mybatis_plus basic introduction
I Basic introduction
Mybatis plus (MP for short) is an enhancement tool for mybatis. Based on mybatis, it only makes enhancements and does not change. It is born to simplify development and improve efficiency. This is an official definition. For more introduction and features of mybatis plus, please refer to Mybatis plus official website . So how is it enhanced? In fact, it has encapsulated some crud methods. We don't need to write xml anymore. Just call these methods directly, which is similar to JPA.
II Basic Usage
- Initialize the project. Use Spring Initializr to quickly initialize a Spring Boot project, version 2.2 1.RELEASE
- Add dependency
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis-plus-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--lombok Used to simplify entity classes-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- Installing lombok plug-in in idea
- Configure mysql related configuration
- Conduct corresponding tests
III Basic CRUD operation
1.insert
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
public void add(){
User user = new User();
user.setAge(18);
user.setName("xhy1");
user.setEmail("2642616973@qq.com");
int insert = userMapper.insert(user);
}
Extension: the primary key policy in mybatis plus:
-
ID_WORKER
The default primary key policy of mybatis plus is ID_WORKER globally unique ID
-
Self increasing strategy
To auto increment the primary key, you need to configure the following primary key policies. You need to set auto increment of the primary key when creating the data table
Configure @ TableId(type = IdType.AUTO) in the entity field
-
You can see the source code of other primary key policy analysis
@Getter
public enum IdType {
/**
* Database ID self increment
*/
AUTO(0),
/**
* The type is not set with primary key
*/
NONE(1),
/**
* User input ID
* This type can be populated by registering its own auto fill plug-in
*/
INPUT(2),
/* The following three types are automatically filled only when the inserted object ID is empty. */
/**
* Globally unique ID (idWorker)
*/
ID_WORKER(3),
/**
* Globally unique ID (UUID)
*/
UUID(4),
/**
* String globally unique ID (string representation of idworker)
*/
ID_WORKER_STR(5);
private int key;
IdType(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
}
2.update
Note: the sql generated during update is dynamic sq automatically. For example, update user set age =? where id = ?
@Test
public void update(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1416234010497044481l);
user.setAge(17);
int i = userMapper.updateById(user);
System.out.println(i+"************");
}
3. Auto fill fields
Some data are often encountered in the project, which are filled in the same way every time, such as the creation time and update time of the record. We can use the auto fill function of MyBatis Plus to complete the assignment of these fields
Use steps:
1. Add corresponding notes to the fields to be filled in
@Data
public class User {
......
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Date createTime;
//@TableField(fill = FieldFill.UPDATE)
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Date updateTime;
}
2. Implement the interface of metadata processing object
Note: the @ Componet annotation must be added and handed over to the spring container management
package com.sunset.handler;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.handlers.MetaObjectHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Date;
@Component
public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler {
//When using mp add operation, this method performs
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
this.setFieldValByName("createTime",new Date(),metaObject);
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime",new Date(),metaObject);
this.setFieldValByName("version",1,metaObject);
}
//When using mp to modify the operation, this method performs
@Override
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime",new Date(),metaObject);
}
}
4.select
@Test
public void query(){
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.ge("age",18);//Age >=
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
System.out.println(users);
}
@Test
void contextLoads() {
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(null);
System.out.println(users);
}
//Batch query by id
@Test
public void testDemo(){
List<User> users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1l, 2l, 3l));
System.out.println(users);
}
5. Pagination
1. Add paging plug-in
/**
* Paging plug-in
* @return
*/
@Bean
public PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor() {
return new PaginationInterceptor();
}
2. Test
@Test
public void page(){
Page<User> page = new Page<>(1,3);
userMapper.selectPage(page, null);
System.out.println(page.getRecords());//list collection per page
System.out.println(page.getTotal());//Total records
System.out.println(page.getPages());//PageCount
System.out.println(page.getSize());//Number of records displayed per page
System.out.println(page.hasPrevious());
System.out.println();
}
6.delete
@Test
public void delete(){
int i = userMapper.deleteById(1L);
System.out.println(i+"****************");
}
@Test
public void testDeleteBatchIds() {
int result = userMapper.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(8, 9, 10));
System.out.println(result);
}
7. Simple condition query
@Test
public void testDeleteByMap() {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "Helen");
map.put("age", 18);
int result = userMapper.deleteByMap(map);
System.out.println(result);
}
8. Logical deletion
Physical delete: real delete, delete the corresponding data from the database, and then query the deleted data
Logical deletion: false deletion. Change the status of the field representing whether to be deleted in the corresponding data to deleted status. After that, you can still see this data record in the database
(1) Add deleted field to database
(2) Add the deleted field to the entity class, and add the @ TableLogic annotation and @ TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT) annotation
(3) Add the deleted insert default value to the meta object processor interface
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
......
this.setFieldValByName("deleted", 0, metaObject);
}
(4) Add configuration file to configuration
mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-delete-value=1 mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-not-delete-value=0
(5) Inject bean s into configuration classes
@Bean
public ISqlInjector sqlInjector() {
return new LogicSqlInjector();
}
(6) Testing
After the test, it was found that the data was not deleted, and the value of the deleted field changed from 0 to 1
After the test, analyze the printed sql statement, which is an update
Note: the value of the deleted field of the deleted data must be 0 to be selected for logical deletion
/**
* Test logical deletion
*/
@Test
public void testLogicDelete() {
int result = userMapper.deleteById(1L);
System.out.println(result);
}
(7) Query after test logic deletion
The query operation in MyBatis Plus will also automatically add the judgment of logically deleting fields
/**
* Query after test logic deletion:
* Records deleted logically are not included
*/
@Test
public void testLogicDeleteSelect() {
User user = new User();
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(null);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
After the test, analyze the printed sql statements, including WHERE deleted=0
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,deleted FROM user WHERE deleted=0
9. Others
If you want to query complex conditions, you need to use the condition constructor Wapper, which involves the following methods
1,delete
2,selectOne
3,selectCount
4,selectList
5,selectMaps
6,selectObjs
7,update
1. Briefly introduce wrapper
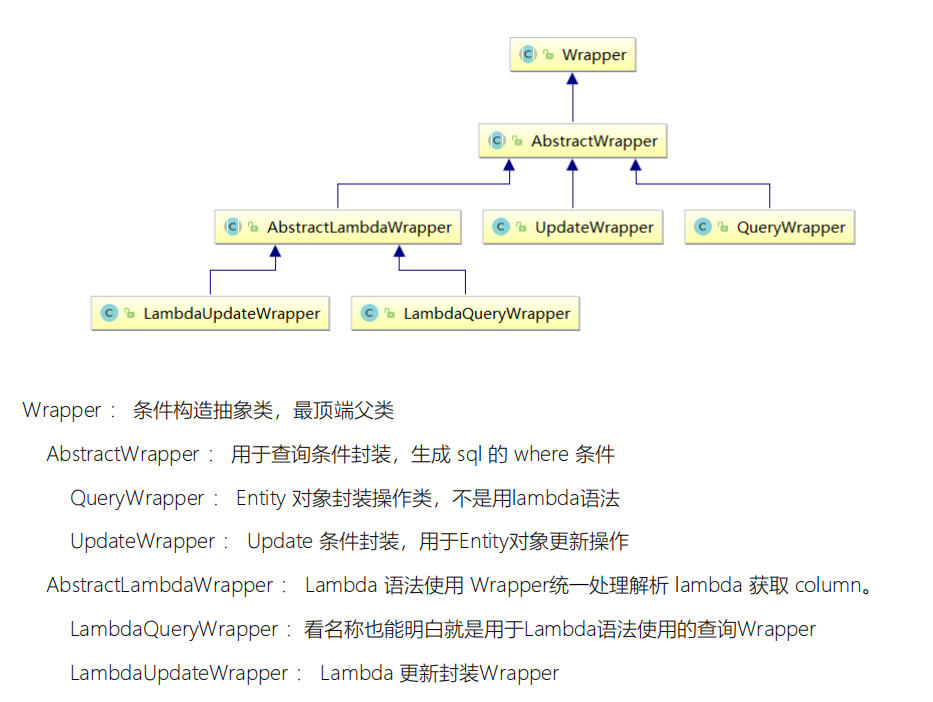
Test:
1,ge,gt,le,lt,isNull,isNotNull
@Test
public void testDelete() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper
.isNull("name")
.ge("age", 12)
.isNotNull("email");
int result = userMapper.delete(queryWrapper);
System.out.println("delete return count = " + result);
}
SQL: UPDATE user SET deleted=1 WHERE deleted=0 AND name IS NULL AND age >= ? AND email IS NOT NULL
2,eq,ne
**Note: * * seletOne returns an entity record. If there are multiple records, an error will be reported
@Test
public void testSelectOne() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq("name", "Tom");
User user = userMapper.selectOne(queryWrapper);
System.out.println(user);
}
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,deleted,version FROM user WHERE deleted=0 AND name = ?
3.between,notBetween
@Test
public void testSelectCount() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.between("age", 20, 30);
Integer count = userMapper.selectCount(queryWrapper);
System.out.println(count);
}
SELECT COUNT(1) FROM user WHERE deleted=0 AND age BETWEEN ? AND ?
4.allEq
@Test
public void testSelectList() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id", 2);
map.put("name", "Jack");
map.put("age", 20);
queryWrapper.allEq(map);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,deleted,version FROM user WHERE deleted=0 AND name = ? AND id = ? AND age = ?
5.like,notLike,likeLeft,likeRight
@Test
public void testSelectMaps() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.notLike("name", "e")
.likeRight("email", "t");
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = userMapper.selectMaps(queryWrapper);//The return value is the Map list
maps.forEach(System.out::println);
}
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,deleted,versionFROM user WHERE deleted=0 AND name NOT LIKE ? AND email LIKE ?
6.in,notIn,inSql,notinSql,exists,notExists

@Test
public void testSelectObjs() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//queryWrapper.in("id", 1, 2, 3);
queryWrapper.inSql("id", "select id from user where id < 3");
List<Object> objects = userMapper.selectObjs(queryWrapper);//The return value is the Object list
objects.forEach(System.out::println);
}
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,deleted,version FROM user WHERE deleted=0 AND id IN (select id from user where id < 3)
7.or and
Note: UpdateWrapper is used here. If or is not called, and is used by default
@Test
public void testUpdate1() {
//Modify value
User user = new User();
user.setAge(99);
user.setName("Andy");
//modify condition
UpdateWrapper<User> userUpdateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
userUpdateWrapper
.like("name", "h")
.or()
.between("age", 20, 30);
int result = userMapper.update(user, userUpdateWrapper);
System.out.println(result);
}
UPDATE user SET name=?, age=?, update_time=? WHERE deleted=0 AND name LIKE ? OR age BETWEEN ? AND ?
9.orderBy,orderByDesc,orderByAsc
@Test
public void testSelectListOrderBy() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.orderByDesc("id");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,deleted,version FROM user WHERE deleted=0 ORDER BY id DESC
10.last
Directly spliced to the end of sql
Note: it can only be called once. The last call shall prevail. There is a risk of sql injection. Please use it with caution
@Test
public void testSelectListLast() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.last("limit 1");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,deleted,version FROM user WHERE deleted=0 limit 1
11. Query the specified column
@Test
public void testSelectListColumn() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.select("id", "name", "age");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
SELECT id,name,age FROM user WHERE deleted=0