Remote Access Control
/ The two files, etc/hosts.allow and/etc/hosts.deny, control remote access by which a client of an IP/IP segment can be allowed or prohibited to access Linux.
sshd:172.25.254. :spawn echo `date` from %c to %s >> /dev/pts/1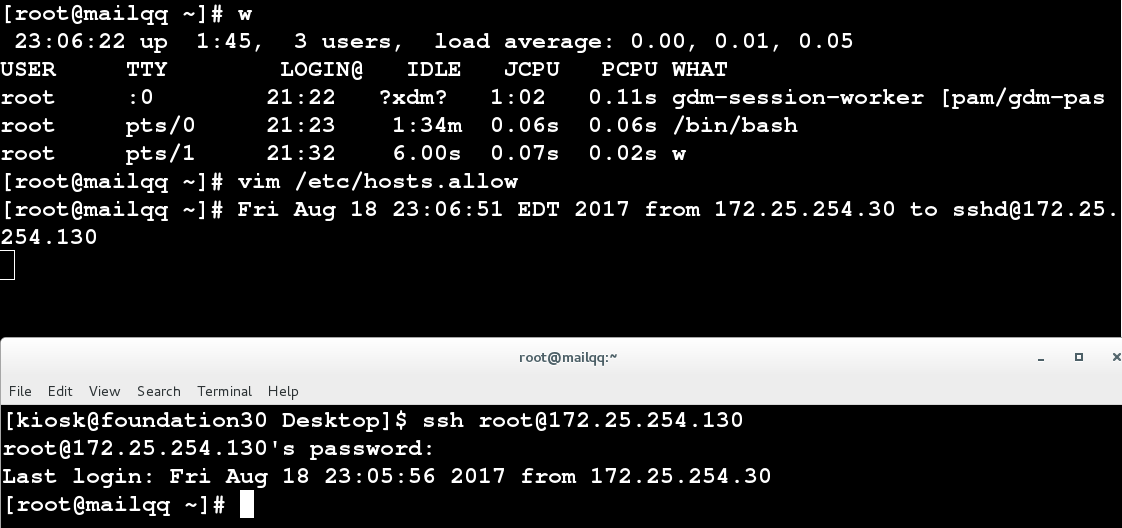
iptables
Summary:
Linux packet filtering software.
Three watches and five chains
There are many tables in iptables, none of which defines their own default policies and rules, and each table has different purposes.
Filter (filter):
Mainly follow-up to Linux this season's packet related, is the default table.
1. INPUT: Mainly related to the packets that want to enter Linux.
2. OUPUT: Mainly related to the packets that Linux wants to send out.
3. FORWARD: It has nothing to do with Linux. It can transfer data packets to the back-end computer. It has a high correlation with NAT table s.
NAT (Address Translation):
It is the abbreviation of Network Address Translation. This form is mainly used to convert IP or port from source to destination. It has nothing to do with native Linux, and is related to computers in local area network after Linux host.
PREROUTING: Rules to be performed before routing decisions are made.
POSTROUTING: The rules to be followed after routing Pando.
OUTPUT: Relating to the packets sent out.
Mangle:
Because of the high correlation between this form and special signs, the usage rate is very low in this environment.
Install the iptables service
yum install iptables-services -y
systemctl status iptables.service
systemctl enable iptables.service
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
systemctl mask firewalldView rules
ipatable
-t #Following table, if this item is omitted, the default filter is used
-L #Rules for listing table s in front of you
-n #Without IP and HOSTNAME checks, information will be displayed much faster.
-v #List more information, including the total number of packets passing the rule, the relevant network interfaces, etc.target: Operations performed by representatives, ACCEPT (release), REJECT (rejection), DROP (discard)
prot: Represents the data package protocol used, including TCP, UDP and IPCM.
opt: Additional options
Source: Representation rule is for which source IP is restricted
destination: Represents which target IP this rule restricts.
Parameters:
-A #Added rules, default after existing rules
-I #Insert rules, default is the first
-io #network interface
-p #agreement
-s #Source ip/network
-d #Target ip/network
-j #Follow-up operationFixed ftp port
pasv_max_port=7000>vim/etc/vstpd/vstpd.conf
pasv_min_port=7000>vim/etc/vstpd/vstpd.conf
iptables -I INPUT 3 -m state --state NEW -p tcp --dport 7000 -j ACCEPTGenerally speaking, the ports on the c side are larger than 1024, while the ports on the s side are less than 1023, so we can discard active connections from remote ports less than 1023.
NAT
POSTROUTING Modifies Source ip, Source NAT(SNAT)
PREROUTING modifies target ip, target NAP (DNA T)
SNAT:
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1>/etc/sysctl.conf
sysctl -p
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j SNAT --to-suource 172.25.254.130DNAT:
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1>/etc/sysctl.conf
sysctl -p
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -o eth1 -j DNAT --to-suource 172.25.0.130In fact, dnat is the reverse of snat, which is easy to understand.
Firewalld
firewalld and iptables are different:
iptables service stores configuration in / etc/sysconfig/iptables
firewalld stores the configuration in
/ usr/lib/firewalld
/ User Configuration Address in various xml files in etc/firewalld/ 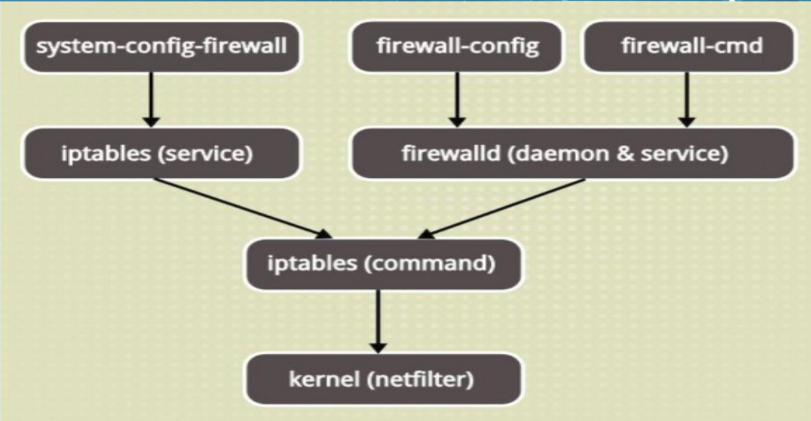
1. zone concept:
Hardware firewalls generally have three default zones. Firealld introduces the concept that the system defaults to the following zones 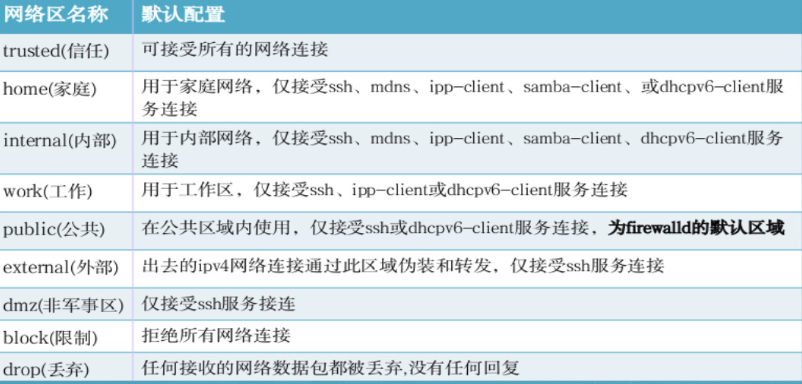
Order:
firewalld-cmd –status ##Firewall state
firewalld-cmd - -get-default-zones ##Display the currently used domain
firewalld-cmd - -set-default-zones=trusted ##Setting default fields
firewalld-cmd - -list-all ##Display Firewall Policy
firewalld-cmd - -add-service= ##Temporary Firewall Policy, Effective Immediately
firewalld-cmd - -permanent - -add-service ##Permanent addition of reload does not take effect
firewalld-cmd - -permanent - -remove-service=
firewalld-cmd - -permanent - -add-port=8080/tcp
firewalld-cmd - -permanent - -remove-port=8080/tcpip credit:
firewalld-cmd - -permanent - -add-source= firewalld-cmd - -permanent - -remove-source= firewalld-cmd - -permanent - -add-source= - -zone= firewalld-cmd - -permanent - -remove-source= - -zone= These policies need reload after change
network interface
firewalld-cmd - -permanent - -add-interface= - -zone= ##Adding a network interface to a domain
firewalld-cmd - -permanent - -remove-interface= - -zone= ##Delete an interface in a domainUpdate firewall rules
firewall-cmd --reload firewall-cmd --complete-reload The difference between the two is that the first one does not need to disconnect, which is one of the firewalld features, adding rules dynamically, and the second one needs to disconnect, similar to restart services.
firewall-cmd --zone=work --add-service = add services firewall-cmd --zone=work --remove-service = remove service
Direct Rules
With the firewall-cmd tool, you can use the direct option to add or remove chains during runtime. The rule of direct port mode addition is preferred.
firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter INPUT ! -s 172.25.254.230 -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
firewall-cmd --reload
systemctl restart firewalldfirewall-cdm --direct --get-all-rulesPs: The level of strategy written under direct is parallel, and there is no order.
rich rules
A more advanced firewall policy language, and can be permanently configured. Is an abstract representation of the iptalbes tool. This taro can be used to configure partitions and still supports the current configuration.
NAT camouflage
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rules="rule family=ipv4 source address=172.25.254.30 forward=port port=22 protocol=tcp to-port=22 to-addr=172.25.0.230"
#dnat
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule='rule family=ipv4 source address=172.25.254.130 masquerade'#snatManaging Se-Linux port labels
getenforce 0
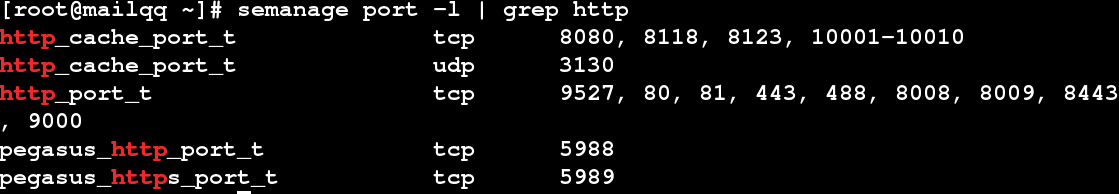
semanage port -l
semanage port -l | grep http
semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 9527