Blog learning address: https://www.cnblogs.com/jason-lu/archive/2013/06/07/3123472.html
1, Frame composition
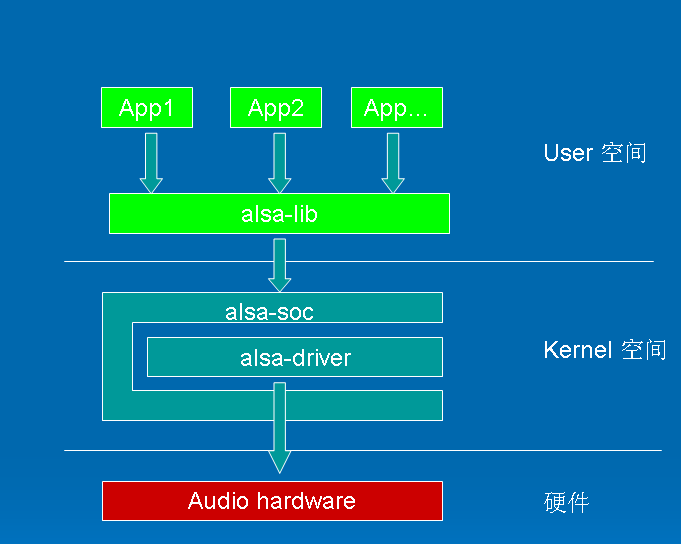
ALSA is the abbreviation of Advanced Linux Sound Architecture. At present, it has become the mainstream Audio Architecture of linux. Whether we develop Android or linux, we are based on this framework.
From this picture, we can see the general framework structure. The upper app calls alsa provided by alsa_lib interface to realize many audio functions such as our playback and recording.
The kernel space is where we, as the underlying developers, modify. The driver is actually the code related to our underlying driver. Many relevant manufacturers have provided corresponding drivers. At the same time, these drivers also correspond to the interface of alsa soc. Many manufacturers have done some in soc so file. This is to prevent the leakage of trade secrets. We don't need to be too concerned, but we need to understand some corresponding interface calls.
2, Use of tinymix
In the process of debugging, we often use the corresponding underlying tools to view the corresponding things.
We need to compile the corresponding tools into the corresponding board so that we can use the corresponding tools.
Generally, in the android/external/tinyalsa directory, one will be generated after compilation so file and tool files of four causes (1, tinycap 2, tinymix 3, tinypcminfo 4, tinyplay)
), the corresponding tool has been uploaded: https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_51178981/33427599
2.1 tinymix
vt_ipc_rk88:/ # tinymix Mixer name: 'rockchip,es8316-codec' Number of controls: 38 ctl type num name value 0 INT 2 HP Playback Volume 0 0 1 INT 2 HPMixer Gain 0 0 2 INT 2 DAC Playback Volume 192 192 3 BOOL 1 Enable DAC Soft Ramp Off 4 INT 1 DAC Soft Ramp Rate 4 5 ENUM 1 Playback Polarity L Invert 6 BOOL 1 DAC Notch Filter Off 7 BOOL 1 DAC Double Fs Mode Off 8 INT 1 DAC Volume Control-LeR 0 9 INT 1 DAC Stereo Enhancement 0 10 BOOL 1 MIC Boost On 11 INT 1 Input PGA 6 12 INT 1 ADC Capture Volume 192 13 BOOL 1 ADC Soft Ramp On 14 ENUM 1 Capture Polarity Normal 15 BOOL 1 ADC Double FS Mode Off 16 INT 1 ALC Capture Target Volume 10 17 INT 1 ALC Capture Max PGA 13 18 INT 1 ALC Capture Min PGA 8 .....
Colleagues who have debugged audio files know that audio files have many channels (switches) to set. Through tinymix, we can see that those switches are on and off. We can modify the value of the register at the bottom to set the switch, and use tools to turn on or off directly during debugging.
You can also change the size of the sound.
tinymix + (ctl number) You can see the corresponding information
vt_ipc_rk88:/ # tinymix 7 DAC Double Fs Mode: Off
You can turn on or off the corresponding interface by setting 0 or 1 (because the switches seem to be of bool type)
vt_ipc_rk88:/ # tinymix 7 DAC Double Fs Mode: Off vt_ipc_rk88:/ # tinymix 7 1 vt_ipc_rk88:/ # vt_ipc_rk88:/ # tinymix 7 DAC Double Fs Mode: On vt_ipc_rk88:/ # tinymix 7 0 vt_ipc_rk88:/ # vt_ipc_rk88:/ # tinymix 7 DAC Double Fs Mode: Off
Modifying the volume is similar to the above
ctl type num name value 0 INT 2 HP Playback Volume 0 0 1 INT 2 HPMixer Gain 5 5 2 INT 2 DAC Playback Volume 192 192 ...... vt_ipc_rk88:/ # tinymix 2 100 100 ctl type num name value 0 INT 2 HP Playback Volume 0 0 1 INT 2 HPMixer Gain 5 5 2 INT 2 DAC Playback Volume 100 100 ....
If there is only one value, you need to enter a value
Modify mode
ctl type num name value ... 13 BOOL 1 ADC Soft Ramp On 14 ENUM 1 Capture Polarity Normal ...... vt_ipc_rk88:/ # tinymix 14 Capture Polarity: >Normal Invert There will be a corresponding prompt to display his mode. The small arrow indicates the current mode vt_ipc_rk88:/ # tinymix 14 Invert ctl type num name value ... 13 BOOL 1 ADC Soft Ramp On 14 ENUM 1 Capture Polarity Invert
2.2 tinypcminfo
tinypcminfo is used to view information about pcm channels
vt_ipc_rk88:/ # tinypcminfo -D /dev/snd
Info for card 0, device 0:
PCM out:
Access: 0x000009
Format[0]: 0x000044
Format[1]: 0x000010
Format Name: S16_LE, S24_LE, S20_3LE
Subformat: 0x000001
Rate: min=8000Hz max=96000Hz
Channels: min=2 max=2
Sample bits: min=16 max=32
Period size: min=4 max=65536
Period count: min=2 max=4096
PCM in:
Access: 0x000009
Format[0]: 0x000044
Format[1]: 0x000010
Format Name: S16_LE, S24_LE, S20_3LE
Subformat: 0x000001
Rate: min=8000Hz max=96000Hz
Channels: min=2 max=2
Sample bits: min=16 max=32
Period size: min=4 max=65536
Period count: min=2 max=4096
2.3 tinycap
Used for recording. It can only be used to record wav audio files
tinycap + name of recorded audio
vt_ipc_rk88:/sdcard # tinycap 1.wav Capturing sample: 2 ch, 44100 hz, 16 bit You can also add corresponding parameters later. For details, you can go to see the corresponding data without adding flowers. That is, according to the default parameters.
2.4 tinyplay
It is used for broadcasting. It can only be used for broadcasting wav audio files
The same way tinycap is used.
vt_ipc_rk88:/sdcard # tinyplay 1.wav vt_ipc_rk88:/sdcard # tinyplay 1.wav Playing sample: 2 ch, 44100 hz, 16 bit 1146880 bytes
3, View corresponding equipment files
vt_ipc_rk88:/ # ls /dev/snd/ controlC0 pcmC0D0c pcmC0D0p pcmC0D1p timer
controlC0 --> Control for sound card,For example, channel selection,Mix,Microphone control, etc pcmC0D0c --> For recording pcm equipment pcmC0D0p --> For playback pcm equipment timer --> timer
C0D0 represents device 0 in sound card 0,pcmC0D0c, the last C represents capture,pcmC0D0p, and the last P represents playback. These are the naming rules in alsa driver.