Tip: pay attention to give the virtual machine a large enough disk, more than 60G
1, Design ideas
-
Download linux kernel source code
-
Add the system call number to the system call table
-
Write custom system call functions in the system call header file
-
Modify the kernel source code and add the implementation of custom system call function
-
Install the dependency tool, recompile the kernel, and use the new kernel
-
Write test code and test
2, Implementation process
1. Download the linux kernel source code
Download the kernel source code from the official website at: https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/
Download address of domestic source code: http://ftp.sjtu.edu.cn/sites/ftp.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/
Check the kernel version of your system, and then find a similar linux version for kernel upgrade. Here I choose 5.14.1

Download the source package and unzip it to / usr/src
mv linux-5.14.1.tar.gz /usr/src tar xvf linux-5.14.1.tar.gz
2. Add the system call number to the system call table
ABI(Application Binary Interface): binary interface. It defines how the application interacts internally, how the application interacts with the kernel, and how to interact with the library to ensure binary compatibility. For the same ABI, the object code can run normally on any system without recompiling. It focuses on function call conventions, byte order, register usage, system calls, links, library behavior, and the format of binary targets. ABI is a function provided by the operating system and architecture. Defining a set of ABI for an architecture is difficult, and binary portability is difficult.
System call table path: / usr/src/linux-5.14.1/arch/x86/entry/syscalls/syscall_64.tbl
<number> <abi> <name> <entry point> 331 common pkey_free sys_pkey_free 332 common statx sys_statx 333 common io_pgetevents sys_io_pgetevents 334 common rseq sys_rseq 335 64 print_all_process sys_print_all_process
3. Write custom system call functions in the system call header file
Add a custom system call declaration in the header file. The path of the header file is: / usr / SRC / linux-5.14.1/arch/x86/include/asm/syscalls h
#ifndef _ASM_X86_SYSCALLS_H #define _ASM_X86_SYSCALLS_H /* Common in X86_32 and X86_64 */ /* kernel/ioport.c */ long ksys_ioperm(unsigned long from, unsigned long num, int turn_on); /* added by me */ asmlinkage long __x64_sys_print_all_process(void); #endif /* _ASM_X86_SYSCALLS_H */
4. Modify the source code of the system call
At / usr / SRC / linux-5.14.1/kernel/sys C can be added. Note that it cannot be written to the macro
// 335 64 print_all_process sys_print_all_process
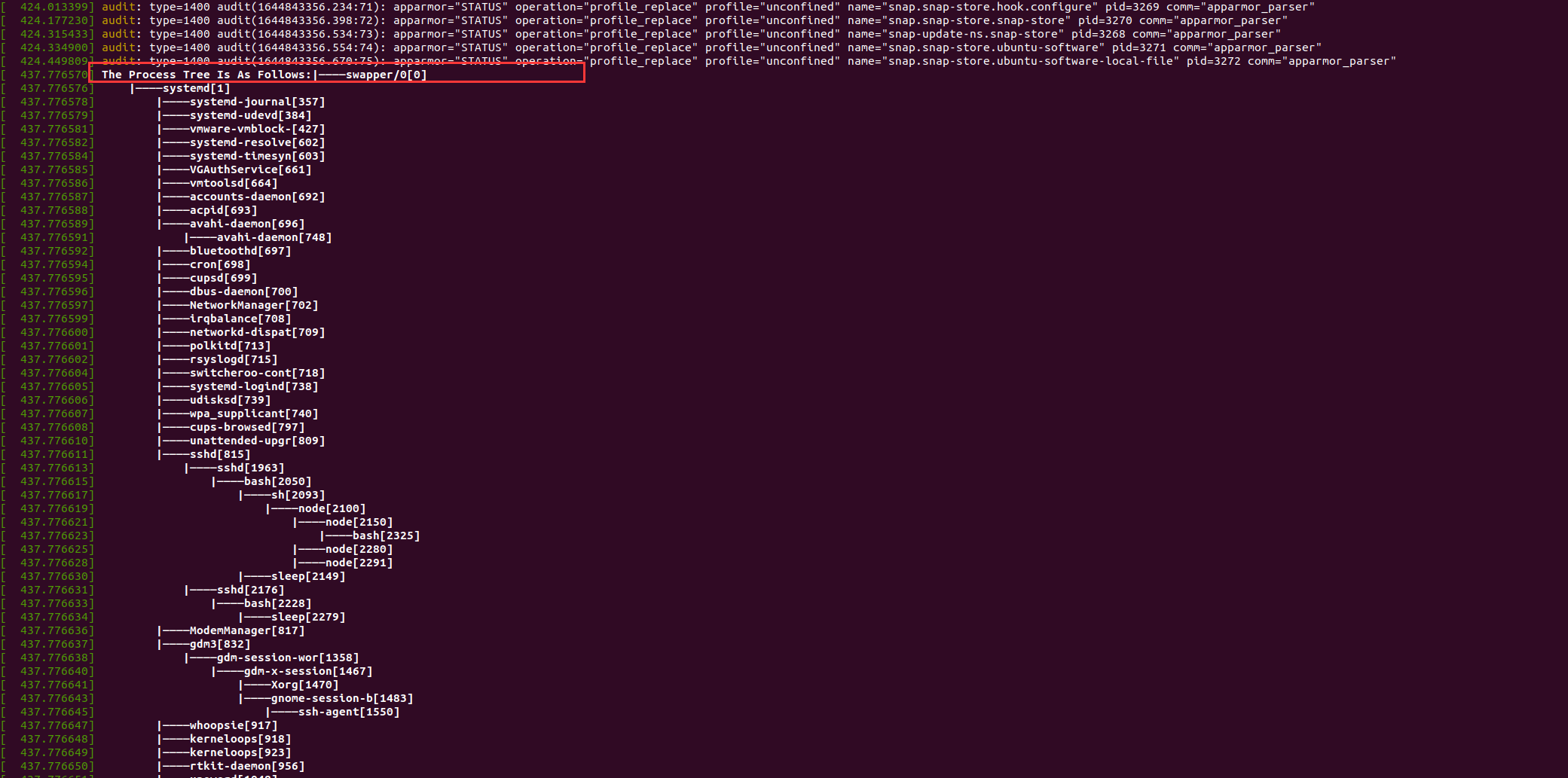
static void print_children(struct task_struct* task, int level){
struct list_head* pos;
struct task_struct* ptr;
// Tree structure output
int i;
for(i = level; i > 0; i--){
printk(KERN_CONT " ");
}
// Process name and pid
printk(KERN_CONT "|--");
printk(KERN_CONT "%s[%d]\n", task->comm, task->pid);
// Use parent task_struct's children two-way linked list, traversing its child processes
list_for_each(pos, &task->children){
// Return task_struct pointer to find the task corresponding to pos_ Struct, cheap equivalent to sibling
ptr = list_entry(pos, struct task_struct, sibling);
if(ptr != NULL){
level++;
// Recursive printing sub process tree
print_children(ptr, level);
level--;
}
}
}
asmlinkage long __x64_sys_print_all_process(void){
printk("The Process Tree Is As Follows:");
print_children(&init_task, 0);
return 0;
}
5. Install the dependency tool, recompile the kernel and use the new kernel
Switch to root user for operation
apt update apt install libncurses5-dev libssl-dev apt install build-essential openssl apt install zlibc minizip apt install libidn11-dev libidn11 apt install flex bison apt install libdw-dev apt install libncurses-dev apt install dwarves apt-get install libdw-dev
make mrproper make clean make menuconfig
Pop up the configuration menu, save - > OK - > Exit - > exit

The process of compiling the kernel is very long and there will be various bug s. The version I use is 5.14.1, which requires at least 60G disk and at least 4 hours of compilation
cd /usr/src/linux-5.14.1 Compile kernel: make After the installation of the module is completed, enter the command in the console: sudo make modules_install After the module is installed, enter the command in the console to install the kernel: sudo make install After installation: reboot
You can see that the kernel version has been updated to 5.14.1

6. Write test code and test
#include <linux/unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
int main(){
syscall(335);
return 0;
}
Since the output statement of the added system call is written by printk, which sends the message to the system log, the console does not output. Enter the command to view the log: dmesg