FFmpeg is in libavcodec module, and avcodec is provided in the old version_ decode_ Video2() as video decoding function, avcodec_decode_audio4() as audio decoding function. Add avcodec in FFmpeg version 3.1_ send_ Packet() and avcodec_receive_frame() as audio and video decoding function. Later, avcodec was implemented in version 3.4_ decode_ Video2 () and avcodec_decode_audio4() is marked as obsolete API. The version change is described as follows:
FFmpeg 3.1 2016-04-21 - 7fc329e - lavc 57.37.100 - avcodec.h Add a new audio/video encoding and decoding API with decoupled input and output -- avcodec_send_packet(), avcodec_receive_frame(), avcodec_send_frame() and avcodec_receive_packet(). FFmpeg 3.4 2017-09-26 - b1cf151c4d - lavc 57.106.102 - avcodec.h Deprecate AVCodecContext.refcounted_frames. This was useful for deprecated API only (avcodec_decode_video2/avcodec_decode_audio4). The new decode APIs (avcodec_send_packet/avcodec_receive_frame) always work with reference counted frames.
avcodec_send_packet() and avcodec_ receive_ The frame() function declaration is located in libavcodec / avcodec.xml h. Let's take a look at the function declaration:
/** * Supply raw packet data as input to a decoder. * * @param avctx codec context * @param[in] avpkt The input AVPacket. Usually, this will be a single video * frame, or several complete audio frames. * * @return 0 on success, otherwise negative error code: * AVERROR(EAGAIN): input is not accepted in the current state - user * must read output with avcodec_receive_frame() * AVERROR_EOF: the decoder has been flushed, and no new packets * AVERROR(EINVAL): codec not opened, it is an encoder, or requires flush * AVERROR(ENOMEM): failed to add packet to internal queue, or similar */ int avcodec_send_packet(AVCodecContext *avctx, const AVPacket *avpkt); /** * Return decoded output data from a decoder. * * @param avctx codec context * @param frame This will be set to a reference-counted video or audio * frame (depending on the decoder type) allocated by the * decoder. Note that the function will always call * av_frame_unref(frame) before doing anything else. * * @return * 0: success, a frame was returned * AVERROR(EAGAIN): output is not available in this state * AVERROR_EOF: the decoder has been fully flushed * AVERROR(EINVAL): codec not opened, or it is an encoder * AVERROR_INPUT_CHANGED: current decoded frame has changed parameters */ int avcodec_receive_frame(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVFrame *frame);
According to the description, avcodec_send_packet() is responsible for sending AVpacket packets to the decoder, avcodec_receive_frame() takes a frame of AVFrame data from the decoder. Return 0, which means decoding is successful; Return EAGAIN, which represents that there is no data to output in the current state; Return EOF, which means reaching the end of the file stream; Return INVAL, which means the decoder is not turned on or the encoder is currently turned on; Return INPUT_CHANGED means that the input parameters have changed, such as width and height.
avcodec_send_packet() and avcodec_ receive_ The decoding flow chart of frame () is as follows:
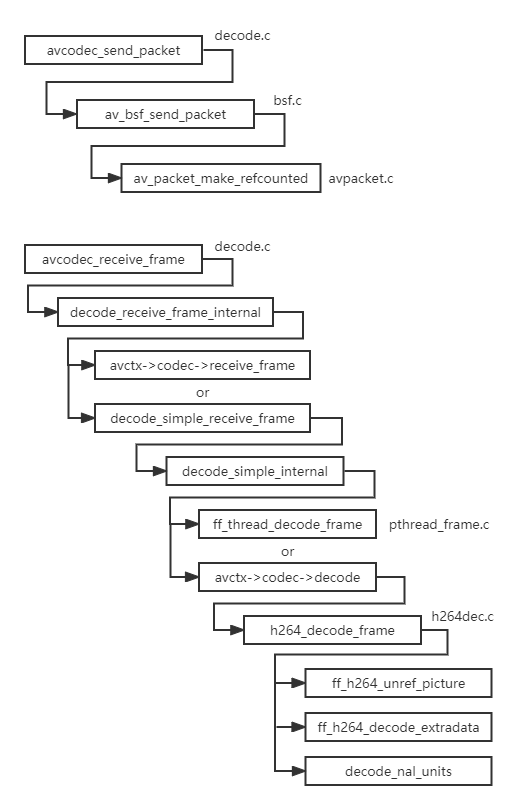
1, avcodec_send_packet send AVPacket
1,avcodec_send_packet
avcodec_ send_ The packet() function is located in libavcodec / decode c. The details are as follows:
int avcodec_send_packet(AVCodecContext *avctx, const AVPacket *avpkt)
{
AVCodecInternal *avci = avctx->internal;
int ret;
if (!avcodec_is_open(avctx) || !av_codec_is_decoder(avctx->codec))
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
if (avctx->internal->draining)
return AVERROR_EOF;
if (avpkt && !avpkt->size && avpkt->data)
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
av_packet_unref(avci->buffer_pkt);
if (avpkt && (avpkt->data || avpkt->side_data_elems)) {
ret = av_packet_ref(avci->buffer_pkt, avpkt);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
}
// Send packet to bitstream filter
ret = av_bsf_send_packet(avci->bsf, avci->buffer_pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
av_packet_unref(avci->buffer_pkt);
return ret;
}
if (!avci->buffer_frame->buf[0]) {
ret = decode_receive_frame_internal(avctx, avci->buffer_frame);
if (ret < 0 && ret != AVERROR(EAGAIN) && ret != AVERROR_EOF)
return ret;
}
return 0;
}2,av_bsf_send_packet
It can be seen that AV is called internally_ bsf_ send_ The packet () function sends the packet to the bitstream filter. The code is located in libavcodec / BSF c. The details are as follows:
int av_bsf_send_packet(AVBSFContext *ctx, AVPacket *pkt)
{
AVBSFInternal *bsfi = ctx->internal;
int ret;
if (!pkt || IS_EMPTY(pkt)) {
bsfi->eof = 1;
return 0;
}
if (bsfi->eof) {
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
if (!IS_EMPTY(bsfi->buffer_pkt))
return AVERROR(EAGAIN);
// Apply for AVPacket memory and copy data
ret = av_packet_make_refcounted(pkt);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
// Assign the pkt pointer to BSFI - > buffer_ pkt
av_packet_move_ref(bsfi->buffer_pkt, pkt);
return 0;
}
av_ bsf_ send_ The packet() function calls AV internally_ packet_ make_ Refcounted() to apply for AVPacket memory and copy data. Then call av_. packet_ move_ The ref() function assigns the pkt pointer to BSFI - > buffer_ pkt.
2, avcodec_receive_frame receive AVFrame
1,avcodec_receive_frame
avcodec_ receive_ The libcode / decode() function is also located in c. It mainly calls the internal function decode_receive_frame_internal() realizes decoding. The specific code is as follows:
int avcodec_receive_frame(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVFrame *frame)
{
AVCodecInternal *avci = avctx->internal;
int ret, changed;
av_frame_unref(frame);
if (!avcodec_is_open(avctx) || !av_codec_is_decoder(avctx->codec))
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
if (avci->buffer_frame->buf[0]) {
av_frame_move_ref(frame, avci->buffer_frame);
} else {
ret = decode_receive_frame_internal(avctx, frame);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
}
if (avctx->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) {
ret = apply_cropping(avctx, frame);
if (ret < 0) {
av_frame_unref(frame);
return ret;
}
}
......
return 0;
}
2,decode_receive_frame_internal
decode_ receive_ frame_ The internal () function determines whether avctx - > codec - > receive is supported_ Frame. If it is supported, call avctx - > codec - > receive_ Frame() function to decode, otherwise call decode_ simple_ receive_ Decode with the frame() function. The details are as follows:
static int decode_receive_frame_internal(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVFrame *frame)
{
AVCodecInternal *avci = avctx->internal;
int ret;
if (avctx->codec->receive_frame) {
ret = avctx->codec->receive_frame(avctx, frame);
if (ret != AVERROR(EAGAIN))
av_packet_unref(avci->last_pkt_props);
} else {
ret = decode_simple_receive_frame(avctx, frame);
}
......
/* free the per-frame decode data */
av_buffer_unref(&frame->private_ref);
return ret;
}3,decode_simple_receive_frame
decode_ simple_ receive_ The frame () function calls decode again_ simple_ Internal() internal function to decode:
static int decode_simple_receive_frame(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVFrame *frame)
{
int ret;
int64_t discarded_samples = 0;
while (!frame->buf[0]) {
if (discarded_samples > avctx->max_samples)
return AVERROR(EAGAIN);
ret = decode_simple_internal(avctx, frame, &discarded_samples);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
}
return 0;
}4,decode_simple_internal
According to the description, decode_ simple_ The internal () function is the core encapsulation function of the decoder. We should call avcodec in a loop_ receive_ Frame() function until EAGAIN is returned. By judging whether a specific thread is required for decoding, FF is called if necessary_ thread_ decode_ Frame() function, otherwise call the decoding function pointed to by avctx - > codec - > decode. The specific calling process is as follows:
/*
* The core of the receive_frame_wrapper for the decoders implementing
* the simple API. Certain decoders might consume partial packets without
* returning any output, so this function needs to be called in a loop until it
* returns EAGAIN.
**/
static inline int decode_simple_internal(AVCodecContext *avctx,
AVFrame *frame,
int64_t *discarded_samples)
{
AVCodecInternal *avci = avctx->internal;
DecodeSimpleContext *ds = &avci->ds;
AVPacket *pkt = ds->in_pkt;
int got_frame, actual_got_frame;
int ret;
if (!pkt->data && !avci->draining) {
av_packet_unref(pkt);
ret = ff_decode_get_packet(avctx, pkt);
if (ret < 0 && ret != AVERROR_EOF)
return ret;
}
if (avci->draining_done)
return AVERROR_EOF;
if (!pkt->data &&
!(avctx->codec->capabilities & AV_CODEC_CAP_DELAY ||
avctx->active_thread_type & FF_THREAD_FRAME))
return AVERROR_EOF;
got_frame = 0;
if (HAVE_THREADS && avctx->active_thread_type & FF_THREAD_FRAME) {
ret = ff_thread_decode_frame(avctx, frame, &got_frame, pkt);
} else {
ret = avctx->codec->decode(avctx, frame, &got_frame, pkt);
......
}
......
return ret < 0 ? ret : 0;
}5,ff_thread_decode_frame
ff_ thread_ decode_ The frame() function is located in libavcodec/pthread_frame.c. The first is to call submit_ The packet () function submits packet to the next decoding thread, and then calls the front thread of the array to decode it. Relevant codes are as follows:
int ff_thread_decode_frame(AVCodecContext *avctx,
AVFrame *picture,
int *got_picture_ptr,
AVPacket *avpkt)
{
FrameThreadContext *fctx = avctx->internal->thread_ctx;
int finished = fctx->next_finished;
PerThreadContext *p;
int err;
async_unlock(fctx);
/*
* Submit a packet to the next decoding thread.
*/
p = &fctx->threads[fctx->next_decoding];
err = submit_packet(p, avctx, avpkt);
if (err)
goto finish;
......
/* Return the next available frame from the oldest thread.*/
do {
p = &fctx->threads[finished++];
if (atomic_load(&p->state) != STATE_INPUT_READY) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&p->progress_mutex);
while (atomic_load_explicit(&p->state, memory_order_relaxed) != STATE_INPUT_READY)
pthread_cond_wait(&p->output_cond, &p->progress_mutex);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&p->progress_mutex);
}
av_frame_move_ref(picture, p->frame);
*got_picture_ptr = p->got_frame;
picture->pkt_dts = p->avpkt->dts;
err = p->result;
p->got_frame = 0;
p->result = 0;
if (finished >= avctx->thread_count) finished = 0;
} while (!avpkt->size && !*got_picture_ptr && err >= 0 && finished != fctx->next_finished);
update_context_from_thread(avctx, p->avctx, 1);
if (fctx->next_decoding >= avctx->thread_count)
fctx->next_decoding = 0;
fctx->next_finished = finished;
/* return the size of the consumed packet if no error occurred */
if (err >= 0)
err = avpkt->size;
finish:
async_lock(fctx);
return err;
}6,h264_decode_frame
Taking h264 decoder as an example, it is located in libavcodec / h264dec c. The corresponding AVCodec is as follows:
AVCodec ff_h264_decoder = {
.name = "h264",
.long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("H.264/AVC/MPEG-4 AVC/MPEG-4 part10"),
.type = AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO,
.id = AV_CODEC_ID_H264,
.priv_data_size = sizeof(H264Context),
.init = h264_decode_init,
.close = h264_decode_end,
.decode = h264_decode_frame,
.capabilities = AV_CODEC_CAP_DR1 |
AV_CODEC_CAP_DELAY | AV_CODEC_CAP_SLICE_THREADS |
AV_CODEC_CAP_FRAME_THREADS,
.flush = h264_decode_flush,
.update_thread_context = ONLY_IF_THREADS_ENABLED(ff_h264_update_thread_context),
.profiles = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL(ff_h264_profiles),
.priv_class = &h264_class,
};At this time, the avctx - > codec - > decode function pointer points to h264_decode_frame. Call FF if extradata exists_ h264_ decode_ The key to the analysis of extradata () function is to call decode_nal_units() function to decode NAL units. Relevant codes are as follows:
static int h264_decode_frame(AVCodecContext *avctx, void *data,
int *got_frame, AVPacket *avpkt)
{
......
ff_h264_unref_picture(h, &h->last_pic_for_ec);
/* end of stream, output what is still in the buffers */
if (buf_size == 0)
return send_next_delayed_frame(h, pict, got_frame, 0);
if (av_packet_get_side_data(avpkt, AV_PKT_DATA_NEW_EXTRADATA, NULL)) {
buffer_size_t side_size;
uint8_t *side = av_packet_get_side_data(avpkt, AV_PKT_DATA_NEW_EXTRADATA, &side_size);
ff_h264_decode_extradata(side, side_size,
&h->ps, &h->is_avc, &h->nal_length_size,
avctx->err_recognition, avctx);
}
if (h->is_avc && buf_size >= 9 && buf[0]==1 && buf[2]==0 && (buf[4]&0xFC)==0xFC) {
// Parsing extradata corresponding to avcc
if (is_avcc_extradata(buf, buf_size))
return ff_h264_decode_extradata(buf, buf_size,
&h->ps, &h->is_avc, &h->nal_length_size,
avctx->err_recognition, avctx);
}
// Decoding NAL unit
buf_index = decode_nal_units(h, buf, buf_size);
if (buf_index < 0)
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
if (!h->cur_pic_ptr && h->nal_unit_type == H264_NAL_END_SEQUENCE) {
av_assert0(buf_index <= buf_size);
return send_next_delayed_frame(h, pict, got_frame, buf_index);
}
if (!(avctx->flags2 & AV_CODEC_FLAG2_CHUNKS) && (!h->cur_pic_ptr || !h->has_slice)) {
if (avctx->skip_frame >= AVDISCARD_NONREF ||
buf_size >= 4 && !memcmp("Q264", buf, 4))
return buf_size;
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
}
if (!(avctx->flags2 & AV_CODEC_FLAG2_CHUNKS) ||
(h->mb_y >= h->mb_height && h->mb_height)) {
if ((ret = ff_h264_field_end(h, &h->slice_ctx[0], 0)) < 0)
return ret;
/* Wait for second field. */
if (h->next_output_pic) {
ret = finalize_frame(h, pict, h->next_output_pic, got_frame);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
}
}
ff_h264_unref_picture(h, &h->last_pic_for_ec);
return get_consumed_bytes(buf_index, buf_size);
}3, avcodec_decode_video2 video decoding
Due to avcodec_ decode_ The video2() function is outdated, so compat is provided internally_ Decode() to be compatible with the version. The specific code is as follows:
int avcodec_decode_video2(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVFrame *picture,
int *got_picture_ptr,
const AVPacket *avpkt)
{
return compat_decode(avctx, picture, got_picture_ptr, avpkt);
}Let's look at compat_code() function source code. In fact, it calls avcodec internally_ send_ Packet() and avcodec_receive_frame(), as follows:
static int compat_decode(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVFrame *frame,
int *got_frame, const AVPacket *pkt)
{
AVCodecInternal *avci = avctx->internal;
int ret = 0;
*got_frame = 0;
if (avci->draining_done && pkt && pkt->size != 0) {
avcodec_flush_buffers(avctx);
}
if (avci->compat_decode_partial_size > 0 &&
avci->compat_decode_partial_size != pkt->size) {
ret = AVERROR(EINVAL);
goto finish;
}
if (!avci->compat_decode_partial_size) {
// Call avcodec_send_packet send packet
ret = avcodec_send_packet(avctx, pkt);
if (ret == AVERROR_EOF)
ret = 0;
else if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN)) {
/* we fully drain all the output in each decode call, so this should not
* ever happen */
ret = AVERROR_BUG;
goto finish;
} else if (ret < 0)
goto finish;
}
while (ret >= 0) {
// Loop call avcodec_receive_frame receive frame
ret = avcodec_receive_frame(avctx, frame);
if (ret < 0) {
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF)
ret = 0;
goto finish;
}
if (frame != avci->compat_decode_frame) {
if (!avctx->refcounted_frames) {
ret = unrefcount_frame(avci, frame);
if (ret < 0)
goto finish;
}
*got_frame = 1;
frame = avci->compat_decode_frame;
} else {
if (!avci->compat_decode_warned) {
avci->compat_decode_warned = 1;
}
}
if (avci->draining || (!avctx->codec->bsfs
&& avci->compat_decode_consumed < pkt->size)) {
break;
}
}
finish:
if (ret == 0) {
/* if there are any bsfs then assume full packet is always consumed */
if (avctx->codec->bsfs)
ret = pkt->size;
else
ret = FFMIN(avci->compat_decode_consumed, pkt->size);
}
avci->compat_decode_consumed = 0;
avci->compat_decode_partial_size = (ret >= 0) ? pkt->size - ret : 0;
return ret;
}4, avcodec_decode_audio4 audio decoding
Avcodec_ decode_ Like the video2() function, avcodec_decode_audio4() function is outdated, and compat is also provided internally_ Decode() to be compatible with the version. The specific code is as follows:
int avcodec_decode_audio4(AVCodecContext *avctx,
AVFrame *frame,
int *got_frame_ptr,
const AVPacket *avpkt)
{
return compat_decode(avctx, frame, got_frame_ptr, avpkt);
}So far, avcodec_send_packet() and avcodec_ receive_ The decoding function composed of frame () has been analyzed.
To learn FFmpeg and code practice, refer to: FFmpegAndroid