Builder Pattern uses several simple objects to build a complex object step by step.This type of design pattern is creative and provides the best way to create objects.
Reference to the novice bird tutorial: https://www.runoob.com/design-pattern/builder-pattern.html
introduce
Intention: Separate a complex build from its representation so that the same build process can create different representations.
Main Solutions: In software systems, sometimes faced with the creation of "a complex object", which is usually composed of sub-objects of each part with a certain algorithm; due to changes in demand, each part of this complex object often faces dramatic changes, but the algorithm that combines them is relatively stable.
When to use: When some basic components do not change and their combinations often change.
How to solve: Separate change from change.
Key Code: Builder: Create and provide instances, Director: Manage the dependencies of built instances.
Examples of applications: 1. To KFC, hamburgers, colas, chips, chicken wings and so on are unchanged, while their combinations are constantly changing, resulting in so-called "meals".2. StringBuilder in JAVA.
Advantages: 1. Builder is independent and easy to expand.2. Easy to control risk in detail.
Disadvantages: 1. Products must have common points and limited scope.2. If the internal changes are complex, there will be many construction classes.
Use scenarios: 1. Objects that need to be generated have complex internal structures.2. The internal attributes of the objects that need to be generated depend on each other.
IMPORTANT: The difference from the factory model is that the builder model pays more attention to the order in which parts are assembled.
UML diagrams
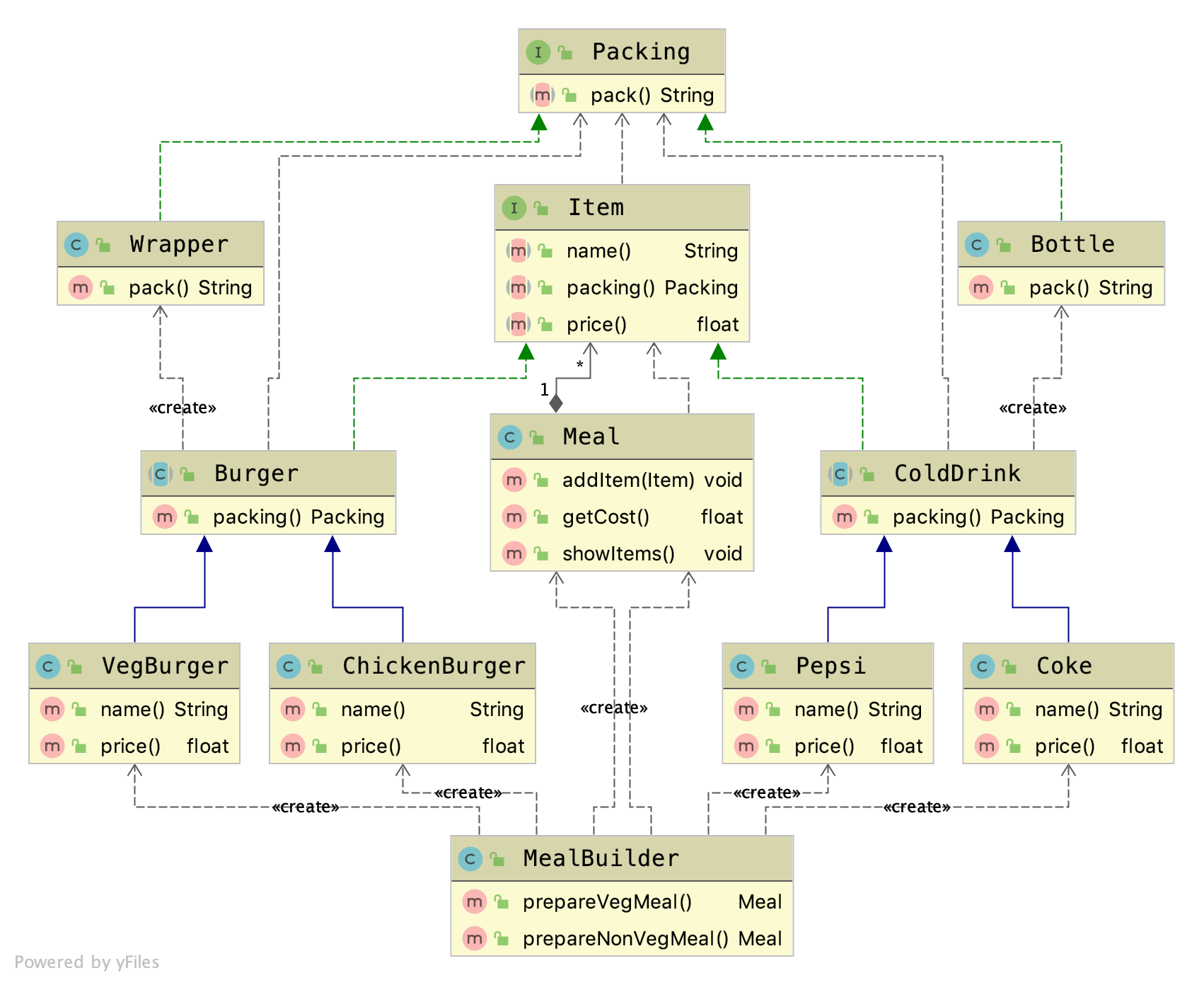
Realization
Item class
public interface Item {
//Name
String name();
//Packing
Packing packing();
//Price
float price();
}Packing and its implementation classes
public interface Packing {
String pack();
}
public class Bottle implements Packing {
@Override
public String pack() {
return "Bottle";
}
}
public class Wrapper implements Packing {
@Override
public String pack() {
return "Wrapper";
}
}Burger class and its implementation class
public abstract class Burger implements Item {
@Override
public Packing packing() {
return new Wrapper();
}
}
public class ChickenBurger extends Burger {
@Override
public String name() {
return "ChickenBurger";
}
@Override
public float price() {
return 50.5f;
}
}
public class VegBurger extends Burger {
@Override
public String name() {
return "Veg Burger";
}
@Override
public float price() {
return 25.0f;
}
}ColdDrink class and its implementation class
public abstract class ColdDrink implements Item {
@Override
public Packing packing() {
return new Bottle();
}
}
public class Coke extends ColdDrink {
@Override
public String name() {
return "Coke";
}
@Override
public float price() {
return 10.5f;
}
}
public class Pepsi extends ColdDrink {
@Override
public String name() {
return "Pepsi";
}
@Override
public float price() {
return 11.5f;
}
}Meal Class
public class Meal {
private List<Item> items = new ArrayList<>();
public void addItem(Item item) {
items.add(item);
}
public float getCost() {
float cost = 0.0f;
for (Item item : items) {
cost += item.price();
}
return cost;
}
public void showItems() {
for (Item item : items) {
System.out.print("Item : " + item.name());
System.out.print(", Packing : " + item.packing().pack());
System.out.println(", Price : " + item.price());
}
}
}MealBuilder class
public class MealBuilder {
public Meal prepareVegMeal() {
Meal meal = new Meal();
meal.addItem(new VegBurger());
meal.addItem(new Coke());
return meal;
}
public Meal prepareNonVegMeal() {
Meal meal = new Meal();
meal.addItem(new ChickenBurger());
meal.addItem(new Pepsi());
return meal;
}
}Run Class
public class BuilderPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MealBuilder mealBuilder = new MealBuilder();
Meal vegMeal = mealBuilder.prepareVegMeal();
System.out.println("Veg Meal");
vegMeal.showItems();
System.out.println("Total Cost: " + vegMeal.getCost());
Meal nonVegMeal = mealBuilder.prepareNonVegMeal();
System.out.println("Non-Veg Meal");
nonVegMeal.showItems();
System.out.println("Total Cost: " + nonVegMeal.getCost());
}
}Differentiation from factory mode
The main job of factory mode is to create parts.
The main task of the Builder Mode is to assemble the parts that are created.