catalogue
1, Concept of array (including some shortcut key usage)
1, Concept of array (including some shortcut key usage)
A collection of multiple data of the same type arranged in a certain order
1. Characteristics of array:
1) orderly arrangement
2) the array is a variable of reference data type. The elements of an array can be either basic data types or reference data types. [array is a reference, and the elements of the array are basic or reference]
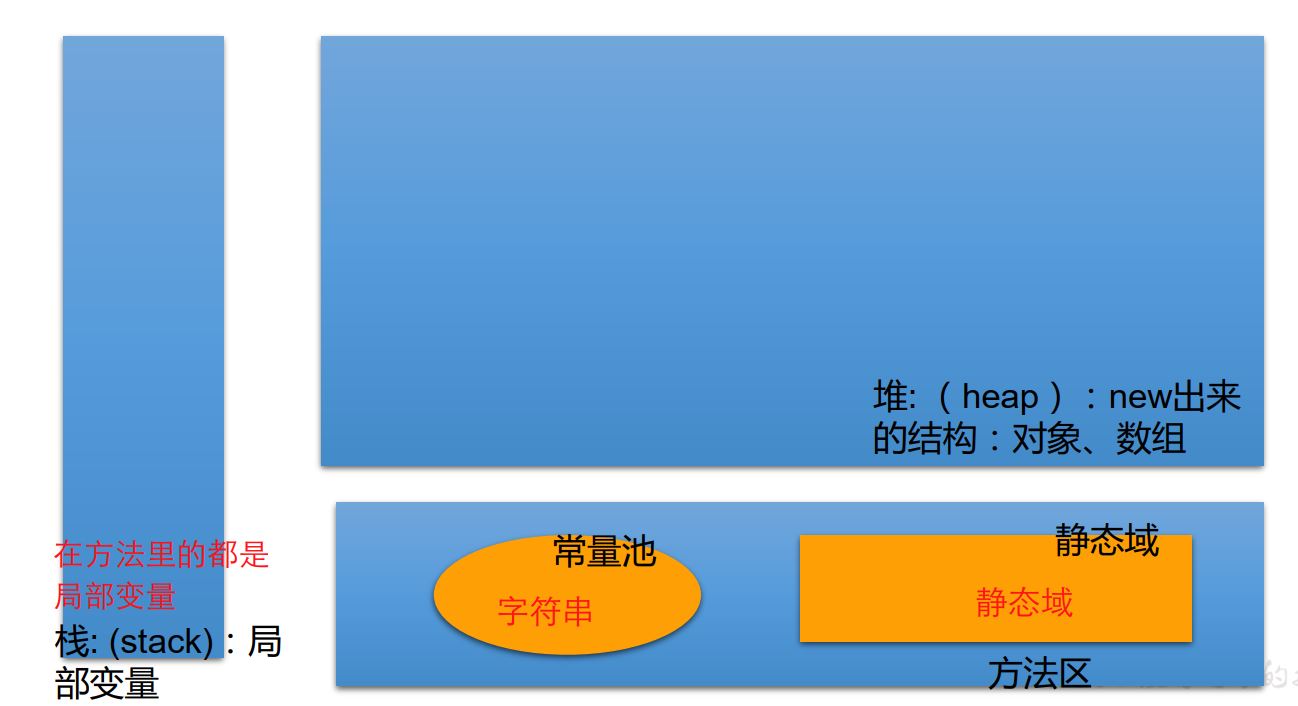
3) creating an array object will open up a whole block of continuous space in memory
4) once the length of the array is determined, it cannot be modified.
2. Array classification:
① according to dimension: one-dimensional array, two-dimensional array...
② according to the type of array elements: array of basic data type elements and array of reference data type elements
3. Use of one-dimensional array
① declaration and initialization of one-dimensional array
int[] ids;//statement
//1.1 static initialization: the initialization of array and the assignment of array elements are performed [simultaneously]
ids = new int[]{1001,1002,1003,1004};
//1.2 dynamic initialization: the initialization of array and the assignment of array elements are performed [separately]
String[] names = new String[5];//[[] means that the names variable is of array type]
//Incorrect wording:
// int[] arr1 = new int[]; Neither the array element nor the array length is assigned
// int[5] arr2 = new int[5];
// int[] arr3 = new int[3]{1,2,3}; movement
//It is also the correct way to write:
int[] arr4 = {1,2,3,4,5};//Type inference
int[] ids;
//1.1 static initialization
ids = new int[]{1001,1002,1003,1004};//[all new structures are opened in heap space]
System.out.println(ids);//[I@15db9742
//1.2 dynamic initialization
String[] names = new String[5];//The length is 5, starting from 0, 0 ~ 4
names[0] = "Zhang San";
names[1] = "Li Si";//Get the first Lee of the four string of Lee and use charAt(0)
names[4] = "Wang Wu";//[copy: ctrl+alt +]
② how to call the element at the specified position of the array
names[4] = "Wang Hongzhi";//charAt(0) get King // System.out.println(names[0]);// Single line comment: ctrl+/ // System.out.println(names[1]);// Multiline comment: ctrl+shift+/ // System.out.println(names[2]);// Delete multiline comment: ctrl+shift+\
③ how to get the length of the array
//Attribute: length System.out.println(names.length);//5 System.out.println(ids.length);
④ how to traverse the array
for(int i = 0;i < names.length;i++){
System.out.println(names[i]);
}
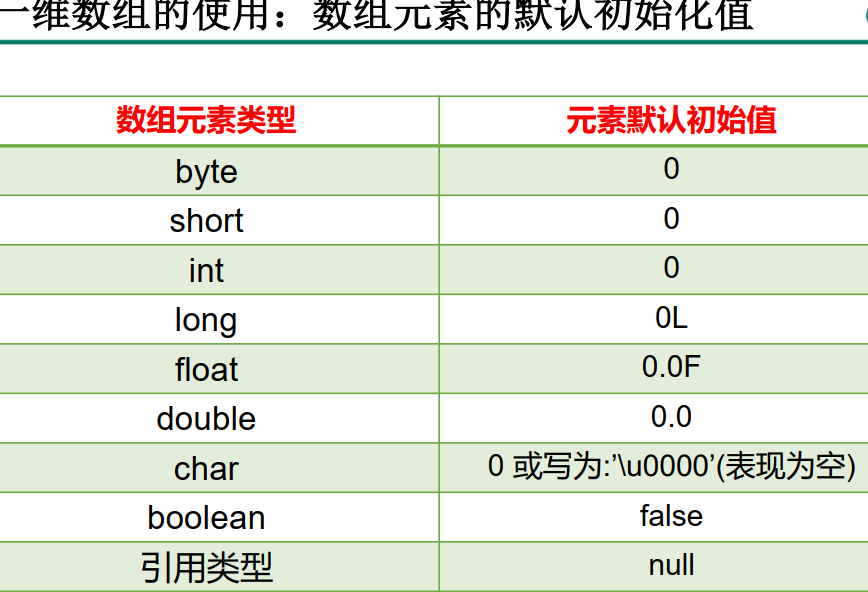
⑤ default initialization value of array elements:
>Array element is integer: 0
> array elements are floating point: 0.0
> array elements are char type: 0 or '\ u0000', not '0'
'a' ascii code is 97
'0' ...
... Is 0 [the default value of char array element is 0, and the output effect is like a space]
- yes
> array elements are boolean type: false [the bottom layer is binary, and false uses 0 as]
> array element is a reference data type: null null null value [not "null", "null" is a string]
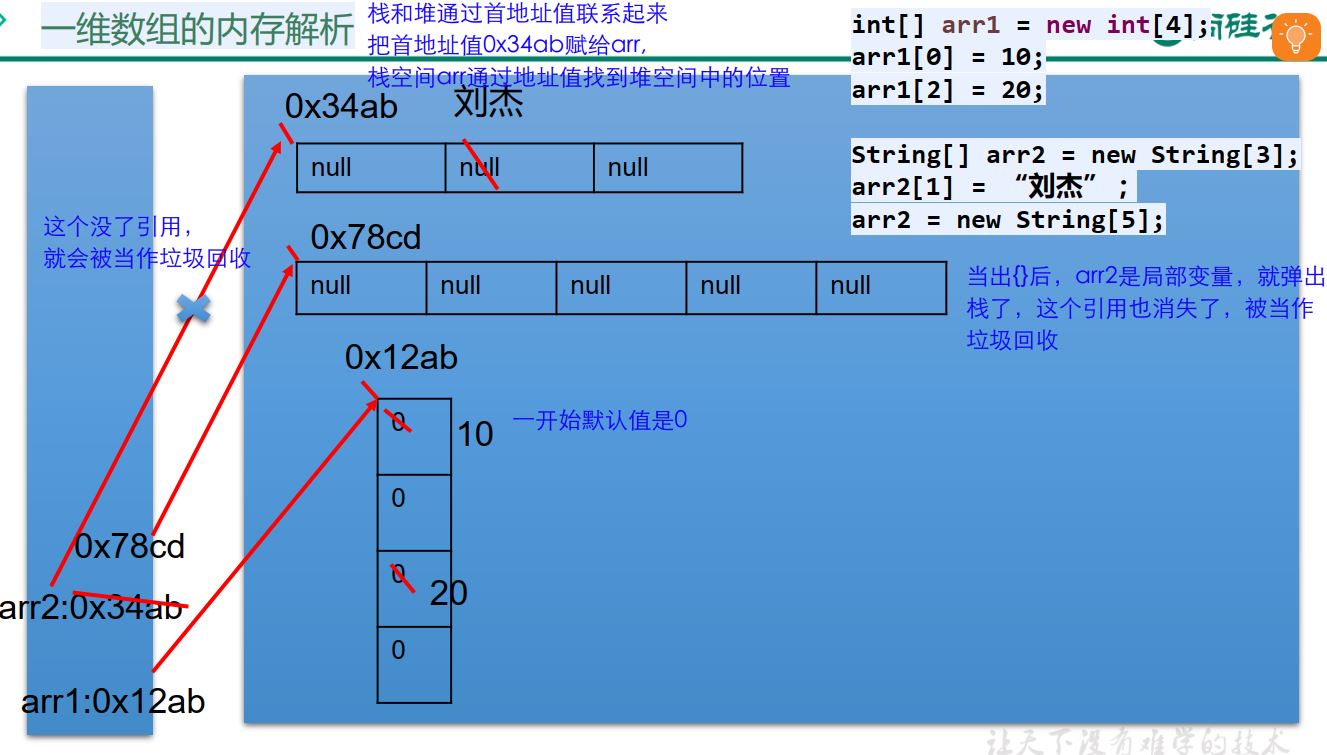
⑥ memory parsing of array:
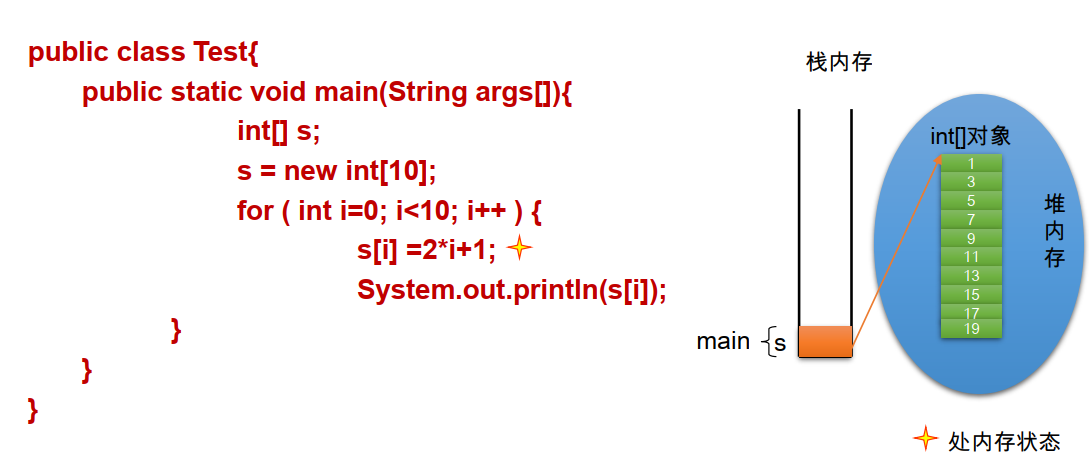
After main {}, s pops up from the stack, the arrow disappears and the int [] object disappears
practice
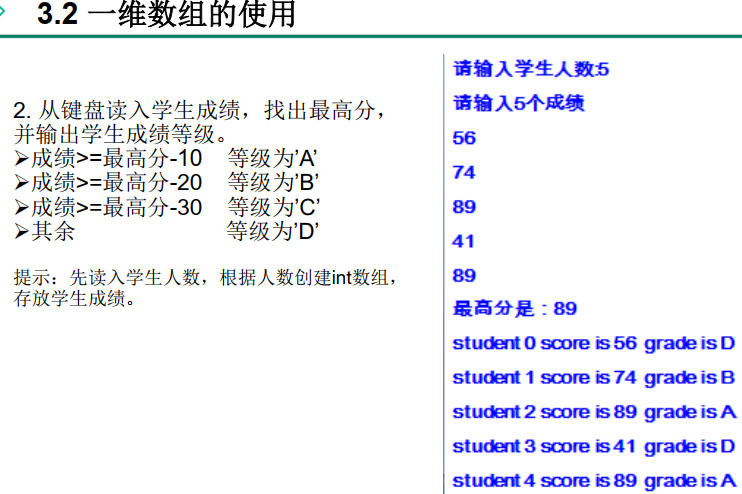
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Double click arraydemo1 Java, the window becomes larger or smaller
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);//Automatic package Guide: ctrl+shift+o
System.out.println("Please enter the number of students:");
//No matter where the cursor is, wrap down: shift+enter
//Wrap up: ctrl+shift+enter
int number = scanner.nextInt();//Automatically supplement variable name and type: ctrl+1
int[] scores = new int[number];
System.out.println("input" + number + "Student grades:");
int maxScore = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < scores.length;i++){
scores[i] = scanner.nextInt();
if(maxScore < scores[i]){
maxScore = scores[i];
}
}
/* //Gets the maximum value of an array element
int maxScore = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < scores.length;i++){
if(maxScore < scores[i]){
maxScore = scores[i];
}
}*/
char level;
for(int i = 0;i < scores.length;i++){
if(maxScore - scores[i] <= 10) {
level = 'A';
}else if(maxScore - scores[i] <= 20){
level = 'B';
}else if(maxScore - scores[i] <= 30){
level = 'C';
}else{
level = 'D';
}
System.out.println("student " + i +
" score is " + scores[i] + " ,grade is " + level);
}
}2, Two dimensional array
[array is a reference data type (class, interface, array). The elements of array can be basic data type or reference data type (array). Two dimensional array is: one-dimensional array, elements of one-dimensional array or array]
1. Understand:
For the understanding of two-dimensional array, we can see that one-dimensional array array1 exists as an element of another one-dimensional array array2.
In fact, from the perspective of the underlying operation mechanism of the array, there is no multidimensional array.
*
* 2. Use of two-dimensional array:
* ① declaration and initialization of two-dimensional array
//1. Declaration and initialization of two-dimensional array
int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3};//One dimensional array
//initiate static
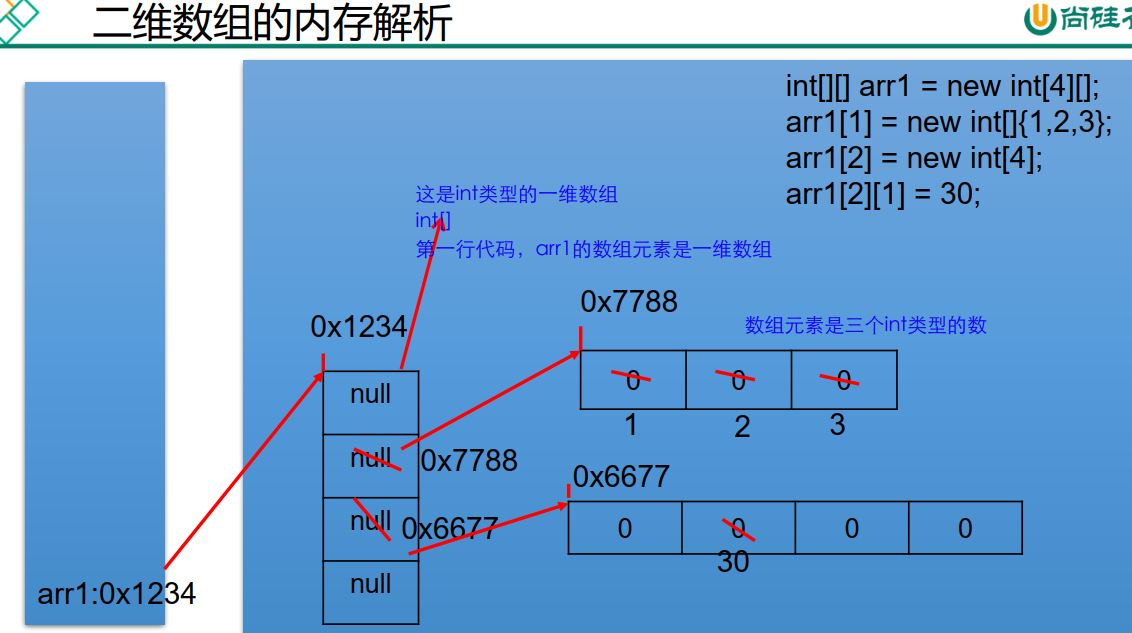
int[][] arr1 = new int[][]{{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7,8}};
//Dynamic initialization 1
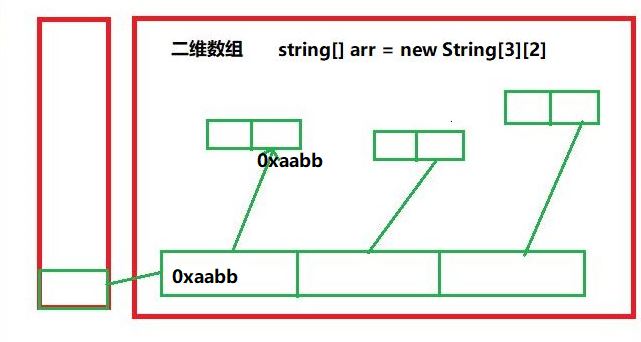
String[][] arr2 = new String[3][2];
//Dynamic initialization 2
String[][] arr3 = new String[3][];
//Wrong situation
// String[][] arr4 = new String[][4];
// String[4][3] arr5 = new String[][];
// int[][] arr6 = new int[4][3]{{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7,8}};
//It is also the correct way to write:
int[] arr4[] = new int[][]{{1,2,3},{4,5,9,10},{6,7,8}};
int[] arr5[] = {{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7,8}};
② how to call the element at the specified position of the array
System.out.println(arr1[0][1]);//2 System.out.println(arr2[1][1]);//Null [the element is of String (Reference) type, and the initialization value is null] System.out.println(arr3[1]); //null [not yet given arr3[1] = new String[4]; //At this time, the array with length of 4 does not exist, so there is no address value. There is no arrow emitted in arr[3], so it is null] //[key understanding] arr3[1] = new String[4]; System.out.println(arr3[1][0]);
③ how to get the length of the array
System.out.println(arr4.length);//3 [because there is no multidimensional array and arr4 is a one-dimensional array, the array length is 3, figure] System.out.println(arr4[0].length);//3 System.out.println(arr4[1].length);//4
④ how to traverse the array
for(int i = 0;i < arr4.length;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < arr4[i].length;j++){
System.out.print(arr4[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
⑤ default initialization value of array elements
Regulation: the two-dimensional array is divided into the elements of the outer array and the elements of the inner array.
[because the initialization values of inner and outer elements are different]
int[][] arr = new int[4][3];
Outer elements: arr[0],arr[1], etc
Inner elements: arr[0][0],arr[1][2], etc
For initialization method 1: for example: int[][] arr = new int[4][3];
The initialization value of the outer element is: address value
The initialization value of the inner element is: the same as that of the one-dimensional array
For initialization mode 2: for example: int[][] arr = new int[4] [];
The initialization value of the outer element is null
The initialization value of the inner element is: it cannot be called, otherwise an error will be reported.
//Source - > format, shortcut key for adjusting format: ctrl+shift+f
int[][] arr = new int[4][3];
System.out.println(arr[0]);//[ I@15db9742 One [represents one dimension, I represents int type, @ hexadecimal
//[analog output one-dimensional array System.out.println(arr);]
System.out.println(arr[0][0]);//0
// System.out.println(arr);//[[I@6d06d69c [[2D array
System.out.println("*****************");
float[][] arr1 = new float[4][3];
System.out.println(arr1[0]);//Address value
System.out.println(arr1[0][0]);//0.0
System.out.println("*****************");
String[][] arr2 = new String[4][2];
System.out.println(arr2[1]);//Address value
System.out.println(arr2[1][1]);//null
System.out.println("*****************");
double[][] arr3 = new double[4][];//[the initialization method is changed, and the second [] is not filled in]
System.out.println(arr3[1]);//null
// System.out.println(arr3[1][0]);// [error reporting]
⑥ memory parsing of array:
Practice

III. Arrays tools
java.util.Arrays: a tool class for manipulating arrays, which defines many methods for manipulating arrays
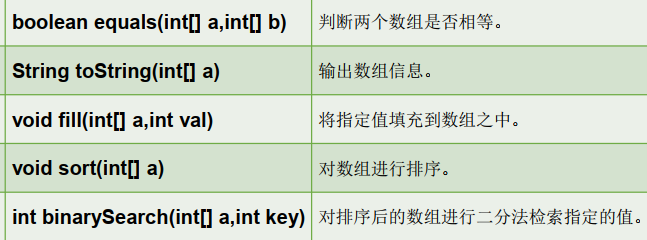
//1.boolean equals(int[] a,int[] b): judge whether two arrays are equal.
int[] arr1 = new int[]{1,2,3,4};
int[] arr2 = new int[]{1,3,2,4};
boolean isEquals = Arrays.equals(arr1, arr2);
System.out.println(isEquals);
//2.String toString(int[] a): output array information.
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
//3.void fill(int[] a,int val): fill the specified value into the array.
Arrays.fill(arr1,10);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
//4.void sort(int[] a): sort the array.
Arrays.sort(arr2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
//5.int binarySearch(int[] a,int key)
int[] arr3 = new int[]{-98,-34,2,34,54,66,79,105,210,333};
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(arr3, 210);
if(index >= 0){
System.out.println(index);
}else{
System.out.println("not found");
}4, Array exception
* 1. Exception of array subscript out of bounds: ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
*
* 2. Null pointer exception: NullPointerException
//1. Exception of array subscript out of bounds: ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};
// for(int i = 0;i <= arr.length;i++){
// System.out.println(arr[i]);
// }
// System.out.println(arr[-2]);
//2.2. Null pointer exception: NullPointerException
//Case 1:
// int[] arr1 = new int[]{1,2,3};
// arr1 = null;// [Arr1 in the stack has no address, and the arrow (the arrow is the pointer) cannot point to the heap]
// System.out.println(arr1[0]);
//Case 2:
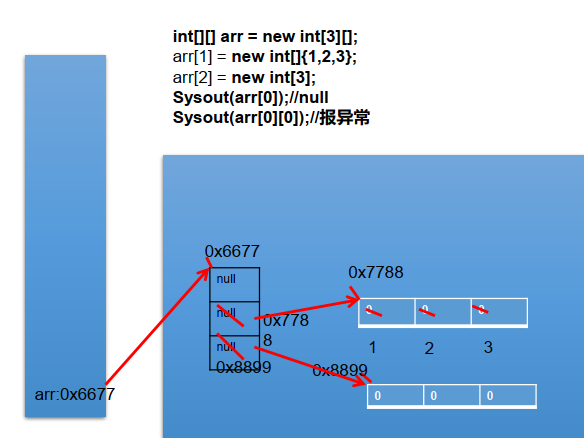
// int[][] arr2 = new int[4][];
//[draw the figure below.
//The initialization value is not firm. The value of arr2[1] is not an address value, but null. Before one-dimensional array is initialized, there is no address value assigned to two-dimensional array]
// System.out.println(arr2[0][0]);//arr2[0] is null, no address, no arrow, null pointer
//Case 3:
String[] arr3 = new String[]{"AA","BB","CC"};
arr3[0] = null;
System.out.println(arr3[0].toString());//Null causes null pointers