catalogue
3, Configure master node masterdb
4, Configure slave node slavedb
5, Validate database master-slave service
1, Installation environment preparation
1. Node planning
Prepare two virtual hosts to act as master dB and slave DB respectively
| IP address | Host name | node |
| 192.168.18.8 | masterdb | Master database node |
| 192.168.18.88 | slavedb | From database node |
2. Master database node settings
[root@red3212 ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname masterdb
[root@red3212 ~]# exit
[root@master ~]# hostnamectl
Static hostname: masterdb
Icon name: computer-vm
Chassis: vm
Machine ID: 651d4c1ca62b4b45aa3f2adb5bfd2230
Boot ID: 75e152eb882c4428b12fe310c4bf91ae
Virtualization: vmware
Operating System: CentOS Linux 8
CPE OS Name: cpe:/o:centos:centos:8
Kernel: Linux 4.18.0-240.el8.x86_64
Architecture: x86-64
[root@masterdb ~]# ifconfig ens33
ens33: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.18.8 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.18.255
inet6 fe80::5fa9:b95a:e382:5831 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:82:a2:fe txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 34325 bytes 47142373 (44.9 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 14183 bytes 1298293 (1.2 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 03. Set from database node
[root@red3212 ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname slavedb
[root@red3212 ~]# exit
[root@slavedb ~]# hostnamectl
Static hostname: slavedb
Icon name: computer-vm
Chassis: vm
Machine ID: d8c2c33a40804fb4abf233975a7e17e5
Boot ID: f72a0bf6ede743f9a8fc1f8606bbeef1
Virtualization: vmware
Operating System: CentOS Linux 8
CPE OS Name: cpe:/o:centos:centos:8
Kernel: Linux 4.18.0-240.el8.x86_64
Architecture: x86-64
[root@slavedb ~]# ifconfig ens33
ens33: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.18.88 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.18.255
inet6 fe80::444d:4556:783:d78f prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:60:ad:70 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 91 bytes 12341 (12.0 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 147 bytes 19041 (18.5 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 04. Configuring firewalls and SELinux services
Although you can directly turn off the firewall (systemctl stop firewalld) and SELinux service (setenforce0), this is not recommended in practical applications.
Both the master and slave nodes execute the following commands for configuration
[root@masterdb ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=mysql success [root@masterdb ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success
5. Configure hosts file
Both nodes are configured as follows
[root@masterdb ~]# vim /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 192.168.18.8 masterdb 192.168.18.88 slavedb
6. Configure local software warehouse
Ensure that the optical drive of the virtual machine remains connected, and use the ISO image file of CentOS8, as shown in the following figure
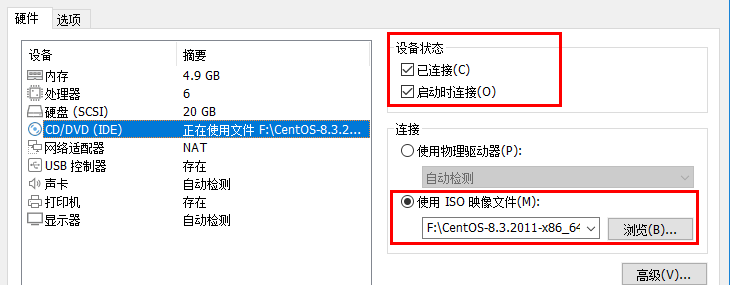
Then create and edit the local software warehouse, and both nodes do the following
[root@masterdb ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/local.repo [centos-appstream] name=centos8-appstream baseurl=file:///opt/centos8/AppStream gpgcheck=0 enabled=1 [centos-baseos] name=centos8-baseos baseurl=file:///opt/centos8/BaseOS gpgcheck=0 enabled=1
Mount the local software warehouse, and both nodes perform the following operations
[root@masterdb ~]# mkdir -p /media/cdrom [root@masterdb ~]# mount /dev/cdrom /media/cdrom mount: /media/cdrom: WARNING: device write-protected, mounted read-only.
7. Install the MariaDB database service program, and both nodes perform the following operations
[root@masterdb ~]# dnf -y install mariadb mariadb-server
8. Start and set the startup self startup mariadb service. Both nodes perform the following operations
[root@masterdb ~]# systemctl start mariadb [root@masterdb ~]# systemctl enable mariadb Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/mysql.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service. Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/mysqld.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service. Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mariadb.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service.
2, Initialize database
To initialize the database, both nodes perform the following operations
[root@masterdb ~]# mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none): #By default, press Enter directly
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] y #Enter y to set the password of the database administrator root
New password: #Enter a password, such as 666666
Re-enter new password: #Enter the password again, such as 666666
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y #Enter y to delete the database anonymous account
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] n #Enter n to allow root remote login
... skipping.
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y #Enter y to delete the test database
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y #Enter y to reload the authorization table
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!3, Configure master node masterdb
1. Modify the database configuration file / etc / my cnf. d/mariadb-server. CNF, add the following last three lines.
[root@masterdb ~]# vim /etc/my.cnf.d/mariadb-server.cnf
......Some information is omitted here
[mysqld]
datadir=/var/lib/mysql
socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
log-error=/var/log/mariadb/mariadb.log
pid-file=/run/mariadb/mariadb.pid
log_bin = mysql-bin #Record operation log
binlog_ignore_db = mysql #Out of sync mysql system database
server_id=8 #Each node ID in the database cluster is different
#server_id is generally the value of the last field of the server IP address. For example, 192.168.18.8 is 8
......Some information is omitted here2. Restart the database service and enter the database
[root@masterdb ~]# systemctl restart mariadb.service [root@masterdb ~]# mysql -u root -p666666 Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 10 Server version: 10.3.28-MariaDB-log MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]>
3. Establish an account on the master node and authorize the slave
Authorization on the master node allows the root user to log in to the database on any client machine, creates a database user named zhangsan on the master node, and authorizes the account to connect to all slave nodes. Here, you can also replace% with the specific slave node host name or IP, and give the slave node the right to synchronize the master node database.
Note:% indicates all hosts.
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on *.* to root@'%' identified by '666666'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.001 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> grant replication slave on *.* to 'zhangsan'@'%' identified by '666666'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.000 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> show master status; +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | mysql-bin.000001 | 709 | | mysql | +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ 1 row in set (0.001 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> exit Bye
4, Configure slave node slavedb
1. Like the master node, make sure to complete the installation, startup, initialization and firewall configuration of the previous database mariadb, and then modify the / etc/hosts file.
2. Next, modify the database configuration file / etc / my cnf. d/mariadb-server. CNF, add the last three lines as shown below.
[root@slavedb ~]# vim /etc/my.cnf.d/mariadb-server.cnf
......Some information is omitted here
[mysqld]
datadir=/var/lib/mysql
socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
log-error=/var/log/mariadb/mariadb.log
pid-file=/run/mariadb/mariadb.pid
log_bin = mysql-bin #Record operation log
binlog_ignore_db = mysql #Out of sync mysql system database
server_id=88 #Each node ID in the database cluster is different
#server_ The ID value is generally the value of the last field of the server IP address, and the value is 88 when the node IP is 192.168.18.88
......Some information is omitted here3. Configure login to database on slave node
Master among them_ Host is used to specify the host name of the primary node, master_user is used to specify the user account created and authorized in the master node, master_password is the corresponding account password.
[root@slavedb ~]# systemctl restart mariadb.service [root@slavedb ~]# mysql -u root -p666666 Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 9 Server version: 10.3.28-MariaDB-log MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]> change master to master_host='masterdb',master_user='zhangsan',master_password='666666'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.004 sec)
4. Enable slave node service
MariaDB [(none)]> start slave;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.001 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> show slave status \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Slave_IO_State: Waiting for master to send event
Master_Host: masterdb
Master_User: zhangsan
Master_Port: 3306
Connect_Retry: 60
Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000002
Read_Master_Log_Pos: 1111
Relay_Log_File: mariadb-relay-bin.000003
Relay_Log_Pos: 1410
Relay_Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000002
Slave_IO_Running: Yes
Slave_SQL_Running: Yes
Replicate_Do_DB:
Replicate_Ignore_DB:
Replicate_Do_Table:
Replicate_Ignore_Table:
Replicate_Wild_Do_Table:
Replicate_Wild_Ignore_Table:
Last_Errno: 0
Last_Error:
Skip_Counter: 0
Exec_Master_Log_Pos: 1111
Relay_Log_Space: 2473
Until_Condition: None
Until_Log_File:
Until_Log_Pos: 0
Master_SSL_Allowed: No
Master_SSL_CA_File:
Master_SSL_CA_Path:
Master_SSL_Cert:
Master_SSL_Cipher:
Master_SSL_Key:
Seconds_Behind_Master: 0
Master_SSL_Verify_Server_Cert: No
Last_IO_Errno: 0
Last_IO_Error:
Last_SQL_Errno: 0
Last_SQL_Error:
Replicate_Ignore_Server_Ids:
Master_Server_Id: 8
Master_SSL_Crl:
Master_SSL_Crlpath:
Using_Gtid: No
Gtid_IO_Pos:
Replicate_Do_Domain_Ids:
Replicate_Ignore_Domain_Ids:
Parallel_Mode: conservative
SQL_Delay: 0
SQL_Remaining_Delay: NULL
Slave_SQL_Running_State: Slave has read all relay log; waiting for the slave I/O thread to update it
Slave_DDL_Groups: 6
Slave_Non_Transactional_Groups: 0
Slave_Transactional_Groups: 0
1 row in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> exit
ByeIf Slave_IO_Running and slave_ SQL_ When the running status is Yes, it indicates that the master-slave database cluster configuration is successful.
5, Validate database master-slave service
1. Create database on master node
First, create the database test in the master node masterdb, create the table company in the database test, insert the table data, and view the table comany data after creation
[root@masterdb ~]# mysql -u root -p666666 Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 41 Server version: 10.3.28-MariaDB-log MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]> create database test; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.000 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> use test; Database changed MariaDB [test]> create table company (id int not null primary key, name varchar(50),addr varchar(255)); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.061 sec) MariaDB [test]> insert into company values(1,"Baidu","BeiJing"); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.013 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from company; +----+-------+---------+ | id | name | addr | +----+-------+---------+ | 1 | Baidu | BeiJing | +----+-------+---------+ 1 row in set (0.001 sec)
2. Verify the data synchronization function on the slave node
Log in to the slave slavedb node's database and view the database list. Find the test database, query the table and the data in it.
[root@slavedb ~]# mysql -u root -p666666 Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 15 Server version: 10.3.28-MariaDB-log MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | mysql | | performance_schema | | test | +--------------------+ 4 rows in set (0.001 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> use test; Reading table information for completion of table and column names You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A Database changed MariaDB [test]> show tables; +----------------+ | Tables_in_test | +----------------+ | company | +----------------+ 1 row in set (0.000 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from company; +----+-------+---------+ | id | name | addr | +----+-------+---------+ | 1 | Baidu | BeiJing | +----+-------+---------+ 1 row in set (0.000 sec)
It can be seen that the master-slave database data can be synchronized successfully.