Article directory
STL (Standard Template Library) is the standard template library of C + +. Many common data structures and algorithms in the competition are available in STL. Mastering them skillfully can greatly simplify programming in many topics.
The vector container is a template class that can hold any type of object.
vector: dynamic array, which can be quickly inserted and deleted from the end, directly accessing any element
I. definition
- Define an int array (also char, double, etc.)
#include<iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; int main() { vector< int >a;//Default initialization, a is empty vector< int >b(a);//Using a to define b vector< int >a(100);//A has 100 elements with a value of 0 vector< int >a(100,6);//A has 100 elements with a value of 6 }
- Defining an array of type string
#include<iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; int main() { vector< string >a(10,"null");//10 elements with null values; vector< string >vec(10,"hello");//10 elements with a value of hello vector< string >b(a.begin(),a.end());//b is a copy of a }
- Defining structural arrays
#include<iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; struct point{ int x,y; }; int main() { vector< point >a;//a is used to store coordinates }
- Define 2D array
vector<int>a[5];
Its one dimension size is fixed, the second dimension is dynamic, and it can also define multidimensional array
Simple application:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<vector>//May not write using namespace std; int main() { vector<int>a[10]; for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { for(int j=0;j<4;j++) { a[i].push_back(5); } } for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { for(int j=0;j<4;j++) { cout<<a[i][j]<<" "; } cout<<endl; } }
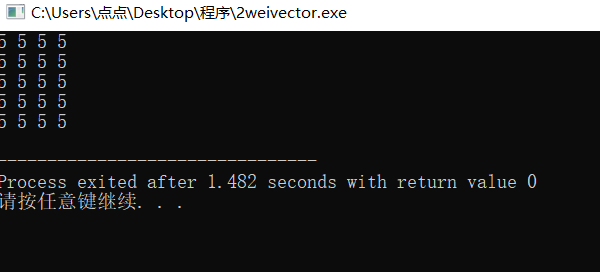
2, Common operations
- Assignment: add element at the end
a.push_back(1);
- Element number
int size; size=a.size(); cout<<size;
- Judge whether it is empty
bool isEmpty; isEmpty=a.empty(); cout<<isEmpty;//If it is empty, return 1, otherwise return 0
- Print first element
cout<<a[0]<<endl;
- Insert in the middle: insert k before the i-th element
a.insert(a.begin()+i,k);
- Tail insertion
Insert single element
a.push_back(100);
Insert multiple elements
a.push_back(10,5);
- Delete tail
a.pop_back();
- Delete interval: delete the element of interval [I, J-1]
a.erase(a.begin()+i,a.begin()+j);//Elements i to j-1 are deleted
- Delete element: delete the i+1 element
a.erase(a.begin()+i);
- Resize: array size to n
a.resize(n);
- Sorting: from small to large (based on fast sorting)
sort(a.begin,a.end);
- Flipped array
reverse(a.begin,a.end);
- empty
a.clear();
3, Code implementation
The following is the code implementation result and detailed code corresponding to the above: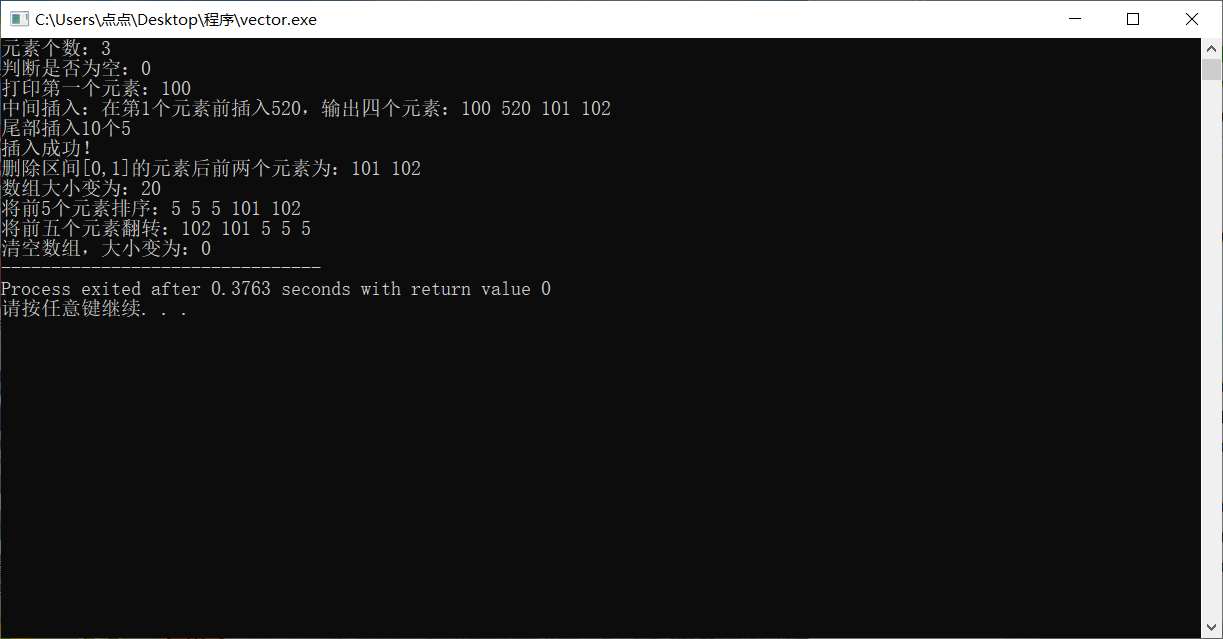
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<vector> using namespace std; int main() { vector<int>a; a.push_back(100); a.push_back(101); a.push_back(102); cout<<"Number of elements:"; int size=a.size(); cout<<size<<endl; cout<<"Judge whether it is empty:"; bool isEmpty=a.empty(); cout<<isEmpty<<endl; cout<<"Print the first element:"; cout<<a[0]<<endl; cout<<"Middle insertion:"; a.insert(a.begin()+1,520); cout<<"Insert 520 before the first element and output four elements:"; cout<<a[0]<<" "<<a[1]<<" "<<a[2]<<" "<<a[3]<<endl; cout<<"Tail insert 10 5"<<endl; a.insert(a.end(),10,5); cout<<"Insert successfully!"<<endl; cout<<"Delete interval[0,1]The first two elements are:"; a.erase(a.begin()+0,a.begin()+2); cout<<a[0]<<" "<<a[1]<<endl; cout<<"The array size changes to:"; a.resize(20); cout<<a.size()<<endl; cout<<"Sort the first five elements:"; sort(a.begin(),a.begin()+5); cout<<a[0]<<" "<<a[1]<<" "<<a[2]<<" "<<a[3]<<" "<<a[4]<<endl; cout<<"Flip the first five elements:"; reverse(a.begin(),a.begin()+5); cout<<a[0]<<" "<<a[1]<<" "<<a[2]<<" "<<a[3]<<" "<<a[4]<<endl; cout<<"Empty the array and change the size to:"; a.clear(); cout<<a.size(); }

