1 View
- The difference between a view and a table: "Is the actual data saved?"
- "Views are not tables. Views are virtual tables. Views depend on tables."

1.1 Create View
CREATE VIEW <View Name>(<Column Name 1>,<Column Name 2>,...) AS <SELECT Sentence>
-- Create views based on multiple tables without using join
-- create The column name of can be saved
CREATE VIEW view_shop_product(product_type, sale_price, shop_name)
AS
SELECT product_type, sale_price, shop_name
FROM product,
shop_product
WHERE product.product_id = shop_product.product_id;
-- Queries based on the above views
SELECT sale_price, shop_name
FROM view_shop_product
WHERE product_type = 'clothes';
- Column 1 in the ELECT statement is column 1 in the view, and column 2 in the SELECT statement is column 2 in the view
- The column name of the view is defined in the list after the view name
- View names need to be unique in the database and cannot be duplicated with other views and tables
- Views can be based not only on real tables, but also on views. However, for most DBMS s, focusing on diagrams can degrade SQL performance.
- ORDER BY statements cannot be used when defining views in general DBMS s because, like views and tables, data rows are out of order
- The definition of a view in MySQL allows the use of ORDER BY statements, but if you select from a particular view and the view uses its own ORDER BY statement, the ORDER BY in the view definition will be ignored
1.2 Modify view structure
ALTER VIEW <View Name> AS <SELECT Sentence>
-- exam1
ALTER VIEW productSum
AS
SELECT product_type, sale_price
FROM Product
WHERE regist_date > '2009-09-11';
1.3 Update View Content

-- Modified above productsum Exclude the above restrictions
UPDATE productsum
SET sale_price = '5000'
WHERE product_type = 'Office Supplies';
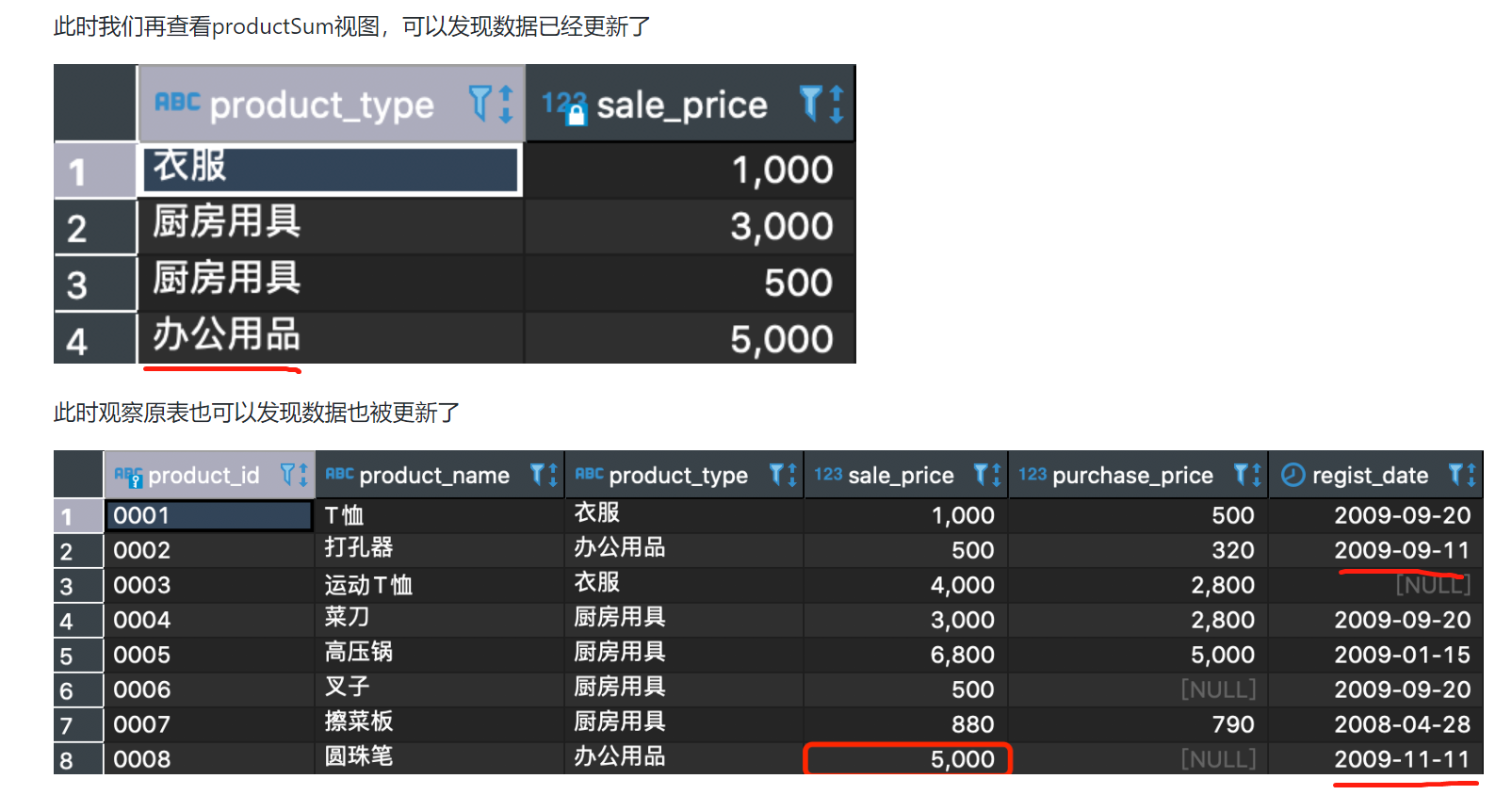
- Only one data in the result is updated, because the view is only a window of the original table, it can only modify what is visible through the window
- Modifying the original table in this way is not recommended
1.4 Delete View
DROP VIEW <View Name 1> [ , <View Name 2> ...]
-- exam
DROP VIEW productSum;
2 Subqueries
2.1 Nested Subquery
SELECT product_type, cnt_product
FROM (SELECT *
FROM (SELECT product_type,
COUNT(*) AS cnt_product
FROM product
GROUP BY product_type) AS productsum
WHERE cnt_product = 4) AS productsum2;
- Table name from sub-query after AS
- Subqueries are one-time, not stored in the storage media like views, but disappear after the SELECT statement executes
- As the number of nested layers of subqueries overlap, SQL statements can be difficult to understand and inefficient to execute, so try to avoid this use
2.2 Scalar Quantum Query
- Scalar quantum query: A select statement executed only returns one value, that is, a column of a specific row in a table
- Scalar quantum queries can be used anywhere a single value can be used
-- One more avg_price Column, values are the same
SELECT product_id,
product_name,
sale_price,
(SELECT AVG(sale_price)
FROM product) AS avg_price
FROM product;
2.3 Associated Subqueries
- This means there is a link between the query and the subquery
- In the following example, the outer product table is marked p1, the inner product is set to p2, and two queries are joined through a WHERE statement
-- Find out in each category, sale Items whose price is higher than the average in the corresponding category
SELECT product_type, product_name, sale_price
FROM product AS p1
WHERE sale_price > (SELECT AVG(sale_price)
FROM product AS p2
WHERE p1.product_type = p2.product_type
GROUP BY product_type);
- The sql execution order tells us:
- First from gets the data to be filtered
- Execute a subquery where p1.producty_type is the type corresponding to the current data of the parent query
3 Functions

3.1 Arithmetic Function



