What can I do with a Class object?
-
Create Class object: call newInstance() method of Class object
- Class must have a parameterless constructor
- The constructor of the class should have sufficient access rights
//Get Class object Class c1 = Class.forName("Annotation and reflection.User"); //Construct an object User user = (User) c1.newInstance(); System.out.println(user);
Can't you create an object without a parameterless constructor? As long as the constructor in the class is explicitly called during the operation and the parameters are passed in, the operation can be instantiated.
-
The steps are as follows:
- Get the specified parameter types of this Class through getdeclaraedconstructor (Class... paramerTypes) of Class class
- Pass an object array into the formal parameters of the constructor, which contains all the parameters required by the constructor
- Instantiate objects through Constructor
//Get Class object Class c1 = Class.forName("Annotation and reflection.User"); //Create an object through a constructor Constructor constructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class, int.class); User user2 = (User) constructor.newInstance("Zhang San", 1, 18); System.out.println(user2);
Call the specified method
Through reflection, the Method in the class is called and completed through the Method class.
- Get a Method object through the getMethod(String name,Class... parameterTypes) Method of Class class and set the parameter type required for the operation of this Method
- Then use Object invoke(Object obj,Object[] args) to call and pass the parameter information of the obj object to be set to the method.
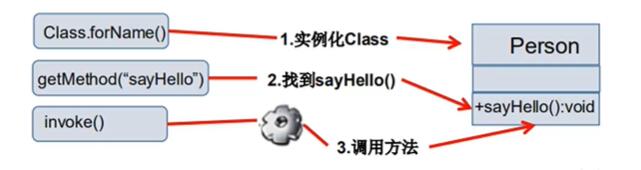
- Object invoke(Object obj,Object ... args)
- object corresponds to the return value of the original method. If the original method has no return value, null is returned
- If the original method is a static method, the formal parameter Object obj can be null at this time
- If the original method parameter list is empty, Object[] args is null
- If the original method is declared as private, you need to explicitly call the setAccessible(true) method of the method object before calling the invoke() method to access the private method.
- setAccessible
- Method, Field and Constructor objects all have setAccessible() methods
- setAccessible is a switch that enables and disables access security checks
- If the parameter value is true, it indicates that the Java language access check should be cancelled when the reflected object is used
- Improve reflection efficiency. If reflection must be used in the code and the code of this sentence needs to be called frequently, please set it to true
- So that private members that cannot be accessed can also be accessed
- If the parameter value is false, it indicates that the reflected object should implement Java language access check
Code demonstration:
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//Create objects dynamically
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
//Normal new an object
//User user1 = new User();
//System.out.println(user1);
//Get Class object
//Class c1 = Class.forName("annotation and reflection. User");
//Construct an object
//User user = (User) c1.newInstance();
//System.out.println(user);
//Create an object through a constructor
//Constructor constructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class, int.class);
//User user2 = (User) constructor.newInstance("Zhang San", 1, 18);
//System.out.println(user2);
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------");
Class c1 = Class.forName("Annotation and reflection.User");
User user3 = (User) c1.newInstance();
//Call normal methods through reflection
//Get a method by reflection
Method setName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class);
//Activate: invoke (object, "method value")
setName.invoke(user3,"Li Si");
System.out.println(user3.getName());
//Operation properties by reflection
User user4 = (User) c1.newInstance();
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
//The properties in User are private and inaccessible by default
//setAccessible(): set accessibility
//setAccessible(): set a method to true to access directly
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(user4,"Wang Wu");
System.out.println(user4.getName());
}
}