Catalogue of series articles
Chapter 4: building RabbitMQ cluster
Article catalogue
preface
Tip: rabbitmq cluster setup.
Tip: the following is the main content of this article. The following cases can be used for reference
1, Preparatory work
First, build many independent RabbitMQ, which can be installed using the pagoda graphical page or by yourself Assuming that two servers have been set up separately, data exchange between servers is required at this time.
2, Cluster construction
1. Cluster building steps
Set server alias
- Server 1: hostnamectl set‐hostname m1 - Server 2: hostnamectl set‐hostname m2
Unify Erlang in m1 server The cookie value in the cookie file will be the value in m1 erlang. Sync cookies to m2
scp /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie m2:/var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie
Note: ip can also be used in m2 the above command Adding nodes to rabbitmq cluster: restart the rabbitmq service in m2 machine and execute it in m2
#Stop user request rabbitmqctl stop_app #Merge m2 into cluster rabbitmqctl join_cluster ‐‐ram rabbit@m2 #Open user request rabbitmqctl start_app #Open the management page rabbitmq‐plugins enable rabbitmq_management #Restart service systemctl restart rabbitmq‐server.service
View cluster information
rabbitmqctl cluster_status
2. Cluster setup load balancing - HAProxy setup
Perform installation
#1. Install yum install haproxy #2. Configure haproxy Refer to the following configuration for the cfg file: haproxy VIM / etc / haproxy / haproxy cfg. Enter the file, find maxconn 3000, delete the following contents, add cluster monitoring, and start haproxy monitoring service. The code is as follows:
#Monitor the MQ cluster
listen rabbitmq_cluster
bind 0.0.0.0:5672
option tcplog
mode tcp
option clitcpka
timeout connect 1s
timeout client 10s
timeout server 10s
balance roundrobin
server node1 Node 1 ip address:5672 check inter 5s rise 2 fall 3
server node2 Node 2 ip address:5672 check inter 5s rise 2 fall 3
#Start haproxy monitoring service
listen http_front
bind 0.0.0.0:1080
stats refresh 30s
stats uri /haproxy_stats
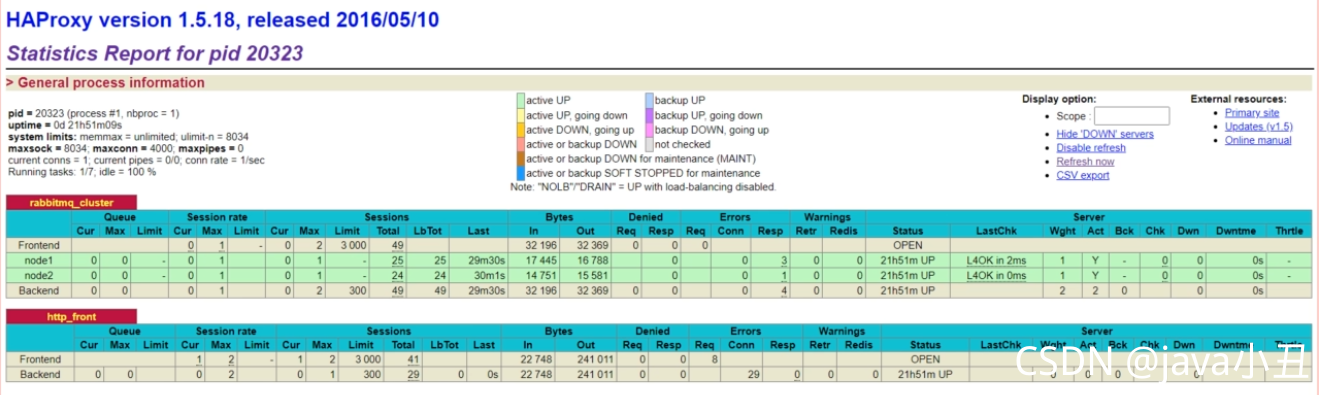
stats auth admin:admin#3. Start haproxy systemctl start haproxy #4. View the haproxy process status systemctl status haproxy service #The status is as follows: it has been started successfully: active (running) #Access the following address to monitor the mq node http: / / server IP:1080/haproxy_stats #If you access the mq cluster address in the code, you will access the haproxy address: 5672
haproxy.cfg configuration details
listen rabbitmg cluster
bind 0.0.0.0:5672#Map M1 and M2 through 5672
option tcplog #Record the status and time of tcp connection
mode tcp#Four layer protocol proxy, that is, forwarding TCP protocol
option clitcpka #Turn on Keep Alive.TCP (long connection mode)
timeout connect 1s #Timeout of establishing connection between haproxy and mq
timeout client 10s#Maximum idle time between client and haproxy.
timeout server 10s #Maximum idle time between server and haproxy
balance roundrobin #Use polling to forward messages
#Send a heartbeat packet every 5 seconds. If there is a response twice in a row, it means that it is in good condition.
#If there is no response for three consecutive times, it will be regarded as a service failure and the node will be eliminated.
server node1 ip1:5672 check inter 5s rise 2 fall 3
server node2 ip2:5672 check inter 5s rise 2 fall 3
listen http front
#Listening port
bind 0.0.0.0:1080
#Statistics page automatic refresh time stats refresh 30s
#Statistics page url
stats uri /haproxy?stats
#Specify the HAproxy access user name and password settings
stats auth admin:adminAt this time, you can connect through haproxy proxy. Of course, haproxy also has its own management page, that is, you can directly access the ip of the server and the configured 1080 port. Of course, HA can also be configured with multiple servers.
summary
Tip: here is a summary of the article: For example, the above is what we want to talk about today. This article only briefly introduces the construction of RabbitMQ cluster and HAProxy proxy.