Introduction
since Hadoop is a software designed for clustering, it is inevitable to configure Hadoop on multiple machines in the process of learning and using, which will cause many obstacles for beginners. There are two main obstacles;
- Expensive computer clusters. A cluster environment composed of multiple computers requires expensive hardware.
- Difficult to deploy and maintain. Deploying the same software environment on many machines is a relatively large amount of work. Moreover, it is relatively inflexible. If it needs to be modified, many contents need to be modified.
in order to solve this problem, a relatively mature solution is to use Docker.
Docker is a container management system. It can run multiple virtual machine containers like virtual machines and form a cluster. Because the virtual opportunity completely virtualizes a computer. Therefore, it will consume a lot of hardware resources. Docker provides an independent and replicable running environment. In fact, all processes in the container are still executed in the host's kernel. So its running effect is almost the same as that in memory. The content of docker will be shared by bloggers in subsequent sharing.
let's take a look at how to deploy Hadoop in Docker
Docker deployment
after entering the Docker command line, you first need to pull a Linux as the Hadoop running environment. It should be noted here that CentOS is recommended as the running environment
Query image
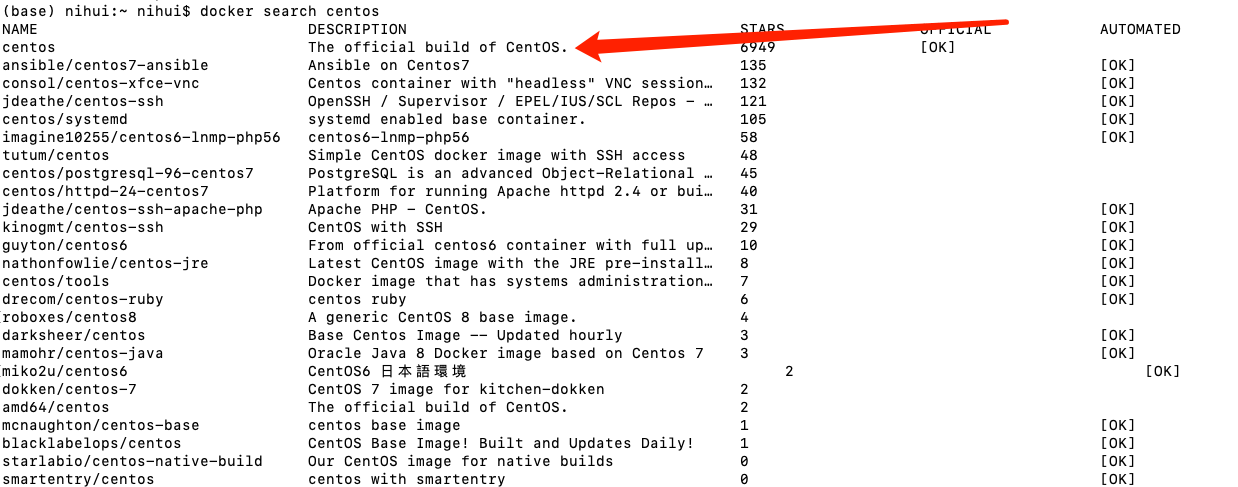
first execute the following command to query the corresponding image content
docker search centos
after execution, you will see the following contents. The first stars is the most frequently used CentOS image. We choose this as the image of the corresponding running environment
Get image
after querying the corresponding image using the above command, the next thing is to obtain the corresponding image content. You can use the following command to pull the image
docker pull centos
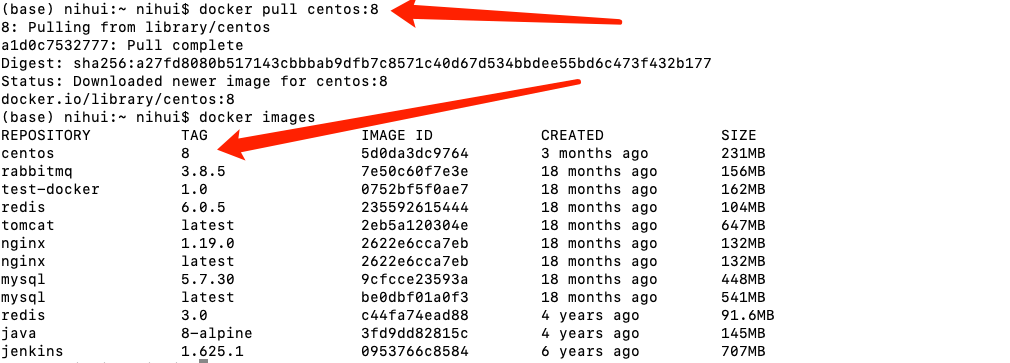
after pulling, you can use the docker images command to view the corresponding downloaded image. The next step is to run the container image.
Create container
after the image is pulled, use the following command to create a container
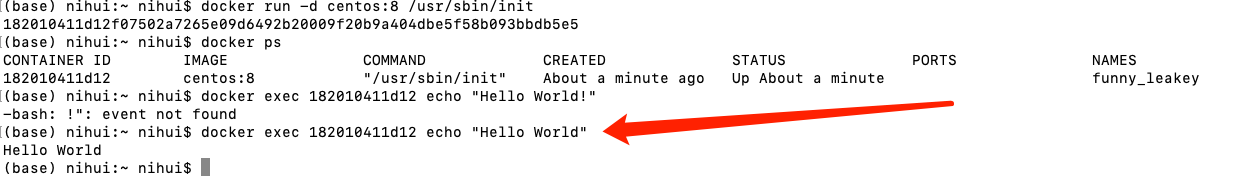
docker run -d centos:8 /usr/sbin/init
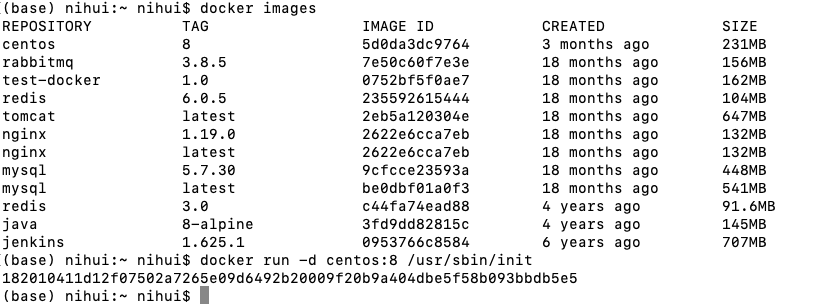
use docker ps to view the container running period;

you can let the container output something, using the following command
docker exec 182010411d12 echo "Hello World!"
Configuring Java and SSH environments
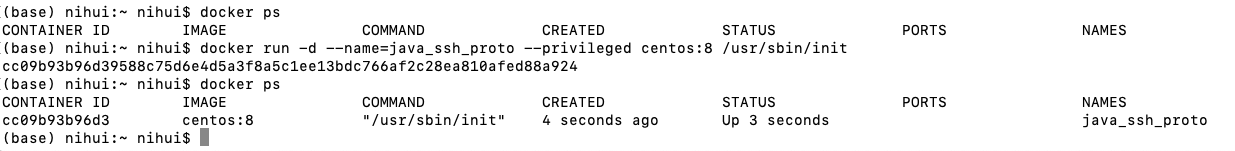
first create a container named java_ssh_proto, used to configure an environment containing Java and SSH.
you need to stop the container running before, using docker stop + container ID.

Create a container
docker run -d --name=java_ssh_proto --privileged centos:8 /usr/sbin/init
Enter the container
docker exec -it java_ssh_proto bash

Configure the source of the mirror
sed -e 's|^mirrorlist=|#mirrorlist=|g' \
-e 's|^#baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/$contentdir|baseurl=https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/centos|g' \
-i.bak \
/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Linux-AppStream.repo \
/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Linux-BaseOS.repo \
/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Linux-Extras.repo \
/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Linux-PowerTools.repo \
/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Linux-Plus.repo
yum makecache
the results are as follows:

Install Open JDK and SSH services
yum install -y java-1.8.0-openjdk-devel openssh-clients openssh-server
Java environment testing

Start SSH service
systemctl enable sshd && systemctl start sshd
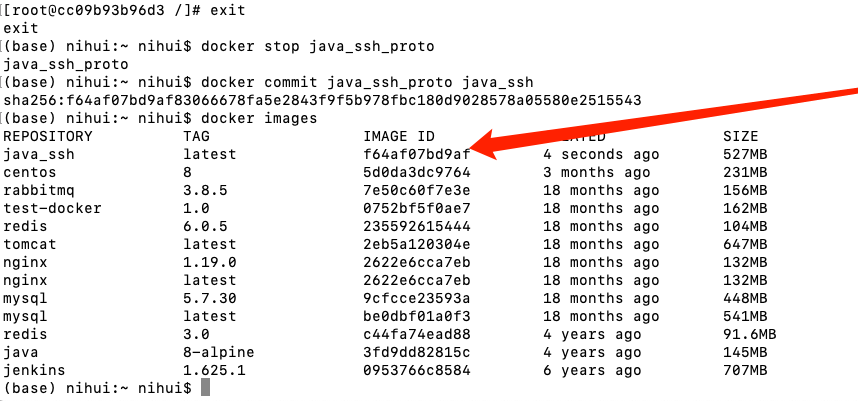
so far, if there is no fault, a container containing Java running environment and SSH environment will be created. This is a very key container. It is recommended to exit with the exit command in the container first, then run the following two commands, and save a container named java_ssh image:
docker stop java_ssh_proto docker commit java_ssh_proto java_ssh
Hadoop installation
Hadoop official website address: http://hadoop.apache.org/
Hadoop distribution Download: https://hadoop.apache.org/releases.html
Create a Hadoop stand-alone container
use the Java saved above_ SSH image creating container hadoop_single;
docker run -d --name=hadoop_single --privileged java_ssh /usr/sbin/init
copy the downloaded hadoop compressed package to the / root directory in the container;
docker cp <You store hadoop Path to the compressed package> hadoop_single:/root/
entering the container
docker exec -it hadoop_single bash
enter the root directory
cd /root
unzip the content just copied
tar -zxvf hadoop-3.3.1.tar.gz
after decompression, copy it to a common place
mv hadoop-3.3.1 /usr/local/hadoop
configure environment variables for response
echo "export HADOOP_HOME=/usr/local/hadoop" >> /etc/bashrc echo "export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME/bin:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin" >> /etc/bashrc
then exit the docker container and re-enter.
echo "export JAVA_HOME=/usr" >> $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh echo "export HADOOP_HOME=/usr/local/hadoop" >> $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh
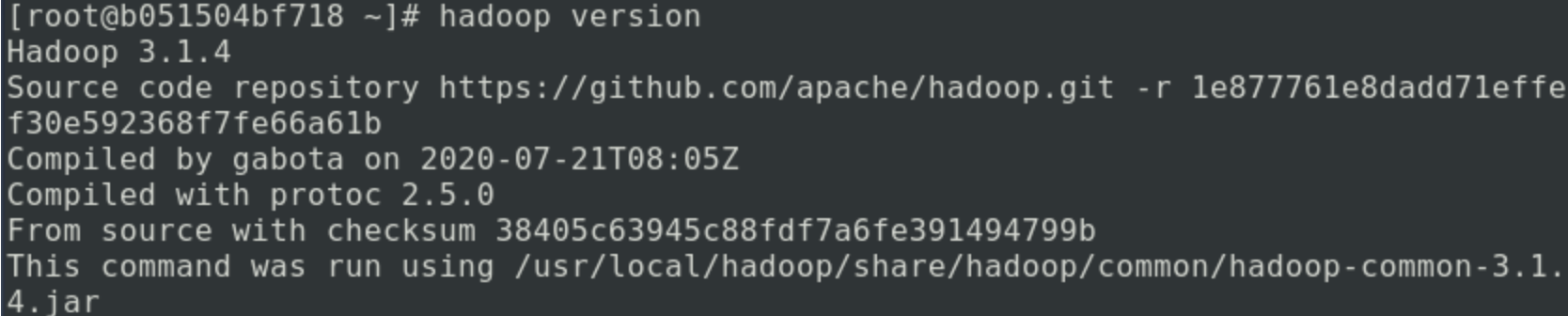
in these two steps, configure the built-in environment variables of hadoop, and then execute the following commands to judge whether it is successful:
hadoop version