Use the MyBatis framework to manipulate data and integrate MyBatis in the SpringBoot framework
Use steps:
1.mybatis start dependency: complete the automatic configuration of mybatis objects, and put the objects in the container
2.pom.xml specifies that the xml files in the src/main/java directory are included in the classpath
3. Create entity class Student
4. Create Dao interface StudentDao and create a method to query students
5. Create Mapper file and xml file corresponding to Dao interface and write sql statement
6. Create the Service layer object, and create the StudentService interface and its implementation class. Method to dao object. Complete database operation
7. Create Controller object and access Service.
8. Write application Properties file to configure the connection information of the database.
1.1 SpringBoot integration MyBatis example
1.1.1 creating database tables
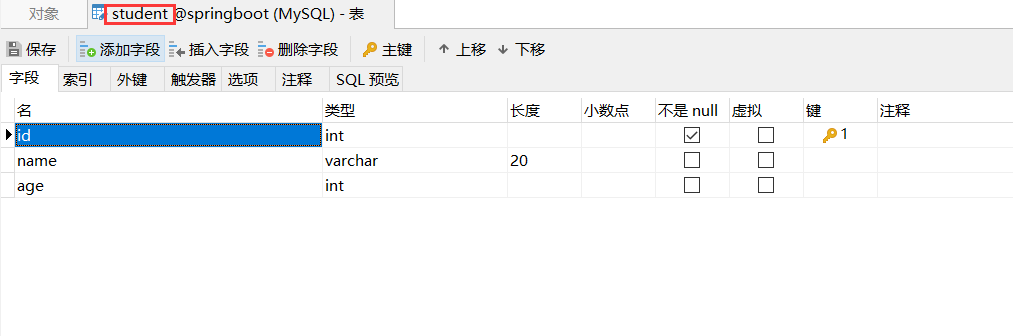
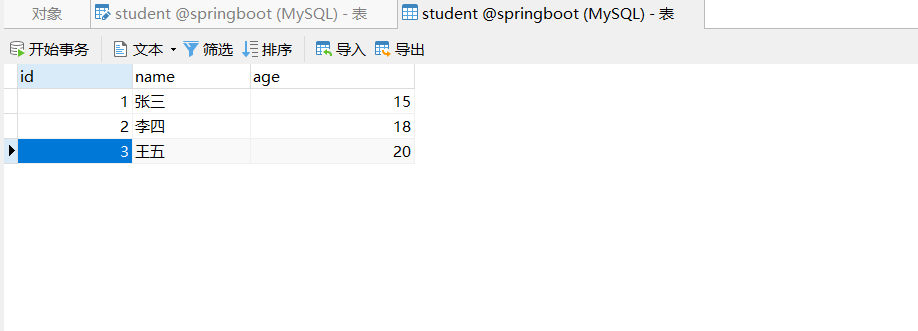
1.1.2 add Maven dependency
<dependencies>
<!--web Start dependence-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis Start dependence-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql drive-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!--test-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
1.1.3 add resources plug-in
<build>
<!--join resource plug-in unit-->
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.*</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
1.1.4 configuring data sources
server.port=9001 server.servlet.context-path=/orm #Connect database spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456
1.1.5 create Student entity class
package com.suyv.model;
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
1.1.6 create StudentDao interface
package com.suyv.dao;
import com.suyv.model.Student;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
/**
* @mapper Tell mybatis that this is the dao interface and create the proxy object of this interface
*/
@Mapper
public interface StudentDao {
Student selectById(@Param("stuId") Integer id);
}
1.1.7 create studentdao xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.suyv.dao.StudentDao">
<select id="selectById" resultType="com.suyv.model.Student">
select * from student where id=#{stuId}
</select>
</mapper>
1.1.8 create StudentService interface
package com.suyv.service;
import com.suyv.model.Student;
public interface StudentService {
Student queryStudent(Integer id);
}
1.1.9 create StudentServiceImpl implementation class
package com.suyv.service.impl;
import com.suyv.dao.StudentDao;
import com.suyv.model.Student;
import com.suyv.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Resource
private StudentDao studentDao;
@Override
public Student queryStudent(Integer id) {
Student student = studentDao.selectById(id);
return student;
}
}
1.1.10 create StudentController class
package com.suyv.controller;
import com.suyv.model.Student;
import com.suyv.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Controller
public class StudentController {
@Resource
private StudentService studentService;
@RequestMapping("/student/query")
@ResponseBody
public String queryStudent(Integer id){
Student student = studentService.queryStudent(id);
return student.toString();
}
}
1.2 use @ MapperScan
Add @ Mapper to Dao interface, and you need to add annotations to each interface. It's inconvenient when there are many Dao interfaces. It can be solved in the following ways.
Add annotation package scanning on the main class: @ MapperScan("com.suyv.dao")
package com.suyv;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* @MapperScan : Scan all dao interfaces of mybatis
* Location: above the main class
* Attribute: basePackages: Specifies the package name of the dao interface.
* dao The interface and mapper files are still in the same directory
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.suyv.dao")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
1.3 Mapper files and Dao interfaces are managed separately
Now put the Mapper file in the resources directory
1) Create a subdirectory (customized) in the resources directory, such as mapper
2) Put the mapper file in the mapper directory
3) In application In the properties file, specify the directory of the mapper file
#Specify mapper file location mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml #mybatis log mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
4) In POM XML specifies to compile the files in the resources directory into the target directory
<!--resources plug-in unit-->
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.*</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
1.4 transactions
Transactions in the Spring framework:
1) Transaction management object: transaction manager (interface, which has many implementation classes)
For example: use Jdbc or mybatis to access the database, and use the transaction manager: DataSourceTransactionManager
2) Declarative transaction: specify the content of transaction control in the xml configuration file or with annotations
Control transactions: isolation level, propagation behavior, timeout
3) Transaction processing method:
1. @ Transactional in spring framework
2.aspectj framework can declare the content of transaction control in xml configuration file
Using transactions in SpringBoot: the above two methods can be used. The bottom layer still adopts the transaction management provided by Spring itself.
Use the annotation @ EnableTransactionManagement in the entry class to enable transaction support
The annotation @ Transactional can be added to the Service method accessing the database
1.4.1 SpringBoot implementation transaction
1)pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<!--join resource plug-in unit-->
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.*</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
2) Configure application properties
server.port=9001 server.servlet.context-path=/orm #Connect database spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 #Specify mapper file location mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml #mybatis log mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
3) Create Student entity class
package com.suyv.model;
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
4) Create StudentDao interface and mapper file
StudentDao.java
package com.suyv.dao;
import com.suyv.model.Student;
public interface StudentDao {
int addStudent(Student student);
}
StudentDao.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.suyv.dao/StudentDao">
<insert id="addStudent">
insert into student(name,age) value (#{name},#{age})
</insert>
</mapper>
5) Create service interface and implementation class
StudentService.java
package com.suyv.service;
import com.suyv.model.Student;
public interface StudentService {
int addStudent(Student student);
}
StudentServiceImpl.java
package com.suyv.service.impl;
import com.suyv.dao.StudentDao;
import com.suyv.model.Student;
import com.suyv.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Resource
private StudentDao studentDao;
@Transactional
@Override
public int addStudent(Student student) {
System.out.println("Business method addStudent");
int rows = studentDao.addStudent(student);
// Throw runtime exception
int m = 10/0;
System.out.println("implement sql sentence");
return rows;
}
}
6) Create Controller
package com.suyv.controller;
import com.suyv.model.Student;
import com.suyv.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Controller
public class StudentController {
@Resource
private StudentService studentService;
@RequestMapping("/addStudent")
@ResponseBody
public String addStudent(String name,Integer age){
Student student = new Student();
student.setName(name);
student.setAge(age);
int rows = studentService.addStudent(student);
return "Add student:" + rows;
}
}
7) Modify main startup class
package com.suyv;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@EnableTransactionManagement
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.suyv.dao")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}