1 SQL overview
1.1 what is SQL
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a "structured query language", which is an operation language for relational databases. It can be applied to all relational databases, such as MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, etc.
SQL standards (ANSI/ISO) include:
1. SQL-92: SQL language standard issued in 1992;
2. SQL: SQL language label issued in 1999;
3. SQL: SQL language label issued in 2003;
These standards are the same as the JDK version. There are always some syntax changes in the new version. Databases in different periods have implemented different standards.
Although SQL can be used in all relational databases, many databases also have some syntax after the standard, which we can call "dialect". For example, the LIMIT statement in MySQL is a unique dialect of MySQL, which is not supported by other databases! Of course, Oracle or SQL Server has its own dialect.
1.2 grammar requirements
1. SQL statements can be written in one or more lines, ending with semicolons;
2. You can use spaces and indents to enhance the readability of statements;
3. Keywords are not case sensitive. It is recommended to use uppercase;
2 SQL classification
DDL: data definition language, which is used to define database objects: database, table, column, etc. (database and table building).
DML: data operation language, which is used to define database records (data) for insertion, deletion and update operations.
DCL: data control language, used to set access rights and security levels.
DQL: data query language, used to query records (data).
3 how to execute SQL statements in Navicat
Double click Navicat to open MySQL80 connection.
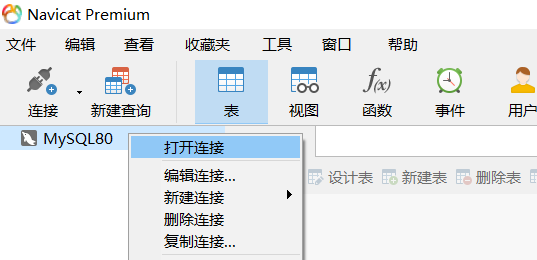
Click "new query".
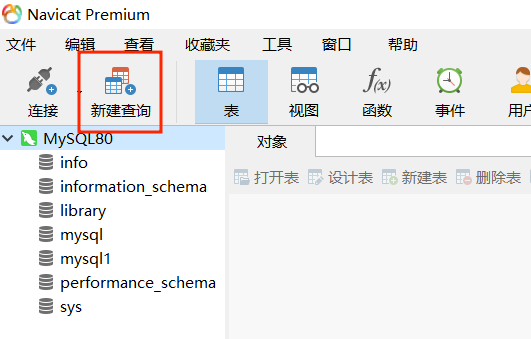
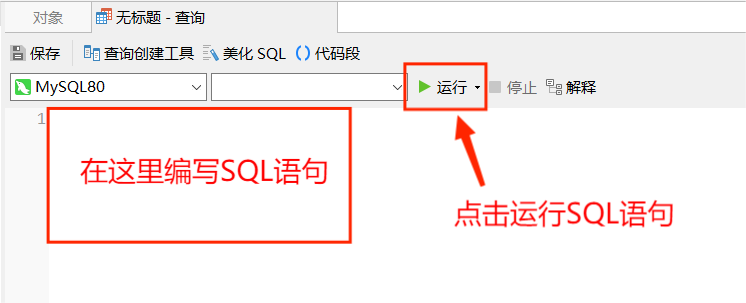
Enter the following page, where you can write SQL statements. Click Run to execute the SQL statement.
4 DDL data definition language (MySQL)
4.1 basic operation
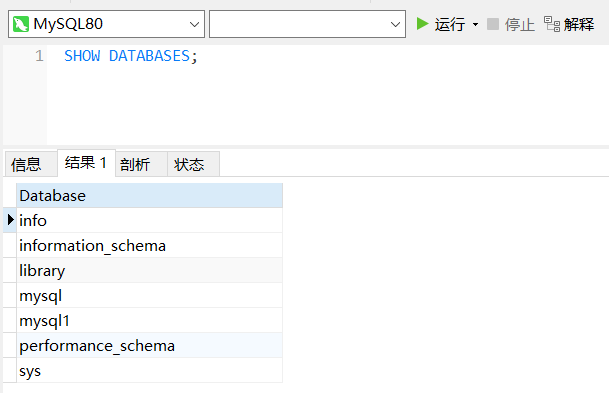
1. View all databases
show databases;
2. Switch database
use Database name;
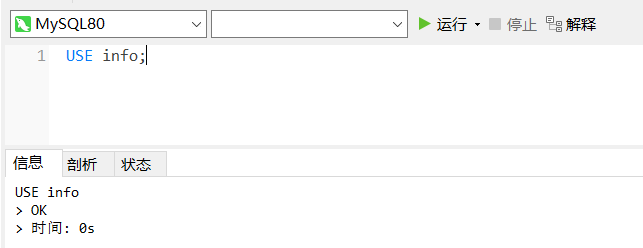
Switch to info database:
use info;
4.2 operation database
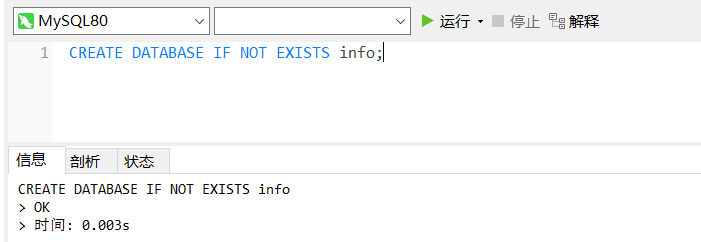
1. Create database
create database [if not exists] Database name;
[if not exists]: indicates that if the given "database name" does not exist, the database will be created; If the database exists, it will not be created again.
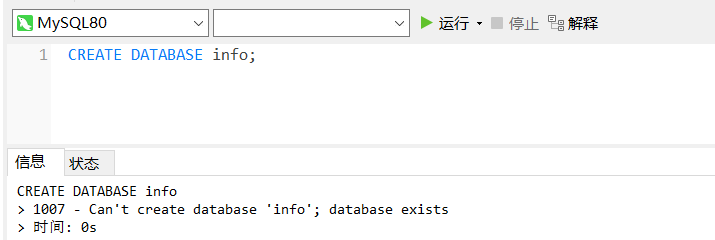
If "IF NOT EXISTS" is not added, an error will be reported when the database to be created exists.
2. Delete database
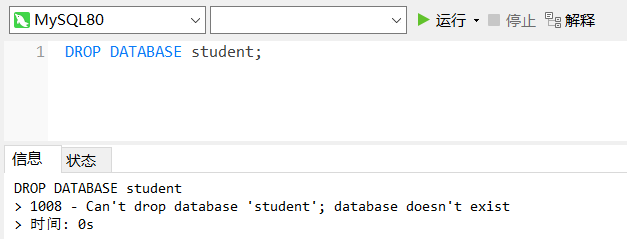
drop database [if exists] Database name;
[if exists]: if the database to be deleted exists, it will be deleted; if it does not exist, it will not be deleted.
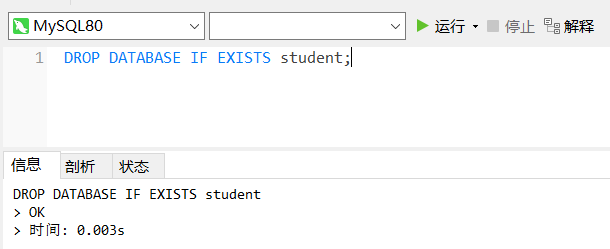
If "IF EXISTS" is not added, an error will be reported if the database does not exist.
3. Modify the encoding format of the database
ALTER DATABASE Database name CHARACTER SET Character set name;
For example, modify the code of database mydb1 to utf8
ALTER DATABASE mydb1 CHARACTER SET utf8
Modify the code of database mydb1 to utf8. Note that all UTF-8 codes in MySQL cannot use the middle "-", that is, UTF-8 should be written as utf8.
5 data type
Mysql, like Java and C, also has data types. Data types in MySQL are mainly used on columns.
| type | describe |
|---|---|
| int | integer |
| double | Floating point type, for example, double(5,2) represents a maximum of 5 digits, in which there must be 2 decimal places, that is, the maximum value is 999.99 |
| decimal | Generic type. It can store both int type and double type without losing the accuracy of data |
| char | Fixed length string (space will be filled in when the input string is not long enough) |
| varchar | Fixed length string (no space will be filled when the input string is not long enough) |
| text | String type |
| blob | Byte type |
| date | Date type (Format: yyyy MM DD) |
| datetime | Date time format (Format: hh:mm:ss) |
| timestamp | time stamp |
6 operation table
6.1 creating tables
CREATE TABLE Table name( Column name column type, Column name column type, ...... );
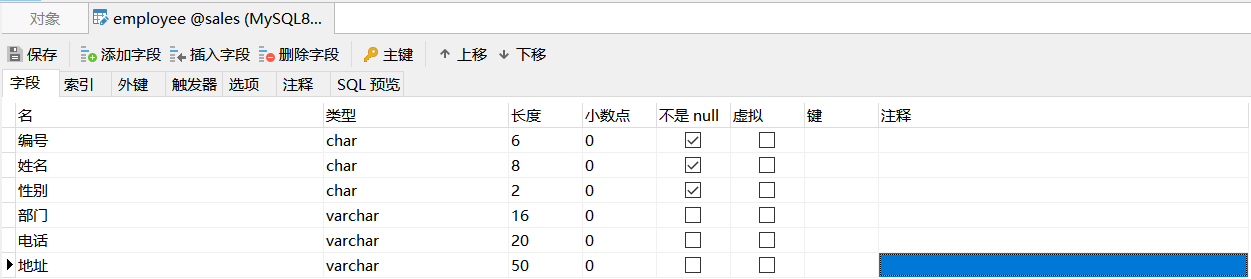
Next, take the Sales database and its table Employees as an example. First, create the table Employees in the Sales database. The data is as follows:
| Listing | data type | Is it empty |
|---|---|---|
| number | char(6) | No |
| full name | char(8) | No |
| Gender | char(2) | No |
| department | varchar(16) | Yes |
| Telephone | varchar(20) | Yes |
| address | varchar(50) | Yes |
Create the Employees table. The SQL statement is as follows:
CREATE TABLE Employees( number CHAR(6) NOT NULL, full name CHAR(8) NOT NULL, Gender CHAR(2) NOT NULL, department VARCHAR(16), Telephone VARCHAR(20), address VARCHAR(50) );
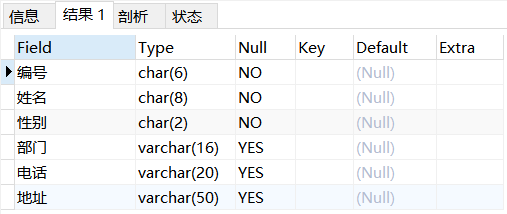
6.2 view table structure
desc Table name;
Example: viewing the employees table
desc employees;
6.3 delete table
drop table Table name;
Example: delete table employees
drop table employees;
6.4 modification table
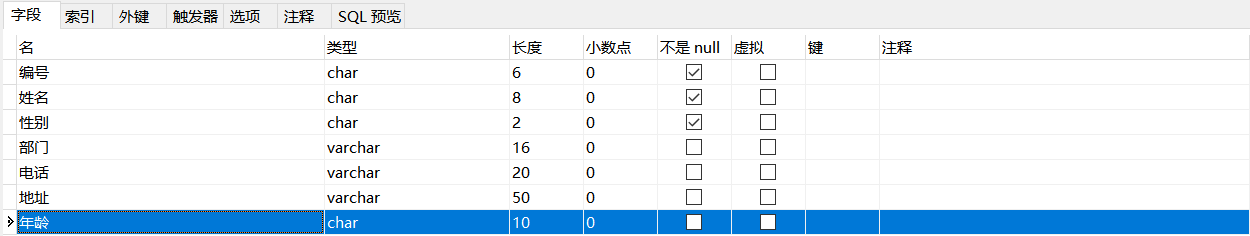
1. Add column
alter table Table name add (Column name data type(length));
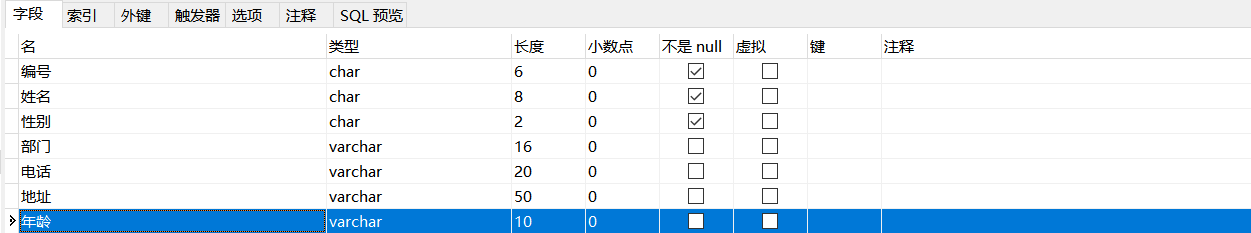
Example: add a column to the employees table: age char(10)
ALTER TABLE Employees ADD (Age CHAR(10));
2. Modify the data type of the column
alter table Table name modify Column name new data type(length);
Example: for the age column in the employees table, modify char(10) to varchar(10)
ALTER TABLE Employees MODIFY Age VARCHAR(10);
3. Modify column name
alter table Table name change Original column name new column name data type(length);
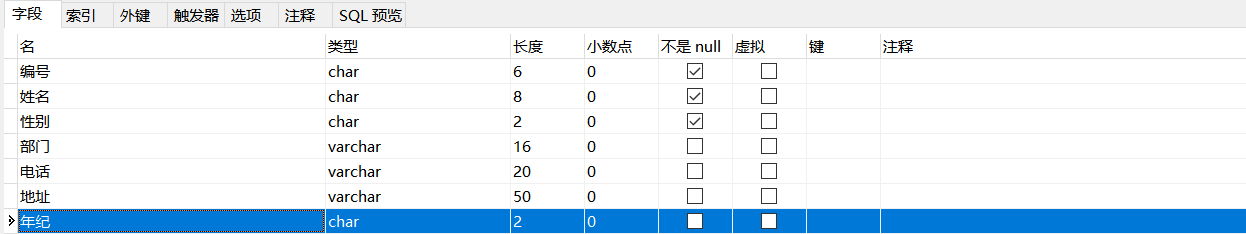
Example: change the age of the column name in the employees table to age
ALTER TABLE employees CHANGE Age age CHAR(2);
4. Delete column
alter table Table name drop Listing;
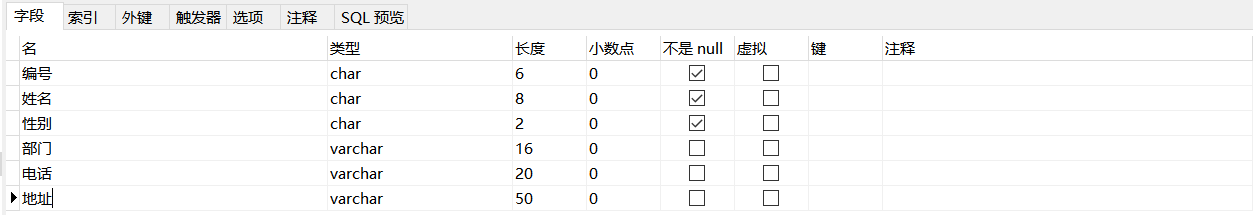
Example: delete a column in the employees table
ALTER TABLE employees DROP Age;
5. Modify table name
alter table Original table name rename to New table name;
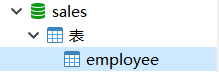
Example: rename the employees table to employee
ALTER TABLE employees RENAME TO employee;
7 DML data operation language
7.1 inserting data
1. Insert data for all columns by default
insert into Table name values(Value 1,Value 2,Value 3......);
Because the column to be inserted is not specified, it means that the values of all columns are inserted in the order of the columns when the table is created (Note: all string type data must be enclosed in single quotes)
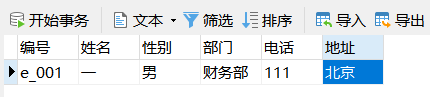
Example: inserting data for the employee table
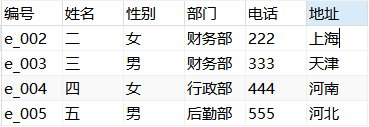
INSERT INTO employee VALUES('e_001','one','male','Finance Department','111','Beijing');
2. Inserts data into the specified column
Premise: columns without inserted data are allowed to be null
insert into Table name(Column name 1,Column name 2,Column name 3,...) values(Value 1,Value 2,Value 3,...);
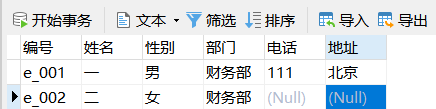
Example: insert data for employee
INSERT INTO employee(number,full name,Gender,department) VALUES('e_002','two','female','Finance Department');
7.2 modifying data
update Table name set Column name 1=Value 1,Listing=Value 2... [where condition];
Note: the method to judge whether the column is empty is null
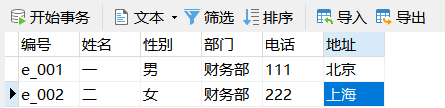
Example: modify the second data in the employee table
UPDATE employee SET Telephone='222',address='Shanghai' WHERE number='e_002';
7.3 deleting data
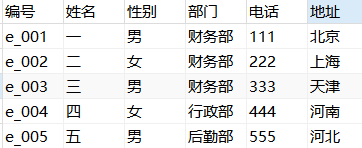
1. Delete records that meet the conditions
delete from Table name where condition;
Example: delete the data numbered "e_001" in the table
DELETE FROM employee WHERE number='e_001';
2. Delete all records:
--Mode 1 TRUNCATE TABLE Table name; --Mode 2 delete from Table name;
Although TRUNCATE and DELETE can DELETE all records of the table, they have different principles. DELETE is not as efficient as TRUNCATE!
TRUNCATE is actually a DDL statement because it first drops table and then creates table. Moreover, records deleted by TRUNCATE cannot be rolled back, but records deleted by DELETE can be rolled back.
8 DCL data control language
8.1 creating users
--The address is a local address or 127.0.0.1. create user 'user name'@address IDENTIFIED BY 'password'; --Or it can be written in the following form CREATE USER 'user name'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password'; --here%Is a wildcard, indicating that users will be created no matter what address
Example: create user1 user with password 123
CREATE USER 'user1'@localhost IDENTIFIED BY '123';
After creation, you can enter cmd to open a command prompt window to verify whether you can log in to the database.
8.2 authorization to users
If you only create a user, the user can only log in to the database and cannot perform any operations. Therefore, you need to authorize the user.
GRANT Authority 1,Authority 2... ON database.* TO 'user name'@address;
The types of permissions mainly include:
| jurisdiction | explain |
|---|---|
| CREATE | establish |
| ALTER | modify |
| DROP | Delete (library, table) |
| INSERT | insert |
| UPDATE | to update |
| DELETE | Delete (record) |
| SELECT | choice |
Granting full permissions to users can be written as:
--In mode 1, the following permissions can also be selected and written to indicate partial authorization GRANT CREATE,ALTER,DROP,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE,SELECT ON database.* TO user@localhost; --Mode 2 GRANT ALL ON database.* TO user@localhost;
Example: granting create permission to user1
GRANT CREATE ON sales.* TO user1@localhost;
In the command prompt window, use user1 to create a table s1.
create table s1(id int,name varchar(20));

Look at the sales database again. There is s1 such a table:

If the user1 user is used to view the structure of the table, an error will be reported because there is no permission:
desc s1;

8.3 viewing user permissions
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'user name'@address;
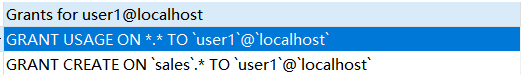
Example: view the permissions of user1 user
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'user1'@localhost;
8.4 display all users
SELECT user from mysql.user;
Example: display all users in the database
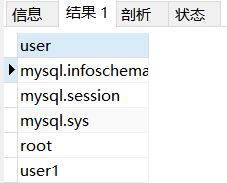
8.5 revocation of authorization
REVOKE Authority 1, ... , jurisdiction n ON database.* FROM 'user name'@address;
Example: revoke the create permission of user1 user
REVOKE CREATE ON sales.* FROM 'user1'@localhost;
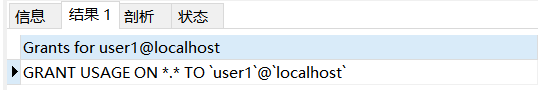
Next, show the permissions of user1: there is only one permission:
SHOW GRANTS FOR user1@localhost;
8.6 modifying user password
alter user 'user name'@localhost identified by 'New password';
Example: change the password of user user1 to 121212
ALTER USER 'user1'@localhost IDENTIFIED BY '121212';
8.7 delete user
drop user 'user name'@address;
Example: delete user1 user
DROP USER 'user1'@localhost;