Build redis cluster based on docker container (3 master and 3 slave)
1, Container preparation
Pull the centos basic image from the image warehouse, then create the container, initialize the environment, install some common commands and environment dependencies such as gcc, tar, ssh and telnet, and then create the test01 user and set the password. Then package the initialized container as an image as the real basic image. The above operation steps are no longer described. Please Baidu by yourself.
This time, the three master and three slave servers are deployed on three servers, with ip and port allocation of 20100 and 20101 of 10.25.27.116
20100 and 20101 of 10.25.27.117
20100 and 20101 of 10.25.27.118
1. Create docker LAN
docker network create --subnet=10.25.27.0/24 mynet1 # mynet1 is the bridge name, which can be customized. 10.25.27.0/24 is the network segment, which can be adjusted according to your own needs.
2. Create three server containers based on the underlying image and specify the ip address
docker run -d --name centos01 -it --net mynet1 --ip 10.25.27.116 --privileged=true -p 20010:22 my-centos:1.0 /usr/sbin/init # centos01 is the container name, - net is to join the container to the mynet1 LAN, - ip is to specify a fixed ip for the container (to be in the mynet1 network segment), -- privileged=true is to prevent the systemctl command in the container from reporting errors, - p 20010:22 is to map the 20100 port of the host to port 22 of the container for remote ssh login, and my CentOS: 1.0 is the basic image and version number prepared in advance. #The other two are the same as above. Modify the ip, container name and mapping port. docker run -d --name centos02 -it --net mynet1 --ip 10.25.27.117 --privileged=true -p 20011:22 my-centos:1.0 /usr/sbin/init docker run -d --name centos03 -it --net mynet1 --ip 10.25.27.118 --privileged=true -p 20012:22 my-centos:1.0 /usr/sbin/init #Set the container to start automatically docker update --restart=always centos01 docker update --restart=always centos02 docker update --restart=always centos03 #At this point, the container is created.
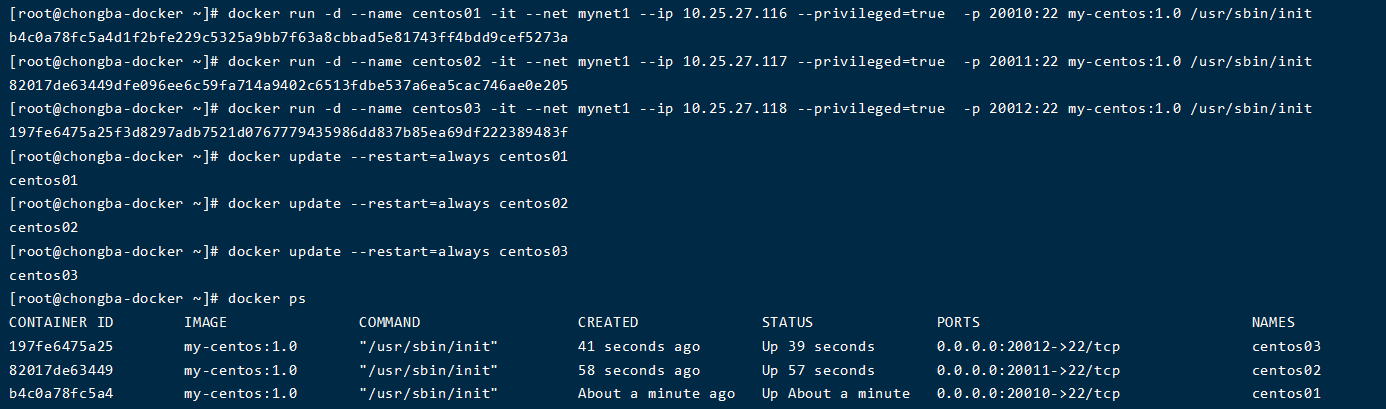
3. Log in to the container and check the internal environment of the container
# Use the docker exec command to log in to the containers one by one, and use ifconfig to check whether the IP is the fixed ip set when creating the container. Then use the ping command to test the connectivity between containers, between containers and host computers, and between containers and the Internet. docker exec -it centos01 /bin/bash #View native ip ifconfig | grep -10 eth0 #Test connectivity ping 10.25.27.118 ping www.baidu.com #Test ssh Remote Login ssh 10.25.27.117 -p 22 #Local test host port mapping ssh 192.168.200.129 -p20010
2, Software preparation
#Use the su command to switch to the test01 user su test01 #Create a software folder in the / home/test01 directory to store the required files cd /home/test01 mkdir software #Then upload the software to this directory using sftp tool
3, Install and compile ruby and gem (just one of the three)
Use 10.25.27.116 to install ruby and compile redis
1. Unzip ruby and enter the folder
tar -zxvf ruby-3.0.0.tar.gz cd ruby-3.0.0
2. Set the installation path and compile the installation
./configure --prefix=/home/test01/ruby # Make and make install can be executed separately if errors are reported together make & make install
3. View execution results
Enter the / home/test01 directory and use the ls command to check that the ruby directory already exists.
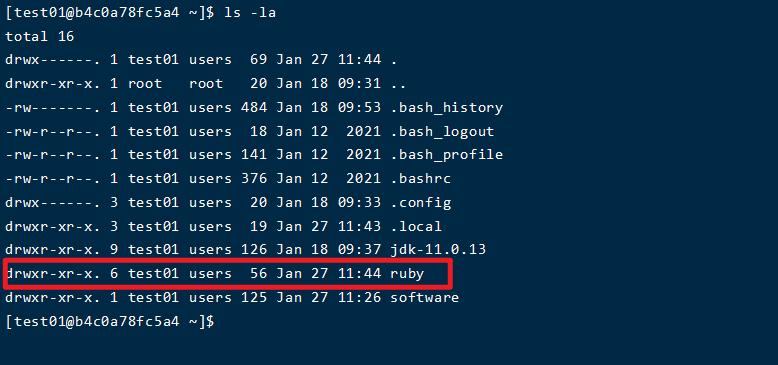
4. Installing gem
gem is a ruby related package
Go to / home/test01/ruby/bin
#Execute the following command, redis-3.3.3 Gem package should be uploaded to / home/test01/software / directory in advance ./gem install -l /home/test01/software/redis-3.3.3.gem
4, Install redis and configure redis
1. Compile and install redis
# Enter the / home/test01/software directory and unzip the redis installation package tar -zxvf redis-5.0.4.tar.gz #Enter the redis-5.0.4 directory, compile reids and specify the installation path make PREFIX=/home/test01/redis #Install redis make install
If make test prompts the following error and needs to install tcl dependency, skip the following steps without prompting https://blog.csdn.net/zjh_746140129/article/details/80807393
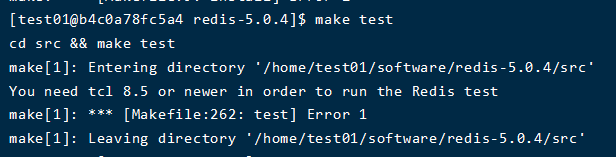
2. Configure redis configuration
After installation, there will be a redis folder in the / home/test01 directory
Create 20100 and 20101 directories in the redis folder
Create config and data directories under the two directories respectively
Add / home / test01 / software / redis-5.0.4 / redis Copy the conf file to config and the configuration file
Go to / home/test01/redis/20100/config and / home/test01/20101/config to modify redis conf
# Port number of each node port 20100 # Enable background startup daemonize yes # Bind current machine IP bind 0.0.0.0 # Data file storage location dir /home/test01/redis/20100/data # Set pid file storage location pidfile /home/test01/redis/20100/redis.pid # Start cluster mode cluster-enabled yes # Cluster configuration file cluster-config-file nodes-20100.conf # Cluster node timeout cluster-node-timeout 15000 appendonly yes
Use the scp command to copy the redis folder to the / home/test01 directory in the other two servers
cd /home/test01 scp -r test01@10.25.27.116:/home/test01/redis ./
3. Configure environment variables
Edit the current user's with vi or vim editor bash_profile file
vim ~/.bash_profile export PATH=/home/test01/ruby/bin:$PATH export REDIS_HOME=/home/test01/redis export PATH=$REDIS_HOME/bin:$PATH source ~/.bash_profile
5, Start redis and build a cluster
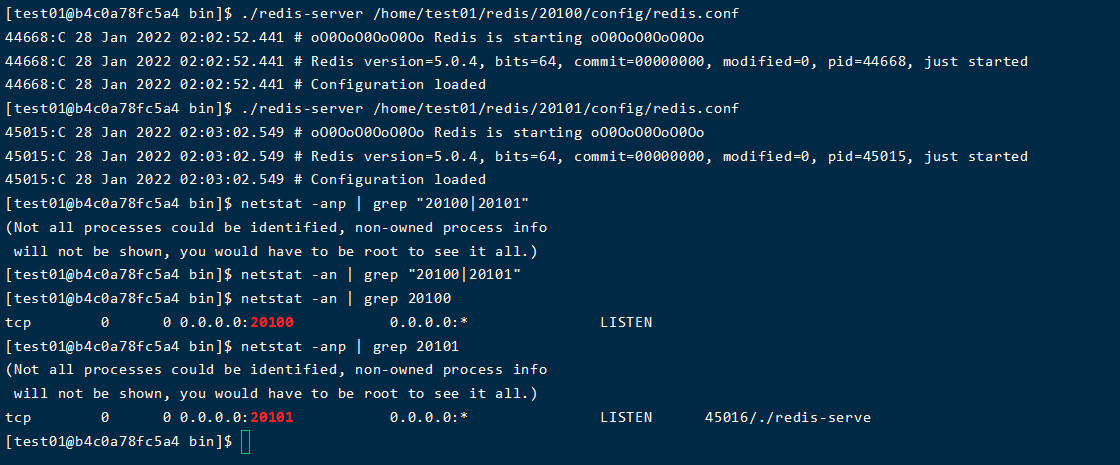
1. Start redis (executed by each server)
cd /home/test01/redis/bin ./redis-server /home/test01/redis/20100/config/redis.conf ./redis-server /home/test01/redis/20101/config/redis.conf # Check start-up netstat -an | grep 20100 netstat -an | grep 20101
2. Cluster networking
Execute the following command on the machine with ruby installed just now for cluster networking
cd /home/test01/redis/bin ./redis-cli --cluster create 10.25.27.116:20100 10.25.27.117:20100 10.25.27.118:20100 10.25.27.116:20101 10.25.27.117:20101 10.25.27.118:20101 --cluster-replicas 1
Note: the firewall must open the redis port for listening, otherwise the creation will fail. If the creation fails and attempts to create again, an error similar to "ERR Slot 0 is already busy (Redis::CommandError)" may appear. At this time, run the following command to clear some traces of the previous time and try again:
./redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 20100 127.0.0.1:20100>flushall 127.0.0.1:20100>cluster reset
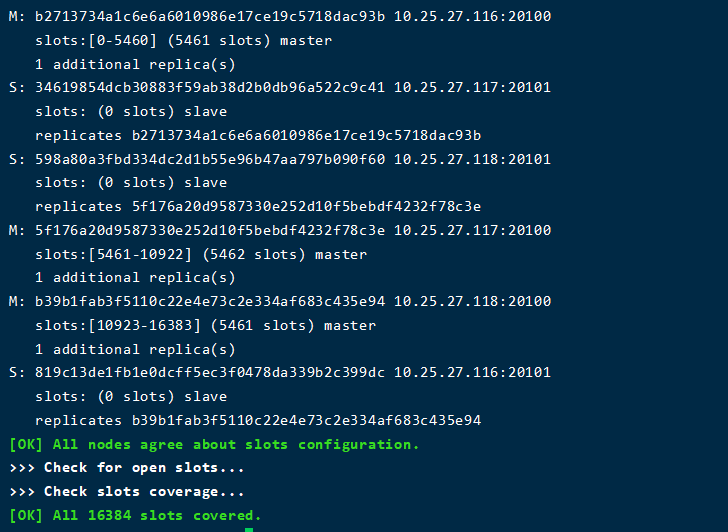
3. Validation cluster
# Execute the following command on the server of 116 cd /home/test01/redis/bin # -c means open in cluster mode ./redis-cli -c -h 10.25.27.117 -p 20100 # Enter cluster nodes to view the cluster node information 10.25.27.117:20100> cluster nodes
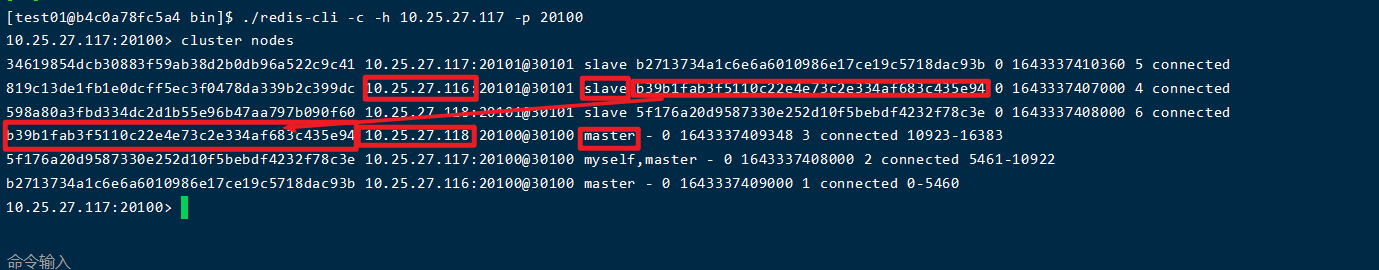
As shown in the figure, the slave node of the master node of 118 is 116116, the slave node of the master node is 117117, and the slave node of the master node is 118. Each server has a master node and a slave node. The port of the master node is 20100 and the port of the slave node is 20101. The master node and the slave node are not on the same server. So far, the three master and three slave redis cluster based on docker has been successfully built.