How to use Python for batch file collation
“ introduction ”
Batch file sorting has always been a headache in daily work. Using Python for batch file sorting can greatly improve work efficiency. Here are some tips for batch file sorting.
Difficulty: ⭐⭐
1, Preparatory work
In order to be used in the experiment, we use the code to generate 200 txt files. The code is as follows.
for i in range(0, 200):
file_name = f'file_{i}.txt'
f = open(f'./file/{file_name}', mode='w')
f.close()Operation results:
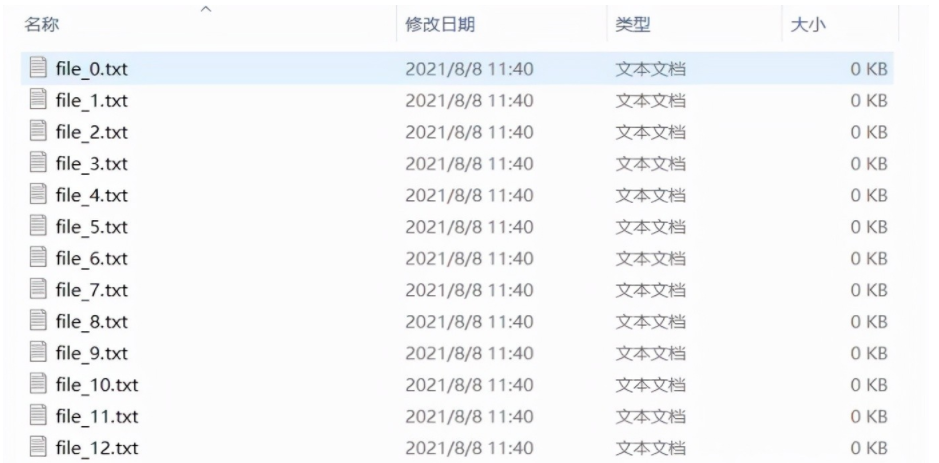
2, Making excel file list
1. Train of thought
Get the file name, and write the serial number and file name into excel.
2. openpyxl installation
This paper uses openpyxl library for excel operation and pip for installation.
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple openpyxl
3. Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
import os
# Get all txt files in the file path
def find_txt(path):
filenames = []
filename_listdir = os.listdir(path)
for filename in filename_listdir:
if filename.find('txt') != -1:
filenames.append(filename)
return filenames
# Generate file list
def add_data(excel_path, filenames):
# Determine whether excel file exists
if os.path.exists(excel_path) is False:
print(excel_path + ' File does not exist, please try again')
exit()
excel_file = load_workbook(excel_path) # Open excel file
excel_sheet = excel_file['Sheet1'] # Select Sheet1
# Add header
excel_sheet.cell(row=1, column=1, value='Serial number') # Serial number
excel_sheet.cell(row=1, column=2, value='file name') # file name
# Add file name
count = 1
for i in filenames[0:]:
count = count + 1
excel_sheet.cell(row=count, column=1, value=count - 1) # Serial number
excel_sheet.cell(row=count, column=2, value=i) # file name
excel_file.save(excel_path)
# File folder
file_path = './file'
# [file list. xlsx] path
excel_path = os.getcwd() + '/file/List of documents.xlsx'
filenames = find_txt(file_path)
print(filenames)
add_data(excel_path, filenames)
print('Success!')Operation results:
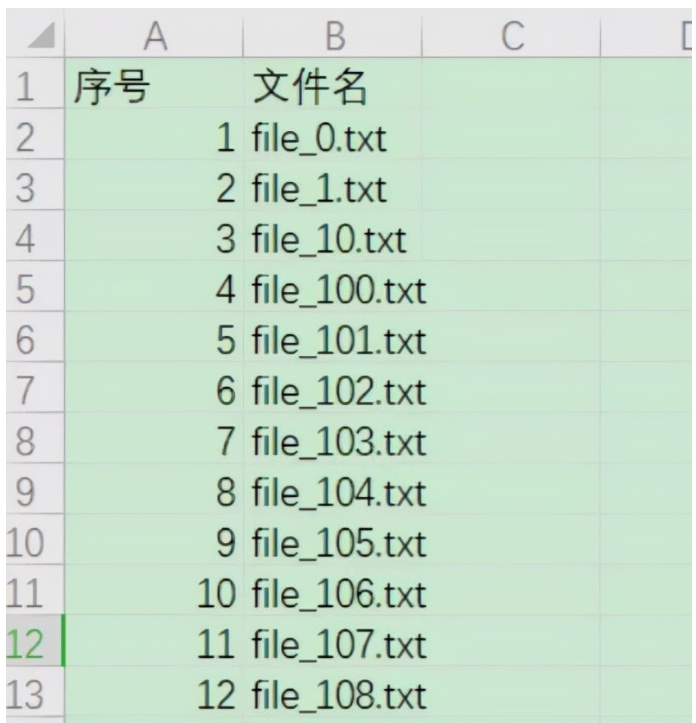
3, Batch renaming of files
1. Add serial number to file name in batch
In the process of file sorting and statistics, it is often necessary to add serial numbers to the file names. In the process of saving the file list above, we can see that the default sorting and saving of scripts is sorted by the first number. Here, we can make up zero to ensure sorting by number size.
1) Rename function:
os.rename(name, new_name)
2) Code
import os
path = os.getcwd() + '\\file'
filenames = os.listdir(path)
a = 1
for filename in filenames:
if filename.find('txt') != -1:
old_dir = f'{path}\\{filename}'
if a < 10:
new_dir = f'{path}\\00{a}-{filename}'
elif a < 100:
new_dir = f'{path}\\0{a}-{filename}'
else:
new_dir = f'{path}\\{a}-{filename}'
os.rename(old_dir, new_dir)
a = a + 1
3) Operation results
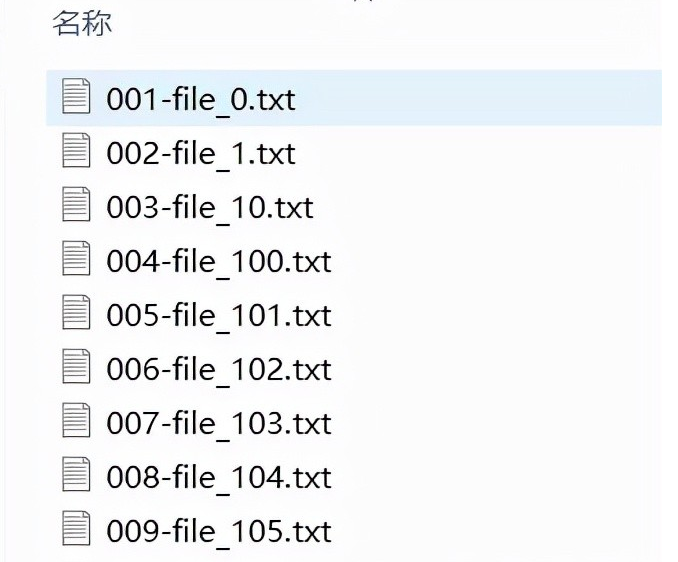
2. Rename the file name in batch to the specified file name
After making the file list, we can use excel to adjust the file name conveniently (such as removing spaces, adding header and footer fields, etc.). After making the modified file name in excel, we can rename the file name in batch.
1) Experimental objectives
As shown in the figure: we try to change the file name to a new file name (use excel to replace file with filename).
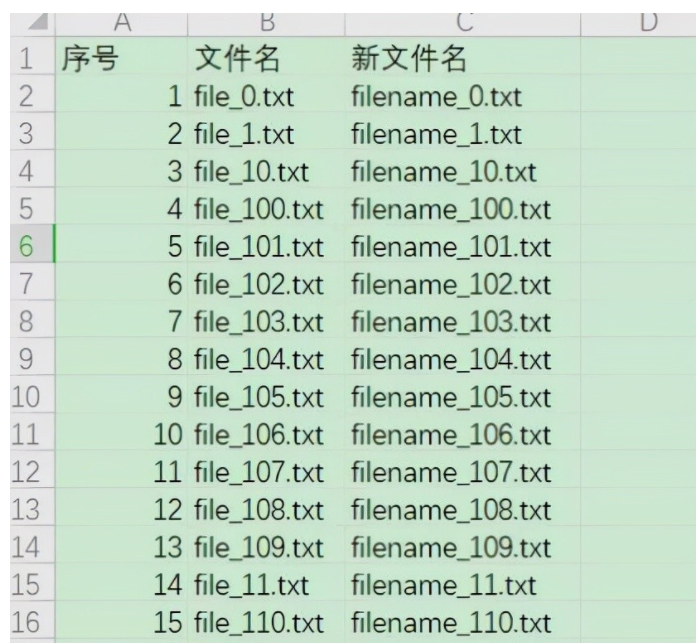
2) Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
import os
# Get file path file name
def find_txt(path):
filenames = []
filename_listdir = os.listdir(path)
for filename in filename_listdir:
if filename.find('txt') != -1:
filenames.append(filename)
return filenames
# CHB Renamer
def change_file_name(file_path, excel_path, filenames):
data = load_workbook(excel_path)
sheet = data['Sheet1']
for i in range(1, sheet.max_row + 1)[1:]:
for filename in filenames:
if filename == sheet.cell(i, 2).value:
old_dir = os.path.join(file_path, filename)
new_dir = os.path.join(file_path, sheet.cell(i, 3).value)
os.rename(old_dir, new_dir)
else:
pass
# File folder
file_path = './file'
# [file list. xlsx] path
excel_path = os.getcwd() + '/file/List of documents.xlsx'
filenames = find_txt(file_path)
print(filenames)
change_file_name(file_path, excel_path, filenames)
print('Success!')Operation effect:
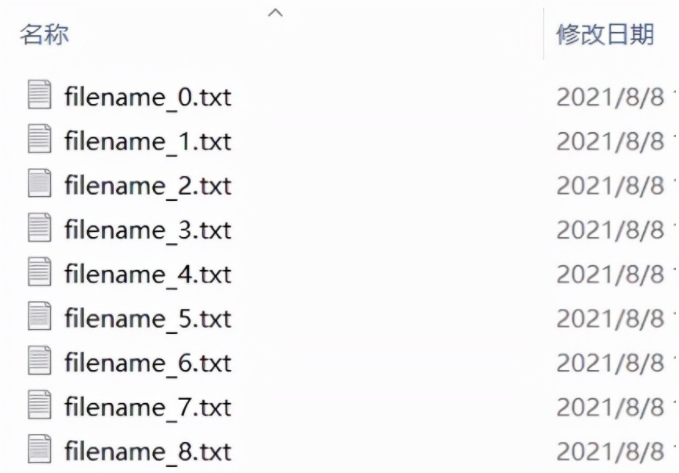
4, Batch deletion of files
1. Experimental objectives
After filtering the file names in excel, we will delete the files listed as 1 and keep the files listed as 0 (as shown in the figure).
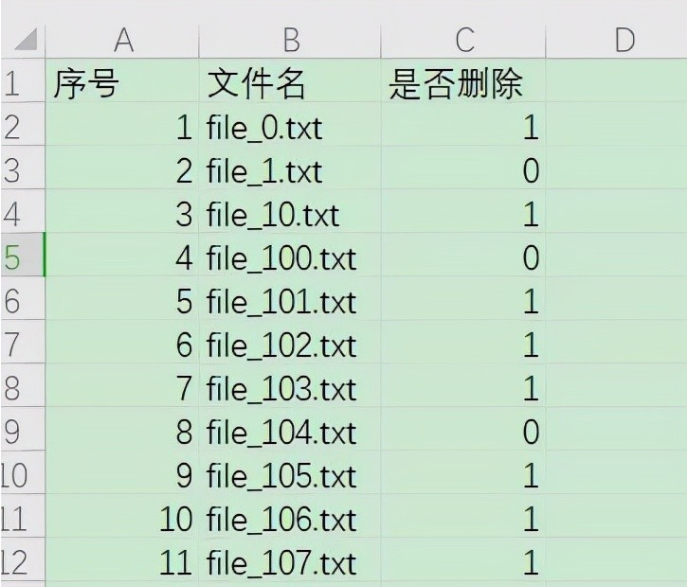
2. Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
import os
# Get file path file name
def find_txt(path):
filenames = []
filename_listdir = os.listdir(path)
for filename in filename_listdir:
if filename.find('txt') != -1:
filenames.append(filename)
return filenames
# CHB Renamer
def change_file_name(file_path, excel_path, filenames):
data = load_workbook(excel_path)
sheet = data['Sheet1']
for i in range(1, sheet.max_row + 1)[1:]:
for filename in filenames:
if filename == sheet.cell(i, 2).value:
file_dir = os.path.join(file_path, filename)
delete_flag = sheet.cell(i, 3).value
if delete_flag:
os.remove(file_dir)
else:
pass
# File folder
file_path = './file'
# [file list. xlsx] path
excel_path = os.getcwd() + '/file/List of documents.xlsx'
filenames = find_txt(file_path)
print(filenames)
change_file_name(file_path, excel_path, filenames)
print('Success!')
Today's Meitu





If you think the article is good, please Like, comment, collect and follow , The next issue will be updated soon.
