CentOS version 7
I Install gitlab
1. Installation
yum install gitlab-ce
2. Configure ports
vi /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb #Modify the access ip and port of gitlab, and the ip is local external_url 'http://192.168.3.166:8099' #Restart gitlab gitlab-ctl reconfigure
II Install gitlab runner
1. Download executable
sudo wget -O/usr/local/bin/gitlab-runner https://gitlab-runner-downloads.s3.amazonaws.com/latest/binaries/gitlab-runner-linux-amd64
2. Set execution permission
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/gitlab-runner
3. Create GitLab CI account
useradd --comment 'GitLab Runner'--create-home gitlab-runner --shell /bin/bash
4. Running services
gitlab-runner install --user=gitlab-runner --working-directory=/home/gitlab-runner
gitlab-runner start
III Gitlab runner registration
1. Open gitlab project - > Settings - > CI / CD - > runners settings. Write down the url and token, and register for use below.
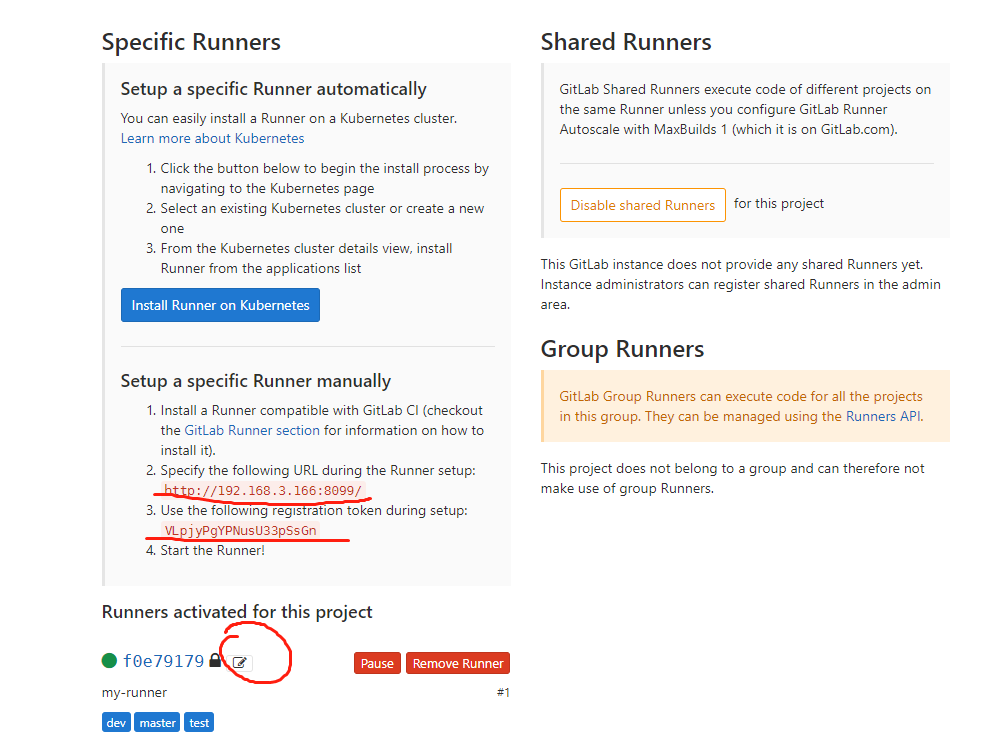
2. Register and enter in the terminal interface
sudo gitlab-runner register
Enter your GitLab URL Please enter the gitlab-ci coordinator URL(e.g. https://gitlab.com ) https://192.168.3.166:8099 (enter the url above) Enter a registration token to register Runner Please enter the gitlab-ci token forthis runner xxx(Enter the above figure token) input Runner explain Please enter the gitlab-ci description forthis runner my-runner input Runner of tags Please enter the gitlab-ci tags forthisrunner(comma separated): my-tag input Runner Execution method, select here shell Please enter the executor: ssh, docker+machine, docker-ssh+machine, kubernetes, docker, parallels, virtualbox, docker-ssh, shell: shell At this point gitlab and gitlab-runner Just configure it
3. Configure ssh to facilitate remote production environment server deployment projects. Input in the terminal interface. (switch to login as gitlab runner)
sudo su - gitlab-runner
4. Generate the secret key and continue to input it at the terminal
ssh-keygen -t rsa
Then keep pressing the space. Do not enter the password.
5. Go to / home / gitlab runner / SSH / directory will see the generated secret key pair, as shown in the figure
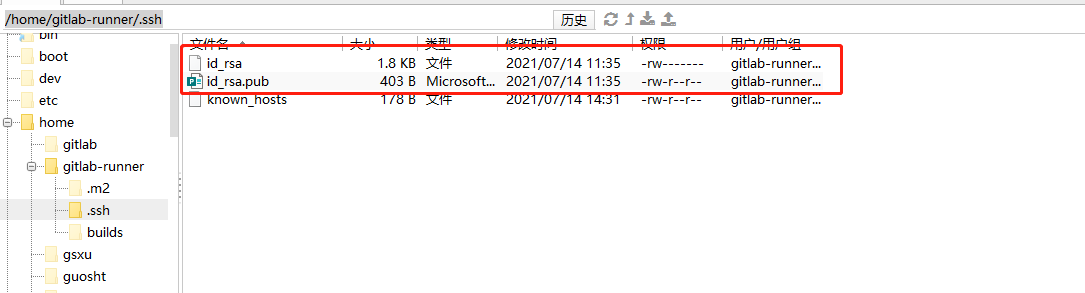
6. Will ID_ rsa. Copy the pub public key file to the production environment server. Input at terminal
cd /home/gitlab-runner/.ssh
ssh-copy-id root@192.168.0.5 (this IP is the production environment server IP)
7. Test whether you can log in without secret
ssh root@192.168.0.5
8. Copy the contents of the private key to gitlab. Input at terminal
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa
The following figure appears:
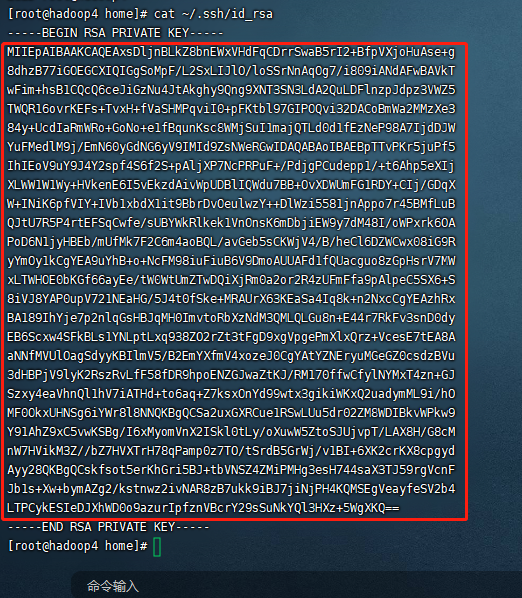
Copy the contents in the red box.
Enter the project that gitlab wants to deploy (no project can create a test project by itself). Select user settings - > CI / CD - > variables
- Add Variable, fill in the secret key and click the "Add Variable" button As shown in the figure below
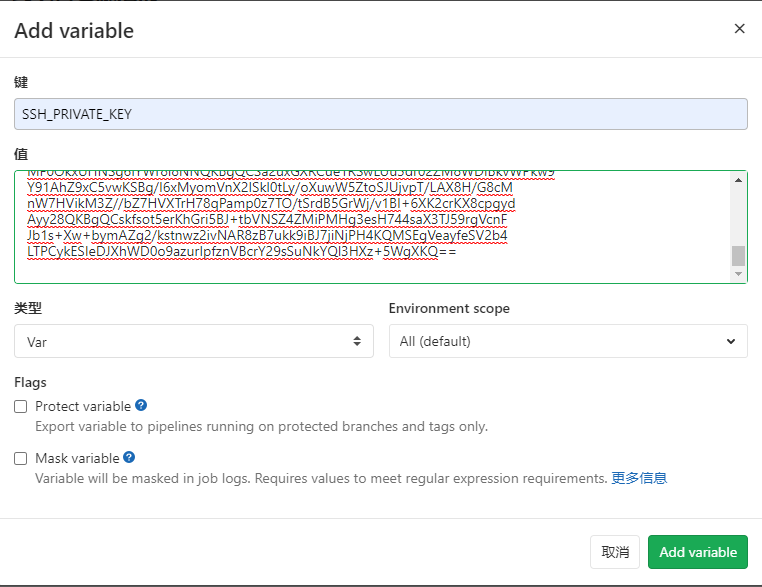
At this point, our configuration is complete. Next is the deployment project
IV Write gitlab CI YML file
1. Create the file "gitlab-ci.yml" in your project root directory. Fill in the following contents (if there is no project, please use IDEA to create SpringBoot project by yourself).
stages:
- build
build:
stage: build
before_script:
- echo "$SSH_KNOWN_HOSTS" >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts
- chmod 644 ~/.ssh/known_hosts
script:
- mvn -Dmaven.test.skip=true clean package
after_script:
- scp $(cd `dirname $0`; pwd)/target/control-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar root@59.110.0.91:/home/robot/robot2_control/control-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
- ssh root@59.110.0.91 "cd /home/robot; docker-compose stop control; docker-compose --compatibility up -d control; exit"explain:
-scp $(cd `dirname $0`; pwd)/target/control-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar root@59.110.0.91 :/home/robot/robot2_ control/control-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar means to copy the packaged files of gitlab to the production environment server. control-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar is my own jar package name. Please replace it with your own jar package name.
- ssh root@59.110.0.91 "CD / home / robot; docker compose stop control; docker compose -- compatibility up - D control; exit" means to restart my project in the server. I deployed it in docker compose mode. If readers use other methods, they can use other methods of commands to restart their projects.
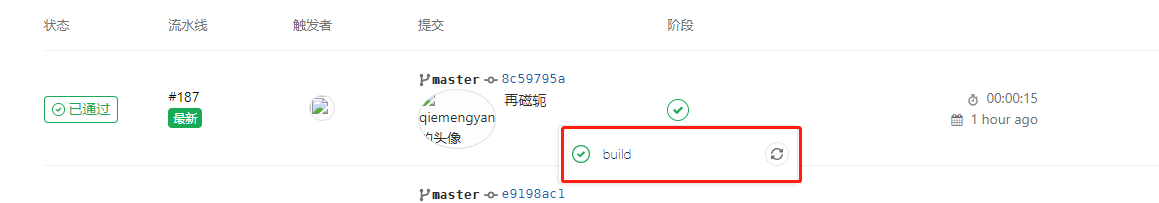
2. Transfer the project to gitlab, enter gitlab's own project, and select CI/CD. You will see the following figure
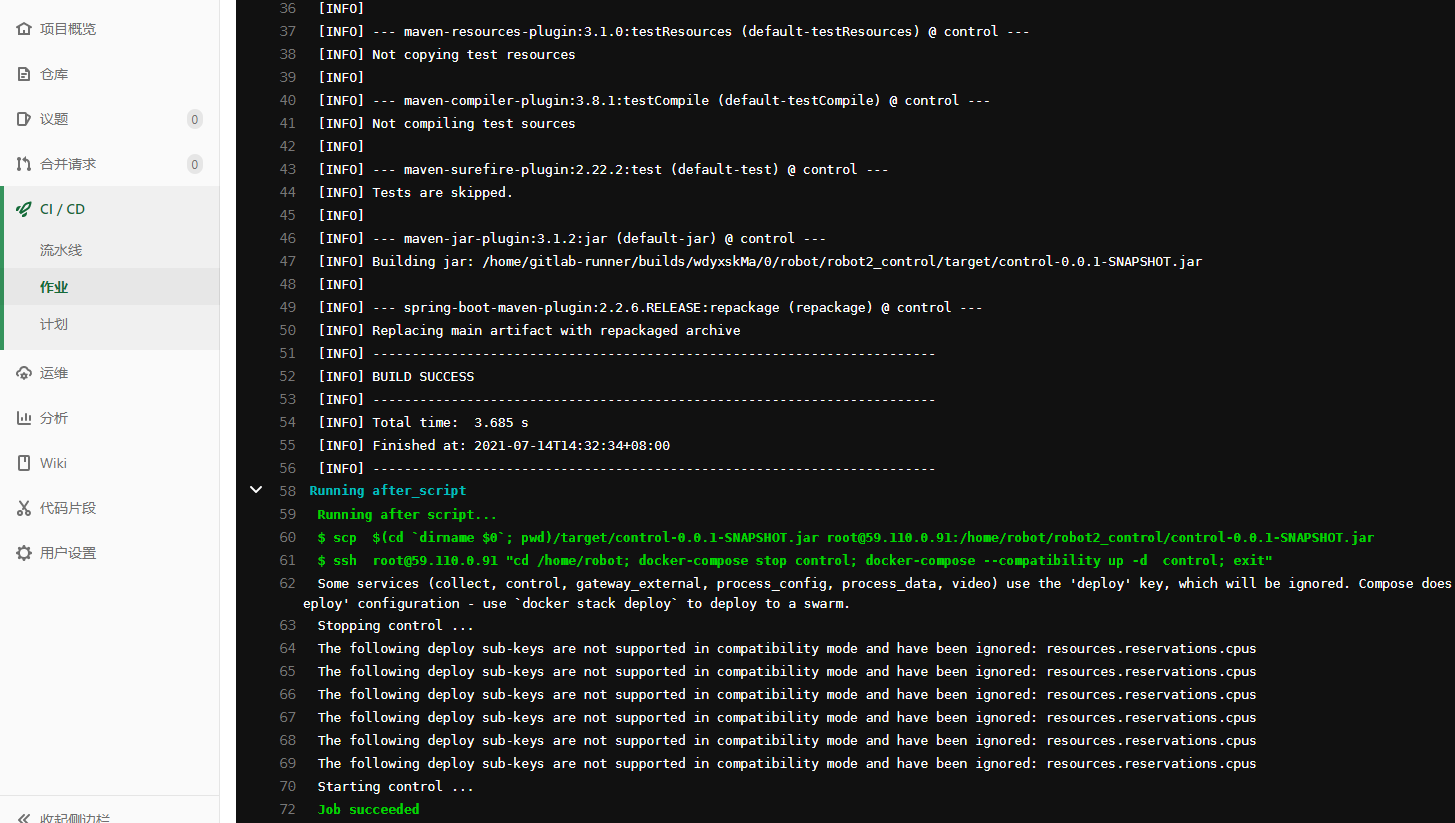
Click the check button - > build. After entering, as shown in the figure below, you will see that your project has been hot deployed.