Author introduction
Hou Yang
SphereEx middleware R & D Engineer, Apache ShardingSphere Contributor.
At present, it focuses on the design and R & D of ShadowDB and full link voltage measurement.
What is full link voltage measurement
With the rapid development of the Internet industry, the business has also entered a rapid expansion stage. It is conceivable that the changeable user needs have an impact on the stability of the whole system. For example, the orders generated by a large number of users of the takeout platform are concentrated in the noon and evening, such as the shopping festival and second kill activities of the e-commerce platform.
Each business is served by a series of different business systems, and each business system is distributed and deployed on different machines. "Flow planning" can not only ensure system stability, but also save costs. It is a major problem for the technical team. In order to accurately obtain the service capacity of a single machine, the pressure test should be carried out in the production environment. It can not only ensure the authenticity of the environment, but also ensure the authenticity of the flow, and greatly improve the accuracy of "flow planning".
Shadow library and full link voltage measurement
However, the risk of online business system pressure measurement is self-evident, such as data pollution or performance problems. Imagine if after the pressure test, users find that their orders are lost or there are more orders to be paid out of thin air, will it greatly affect the user experience?
Full link on-line pressure measurement is a complex and huge work, which needs the cooperation between various microservices and middleware. Apache ShardingSphere focuses on the database level solution in the full link online pressure test scenario and introduces the pressure test shadow library function. With the help of ShardingSphere's powerful SQL parsing ability, shadow judgment is performed on the executed SQL, and the shadow algorithm is flexibly configured to meet the online pressure measurement requirements of complex business scenarios; The pressure measurement flow is routed to the shadow library, and the normal online flow is routed to the production library, so as to help users isolate the pressure measurement data and solve the problem of data pollution.
Shadow library function upgrade
The shadow library function was first implemented in v4 During 1.0, by adding a logical shadow column, Apache ShardingSphere parses and executes SQL, routes and rewrites it, and deletes the logical shadow column and column value. Users do not need to pay attention to the specific process. When using, they can only modify the SQL and add shadow fields and corresponding configurations.
There are two pain points in adding shadow columns:
- Before the pressure test, the user needs to modify the SQL related to the pressure test according to the actual business needs.
- SQL rewriting will increase execution damage and reduce the accuracy of pressure test results.
After discussion in the ShardingSphere community, it was decided to reconstruct the shadow library function.
Apache ShardingSphere 4.1. 1. The shadow library API of GA version has relatively simple functions on the whole. Judge whether to open the shadow library according to the value corresponding to the logical column.
rules:
- !SHADOW
column: # Shadow field name
shadowMappings:
ds: shadow_ds # Production data source name list: Shadow database name list5.0. The shadow library API after 0 GA reconstruction is more powerful. The user can control whether the shadow library function is enabled through the enable attribute. The configurable shadow table can control the range of pressure measurement according to the dimension of the table, and support a variety of different shadow algorithms, such as column value matching algorithm, column regular expression matching algorithm and SQL annotation matching algorithm.
rules:
- !SHADOW
enable: true # Shadow library switch. Optional values: true/false. The default value is false
dataSources:
shadowDataSource:
sourceDataSourceName: ds # Production data source name
shadowDataSourceName: shadow_ds # Shadow data source name
tables:
<shadow-table-name>:
dataSourceNames: shadowDataSource # Shadow table associated shadow data source name list (multiple values are separated by ",")
shadowAlgorithmNames:
- <shadow-algorithm-name> # Shadow table association algorithm name list
shadowAlgorithms:
<shadow-algorithm-name>:
type: # Shadow algorithm type
props:
xxx: xxx # Shadow algorithm attribute configurationShadow library actual combat
Architecture diagram of online full link voltage measurement:
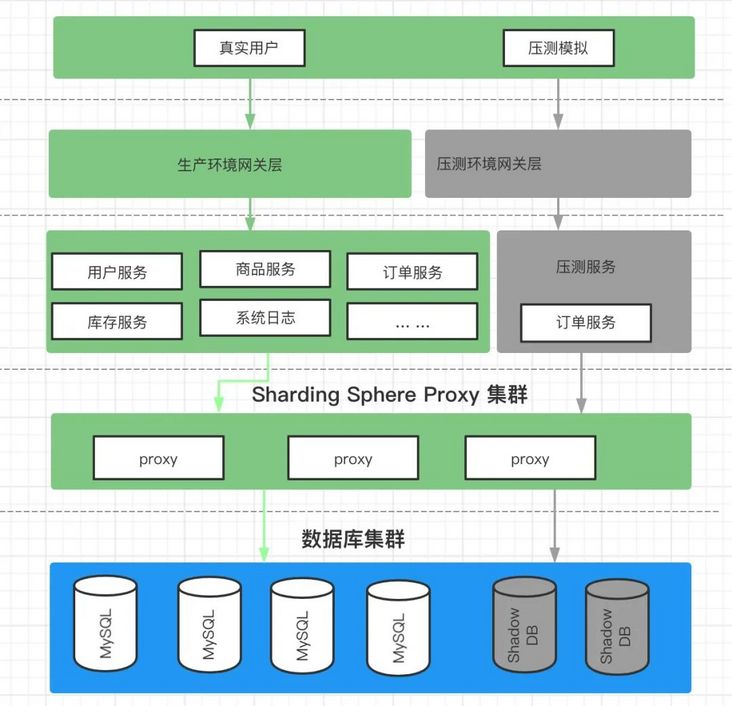
Prepare the pressure measurement environment
Suppose an e-commerce website wants to conduct online pressure test on the order business. (demonstrate using stand-alone deployment)
Hypothetical pressure test related table t_ In the order table, the ID of the test user is 0. Test the data generated by the user's order to ds_shadow shadow database, the production data is executed to ds production database.
Test environment preparation:
- Download shardingsphere proxy 5.0 0 GA Download Page,Refer to shardingsphere proxy quick start for installation and configuration details
- Configure shardingsphere proxy. Take the pressure test scenario as an example:
server.yaml
rules:
- !AUTHORITY
users:
- root@%:root
- sharding@:sharding
provider:
type: NATIVE
- !TRANSACTION
defaultType: XA
providerType: Atomikos
props:
max-connections-size-per-query: 1
executor-size: 16 # Infinite by default.
proxy-frontend-flush-threshold: 128 # The default value is 128.
proxy-opentracing-enabled: false
proxy-hint-enabled: false
sql-show: true
check-table-metadata-enabled: false
lock-wait-timeout-milliseconds: 50000 # The maximum time to wait for a lock
show-process-list-enabled: false
# Proxy backend query fetch size. A larger value may increase the memory usage of ShardingSphere Proxy.
# The default value is -1, which means set the minimum value for different JDBC drivers.
proxy-backend-query-fetch-size: -1
check-duplicate-table-enabled: false
sql-comment-parse-enabled: true
proxy-frontend-executor-size: 0 # Proxy frontend executor size. The default value is 0, which means let Netty decide.
# Available options of proxy backend executor suitable: OLAP(default), OLTP. The OLTP option may reduce time cost of writing packets to client, but it may increase the latency of SQL execution
# if client connections are more than proxy-frontend-netty-executor-size, especially executing slow SQL.
proxy-backend-executor-suitable: OLAPconfig-shadow.yaml
schemaName: shadow_poc_database
dataSources:
ds:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/ds?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
username: root
password:
connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
maxPoolSize: 50
minPoolSize: 1
ds_shadow:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/ds_shadow?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
username: root
password:
connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
maxPoolSize: 50
minPoolSize: 1
rules:
- !SHADOW
enable: true
dataSources:
shadowDataSource:
sourceDataSourceName: ds
shadowDataSourceName: ds_shadow
tables:
t_order:
dataSourceNames:
- shadowDataSource
shadowAlgorithmNames:
- user-id-insert-match-algorithm
- simple-note-algorithm
shadowAlgorithms:
user-id-insert-match-algorithm:
type: COLUMN_REGEX_MATCH
props:
operation: insert
column: user_id
regex: "[0]"
simple-note-algorithm:
type: SIMPLE_NOTE
props:
foo: bar- Order service
Order related businesses are not discussed here. Take the simplest receipt request directly inserted into the order table as an example. The order table structure is as follows:
- Order table structure
CREATE TABLE `t_order` (
`id` INT(11) AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'order ID',
`user_id` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Order user ID',
`sku` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Order item sku',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
)ENGINE = InnoDB COMMENT = 'Order form';Analog pressure measurement process
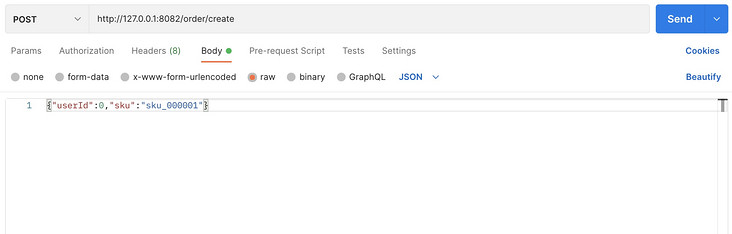
- Use postman to simulate the test user to create an order request, as shown in the following figure:
- In the execution log of shardingsphere proxy, you can see that the execution SQL is routed to the shadow database for execution

Verify the pressure test results
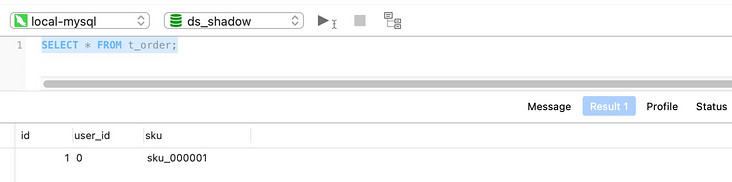
- Shadow library ds_shadow execute query statement
SELECT * FROM t_order;
Query results:
- The production library ds executes query statements
SELECT * FROM t_order;
Query results:
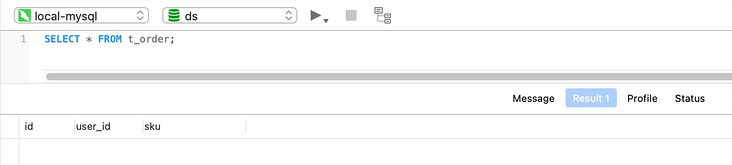
The data generated by the order created by the test user will be routed to the shadow library. Refer to for more complex configurations ShardingSphere official document shadow library pressure test.
Full link online voltage measurement complete solution - CyborgFlow
As mentioned earlier, the full link online pressure test is a complex and huge work, which requires the cooperation and adjustment between various micro services and middleware to deal with the transparent transmission of different traffic and pressure test marks, and the test service should be stateless and out of the box.
A project jointly maintained by Apache ShardingSphere, Apache APIs IX and Apache SkyWalking CyborgFlow Provide out of the box (OOTB) solutions to perform load testing on your online systems.
Apache apisid is responsible for marking the test data at the gateway layer, and Apache SkyWalking is responsible for transmitting it on the whole call link. Finally, Apache shardingsphere proxy is responsible for data isolation, and the pressure test data is routed to the shadow database.
Project published 0.1 0 version, welcome to download:
https://github.com/SphereEx/CyborgFlow/releases
Welcome to add Community Manager wechat (ss_assistant_1) to join the wechat communication group to communicate and discuss with more ShardingSphere lovers.