catalogue
5) selector grouping (Union selector)
6) Composite selector (intersection selector)
8) Descendant element selector
I Definition of css
css is a cascading style sheet
The web page is actually a multi-layer structure, which can be edited for each part of the web page through css.
II Style type
1) Inline style
Method: use style attributes in related labels.
Function: only write the style for the current element content, which is not convenient for future modification.
Example:
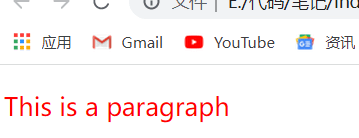
<p style="color: red; font-size: 20px"> This is a paragraph </p>
effect:
2) Internal style sheet
Method: write the style into the style tag in the head, then select the element through the css selector and set various styles for it
Function: you can set styles for multiple labels at the same time, and you only need to change one place when modifying.
Disadvantages: it can only work on one page, and the style inside cannot cross pages.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title></title>
<style>
p{
color: red;
font-size: 20px
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
This is a paragraph
</p>
</body>
</html>
Effect: (ditto)
3) External style sheet
Method: it needs to be introduced through the link tag and reused on different pages
Function: can maximize the use of the browser's cache mechanism, plus
Fast loading speed and improve user experience.
Example:
style.css
p{
color: blue;
font-size: 30px;}Using css files
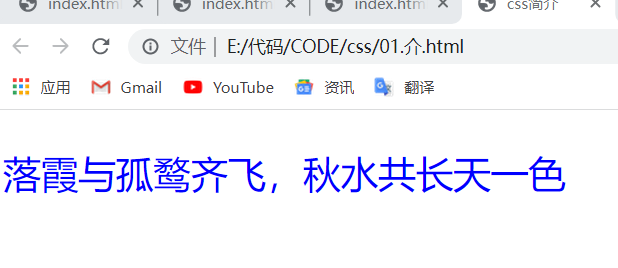
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>css brief introduction</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="./style.css"/> </head> <body> <p>Sunset clouds and solitary ducks fly together, and the autumn water is the same color as the sky</p> </body> </html>
effect:
III Basic grammar
Syntax is divided into: selector and declarative block
1) Selector
Select the specified elements in the page through the selector. For example, the function of p is to select all p elements in the page
2) Declaration block
To specify the style to be set for the element, the selector consists of a declaration block, which is actually a group of name value pair structures.
Multiple declarations are separated by semicolons, and the declared style name and style value are connected by colons.
3) css comments
Start with / * and end with * /
IV Element relation
Parent element: an element that directly contains child elements
Child element: an element directly contained by the parent element
Ancestor element: an element that directly or indirectly contains descendant elements
Descendant element: an element contained directly or indirectly by an ancestor element
Sibling element: an element that has the same parent element
V css selector
1) Element selector
Select an HTML element based on the element name
Syntax: tag name {} such as p {}
Example:
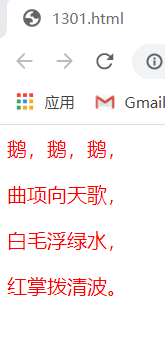
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
p{
color:red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="blue abc">
Goose, goose, goose,</p>
<p> Song Xiang Tiange,</p>
<p id="red"> White hair floating green water,</p>
<p class="blue"> Red palm stirs clear waves.</p>
</body>
</html>effect:
2) id selector
Function: select an element according to its id attribute
The id of the element is unique in the page, so the id selector is used to select a unique element
Syntax: #id attribute value {}
Example:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
#red{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="blue abc">
Goose, goose, goose,</p>
<p> Song Xiang Tiange,</p>
<p id="red"> White hair floating green water,</p>
<p class="blue"> Red palm stirs clear waves.</p>
</body>
</html>effect:

In addition, class is also a tag attribute, but class can be reused
3) Class selector
Function: select an element according to its class attribute value to specify multiple class attributes for the same element
Syntax: class attribute value {}
Example:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.blue{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="blue abc">
Goose, goose, goose,</p>
<p> Song Xiang Tiange,</p>
<p id="red"> White hair floating green water,</p>
<p class="blue"> Red palm stirs clear waves.</p>
</body>
</html>effect:

4) universal selector
Function: used to select all elements in the page
Syntax: * {}
Example:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
*{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="blue abc">
Goose, goose, goose,</p>
<p> Song Xiang Tiange,</p>
<p id="red"> White hair floating green water,</p>
<p class="blue"> Red palm stirs clear waves.</p>
</body>
</html>effect:

5) selector grouping (Union selector)
Function: select elements corresponding to multiple selectors at the same time
Syntax: selector 1, selector 2, selector 3 Selector n{}
Example:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.blue,#red{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="blue abc">
Goose, goose, goose,</p>
<p> Song Xiang Tiange,</p>
<p id="red"> White hair floating green water,</p>
<p class="blue"> Red palm stirs clear waves.</p>
</body>
</html>effect:

6) Composite selector (intersection selector)
Function: select the element that satisfies multiple selectors at the same time.
Syntax: selector 1 selector 2 selector 3 Selector n{}
Example:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.blue.abc{
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="blue abc">
Goose, goose, goose,</p>
<p> Song Xiang Tiange,</p>
<p id="red"> White hair floating green water,</p>
<p class="blue"> Red palm stirs clear waves.</p>
</body>
</html>
effect:

7) sub element selector
Role: select the child element in the specified parent element
Syntax: parent element > child element
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
div>span{
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
I am a div
<p>
I am div Medium p element
<span>I am p Element span element</span>
</p>
<span>I am div Medium span element</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>effect:

8) Descendant element selector
Effect: select the descendant element in the specified element
Syntax: ancestor element {descendant element
Example:
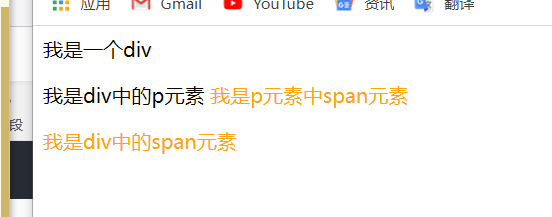
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
div span{
color: orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
I am a div
<p>
I am div Medium p element
<span>I am p Element span element</span>
</p>
<span>I am div Medium span element</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>effect:
9) Sibling element selector
| grammar | effect |
| Previous + next {} | The last selected element |
| Previous ~ all {} | Select all subsequent sibling elements |
Example:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<style type="text/css">
li + li {font-weight:bold;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<ul>
<li>List item 1</li>
<li>List item 2</li>
<li>List item 3</li>
</ul>
<ol>
<li>List item 1</li>
<li>List item 2</li>
<li>List item 3</li>
</ol>
</div>
</body>
</html>
effect:

10) pseudo class selector
(nonexistent class, special class)
Function: used to describe the special state of an element
For example: the first element, the clicked element and the element moved in by the mouse
Pseudo classes generally start with:.
1. Common pseudo classes
| Common pseudo class | effect |
| :first-child | First child element |
| :last-child | Last child element |
| :nth-child(n) | Select 0 to infinite child elements |
| :nth-child(2n/even) | Select even bit elements |
| :nth-child(2n+1/odd) | Select odd elements |
| :first-of-type | Select the first of the same type |
| :last-of-type | Select the last one of the same type |
| :nth-of-type | Select the n th of the same type |
| :not() | Negate the pseudo class and remove the qualified elements from the selector |
2. Pseudo class order of < a > < / a > tags
| Common pseudo class | effect |
| :link | Used to indicate links that have not been visited |
| :visited | Used to indicate visited links |
| :hover | Used to indicate the state of the mouse moving in |
| :active | Used to indicate the state of mouse click |
3. Pseudo element
Function: indicates some special and unreal elements (special positions) in the page
Syntax: starts with::
| Common elements | effect |
| ::first-letter | Represents the first letter |
| ::first-line | Represents the first line |
| ::selection | Indicates the selected content |
| ::before | Represents the beginning of the selected element |
| ::after | Indicates the end of the selected element |
Note: befor and after must be used in combination with content
11) Attribute selector
Function: select elements according to their attributes and attribute values.
| grammar | effect |
| [attribute name] | Select the element that contains the specified attribute |
| [attribute name = attribute value] | Select the element that contains the specified attribute value |
| [attribute name ^ = attribute value] | Selects an element whose attribute value begins with the specified content |
| [attribute name $= attribute value] | Pick the element whose attribute value ends with the specified content |
| [attribute name * = attribute value] | Select the attribute value to contain the element of the specified content |
Vi Style inheritance
Objective: to facilitate development.
Function: the style we set for an element will also be applied to its descendant elements. Inheritance occurs between ancestors and descendants. In this way, you only need to set it once to make all elements have the style.
Note: not all styles will be inherited. For example, background related and layout related styles will not be inherited.
VII Weight of selector
1) Style conflict:
When we select the same element through different selectors and set different values for the same element, a style conflict occurs.
2) Weight
| selector | priority |
| inline style | 1000 |
| id selector | 100 |
| Class and pseudo class selectors | 10 |
| element selector | 1 |
| universal selector | 0 |
| Inherit style | No priority |
be careful:
1. The priority of Union (grouping) selector is calculated separately
2. When comparing priorities, you need to add the priority of the selector and calculate
3. The accumulation of selectors will not exceed the maximum order of magnitude.