Chapter 6 Consul service registration and discovery of spring cloud
6, Consul service registration and discovery
1. About Consul
1.1 what is it
https://www.consul.io/intro/index.html
[the external chain picture transfer fails. The source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (img-z1ASUTjV-1628750641870)
Consul is an open source distributed service discovery and configuration management system developed by HashiCorp in Go language
It provides the functions of service governance, configuration center, control bus and so on. Each of these functions can be used alone or together to build a comprehensive service grid. In short, Consul provides a complete service grid solution.
It has many advantages. Including: Based on raft protocol, relatively simple; It supports health check, HTTP and DNS protocols, WAN clusters across data centers, graphical interfaces across platforms, Linux, Mac and Windows
1.2 what can I do
Spring cloud consult has the following features:
[external chain picture transfer failed. The source station may have anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (img-dfJkqfgk-1628750641871)
-
Service discovery
Provides HTTP and DNS discovery methods.
-
Health monitoring
Support a variety of ways, such as HTTP, TCP, Docker and Shell script customized monitoring
-
KV storage
Storage method of Key and Value
-
Multi data center
Consul supports multiple data centers
-
Visual Web interface
1.3. Where to go
https://www.consul.io/downloads.html
1.4. How to play
https://www.springcloud.cc/spring-cloud-consul.html
2. Install and run Consul
-
Official website installation instructions
https://learn.hashicorp.com/consul/getting-started/install.html
-
After downloading, there is only one consumer Exe file, double-click to run under the hard disk path to view the version number information
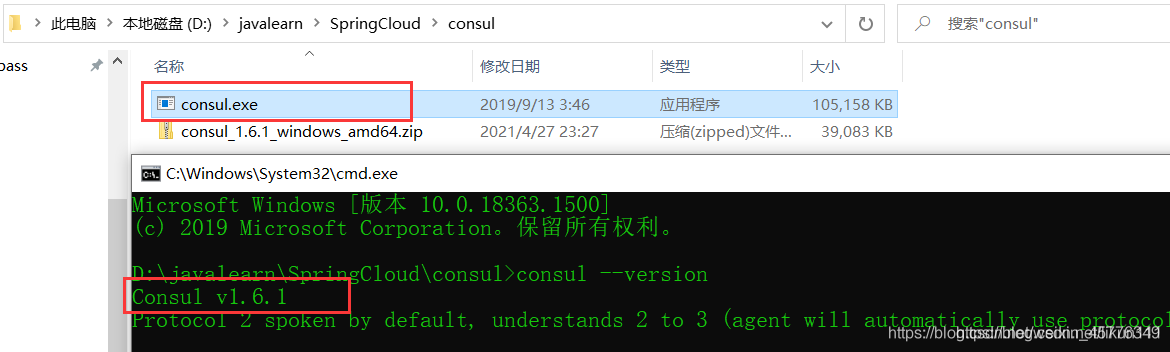
-
Start using development mode
consul agent -dev
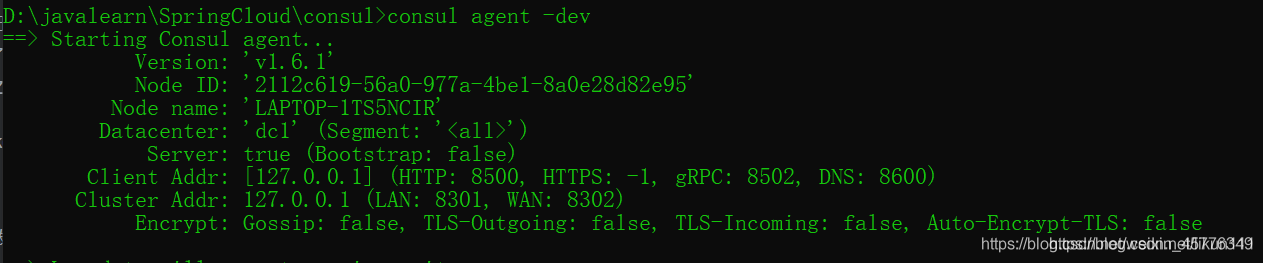
-
Consul t's home page can be accessed at the following address: http://localhost:8500
-
Results page
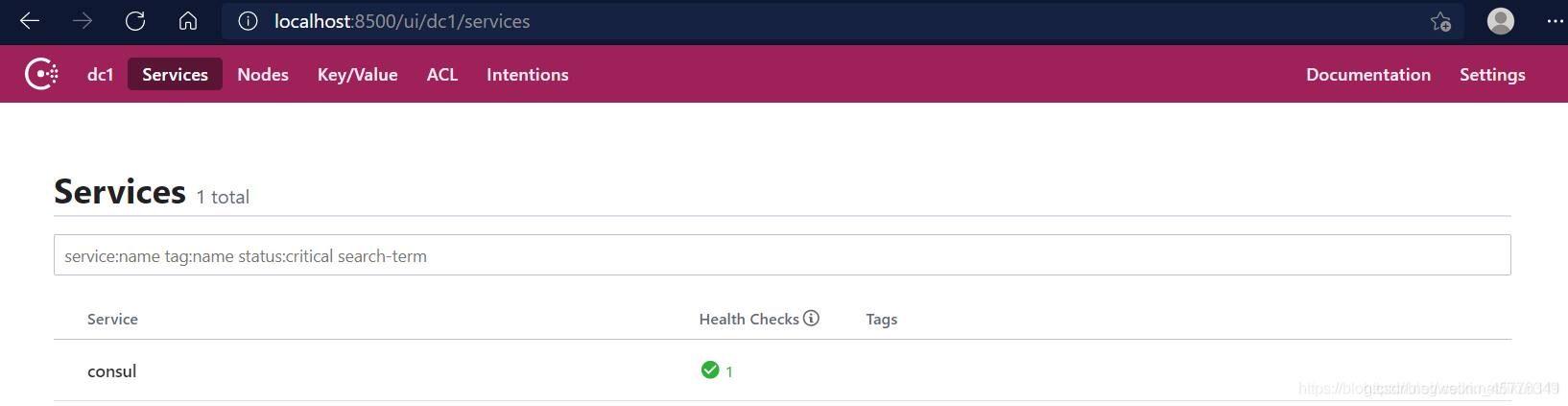
-
3. Service provider
-
Create a new Module payment service provider 8006
cloud-providerconsul-payment8006
-
POM
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <parent> <artifactId>cloud2020</artifactId> <groupId>com.likun.springcloud</groupId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <artifactId>cloud-providerconsul-payment8006</artifactId> <dependencies> <!--SpringCloud consul-server --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-consul-discovery</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- SpringBoot integration Web assembly --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> <!--Daily general jar Package configuration--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
YML
###Consumer service port number
server:
port: 8006
spring:
application:
name: consul-provider-payment
####Consumer registry address
cloud:
consul:
host: localhost
port: 8500
discovery:
#hostname: 127.0.0.1
service-name: ${spring.application.name}
-
Main startup class
package com.likun.springcloud; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient; /** * @author likun * @create 2021-04-27 23:52 */ @SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient public class PaymentMain8006 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(PaymentMain8006.class, args); } } -
Business class Controller
package com.likun.springcloud.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import java.util.UUID; /** * @author likun * @create 2021-04-27 23:54 */ @RestController public class PaymentController { @Value("${server.port}") private String serverPort; @GetMapping("/payment/consul") public String paymentInfo(){ return "SpringCloud with consul" + serverPort + "\t\t" + UUID.randomUUID().toString(); } }
4. Service consumers
-
Create a new Module consumer service order80
cloud-consumerconsul-order80
-
POM (same)
-
YML
###Consumer service port number server: port: 80 spring: application: name: cloud-consumer-order ####Consumer registry address cloud: consul: host: localhost port: 8500 discovery: #hostname: 127.0.0.1 service-name: ${spring.application.name} -
Main startup class
package com.likun.springcloud; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient; /** * @author likun * @create 2021-04-28 0:29 */ @SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient public class OrderConsulMain80 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderConsulMain80.class, args); } } -
Configure Bean
ApplicationContextBean
package com.likun.springcloud.config; import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; /** * @author likun * @create 2021-04-28 0:31 */ @Configuration public class ApplicationContextBean { @Bean @LoadBalanced public RestTemplate getRestTemplate() { return new RestTemplate(); } } -
Business class Controller
package com.likun.springcloud.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; /** * @author likun * @create 2021-04-28 0:36 */ @RestController public class OrderConsulController { public static final String INVOKE_URL = "http://consul-provider-payment"; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/consul") public String paymentInfo() { String result = restTemplate.getForObject(INVOKE_URL + "/payment/consul", String.class); System.out.println("Consumer invokes payment service(consul)--->result:" + result); return result; } } -
Verification test
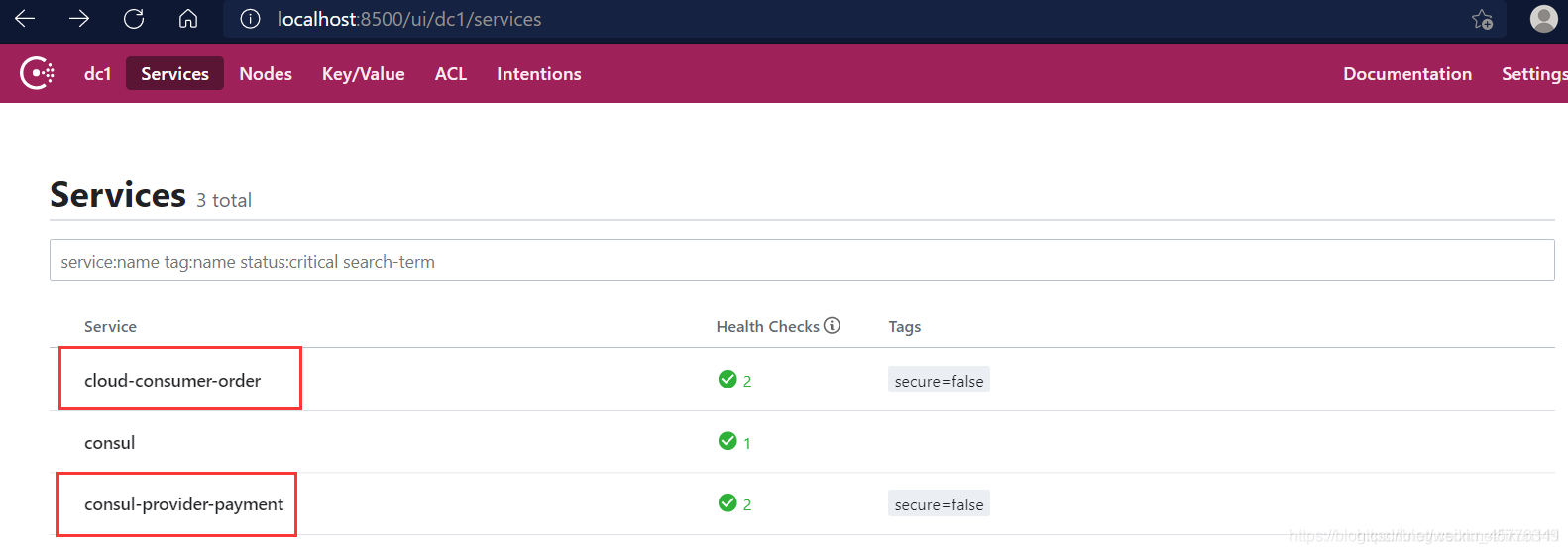
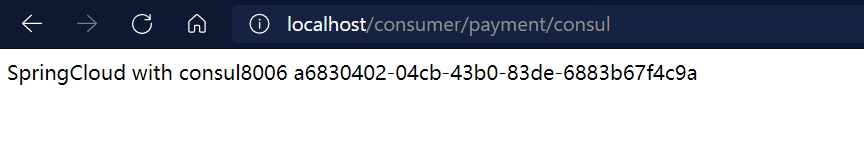
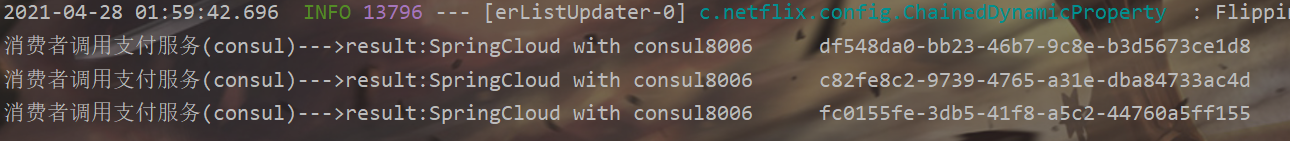
5. Similarities and differences of the three registration centers
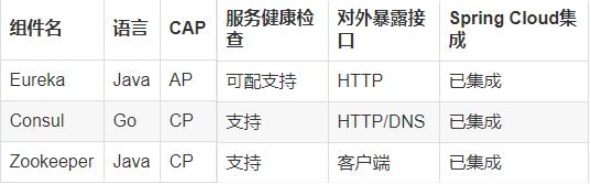
-
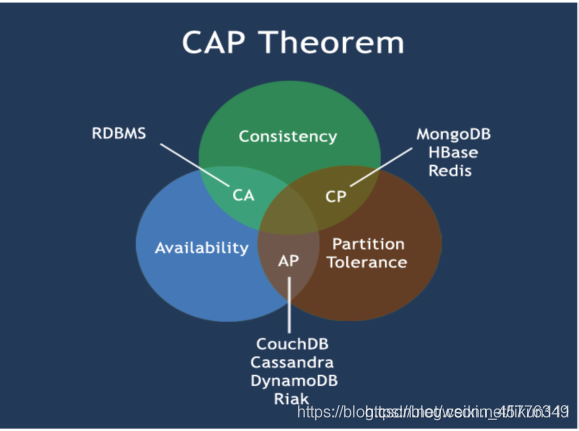
CAP
C:Consistency (strong consistency)
A:Availability
P:Partition tolerance
CAP theory focuses on granularity, which is data, not the strategy of overall system design
Take the simplest user management system as an example. The user management system includes user account data (user ID, password) For user information data (nickname, interest, hobby, gender, self introduction, etc.), generally, CP is selected for user account data, and AP is selected for user information data. If the whole system is limited to CP, it does not meet the application scenario of user information data; if the whole system is limited to AP, it does not meet the application scenario of user account data
Therefore, when the CAP theory is put into practice, we need to classify the data in the system according to different application scenarios and requirements, and select different strategies (CP or AP) for each type of data, rather than directly limiting that all data in the whole system are the same strategy -
Classical CAP graph
At most, two can be satisfied at the same time.
The core of CAP theory is that a distributed system cannot meet the three requirements of consistency, availability and partition fault tolerance at the same time,
Therefore, according to the CAP principle, NoSQL database is divided into three categories: meeting the CA principle, meeting the CP principle and meeting the AP principle:
CA - single point cluster, a system that meets consistency and availability, is usually not very powerful in scalability.
CP - systems that meet consistency and partition tolerance, usually have low performance.
AP - a system that meets the requirements of availability and partition tolerance. Generally, it may have lower requirements for consistency
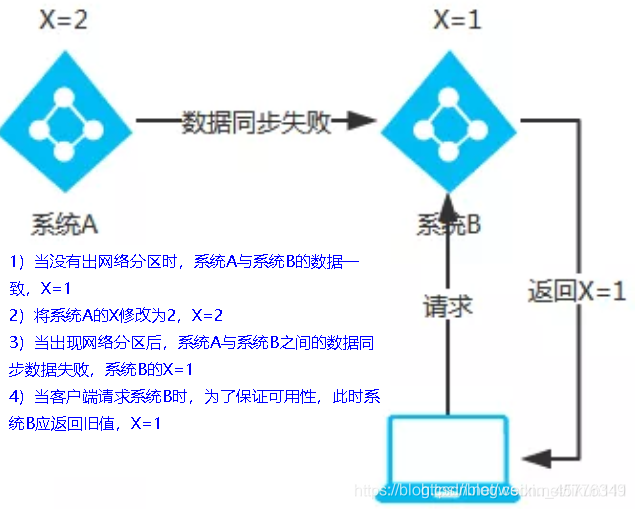
AP(Eureka)
AP architecture
After the network partition appears, in order to ensure the availability, system B can return the old value to ensure the availability of the system.
Conclusion: it violates the requirements of consistency C and only meets the availability and partition fault tolerance, that is, AP
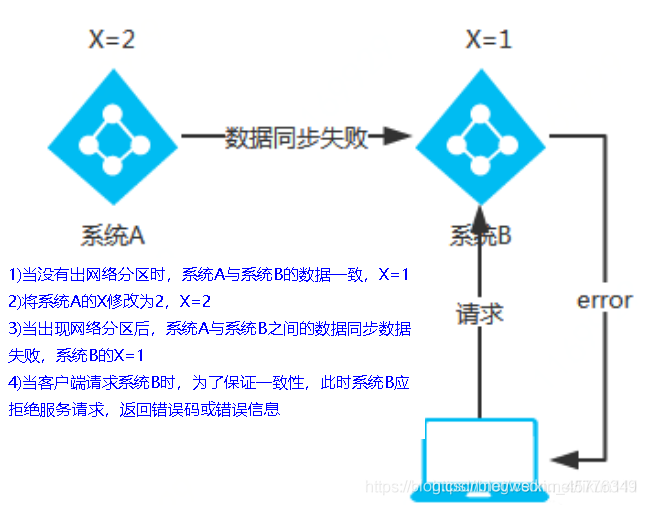
CP(Zookeeper/Consul)
CP architecture
When the network partition appears, in order to ensure consistency, the request must be rejected, otherwise the consistency cannot be guaranteed
Conclusion: it violates the requirements of availability A and only meets consistency and partition fault tolerance, that is, CP
Constant performance is not particularly high.
AP - a system that meets the requirements of availability and partition tolerance. Generally, it may have lower requirements for consistency
AP(Eureka)
AP architecture
After the network partition appears, in order to ensure the availability, system B can return the old value to ensure the availability of the system.
Conclusion: it violates the requirements of consistency C and only meets the availability and partition fault tolerance, that is, AP
[external chain picture transferring... (img-9ya5BUFd-1628750641880)]
CP(Zookeeper/Consul)
CP architecture
When the network partition appears, in order to ensure consistency, the request must be rejected, otherwise the consistency cannot be guaranteed
Conclusion: it violates the requirements of availability A and only meets consistency and partition fault tolerance, that is, CP
[external chain picture transferring... (img-jxPkuz3C-1628750641881)]