preface
Automated operation and maintenance tool ansible
1, ansible introduction
ansible is a lightweight automatic operation and maintenance management tool developed based on python. It integrates the advantages of many operation and maintenance tools (saltstack, chef and puppet). It can be used to execute commands in batch, install programs and support playbook layout. It connects the host through ssh protocol and is decentralized. Ansible only provides a framework, which works based on modules and does not have batch deployment.
modular:
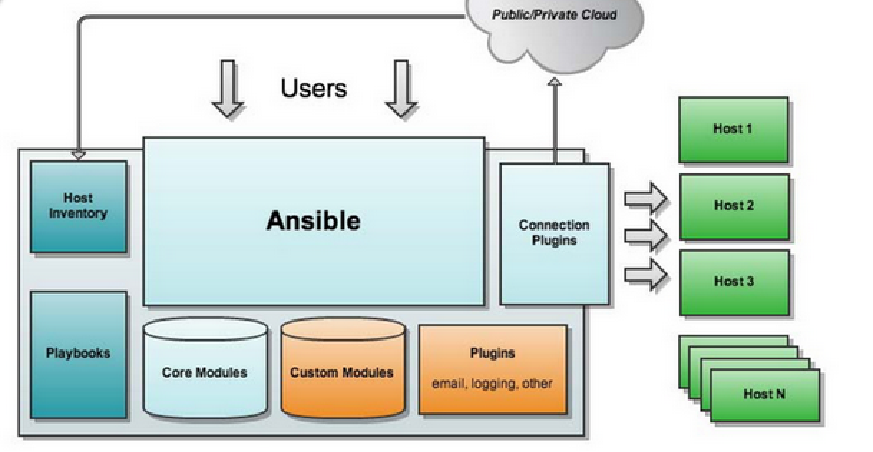
ansible: main program
Core Modules: modules of ansible
Custom Modules: extension modules (Python)
Plugins: plug-in to realize logging, sending mail or other functions
Playbooks: Script
Connector plugins: plug-in that can connect to the host. ssh is the default
Host Inventory: host list, which records the list of manageable hosts. The default is / etc / manageable / hosts
2, ansible feature
- Simple deployment, only need to deploy Ansible environment at the master control end, and the controlled end does not need to do any operation;
- SSH protocol is used to manage the equipment by default;
- There are a large number of conventional operation and maintenance modules, which can realize most of the daily operations;
- Simple configuration, powerful function and strong expansibility;
- Support API and user-defined modules, which can be easily extended through Python;
- Customize powerful configuration and state management through Playbooks;
- Lightweight, no need to install agent on the client. When updating, you only need to update it once on the operating machine;
3, ansible use
1. Installation
1) yum install
yum -y install epel-release yum -y install ansible
2) pip installation
yum install python-pip python-devel yum install gcc glibc-devel zibl-devel rpm-bulid openssl-devel pip install --upgrade pip pip install ansible--upgrade
3) git installation
git clone git://github.com/ansible/ansible.git --recursive cd ./ansible source ./hacking/env-setup
2. Basic knowledge
1) Master configuration
/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg Mainly set some ansible Initialization information, such as log storage path, module, plug-in and other configuration information
2) Host manifest file
/etc/ansible/hosts Define managed host groups and hosts,You can specify the location and name of the manifest file in the main configuration file vim /etc/ansible/hosts # Store all hosts managed by ansible node-1 # Specify the host separately, which needs to be resolved by / etc/hosts node-2 +------------------------------------ [node-one] # The specified host group can contain multiple hosts node-[2:3] # node-2 node-3 ===> node-[2:3] [node-two] # When adding host information, you can configure user and password, or you can do password free through SSH keygen node-4 ansible_ssh_user='root' ansible_ssh_pass='xx' #ansible_ssh_port='2233' [node-one:vars] # Specify a variable for a group that can be used by each host in the group ansible_ssh_user='root' ansible_ssh_pass='xx' [NODE:children] # Creating a group can contain multiple groups node-one node-two
3) Module function view
/usr/bin/ansible-doc /usr/bin/ansible-doc -l Get all module information /usr/bin/ansible-doc -s MOD_NAME Gets the usage method of the specified module
4) ansible use (secret free)
1.modify/etc/sshd/ssh_config StrictHostKeyChecking no # ssh login cancels yes/no authentication 2.install sshpass Conduct secret free ssh-keygen -P "" -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa # Generate secret key sshpass -p'' ssh-copy-id [ip] # Secret free communication with target host
3. Common ad hoc
ping - detection module
ansible node-2 -m ping # Test host connectivity ansible node-2 -m ping -o # -o is concise output ansible node-2 -m ping -u root -k -o # Manually enter the password for connectivity test
shell - command module
ansible node-2 -m shell -a'uptime' -o # You can use any shell command
Copy - copy module
ansible node-2 -m copy -a'src=/root/testfile dest=/tmp/testfile owner=root group=root mode=711 backup=yes' backup=yes Indicates that if there are files on the controlled node, they will be backed up first and then copied
File - file / directory operation module
ansible node-2 -m file -a'path=/tmp/99.txt mode=666 state=touch' ansible node-2 -m file -a'path=/tmp/99 mode=777 state=directory' ansible node-2 -m file -a'path=/tmp/99.txt state=absent' mode: file/directory right state: establish/Delete and other operations
Script - script module
ansible node-2 -m script -a'/root/ansible/test.sh' # Execute test on the node-2 host SH script, the target host that does not need to copy the script, which is equivalent to ssh node-2 "./test.sh" ansible node-2 -m script -a "creates=/tmp/testfile /tmp/testscript.sh" # If the file exists, the script will not be executed. If / tmp/testfile exists on node-2 host, execute / TMP / testscript. Of ansible host sh ansible node-2 -m script -a "removes=/tmp/testfile /tmp/testscript.sh" # If the file does not exist, execute the script. If the node-2 host does not exist, / tmp/testfile, execute / TMP / testscript. Of the ansible host sh
yum - package management module
ansible node-2 -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=latest' # Install httpd, yum -y install httpd ansible node-2 -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=removed' # Uninstall httpd, yum -y remove httpd
User - user management module
ansible node-2 -m user -a 'name=liang state=present' # Creating a user: useradd ansible node-2 -m user -a 'name=liang state=absent' # Delete the user userdel -r liang echo '777777' | openssl passwd -1 -stdin # Generate password ansible node-2 -m user -a 'name=liang password="$1$XVzsJMDr$5wI4oUaQ.emxap6s.N272."' # Set password
Service - service management module
ansible node-2 -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started enabled=yes' # Start httpd and set it to start from start systemctl start httpd & & systemctl enable httpd ansible node-2 -m service -a 'name=httpd state=stopped enabled=no' # Stop httpd, turn off and turn on self starting systemctl stop httpd & & systemctl disable httpd
setup - host information collection module
ansible node-2 -m setup # Get all the information of node-2 host and set it as a built-in variable in playbook
ansible node-2 -m setup -a'filter=ansible_hostname' # Get ansible only_ The value of hostname. filter is used for filtering, similar to grep
Common information:
ansible_all_ipv4_addresses: Show only ipv4 Information about.
ansible_devices: Only disk device information is displayed.
ansible_distribution: Display what system it is, for example: centos,suse Wait.
ansible_distribution_major_version: The main version of the system is displayed.
ansible_distribution_version: Only the system version is displayed.
ansible_machine: Displays the system type, for example: 32-bit or 64 bit.
ansible_eth0: Show only eth0 Information about.
ansible_hostname: Only host names are displayed.
ansible_kernel: Only the kernel version is displayed.
ansible_lvm: display lvm Relevant information.
ansible_memtotal_mb: Displays the total memory of the system.
ansible_memfree_mb: Displays the available system memory.
ansible_memory_mb: Detailed display of memory.
ansible_swaptotal_mb: Show total swap Memory.
ansible_swapfree_mb: display swap Available memory for memory.
ansible_mounts: Displays the system disk mount.
ansible_processor: display cpu number(Specific display of each cpu Model of)
ansible_processor_vcpus: display cpu number(Only the total number is displayed)
Replace - replace module
ansible node-2 -m replace -a'path=/testdir/test regexp="ABC" replace=abc backup=yes' # Back up the node-2 host / testdir/test file and replace "ABC" with "ABC" in the file
lineinfile - text modification module
# Make sure the text exists in the file. If it exists, do not do anything. If it does not exist, insert line content at the end ansible node-2 -m lineinfile -a 'path=/testdir/test line="test lineinfile"' # Match and replace a line of text in the file. If multiple lines are matched, only the last line is replaced with the content of line. If there is no matching line, the content of line is added at the end of the file ansible node-2 -m lineinfile -a 'path=/testdir/test regexp="^line" line="test lineinfile"' # Match and replace a line of text in the file. If multiple lines are matched, only the last line is replaced with the content of line. If there is no matching line, there is no processing ansible node-2 -m lineinfile -a 'path=/testdir/test regexp="^line" line="test lineinfile" backrefs=yes' # Delete the corresponding row according to the regular expression. If multiple rows meet the regular expression, all matching rows will be deleted ansible node-2 -m lineinfile -a 'path=/testdir/test regexp="^test" state=absent'
cron - timed task module
ansible node-2 -m cron -a'user=linag name="crontabtest" minute=*/1 job="echo xxx"' # If the scheduled task already exists, delete the scheduled task and back it up, which is equivalent to * * / 1 * * echo "XXX"
unarchive - decompression module
ansible node-2 -m unarchive -a'src=foo.tgz dest=/var/lib/foo copy=yes mode=755' # When copy=yes, copy the compressed package from the ansible host to / var/lib/foo of node-2. The permission is 755. When copy=no, it is extracted from the compressed package of node-2 host to / var/lib/foo. The permission is 755