I. Experimental Purpose
_Master assembly programming specifications, familiar with the programming environment.
II. EXPERIMENTAL CONTENTS
Write subroutines to convert lower-case letters into upper-case letters in strings (see Textbook Experiment 11).
_2. Write No. 0 interrupt processing program to display "divide error!" in the middle of the screen when division overflow occurs (see Textbook Experiment 12). (Please preview Chapter 12 and complete the experiment. If you don't have enough time, do it after class.)
3. Algorithms and key codes of experimental steps
1. Write subroutines to convert lower-case letters into upper-case letters in strings (see Textbook Experiment 11).
1.1 Algorithmic Steps
_________
________________
1.2 Key Codes
assume cs:code data segment db "Life is a chain of moments of enjoyment, not only about survival.",0 data ends code segment start:mov ax,data mov ds,ax mov si,0 ;Set the starting address to the data address call letterc ;Call a subroutine that converts lowercase letters into uppercase letters in a string mov ah,4ch int 21h letterc:mov al,ds:[si] ;Remove the address of the data segment cmp al,0 ;Judge whether it is 0 or not je finish ;If equal to 0, jump to finish Segment, End Continue Conversion and al,11011111B ;Convert letters to uppercase mov ds:[si],al ;Return uppercase letters to strings inc si ;Read the next letter loop letterc ;Continue subprogram finish:ret ;The subroutine ends and goes back to the main program code ends end start
1.3 Screenshots of experimental results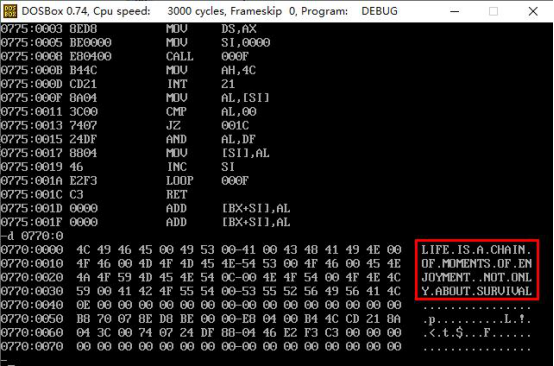
2. Write No. 0 interrupt processing program to display "divide error!" in the middle of the screen when division overflow occurs (see Textbook Experiment 12).
2.1 Algorithmic Steps
Firstly, pseudocode and program framework are written according to program requirements, that is, interrupt processing program is installed first, then vector table is modified, and interrupt processing program is written well.
_________
_3. Modify the interrupt vector table so that the processing address of interrupt No. 0 points to 0:200.
___________
2.2 Key Codes
assume cs:code code segment start:;do0 Installation program, will do0 Copy the code to memory 0:200 place mov ax,0 mov es,ax mov di,200h ;Set up es:di Point to destination address mov ax,cs mov ds,ax mov si,offset do0 ;Set up ds:si Point to the source address mov cx,offset do0end - offset do0 ;Set up cx For transmission length cld ;Set the transmission direction to be positive rep movsb ;Automatic Continuous Copy Code ;Setting Interrupt Vector Table,take do0 The entry address is 0.:200 Save it to Table Number 0 mov word ptr es:[0*4],200h mov word ptr es:[0*4+2],0 ;Division Overflow Segment mov ax,1000h mov bl,1h div bl mov ah,4ch int 21h ;Display string“ divide error!"In the middle of the screen do0: jmp short do0start db 'divide error!' do0start:mov ax,cs mov ds,ax mov si,202h ;Set up ds:si Point to a string mov ax,0B800h mov es,ax mov di,12*160+36*2 ;Set up es:di Point to the middle of the display memory space mov cx,13 ;Set up cx For string length s:mov al,[si] mov es:[di],al inc si add di,2 loop s mov ax,4c00h int 21h do0end:nop code ends end start
2.3 Screenshots of experimental results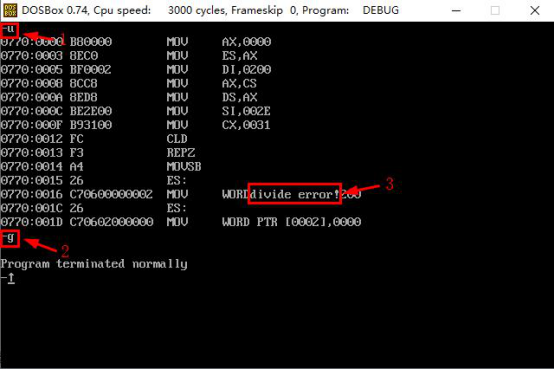
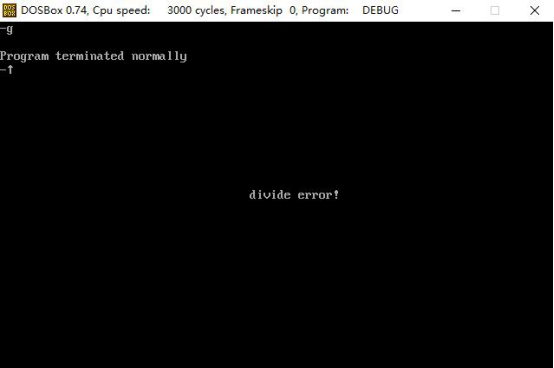
4. Summary of the experiment (brief description of the problems and solutions in the process of the experiment)
_4.1 The first sub-program is mainly unfamiliar with the program framework. Read more about the book experiment 11 and the related contents of the and and or operation. The actual operation can be done by converting lower-case letters to upper-case letters using and directly converting the corresponding bits.
_4.2 The main difficulty of the second problem lies in the design of program ideas, which can be solved in three steps. The first difficulty is that the length of the program is unknown when the user-defined interrupt handler is copied to the specified memory. The second difficulty is that the strings needed by the user-defined interrupt handler are placed in the program. It can be solved by understanding more about the knowledge mentioned in Chapter 12 of the book and PPT of the teacher in class.