Preface
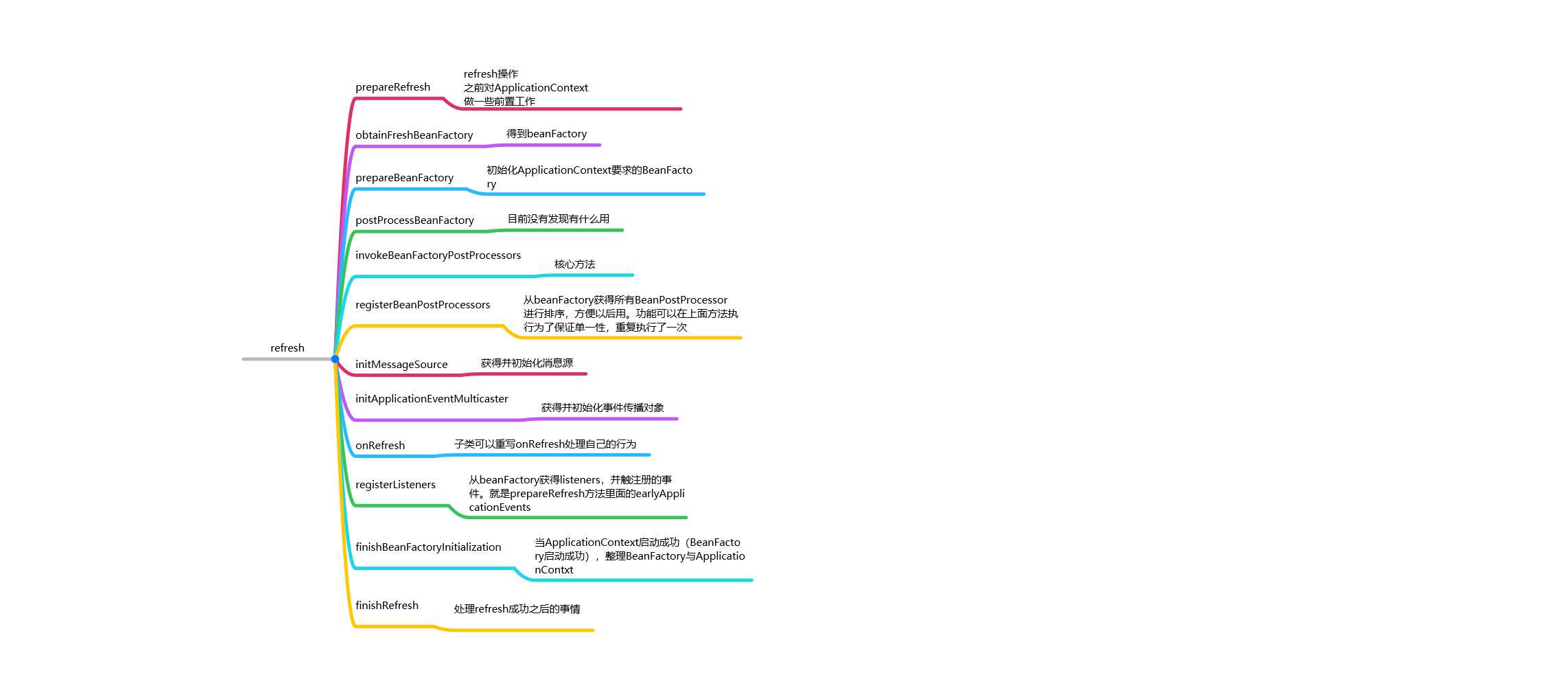
refresh is the core method of ApplicationContext, if you do this method, the ApplicationContext is all done.
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { prepareRefresh(); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); initMessageSource(); initApplicationEventMulticaster(); onRefresh(); registerListeners(); finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); finishRefresh(); }catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } destroyBeans(); cancelRefresh(ex); throw ex; }finally { resetCommonCaches(); } } }
prepareRefresh
Declare and implement AbstractApplicationContext class
protected void prepareRefresh() { // Start-up time this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis(); // Whether to go out and close this.closed.set(false); // Whether it's active or not is important. this.active.set(true); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Refreshing " + this); } initPropertySources(); // Verification Configuration getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties(); // Early events this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<ApplicationEvent>(); }
initPropertySources
InitProperty Sources states that in AbstractApplication Context, which is rewritten by AbstractRefreshable Web Application Context and Generic Web Application Context, you can simply add the web servletContext and servletConfig to the configuration.
protected void initPropertySources() { // For subclasses: do nothing by default. }
GenericWebApplicationContext
protected void initPropertySources() { ConfigurableEnvironment env = getEnvironment(); if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) { ((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(this.servletContext, null); } }
AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext
protected void initPropertySources() { ConfigurableEnvironment env = getEnvironment(); if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) { ((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(this.servletContext, this.servletConfig); } }
obtainFreshBeanFactory
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { refreshBeanFactory(); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory); } return beanFactory; }
refreshBeanFactory
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { if (hasBeanFactory()) { // To refresh, all bean s must fail destroyBeans(); // close down a factory closeBeanFactory(); } try { // Create bean s. Students who have read the BeanFactory series should know that they will create that object. DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); // For the content of customize BeanFactory, see the section in the BeanFactory series customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); } }
loadBeanDefinitions
Create Annotated Bean Definition Reader and ClassPathBean Definition Scanner and load corresponding classes and base packages. Note that there are no classes and basePackages without calling the method of ApplicationContext. spring Default scan path is not here
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader = getAnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = getClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(beanFactory); BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator = getBeanNameGenerator(); if (beanNameGenerator != null) { reader.setBeanNameGenerator(beanNameGenerator); scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(beanNameGenerator); beanFactory.registerSingleton(AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR, beanNameGenerator); } ScopeMetadataResolver scopeMetadataResolver = getScopeMetadataResolver(); if (scopeMetadataResolver != null) { reader.setScopeMetadataResolver(scopeMetadataResolver); scanner.setScopeMetadataResolver(scopeMetadataResolver); } if (!this.annotatedClasses.isEmpty()) { if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Registering annotated classes: [" + StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(this.annotatedClasses) + "]"); } reader.register(ClassUtils.toClassArray(this.annotatedClasses)); } if (!this.basePackages.isEmpty()) { if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Scanning base packages: [" + StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(this.basePackages) + "]"); } scanner.scan(StringUtils.toStringArray(this.basePackages)); } String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); if (configLocations != null) { for (String configLocation : configLocations) { try { Class<?> clazz = getClassLoader().loadClass(configLocation); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Successfully resolved class for [" + configLocation + "]"); } reader.register(clazz); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not load class for config location [" + configLocation + "] - trying package scan. " + ex); } int count = scanner.scan(configLocation); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { if (count == 0) { logger.info("No annotated classes found for specified class/package [" + configLocation + "]"); } else { logger.info("Found " + count + " annotated classes in package [" + configLocation + "]"); } } } } } }
prepareBeanFactory
Add some bean s or rules to BeanFactory
*/ protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc. beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader()); beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment())); // Configure the bean factory with context callbacks. beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this)); // Next is ignoring dependencies and automatically ignoring the dependencies of the following objects. beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class); // BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory. // MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean. beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this); // Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners. beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this)); // Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found. if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory)); // Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching. beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); } // Register default environment beans. if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment()); } if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties()); } if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment()); } }
postProcessBeanFactory
This subclass AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServer Application Context overrides the method of the parent class, so the postProcessBeanFactory function is designed to provide the subclass with its own behavior. Its function is exactly the same as prepareBeanFactory. Just face different objects.
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext, this.servletConfig)); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletConfigAware.class); WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext); WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext, this.servletConfig); }
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()); // Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime // (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor) if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory)); beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); } }
registerBeanPostProcessors
The implementation class of BeanPostProcessors and sub-interface is obtained from BeanFactory. Sort and then add to the BeanPostProcessor collection of beanFactory for subsequent aspect operations. Functions can be executed in the above methods and repeated once in order to ensure simplicity.
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this); }
initMessageSource
protected void initMessageSource() { ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) { this.messageSource = beanFactory.getBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, MessageSource.class); // Make MessageSource aware of parent MessageSource. if (this.parent != null && this.messageSource instanceof HierarchicalMessageSource) { HierarchicalMessageSource hms = (HierarchicalMessageSource) this.messageSource; if (hms.getParentMessageSource() == null) { // Only set parent context as parent MessageSource if no parent MessageSource // registered already. hms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource()); } } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using MessageSource [" + this.messageSource + "]"); } } else { // Use empty MessageSource to be able to accept getMessage calls. DelegatingMessageSource dms = new DelegatingMessageSource(); dms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource()); this.messageSource = dms; beanFactory.registerSingleton(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, this.messageSource); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Unable to locate MessageSource with name '" + MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME + "': using default [" + this.messageSource + "]"); } } }
initApplicationEventMulticaster
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() { ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) { this.applicationEventMulticaster = beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]"); } } else { this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory); beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Unable to locate ApplicationEventMulticaster with name '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "': using default [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]"); } } }
onRefresh
protected void onRefresh() { this.themeSource = UiApplicationContextUtils.initThemeSource(this); }
registerListeners
protected void registerListeners() { // Register statically specified listeners first. for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener); } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them! String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false); for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName); } // Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster... Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents; this.earlyApplicationEvents = null; if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) { for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent); } } }
finishBeanFactoryInitialization
Finish bean factory. Because containers with different functions require multiple factories to perform different operations after successful startup.
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // If conversion services exist, get and set from the bean Factory to the bean Fctory if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) { beanFactory.setConversionService( beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)); } if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) { beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(new StringValueResolver() { @Override public String resolveStringValue(String strVal) { return getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal); } }); } // A Function of Comparing Chicken Ribs String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false); for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) { getBean(weaverAwareName); } // Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching. beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null); // Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes. beanFactory.freezeConfiguration(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); }
finishRefresh
Refesh's Successful Handling
protected void finishRefresh() { // Initialize the Application Context lifecycle initLifecycleProcessor(); // Execution Life Cycle onRefresh getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh(); // Execute the CntextRefreshed event publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this)); // Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active. LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this); }
summary
- prepareRefresh lets Application Context do some preparation
- obtainFreshBeanFactory solves what BeanFactory to use by subclasses, letting some subclasses handle BeanFactory's own business.
- prepareBeanFactory is the behavior of the AbstractApplication Context specification BeanFactory unification
- invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors executes BeanPostProcessors
- RegiserBeanPostProcessors sort BeanPostProcessors and add beanFactory. Next is the initialization and execution of the ApplicationContext behavior.
- initMessageSource initializes MessageSource
- InitApplication Event Multicaster Initializes Application Event Multicaster
- onRefresh is useless
- RegiserListeners execute events
- FinishBeanFactory Initialization collates beanFactory
- finishRefresh