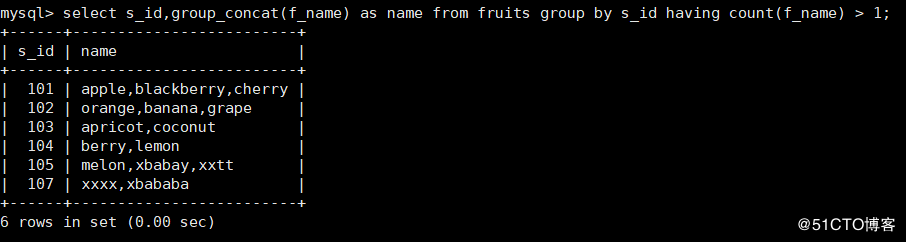
1. Query every s in fruits table_ All f corresponding to ID_ Name value
#Compact in groups mysql> select s_id,group_concat(f_name) as name from fruits group by s_id having count(f_name) > 1;
2. Same statistics s_ What are the rows of ID values?
mysql> select s_id,count(*) as total from fruits group by s_id with rollup;
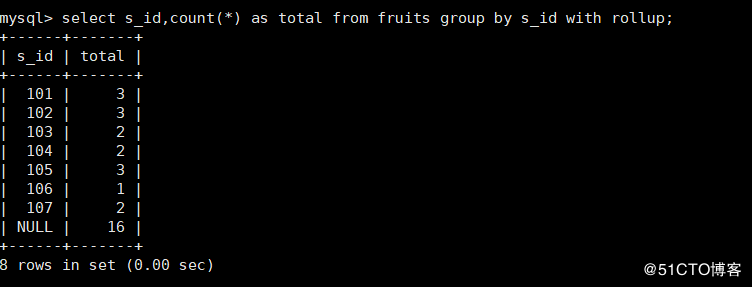
Note: the role of with roll up is to_ The sum after ID grouping is added again, and the total number is 16.
3. Create a new table and insert data
#Create a new table
mysql> create table orderitems(
-> o_num int not null,
-> o_item int not null,
-> f_id char(10) not null,
-> quantity int not null,
-> item_price decimal(8,2) not null,
-> primary key(o_num,o_item)
-> );
#insert data
mysql> insert into orderitems(o_num,o_item,f_id,quantity,item_price)
-> values(30001,1,'a1',10,'5.2'),
-> (30001,2,'b2',3,'7.6'),
-> (30001,3,'bs1',5,'11.2'),
-> (30001,4,'bs2',15,'9.2'),
-> (30002,1,'b3',2,'20.0'),
-> (30003,1,'c0',100,10),
-> (30004,1,'o2',50,'2.50'),
-> (30005,1,'c0',5,'10'),
-> (30005,2,'b1',10,'8.99'),
-> (30005,3,'a2',10,'2.2'),
-> (30005,4,'m1',5,'14.99');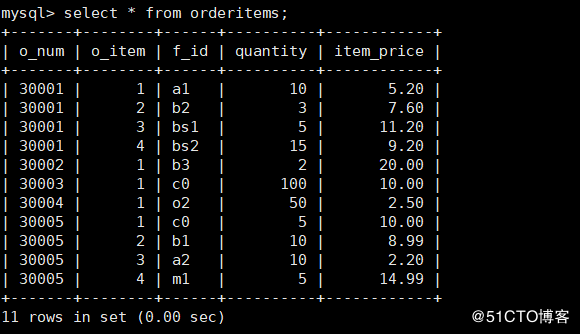
4. Query the same o_ quantity and item of num column_ Lines whose price multiplication result is greater than 100
mysql> select o_num,SUM(quantity*item_price) as total from orderitems
-> group by o_num having total > 100 order by total;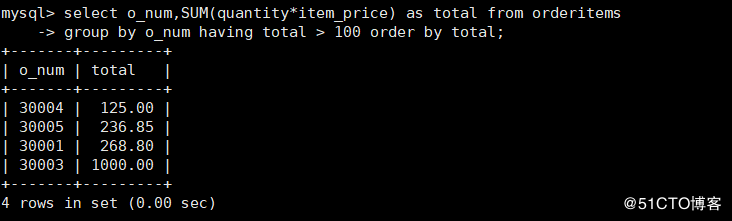
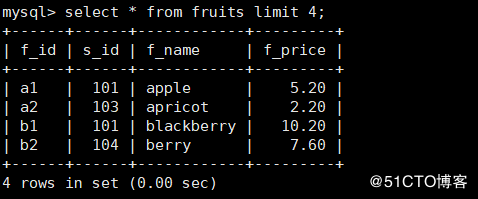
5. Limit -- limit the number of rows returned
Limit 1: #Show only the first four rows in the table mysql> select * from fruits limit 4;
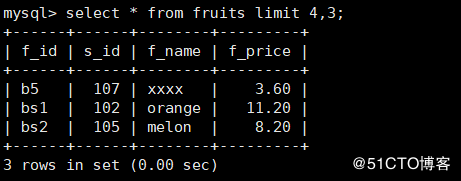
Limit 2: #Starting from the fourth line, display the next three lines mysql> select * from fruits limit 4,3;
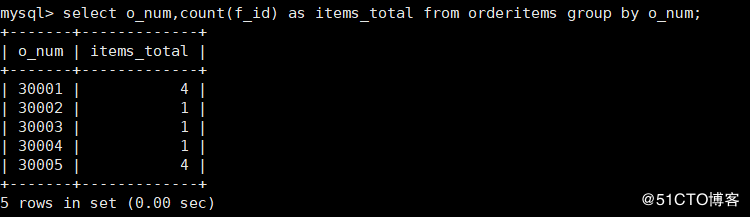
6. Query each o_ F corresponding to num_ How many IDS do you have
mysql> select o_num,count(f_id) as items_total from orderitems group by o_num;
7. Query o_ What is the quantity with num of 30005
mysql> select sum(quantity) as items_total from orderitems where o_num = 30005;
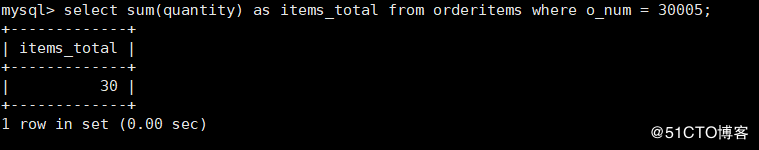
8. Queries_ F with ID 103_ What is the average price (s_ What is the average price of ID)
mysql> select avg(f_price) as avg_price from fruits where s_id = 103;
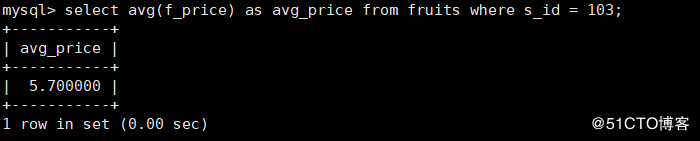
9. Query each s_ Average price corresponding to ID (f_ What is price?
mysql> select s_id,avg(f_price) as avg_price from fruits group by s_id;
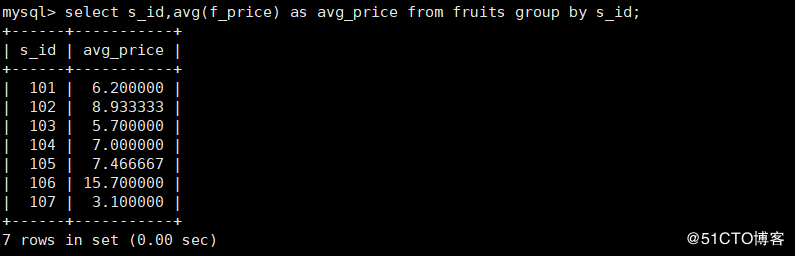
10. Query each s_ F in ID_ Which row has the highest price value?
mysql> select s_id, max(f_price) as max_price from fruits group by s_id;
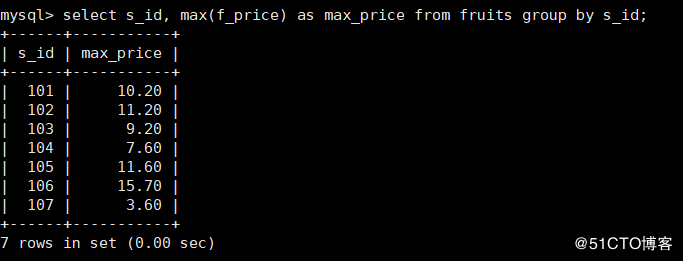
Note: similarly, to see the smallest row, just change max to min.
11. Query each f_ The maximum value of price and its corresponding s_id,f_name
mysql> select s_id,f_price,f_name from fruits
-> where f_price in(select max(f_price) from fruits group by s_id);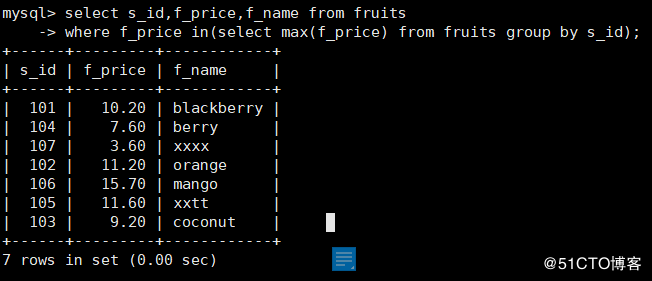
12. Create the required table again and insert the data
#Create table
mysql> create table suppliers(
-> s_id int not null auto_increment,
-> s_name char(50) not null,
-> s_city char(50) null,
-> s_zip char(10) null,
-> s_call char(50) not null,
-> primary key(s_id)
-> );
mysql> create table orders(
-> o_num int not null auto_increment,
-> o_date datetime not null,
-> c_id int not null,
-> primary key(o_num)
-> );
#insert data
mysql> insert into suppliers(s_id,s_name,s_city,s_zip,s_call)
-> values(101,'FastFruit Inc.','tianjin','300000','48075'),
-> (102,'LT Supplies','chongqing','400000','44333'),
-> (103,'acme','shanghai','200000','90046'),
-> (104,'fnk inc.','zhongshan','528437','11111'),
-> (105,'good set','taivuang','030000','22222'),
-> (106,'just eat ours','beijing','010','45678'),
-> (107,'dk inc.','zhengzhou','450000','33332');
mysql> insert into orders(o_num,o_date,c_id)
-> values(30001,'2008-09-01',10001),
-> (30002,'2008-09-12',10003),
-> (30003,'2008-09-30',10004),
-> (30004,'2008-10-03',10005),
-> (30005,'2008-10-08',10001);13. The concept of table join type
In the next query, it is necessary to talk about the related concepts of multi table query
1) Internal connection
inner join is the most common join method. It only returns the rows of matching relationship between two data sets, and joins the data rows within the overlapping part of two cross data sets.
Inner joins use comparison operators to compare some column data between tables and list the data rows in these tables that match the join.
2) External connection
outer join is an extension of inner join. In addition to joining the data rows within the repeating parts of two data sets, it can also return the unmatched data or all the data in the left or right tables as required.
The external connection can also be divided into the following types:
The result of the left outer join (left join or left outer join) includes all the rows in the left table. If a row in the left table does not match a row in the right table, the right table returns a null value, otherwise it returns a corresponding value.
The right outer join (right join or right outer join) is the reverse join of the left outer join. It will return all rows of the right table. If a row of the right table does not match a row in the left table, the left table will return a null value, otherwise it will return a corresponding value.
Full join (full join or full outer join) will return all rows in the left and right tables. When a row does not match in another table, the other table will return a null value. Otherwise, the corresponding value will be returned.
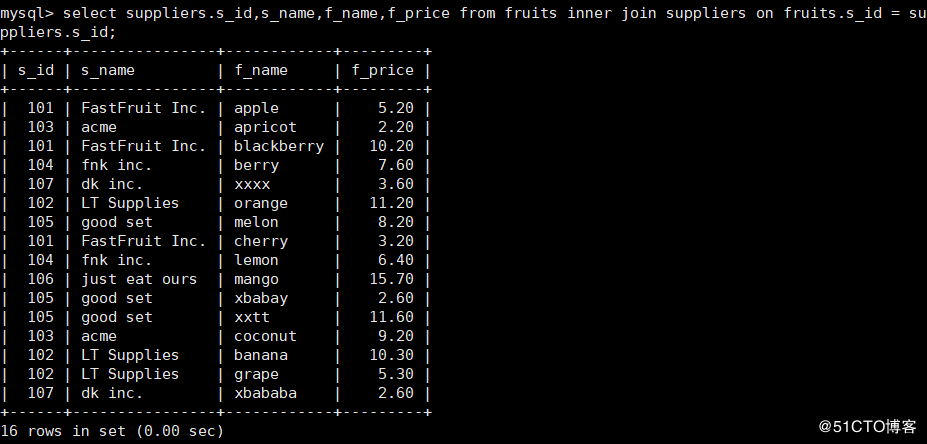
14. Inner join query generates a new table from the specified columns of two tables
mysql> select suppliers.s_id,s_name,f_name,f_price from fruits inner join suppliers on fruits.s_id = suppliers.s_id;
15. Example of left outer join query
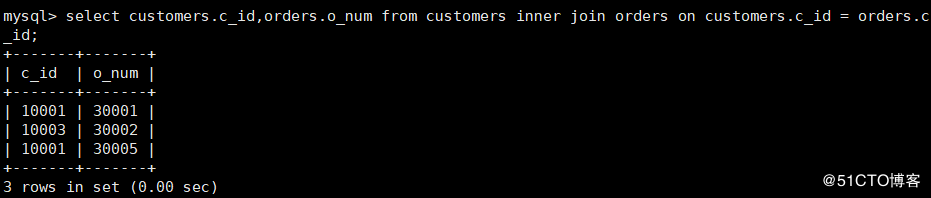
mysql> select customers.c_id,orders.o_num from customers
-> left outer join orders on customers.c_id = orders.c_id;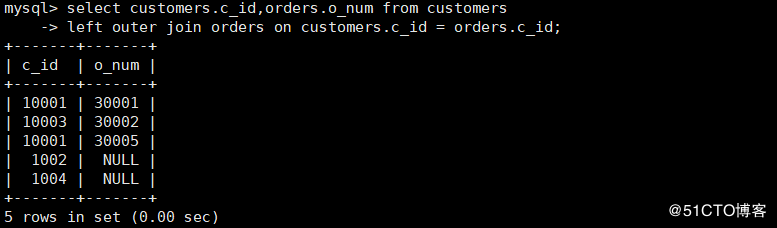
16. Specify other conditions when inner join query
mysql> select customers.c_id,orders.o_num from customers inner join orders on customers.c_id = orders.c_id;