Article directory
4, DDL data definition
4.1 create database
Create a database. The default storage path of the database on HDFS is / user/hive/warehouse/*.db.
To avoid errors in the database to be created, add if not exists judgment. (standard writing)
create database if not exists db_hive;
Create a database, specify the location where the database is stored on HDFS, and add location 'path';
create database db_hive2 location '/db_hive2.db';
4.2 query database
-
Display database information
desc database db_hive;
-
Display the database details, extended. You can view the additional properties of the database (the same as above if there is no additional property)
desc database extended db_hive;
4.3 modify database
The ALTER DATABASE command sets key value pair property values for DBPROPERTIES of a database to describe the property information of the database.
Other metadata information of the database is unchangeable, including the database name and the directory location of the database.
alter database db_hive set dbproperties('createtime'='2019/7/31');
See the modification result
desc database extended db_hive;

4.4 delete database
-
Delete empty database
drop database db_hive2;
-
if exists is used to judge whether the database exists and delete
drop database if exists db_hive2;
-
If the database is not empty, you can use the cascade command to force deletion
drop database db_hive cascade;
4.5 create table
-
Table grammar
Create [external] table [if not exists] table [name -- create table [(Col [name data] type [comment col [comment],...)] -- add a comment to the table [COMMENT table_comment] -- add a comment to the column [partitioned by (col name data type [comment col comment],...)] -- create partition table [CLUSTERED BY (col_name, col_name,...) -- create bucket table [sorted by (col_name [asc|desc],...)] into num_buckets buckets] - not commonly used [row format row] format [stored as file [format] -- specifies the storage file type [location HDFS? Path] -- specifies the storage location of the table on HDFS
-
Management table (internal table)
When we delete a management table, Hive will also delete the data in this table.
Common create table
create table if not exists student2( id int, name string ) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t' stored as textfile location '/user/hive/warehouse/student';
Create a table based on the query results (the query results will be added to the newly created table using MapReduce)
create table if not exists student3 as select id, name from student;
Create a table from an existing table structure
create table if not exists student4 like student;
Type of query table
desc formatted student2; Table Type: MANAGED_TABLE
When student2 is deleted, student2 data in HDFS is also deleted.
drop table student2;
-
External table
On the basis of external tables (such as the company's massive log files, which can be used by different developers, but cannot be deleted at will), a lot of statistical analysis is done. The intermediate tables and result tables used are stored in internal tables, so that even if the external table is deleted in hive, the original data will not be deleted, but the metadata information describing the table will be deleted.
Create dept.txt and emp.txt
dept.txt 10 ACCOUNTING 1700 20 RESEARCH 1800 30 SALES 1900 40 OPERATIONS 1700 emp.txt 7369 SMITH CLERK 7902 1980-12-17 800.00 20 7499 ALLEN SALESMAN 7698 1981-2-20 1600.00 300.00 30 7521 WARD SALESMAN 7698 1981-2-22 1250.00 500.00 30 7566 JONES MANAGER 7839 1981-4-2 2975.00 20 7654 MARTIN SALESMAN 7698 1981-9-28 1250.00 1400.00 30 7698 BLAKE MANAGER 7839 1981-5-1 2850.00 30 7782 CLARK MANAGER 7839 1981-6-9 2450.00 10 7788 SCOTT ANALYST 7566 1987-4-19 3000.00 20 7839 KING PRESIDENT 1981-11-17 5000.00 10 7844 TURNER SALESMAN 7698 1981-9-8 1500.00 0.00 30 7876 ADAMS CLERK 7788 1987-5-23 1100.00 20 7900 JAMES CLERK 7698 1981-12-3 950.00 30 7902 FORD ANALYST 7566 1981-12-3 3000.00 20 7934 MILLER CLERK 7782 1982-1-23 1300.00 10
Create department table
create external table if not exists default.dept( deptno int, dname string, loc int ) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
Create employee table
create external table if not exists default.emp( empno int, ename string, job string, mgr int, hiredate string, sal double, comm double, deptno int) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
Import data to two external tables respectively
load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/dept.txt' into table default.dept; load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/emp.txt' into table default.emp;
View table format data
desc formatted dept; Table Type: EXTERNAL_TABLE
Delete a table to see if the data on HDFS is deleted.
-
Manage the conversion between tables and external tables
Type of query table
desc formatted student2; Table Type: MANAGED_TABLE
Modify internal table student2 to external table
alter table student2 set tblproperties('EXTERNAL'='TRUE');
Type of query table
desc formatted student2; Table Type: EXTERNAL_TABLE
Modify external table student2 to internal table
alter table student2 set tblproperties('EXTERNAL'='FALSE');
Type of query table
desc formatted student2; Table Type: MANAGED_TABLE
Note: ('EXTERNAL '='TRUE') and ('EXTERNAL '='FALSE') are fixed and case sensitive!
4.6 zoning table
The partition table is actually a separate folder on the corresponding HDFS file system, under which all the data files of the partition are located. A partition in Hive is a subdirectory.
-
Basic operation of partition table
Create partition table
create table dept_partition( deptno int, dname string, loc string ) partitioned by (month string) -- Set up month Is a partition field row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
Load data into partition table
-- Add data and mark different groups load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/dept.txt' into table default.dept_partition partition(month='201709'); load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/dept.txt' into table default.dept_partition partition(month='201708'); load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/dept.txt' into table default.dept_partition partition(month='201707');
Query data in partition table
-- Specify group query select * from dept_partition where month='201709' or month='201708'; -- Do not specify group query, all grouped data will be found together select * from dept_partition;
Increase partition
-- Add a partition alter table dept_partition add partition(month='201706') ; -- When adding multiple partitions, separate them with spaces alter table dept_partition add partition(month='201705') partition(month='201704');
delete a partition
-- Delete a partition alter table dept_partition drop partition (month='201704'); -- Comma separated when deleting multiple partitions alter table dept_partition drop partition (month='201705'), partition (month='201706');
Check how many partitions are in the partition table
show partitions table name;
View partition table structure
esc formatted table name;
-
Two level zoning
Create secondary partition table
create table dept_partition2( deptno int, dname string, loc string ) partitioned by (month string, day string) -- Set up month and day Is a partition field row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
Normal loading data
load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/dept.txt' into table dept_partition2 partition(month='201709', day='13');
Query partition data
select * from dept_partition2 where month='201709' and day='13';
-
Create folders directly on HDFS and upload data directly to partition folders. There are three ways to associate partition tables and data
① Repair after uploading data
msck repair table dept_partition2;
② Add partition after uploading data
alter table dept_partition2 add partition(month='201709', day='11');
③ load data to partition after creating folder
load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/dept.txt' into table dept_partition2 partition(month='201709',day='10');
4.7 modification table
-
rename table
ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME TO new_table_name
-
Add, modify, and delete table partitions
See 4.6
-
Add / modify / replace column information
Update column
ALTER TABLE table_name CHANGE [COLUMN] col_old_name col_new_name column_type [COMMENT col_comment] [FIRST|AFTER column_name] -- Example alter table dept_partition add columns(deptdesc string);
Add and replace columns
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD|REPLACE COLUMNS (col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...) -- New column instance alter table dept_partition change column deptdesc desc int; -- Replace column instance (Note: replace column to redefine all columns) alter table dept_partition replace columns(deptno string, dname string, loc string);
-
Delete table
drop table table name;
5, DML data operation
5.1 data import
-
Load data into a table
grammar
load data [local] inpath 'path' overwrite | into table student [partition (partcol1=val1,...)];
Explanation: load data: indicates load data.
Local: indicates that the data is loaded from the local. If omitted, it indicates that the data is loaded from HDFS.
inpath: indicates the path to load data.
Overwrite: indicates to overwrite the existing data in the table; otherwise, indicates to append.
into table: indicates which table to load.
student: represents a specific table.
Partition: indicates to upload to the specified partition.
Note: importing data from HDFS is mobile; importing data from local is replication.
-
Insert data into a table through a query statement
Basic way to insert data
insert into table student partition(month='201709') values(1,'wangwu');
Use single table query result as insert data
insert overwrite table student partition(month='201708') select id, name from student where month='201709';
Use query results of multiple tables as insert data
from student insert overwrite table student partition(month='201707') select id, name where month='201709' insert overwrite table student partition(month='201706') select id, name where month='201709';
-
Create table and load data in query statement (As Select)
create table if not exists student3 as select id, name from student;
-
Specify the load data path through Location when creating the table
create table if not exists student5( id int, name string ) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t' location '/user/hive/warehouse/student5';
-
Import data to the specified Hive table (Note: export first, then import)
import table student2 partition(month='201709') from '/user/hive/warehouse/export/student';
5.2 data export
-
Insert export
Export query results to local
insert overwrite local directory '/opt/module/datas/export/student' select * from student;
Export the result format of query to local
insert overwrite local directory '/opt/module/datas/export/student1' ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t' select * from student;
Export the results of the query to HDFS (no local)
insert overwrite directory '/user/hive/warehouse/student3' ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t' select * from student;
-
Hadoop command export to local
dfs -get /user/hive/warehouse/student3/000000_0 /opt/module/datas/export/student3.txt; -
Hive Shell command export (use hive -f/-e to execute statement or script > file directly without entering hive client)
hive -e 'select * from default.student;' > /opt/module/datas/export/student4.txt;
-
Export to HDFS
export table student to '/user/hive/warehouse/export/student';
-
Sqoop export
Follow up instructions
5.3 clear data in the table (Truncate)
Truncate can only clear the data in the management table, and cannot delete the data in the external table
truncate table student;
Six, query
Query syntax
SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] select_expr, select_expr, ... FROM table_reference [WHERE where_condition] [GROUP BY col_list] -- Grouping [ORDER BY col_list] -- Global ranking [CLUSTER BY col_list -- Pail ( DISTRIBUTE and SORT Use the same field) | [DISTRIBUTE BY col_list] -- Specify partition fields [SORT BY col_list] ] -- Intra regional ranking [LIMIT number] -- Restricted row number
6.1 basic query (Select From)
-
Full table and specific column queries
select * from emp; select empno, ename from emp;
-
Column alias (as can be omitted)
select ename AS name, deptno dn from emp;
-
Arithmetic operator
operator describe A+B Additivity of A and B A-B A minus B A*B A and B multiply A/B A divided by B A%B A to B A&B A and B take and A|B A and B are bitwise OR A^B A and B take exclusive or by bit ~A A reverse by bit
-- After finding out the salary of all employees, add 1 to display select sal +1 from emp;
-
Limit statement
-- LIMIT Clause to limit the number of rows returned select * from emp limit 5;
6.2 Where statement
The WHERE clause is a conditional filter clause followed by the FROM clause.
- Comparison operator (Between/In/ Is Null)
| Operator |
|---|
| A=B returns TRUE if a equals B, FALSE otherwise |
| A < = > b if both a and B are NULL, TRUE will be returned; if either is NULL, NULL will be returned; if a and B are equal, TRUE will be returned; otherwise, FALSE will be returned; |
| A<>B, A!=B |
| A<B |
| A<=B |
| A>B |
| A>=B |
| A [NOT] BETWEEN B AND C |
| A IS NULL |
| A IS NOT NULL |
| In (value 1, value 2) |
| A [NOT] LIKE B |
| A rlike B, a regexp B B is a regular expression. If a matches a, it returns TRUE; otherwise, it returns FALSE. |
Find out all employees with salary equal to 5000
select * from emp where sal =5000;
Query employee information with salary between 500 and 1000
select * from emp where sal between 500 and 1000;
Query all employee information with comm empty
select * from emp where comm is null;
Query employee information with salary of 1500 or 5000
select * from emp where sal IN (1500, 5000);
-
Like and RLike
%Represents zero or more characters (any character).
_Represents a character.
RLIKE clause is an extension of Hive
Find employee information starting with 2
select * from emp where sal LIKE '2%';
Find the employee information of the salary with the second value of 2
select * from emp where sal LIKE '_2%';
Find employee information with 2 in salary
select * from emp where sal RLIKE '[2]';
-
And/Or/Not
Query salary greater than 1000, department is 30
select * from emp where sal>1000 and deptno=30;
Query salary is greater than 1000, or department is 30
select * from emp where sal>1000 or deptno=30;
Query employee information except 20 and 30 departments
select * from emp where deptno not IN(30, 20);
6.3 grouping
-
Group By statement
GROUP BY statements are usually used with aggregate functions to GROUP BY one or more queue results, and then aggregate each group.
Calculate the average wage of each department in emp table
select t.deptno, avg(t.sal) avg_sal from emp t group by t.deptno;
Calculate emp maximum salary for each position in each department
select t.deptno, t.job, max(t.sal) max_sal from emp t group by t.deptno, t.job;
-
Having statement
having is different from where:
where works for the columns in the table to query data, and having works for the columns in the query results to filter data.
where cannot be followed by aggregate function, while having can be followed by aggregate function.
having is only used for group by group statistics statement.
For each department with an average salary greater than 2000
select deptno, avg(sal) avg_sal from emp group by deptno having avg_sal > 2000;
6.4 Join statement
-
Equivalent Join
Hive supports normal SQL JOIN statements, but only supports equivalent connections, not non equivalent connections.
Query the employee number, employee name and department name according to the equal department number in the employee table and department table;
select empno, ename, dname from emp e join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
-
Table aliases
Use alias to simplify query; use table name prefix to improve execution efficiency
Consolidated employee and department tables
select e.empno,e.ename,d.dname from emp e join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
-
Internal connection
Only if there is data matching the join condition in both tables that are joined will it be preserved.
select e.empno,e.ename,d.dname from dept d join emp e on d.deptno=e.deptno;
-
Left outer join
All records in the left table of the JOIN operator that conform to the WHERE clause will be returned.
select e.empno e.ename d.dname from emp e left join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
-
Right outer join
All records in the table to the right of the JOIN operator that conform to the WHERE clause will be returned.
select e.empno e.ename d.dname from emp e right join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
-
All external connection
All records in all tables that meet the conditions of WHERE statement will be returned. If the specified field of any table does not have a qualified value, then NULL is used instead.
select e.empno,e.ename, d.dname from emp e full join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
-
Multi table connection
Connect n tables, at least n-1 connection conditions are required
Hive always performs table connection from left to right. At the same time, hive will choose whether to cache the table according to the situation rather than enabling multiple MR's
select e.empno,e.ename,d.dname,l.loc_name from emp e join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno join location l on d.loc=l.loc;
-
Cartesian product
All rows in all tables are interconnected (infrequently)
6.5 ranking
-
Global Order (Order By)
Order By: Global sorting, which means there is only one Reducer in the end
ASC (ascend): ascending (default)
DESC (descend): descending
Query employee information in ascending order of salary
select * from emp order by sal;
Query employee information in descending order of salary
select * from emp order by sal desc;
-
Sort by alias
Sort by 2 times the employee's salary
select ename, sal*2 twosal from emp order by twosal;
-
Multiple column sorting
Sort by department and salary in ascending order
select ename, deptno, sal from emp order by deptno, sal ;
-
Sort By within each MapReduce
Note: the data in each Reducer (Partition) in Sort By is random.
Sort By: sort within each Reducer, not for global result set. Usually used in combination with Distribute By
Set the number of reduce
set mapreduce.job.reduces=3;
View the number of reduce settings
set mapreduce.job.reduces;
View employee information in descending order according to department number
select * from emp sort by empno desc;
Import query results into file (sorted by department number descending)
insert overwrite local directory '/opt/module/datas/sortby-result' select * from emp sort by deptno desc;
-
Partition by
Distribute By: similar to partition in MR, it is used in combination with sort by.
Hive requires the DISTRIBUTE BY statement to be written before the SORT BY statement.
When testing distribution by, you must allocate more reduce to process, otherwise you cannot see the effect of distribution by.
First by department number, then by employee number in descending order.
set mapreduce.job.reduces=3; insert overwrite local directory '/opt/module/datas/distribute-result' select * from emp distribute by deptno sort by empno desc;
-
Cluster By
cluster by not only has the function of distributing by, but also has the function of sort by. But sorting can only be ascending, and the sorting rule cannot be ASC or DESC.
Division by department number is not necessarily a fixed value. Departments 20 and 30 can be divided into one division.
-- The following two writing methods are equivalent select * from emp cluster by deptno; select * from emp distribute by deptno sort by deptno;
6.6 bucket and sampling query
-
Bucket table data storage
Partition is for data storage path; bucket is for data file.
Bucket splitting is another technique that breaks down a data set into parts that are easier to manage.
Create bucket table
create table stu_buck(id int, name string) clustered by(id) into 4 buckets row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
View table structure
desc formatted stu_buck; Num Buckets: 4
Set barrel splitting attribute, otherwise barrel splitting effect will not be seen
-- Opening bucket set hive.enforce.bucketing=true; -- Set up reduce Automatic identification for the system set mapreduce.job.reduces=-1;
Import data to bucket table
load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/stu_buck.txt' into table stu_buck;
-
Barrel sampling query
For very large datasets, sometimes users need to use a representative query result rather than all the results. Hive can meet this requirement by sampling tables.
Syntax: tablesample is a sampling statement, TABLESAMPLE(BUCKET x OUT OF y).
Y must be a multiple or factor of the number of buckets in the tabl (because of the Division). hive determines the proportion of samples according to the size of Y. For example, the table is divided into four parts. When y=2, extract (4 / 2 =) data from two buckets, and when y=8, extract (4 / 8 =) data from 1 / 2 buckets.
X indicates which bucket to start extraction from. If multiple partitions need to be taken, the future partition number is the current partition number plus y. For example, if the total number of buckets in a table is 4, the table sample (bucket 1 out of 2) means to extract the data of (4 / 2 =) 2 buckets in total, and extract the data of the first (x) and third (x + y) buckets.
Note: the value of x must be less than or equal to the value of y, otherwise the last bucket of data extracted will exceed the total number of buckets.
Query the data in the table stu.
-- There are 4 barrels in total. Take 4/2 Barrels, starting from the first one and the second from the third. select * from stu_buck tablesample(bucket 1 out of 2 on id);
6.7 other common query functions
-
Empty field assignment
NVL: assign a value to NULL data in the format of NVL (string1, replace with). Take the value of string1 first. If string1 is NULL, the NVL function returns the value of replace with, which can be either the default value or a column.
If the comm of the employee is NULL, use - 1 instead
select nvl(comm,-1) from emp;
If the employee's comm is NULL, the leader id is used instead
select nvl(comm,mgr) from emp;
-
CASE WHEN
Demand: find out how many men and women are in different departments.
Create hive table and import data
create table emp_sex( name string, dept_id string, sex string) row format delimited fields terminated by "\t"; load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/emp_sex.txt' into table emp_sex;
Query data by demand
select dept_id, -- Be careful CASE WHEN Use sum(case sex when 'male' then 1 else 0 end) male_count, sum(case sex when 'female' then 1 else 0 end) female_count from emp_sex group by dept_id;
-
Row to column
CONCAT(string A/col, string B/col… ): returns the result after connecting the input string. Any input string is supported;
CONCAT_WS(separator, str1, str2,… ): it is a special form of CONCAT(). The separator between the remaining parameters of the first parameter. The separator can be the same string as the remaining parameters. If the separator is NULL, the return value will also be NULL.
Collect set (Col): the function only accepts basic data types. Its main function is to de summarize the values of a field and generate array type fields.
Need: group people with the same horoscope and blood type.
-- metadata Monkey King Aries A Sagittarius A Aries B in Song Dynasty Pig Bajie Aries A Sagittarius A --Expected output Sagittarius, A sea Aries, A monkey king Aries, B song song
Create hive and import data
create table person_info( name string, constellation string, blood_type string) row format delimited fields terminated by "\t"; load data local inpath "/opt/module/datas/person_info.txt" into table person_info;
Query data by demand
select t1.c_b, concat_ws('|', collect_set(t1.name)) name -- Temporary table name Summarize into an array and use | Connect from (select name, concat(constellation, ",", blood_type) c_b -- Merging constellations and blood groups from person_info) t1 -- cursor t1 group by t1.base;
-
Column switching
EXPLODE(col): split the complex array or map structure in the hive column into multiple rows.
LATERAL VIEW
Usage: later view udtf (expression) tablealias as columnalias
Explanation: used with split, expand and other UDTF, it can split a column of data into multiple rows of data, on this basis, the split data can be aggregated.
Requirement: expand the array data in movie classification.
--Raw data Suspect tracking suspense, action, science fiction, plot Lie to me suspense, police, action, psychology, plot Wolf 2 war, action, disaster --Expected data Suspect tracking suspense Suspect tracking action Suspect tracking science fiction The plot of "suspect tracking" "Lie to me" suspense Lie to me police "Lie to me" action The psychology of Lie to me The plot of Lie to me Wolf 2 War Action of wolf 2 Wolf 2 disaster
Create hive table and import data
create table movie_info( movie string, category array<string>) row format delimited fields terminated by "\t" collection items terminated by ","; load data local inpath "/opt/module/datas/movie.txt" into table movie_info;
Query data by demand
Select movie, category_name from movie_info lateral view explode(category) table_tmp as category_name; -- explode(category) Split this column of data, table 1 later view Aggregate the data of the original table into each row according to the split data instead.
-
Window function
OVER(): Specifies the data window size of the analysis function. The data window size may change with the row
CURRENT ROW: CURRENT ROW
N forecasting: forward n rows of data
n FOLLOWING: next n rows of data
UNBOUNDED: starting point, UNBOUNDED prediction means starting from the front, UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING means ending from the back
LAG(col,n): data in line n ahead
LEAD(col,n): data in the next N lines
NTILE(n): distribute the rows in the ordered partition to the specified data groups. Each group has a number, starting from 1. For each row, NTILE returns the number of the group to which this row belongs. Note: n must be of type int.
Raw data
jack,2017-01-01,10 tony,2017-01-02,15 jack,2017-02-03,23 tony,2017-01-04,29 jack,2017-01-05,46 jack,2017-04-06,42 tony,2017-01-07,50 jack,2017-01-08,55 mart,2017-04-08,62 mart,2017-04-09,68 neil,2017-05-10,12 mart,2017-04-11,75 neil,2017-06-12,80 mart,2017-04-13,94
Create hive table and import data
create table business( name string, orderdate string, cost int ) ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','; load data local inpath "/opt/module/datas/business.txt" into table business;
demand
(1) Query customers and total number of customers purchased in April 2017
select name,count(*) over () from business where substring(orderdate,1,7) = '2017-04' group by name;

(2) Query customer's purchase details and monthly total purchase amount
select name,orderdate,cost,sum(cost) over(partition by month(orderdate)) from business;
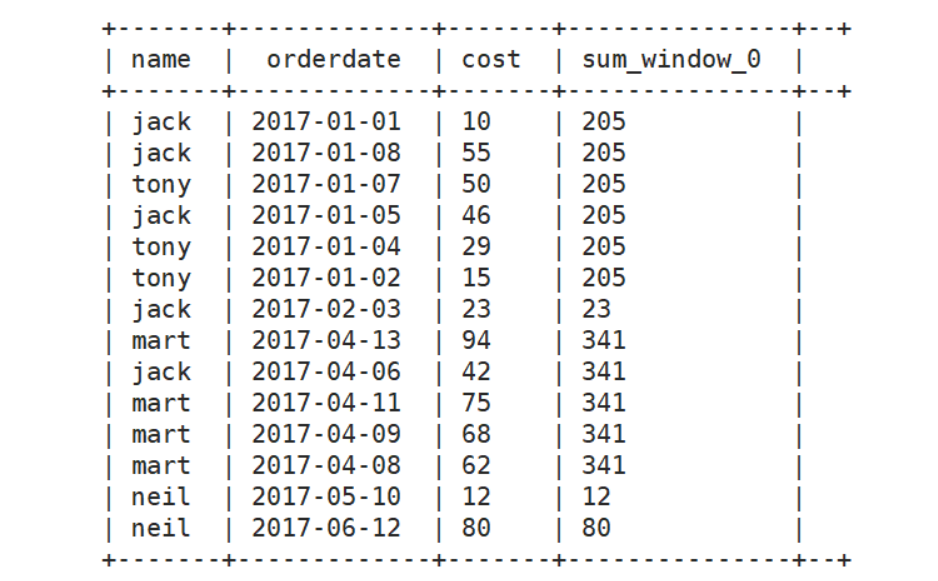
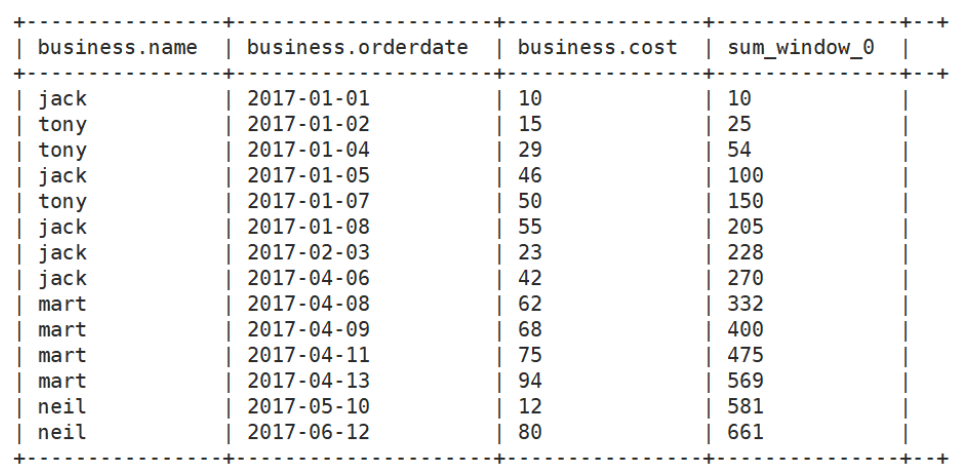
(3) In the above scenario, cost should be accumulated by date
select *,sum(cost) over(sort by orderdate rows between UNBOUNDED PRECEDING and CURRENT ROW ) from business;
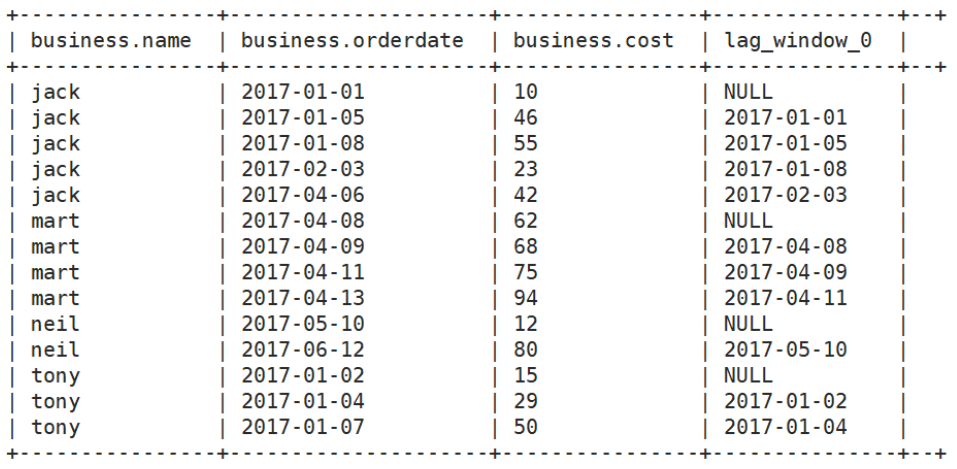
(4) Query customer's last purchase time
select *, lag(orderdate,1) over(distribute by name sort by orderdate) from business;
(5) Query the order information in the first 20% of the time
select * from ( select name, orderdate, cost, ntile(5) over(sort by orderdate) gid from business ) t where gid = 1;
[failed to save the image in the external link. The source station may have anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the image and upload it directly (img-wipuop4e-1582446297431) (C: \ users \ Maben \ appdata \ roaming \ typora \ typora user images \ 1564805328730. PNG))
-
Rank
RANK() will repeat at the same time, and the total number will not change
The same degree of rank() will be repeated, and the total number will be reduced
ROW_NUMBER() is calculated in order
Demand: calculate the ranking of each subject.
Create hive table and import data
create table score( name string, subject string, score int) row format delimited fields terminated by "\t"; load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/score.txt' into table score;
Query results according to requirements
select name, subject, score, rank() over(partition by subject order by score desc) rp, dense_rank() over(partition by subject order by score desc) drp, row_number() over(partition by subject order by score desc) rmp from score;

