Factory class:
// Specific factory -- Lenovo computer
public class LenovoComputerFactory extends ComputerFactory {
@Override
public CPU createCPU() {
return new IntelCPU();
}
@Override
public Memory createMemory() {
return new SamsungMemory();
}
@Override
public HD createHD() {
return new SeagateHD();
}
}
// Specific factory -- ASUS computer
public class AsusComputerFactory extends ComputerFactory {
@Override
public CPU createCPU() {
return new AmdCPU();
}
@Override
public Memory createMemory() {
return new KingstonMemory();
}
@Override
public HD createHD() {
return new WdHD();
}
}
// Specific factory category - HP computer
public class HpComputerFactory extends ComputerFactory {
@Override
public CPU createCPU() {
return new IntelCPU();
}
@Override
public Memory createMemory() {
return new KingstonMemory();
}
@Override
public HD createHD() {
return new WdHD();
}
}
2.5 test method
public void test() {
System.out.println("--------------------Production of Lenovo computers-----------------------");
ComputerFactory lenovoComputerFactory = new LenovoComputerFactory();
lenovoComputerFactory.createCPU().showCPU();
lenovoComputerFactory.createMemory().showMemory();
lenovoComputerFactory.createHD().showHD();
System.out.println("--------------------Production of ASUS computers-----------------------");
ComputerFactory asusComputerFactory = new AsusComputerFactory();
asusComputerFactory.createCPU().showCPU();
asusComputerFactory.createMemory().showMemory();
asusComputerFactory.createHD().showHD();
System.out.println("--------------------Production of HP computers-----------------------");
ComputerFactory hpComputerFactory = new HpComputerFactory();
hpComputerFactory.createCPU().showCPU();
hpComputerFactory.createMemory().showMemory();
hpComputerFactory.createHD().showHD();
}
The output result is:
--------------------Production of Lenovo computers----------------------- Intet CPU Samsung memory Seagate hard disk --------------------Production of ASUS computers----------------------- AMD CPU Kingston memory Western data hard disk --------------------Production of HP computers----------------------- Intet CPU Kingston memory Western data hard disk
III. summary
3.1 application scenarios
When producing objects for multiple assortments.
3.2 advantages
The code is decoupled, and the work of creating instances is separated from that of using instances. Users do not have to care about how to create class objects.
3.3 disadvantages
If a new product is added, the abstract factory and all concrete factories will be modified, which violates the open and closed principle.
3.4 comparison between factory method pattern and abstract factory pattern
- In the factory method mode, specific factories are responsible for producing specific products. Each specific factory corresponds to a specific product, and the factory method is unique
- The abstract factory pattern can provide multiple product objects instead of a single product object