catalogue
1, Input and output
1. Format and modifier
| d,i | Decimal integer | int a=456;printf("%d",a); | 456 |
| x,X | Hexadecimal unsigned integer | int a= 255;printf("%x",a); | ff |
| o | Octal unsigned integer | int a=65;printf("%o",a); | 101 |
| u | Unsigned decimal integer | int a=211;printf("%u",a); | 211 |
| c | Single character | char a=65;printf("%c",a); | A |
| s | character string | printf("%s","Hello world") | Hello world |
| e,E | Floating point decimal in exponential form | float a = 456.789;printf("%e",a); | 4.567890e+2 |
| f | Decimal form floating point decimal | float a = 456.789;printf("%f",a); | 456.789000 |
| g | The shorter of e and f | float a = 456.789;printf("%g",a); | 456.789 |
| %% | Percent sign itself | printf("%%"); | % |
2.ASCII table
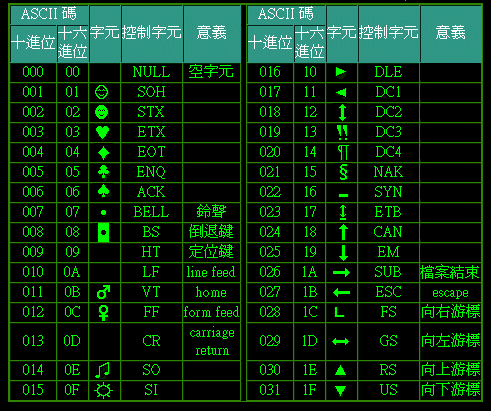
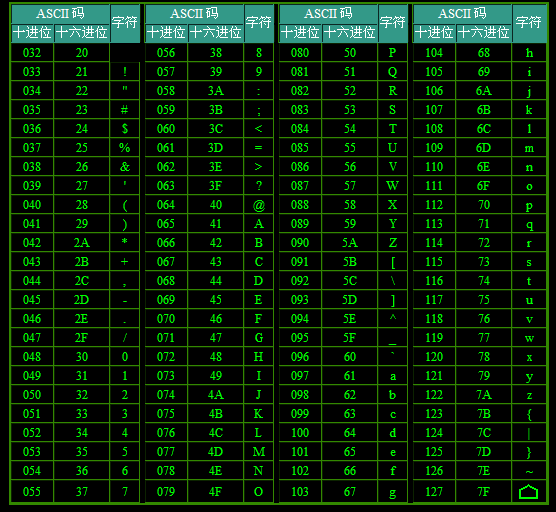
Common: 0 ¢ is empty ¢ 48 is 0 ¢ 65 is a , 97 is a
3.scanf and printf
scanf
scanf("format",&var);
format:% [modifier]
scanf puts the data into the input buffer
Return: the number of variables returned successfully
printf
printf("format",var);
format:% [modifier]
Return: the number of characters returned successfully
2, Process control
1. Branch statement
1).if else
Format: ① if (condition) {statement 1; statement 2;}
② if (condition) {statement 1; statement 2;}
else {statement 1; statement 2;}
③ if (condition 1) {statement 1; statement 2;}
Else if (condition 2) {statement 1; statement 2;}
else {statement 1; statement 2;}
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 1,b = 1;
if(a == b)
{
printf("a == b\n");
}
else
printf("a != b\n");
return 0;
}Output result: a ==b
Note: when nesting with if # else, if # else corresponds to. Else corresponds to the nearest if by default
If else exercise:
1. Implementation level judgment (score)
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int score;
scanf("%d",&score);
if(score<0||score>100)
{
printf("Input error\n");
}
if(score>=90 && score<=100)
{
printf("The student's grade is a\n");
}
if(score>=80 && score<90)
{
printf("The student's grade is b\n");
}
if(score>=70 && score<80)
{
printf("The student's grade is c\n");
}
if(score>=60 && score<70)
{
printf("The student's grade is d\n");
}
if(score<60)
{
printf("The student's grade is e\n");
}
return 0;
}
2. For the calculation of leap year, the conditions for judging whether it is a leap year: it can be divided by 4, but not by 100 or 400.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int year;
scanf("%d",&year);
if(year%4==0 && year%100!=0 || year%400==0)
{
printf("This year is a leap year\n");
}else
{
printf("This year is not a leap year\n");
}
return 0;
}2).switch case
switch(expression)
{
case constant integer 1: / / constant integer: 3 25 'a' \ n '2 + 3
;
;
break;
case constant shaping 2:
;
;
break;
...
default:
break;
}
switch part exercise:
1. According to the input letter, the animal information with the letter as the switch is output
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int ch;
ch = getchar();
switch(ch)
{
case 'a':
case 'A':
printf("Ant:a small insect which lives in group.\n");
break;
case 'b':
case 'B':
printf("Bee:a small flying insect which dangerous.\n");
break;
case 'c':
case 'C':
printf("Cobra:a type of snake which very dangerous.\n");
break;
case 'd':
case 'D':
printf("Donkey:a lovely animal which has long ears and shourt legs.\n");
break;
default:
printf("Input Error.\n");
break;
}
return 0;
}
2. Completion score grading
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int s;
scanf("%d",&s);
if(s > 100 || s < 0)
{
printf("Input error.\n");
return 1;
}
switch(s/10)
{
case 10:
case 9:
printf("A\n");
break;
case 8:
printf("B\n");
break;
case 7:
printf("C\n");
break;
case 6:
printf("D\n");
break;
default:
printf("E\n");
break;
}
return 0;
}
2. Circular statement
There are three conditions in the loop
/*Initialization, cycle established / not established, step change*/
① for (initialization; loop establishment condition; change) {}
Example: int i,sum = 0;
for( i=1 ; i <= 100; i++)
{
sum += i;
}
② while (loop establishment condition) {}
Example: int i=0,sum = 0;
while(i <= 100)
{
sum += i;
i++;
}
③ Do {} while (loop establishment condition)
Example: int i=0,sum = 0;
do
{
sum += i;
i++;
}while(i <= 100);
Loop part exercise:
Introduction of nested loop: output of 99 multiplication table.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i=1;i<10;i++)
{
for(int j = 1;j<i+1;j++)
{
printf("%d*%d=%-5d",j,i,i*j);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}Note: This article is based on the notes taken by teacher Li Huiqin in class. If you don't understand it in place, please forgive me and give me more advice.