SQL syntax
SQL add
INSERT INTO Table name VALUES (Value 1, Value 2,....) INSERT INTO table_name (Column 1, Column 2,...) VALUES (Value 1, Value 2,....)
SQL query
Digital condition query
SELECT col,col,col what are you looking for?
Where can I find the FROM table?
What is the WHERE col condition?

select * from table where col = 1;
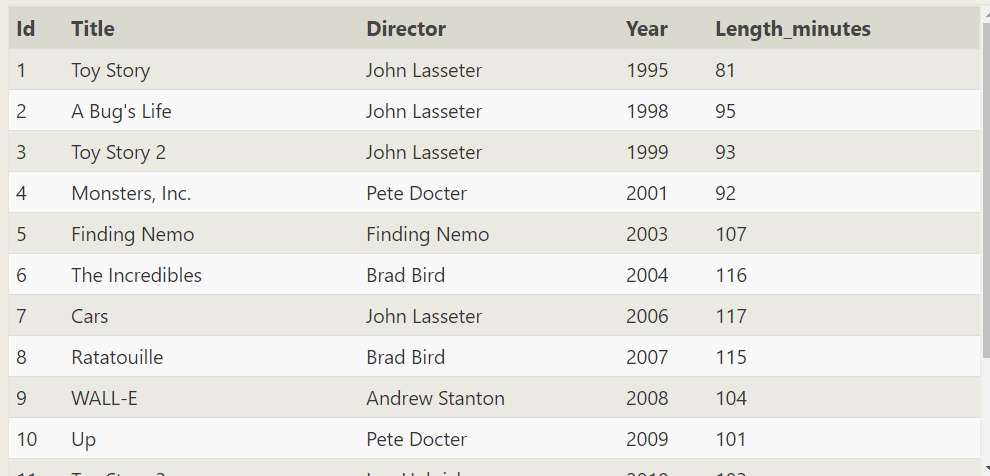
SELECT * FROM movies WHERE year=2010;

SELECT id,title,director FROM movies WHERE year=2010; //Find some of these columns

SELECT * FROM movies WHERE year between 2000 and 2010;
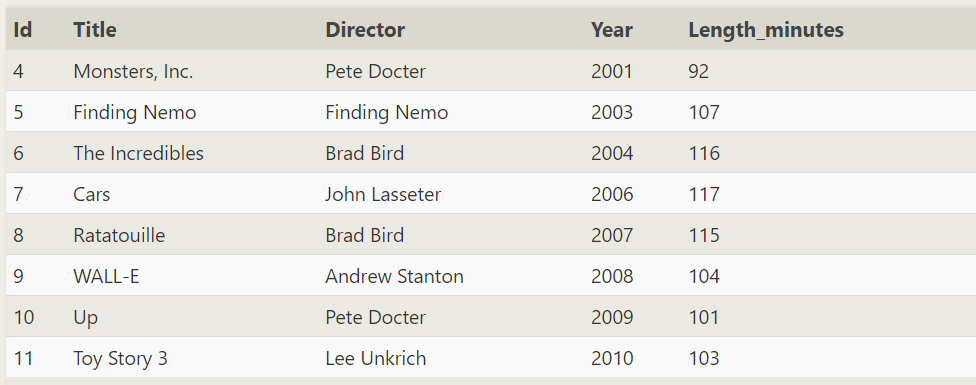
SELECT * FROM movies WHERE year in (2001,2002,2010);
Condition search
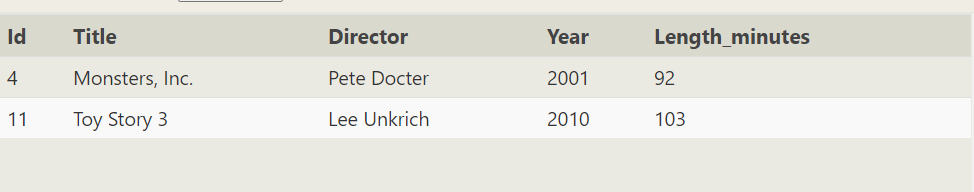
SELECT * FROM movies WHERE year>=2005 or year<=2004;
Text condition query
select * from table where col like '%jin'
You must look for a string object
SELECT * FROM movies WHERE year like 2005;
year is not a string, so I can't find anything

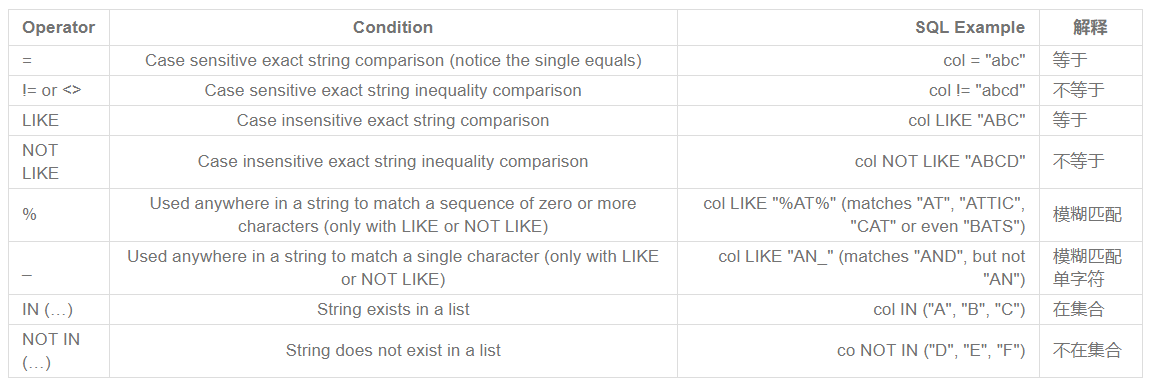
SELECT * FROM movies WHERE Title like 'Cars';
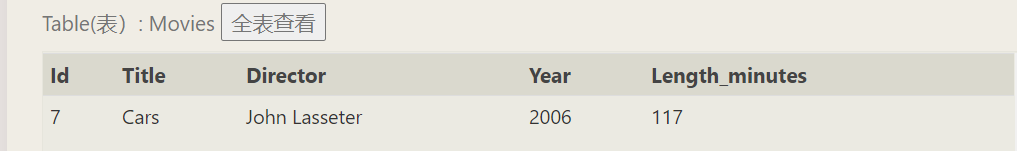
SELECT * FROM movies WHERE Title like '%ar%';
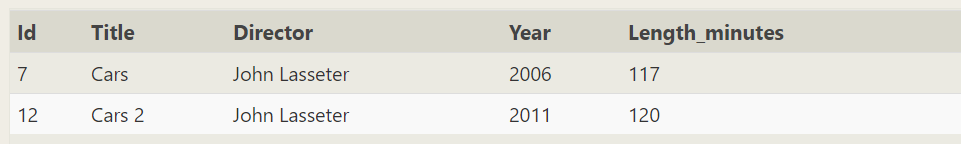
SELECT * FROM movies WHERE Title like 'Cars_%';

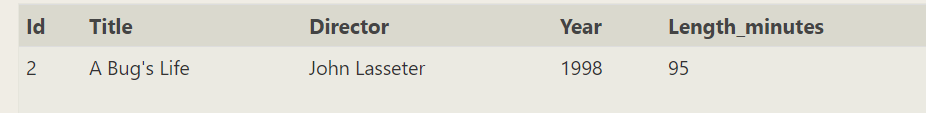
SELECT * FROM movies where YEAR=1998 and title like '%B%'
Use and for both numeric and character conditions
Sorting of search results
The results need to be evaluated rows Sorting and filtering section rows select * from table where col > 1 order by col asc limit 2 offset 2

SELECT * FROM movies WHERE year between 1999 and 2009 order by Length_minutes
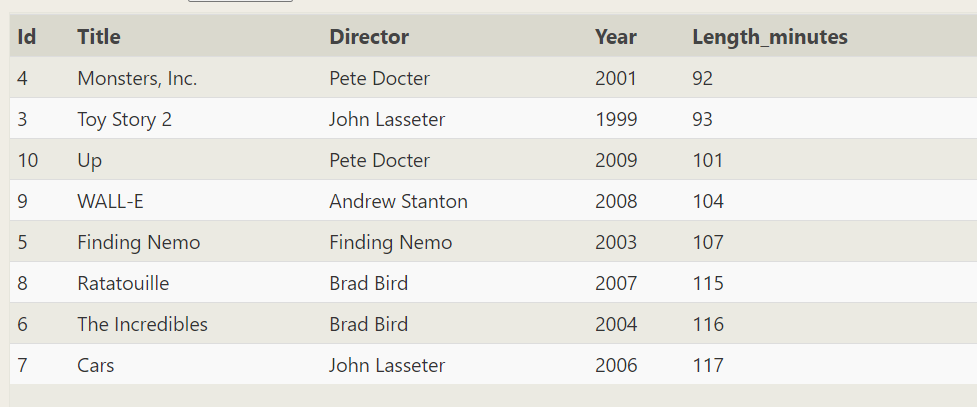
SELECT * FROM movies WHERE year between 1999 and 2009 order by Length_minutes desc
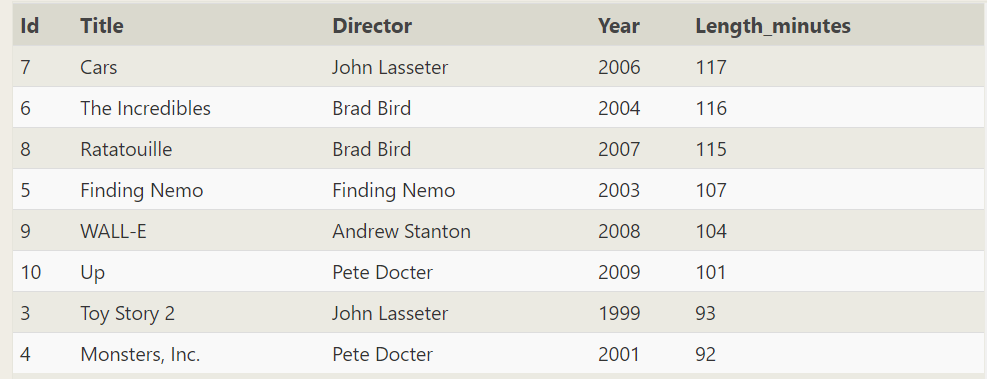
For example, select * from article LIMIT 3 OFFSET 1 means skipping one piece of data, starting from the second piece of data and taking three pieces of data, that is, taking two, three and four pieces of data
SELECT * FROM movies WHERE year between 1999 and 2009 order by Length_minutes desc limit 200 offset 1
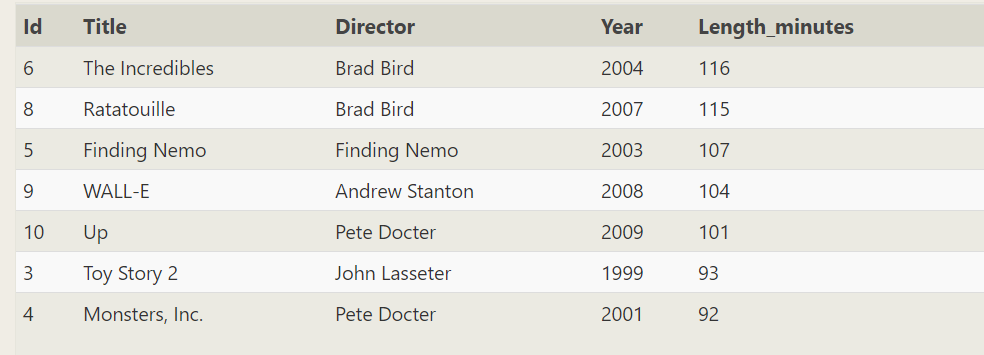
SELECT * FROM movies WHERE year between 1999 and 2009 order by Length_minutes desc limit 200 offset 2;
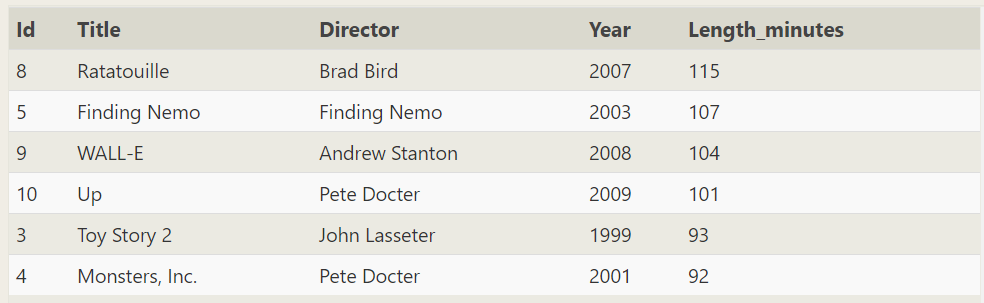
SELECT * FROM movies WHERE year between 1999 and 2009 order by Length_minutes desc limit 200 offset 3;
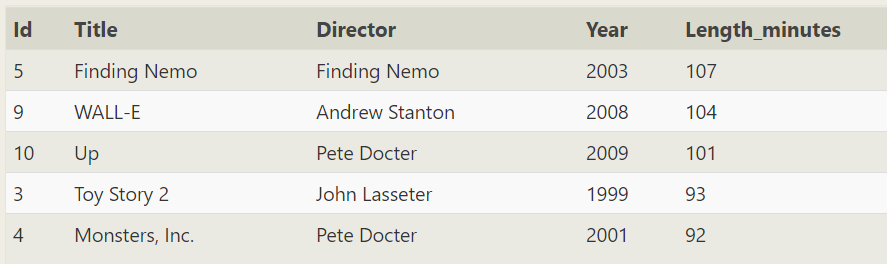
Weight removal
SELECT director FROM movies ORDER BY director
Repeat director

SELECT director FROM movies GROUP BY director

For complex query, first select according to the director's name, and then sort the results
SELECT title FROM movies where director like '%jo%' order by length_minutes limit 1 offset 2
Multi table link
When the searched data is in multiple associated table s
select * from table1 left join table2 on table1.id = table2.id where col > 1
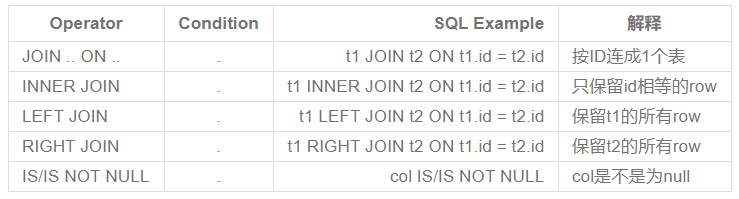

It can be seen intuitively that inner keeps only the middle C, left the left half, right the right half, and full connection is to save all
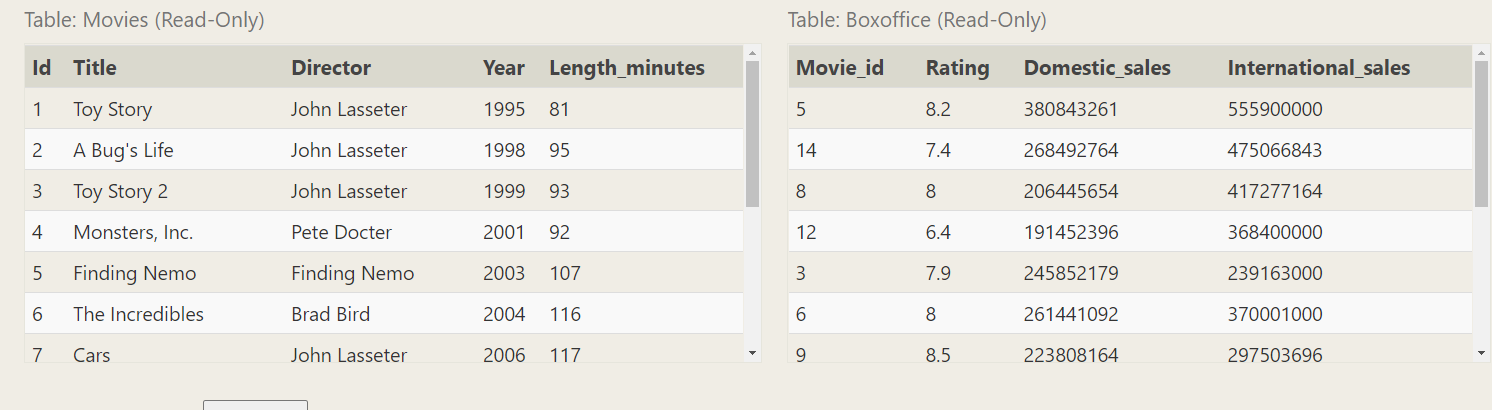
[joint table] find domestic domestic domestic films of all films_ Sales and international sales
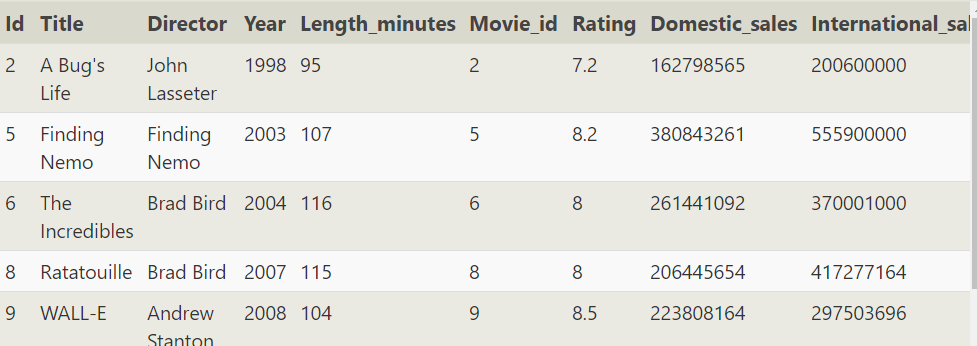
SELECT * FROM movies LEFT JOIN Boxoffice ON MOVIES.ID=Boxoffice.MOVIE_ID
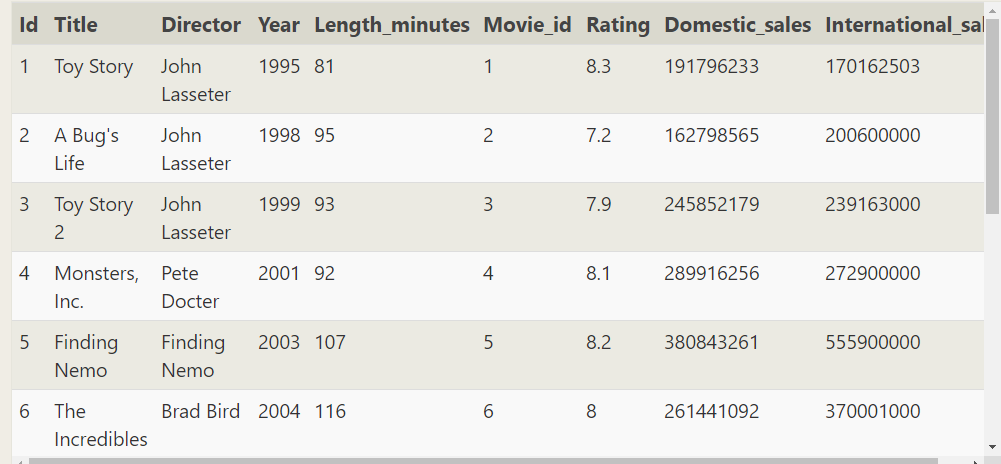
This is equivalent to generating a new table
SELECT Domestic_sales FROM movies LEFT JOIN Boxoffice ON MOVIES.ID=Boxoffice.MOVIE_ID
It is equivalent to filtering in the new table
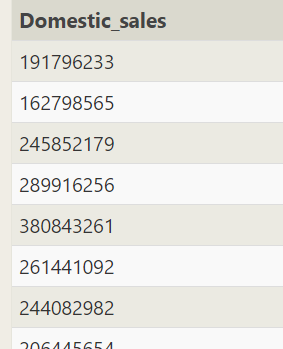
--Please enter sql SELECT * FROM movies LEFT JOIN Boxoffice ON MOVIES.ID=Boxoffice.MOVIE_ID where International_sales>Domestic_sales
External connection
[review] find the names of all the buildings with employees
SELECT BUILDING FROM employees join Buildings on employees.Building=Buildings.Building_name group by Building
SELECT Building_name,role FROM BUILDINGS left JOIN EMPLOYEES ON buildings.Building_name=Employees.Building group by role,building_name
In fact, this group by multi column is also very good. It is equivalent to taking both columns as states
If you do not write link conditions, it is equivalent to a simple arrangement and combination
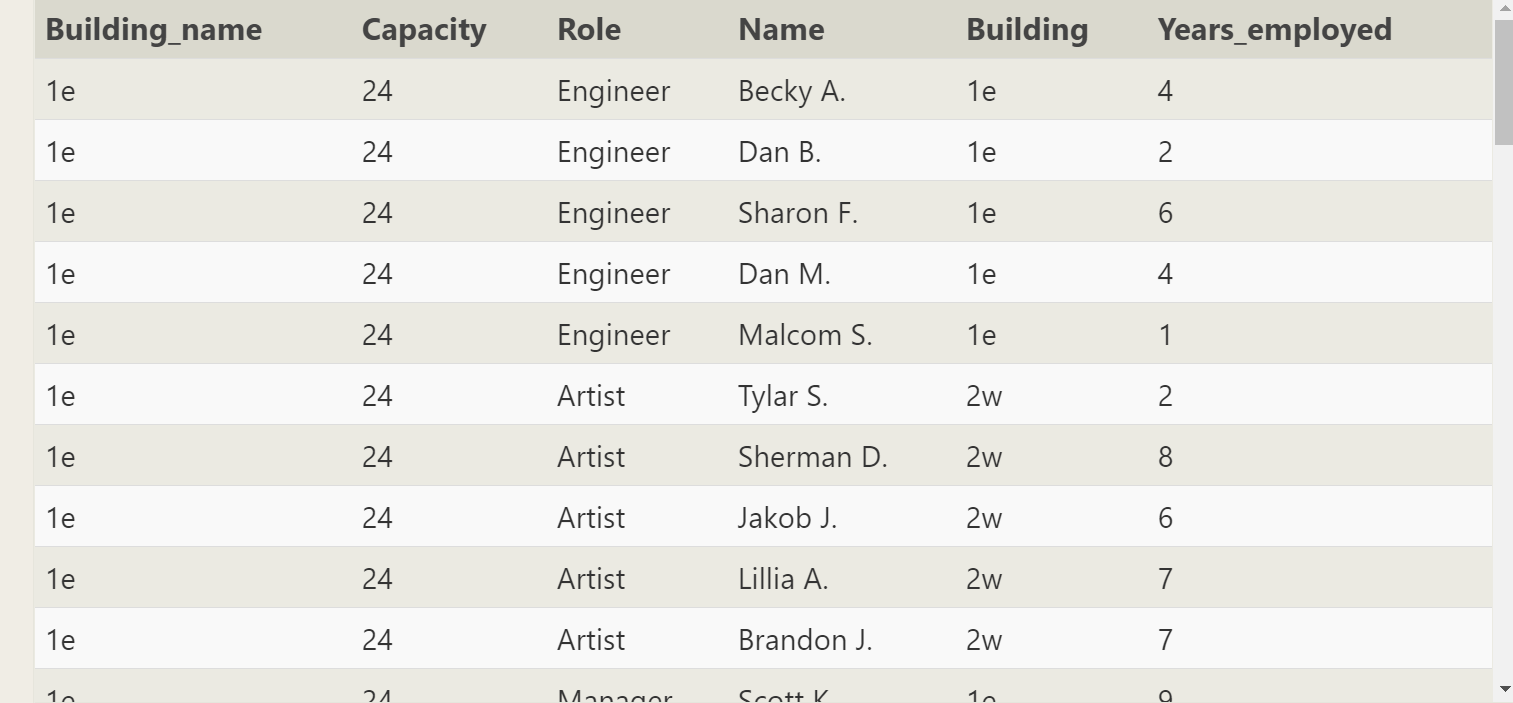
SELECT * FROM Buildings left join employees
Processing of NULL
Processing in query criteria NULL SELECT column, another_column, ... FROM mytable WHERE column IS/IS NOT NULL AND/OR another_condition AND/OR ...;
Use expressions in queries
It is equivalent to making an alias for the row obtained by the expression, which is equivalent to inserting a column
SELECT particle_speed / 2.0 AS half_particle_speed (Divide the result by 2)
FROM physics_data
WHERE ABS(particle_position) * 10.0 >500
(The condition requires that the absolute value of this attribute be multiplied by 10 (greater than 500);
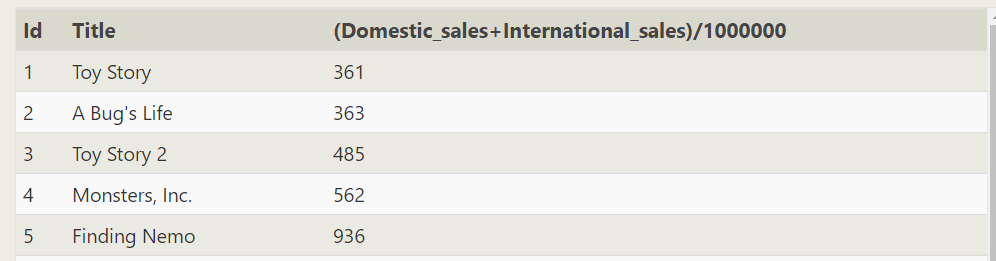
--Please enter sql SELECT id, title,(Domestic_sales+International_sales)/1000000 FROM movies left join Boxoffice on movies.id=Boxoffice.movie_id
Filter all even movie years
--Please enter sql SELECT id, title,year FROM movies left join Boxoffice on movies.id=Boxoffice.movie_id where year%2==0
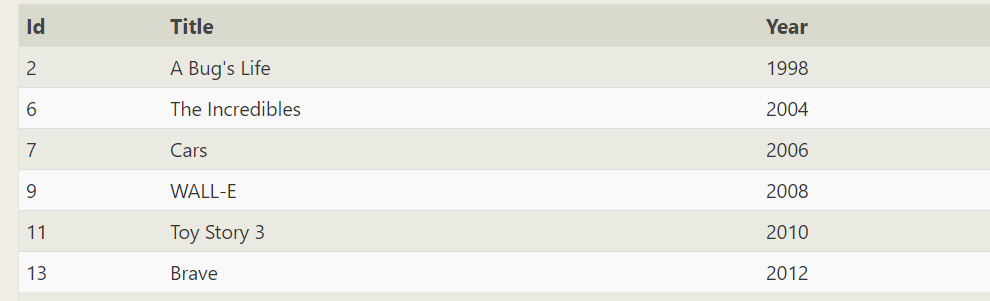
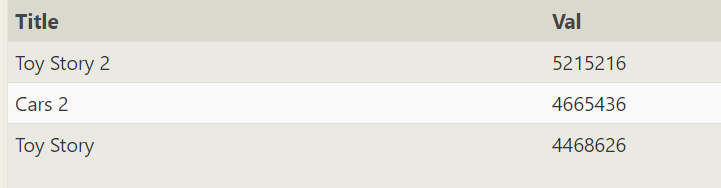
[difficult problem] how much is each movie directed by John Lasseter worth per minute? Just tell me the top three movie names and values
SELECT title, (Domestic_sales+International_sales)/Length_minutes as val FROM movies left join Boxoffice on movies.id=Boxoffice.movie_id where director like '%joh%' order by val desc limit 3;
Make statistics on the table
Make statistics on all result data SELECT AGG_FUNC(column_or_expression) AS aggregate_description, ... FROM mytable WHERE constraint_expression;
Statistics by grouping SELECT AGG_FUNC(column_or_expression) AS aggregate_description, ... FROM mytable WHERE constraint_expression GROUP BY column;
Using Group by, if there are several years in the list, several pieces of data will be returned
SELECT * FROM employees group by Years_employed
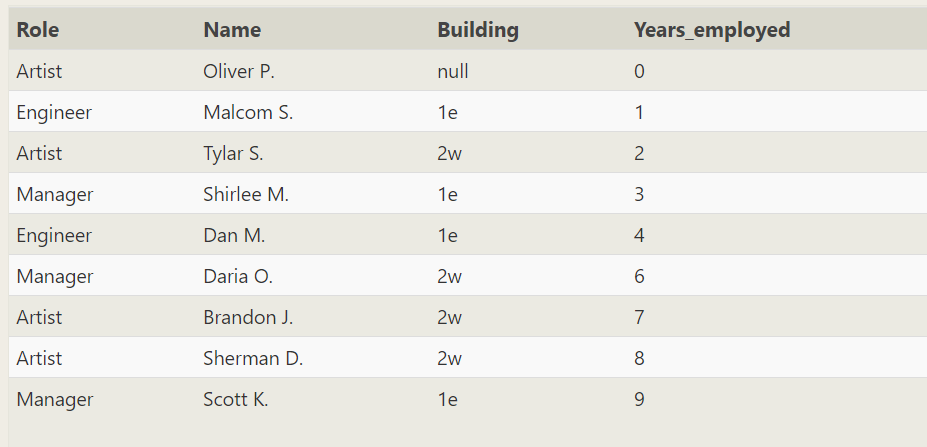
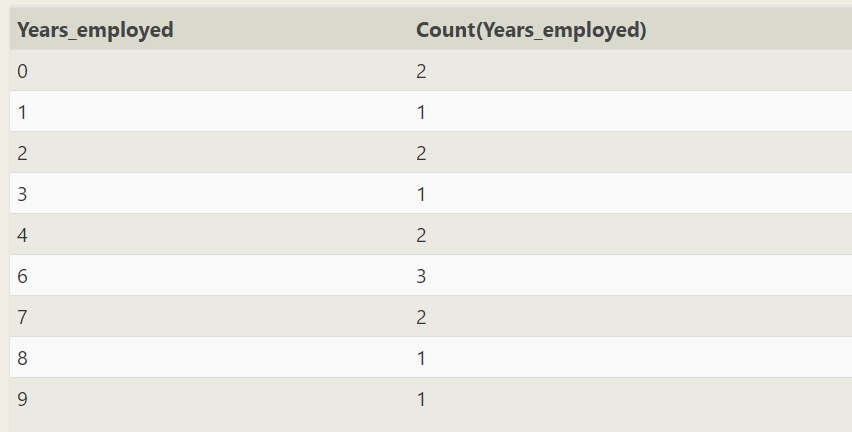
Group by is not useful for direct grouping statistics
--Please enter sql SELECT Years_employed,count(Years_employed) FROM employees group by Years_employed
Group counting according to the number of years
Count the average age of each role:
First group according to the role, and then make mean statistics within the group
--Please enter sql SELECT role,avg(Years_employed) FROM employees group by role
[problem] each office is ranked according to the number of people. Don't count the employees without an office
SELECT building,count(name) FROM employees where building is not null group by Building
SQL statement execution order:
1st) FROM sentence: the execution order is from back to front, from right to left. Tables with large amount of data shall be placed behind as far as possible.
2nd) WHERE sentence: the execution order is from bottom to top and from right to left. Write the condition that can filter out the maximum number of records on the far right of the WHERE sentence.
3rd) GROUP BY: the execution sequence is from right to left. It is better to use WHERE before GROUP BY to filter out unnecessary records before GROUP BY
4th) HAVING sentence: consume resources. Try to avoid using it. HAVING will filter the results after retrieving all records. Sorting and other operations are required.
5th) SELECT sentence: use fewer numbers and try to use field names. In the process of parsing, oracle converts the numbers into all column names by querying the data dictionary, which consumes time.
6th) ORDER BY sentence: the execution order is from left to right, which consumes resources
[difficult problem] calculate the number of people with and without offices for each role by grouping according to roles (list the roles, quantity and whether there are offices. Note that if there are offices for one role, some do not need to be counted separately) ‡
SELECT role,count(name),building is not null FROM employees group by building is null,role
group can have multiple targets, and the judgment expression can be written in the front
[difficult problem] calculate the total sales by directors in groups and find the average sales champion (the statistical results filter out the directors with only a single film, and list the director's name, total sales, number of films and average sales) ‡
SELECT sum(Domestic_sales+International_sales)/count(id) as ii,director,sum(Domestic_sales+International_sales),count(id) FROM movies left join Boxoffice on movies.id=Boxoffice.movie_id group by director having count(id)>=2 order by ii desc limit 1

having can be filtered again after the group
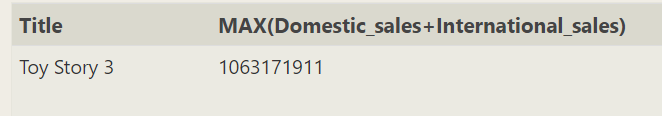
SELECT title,((select MAX(Domestic_sales+International_sales) from Boxoffice)-(Domestic_sales+International_sales))as li FROM movies left join Boxoffice on movies.id=Boxoffice.movie_id order by li desc
select MAX(Domestic_sales+International_sales) from Boxoffice This sentence is equivalent to taking out the maximum value
The sentence used before is equivalent to getting or
SELECT title,MAX(Domestic_sales+International_sales) FROM movies left join Boxoffice on movies.id=Boxoffice.movie_id