1, One way circular list
1. One way circular list details
In fact, a unidirectional circular list is a pointer to the head node of the end node. Generally, the end node of the list points to null.
When adding a node, the tail situation is the same as the normal situation, and no special processing is needed (because the tail refers to the pointer to the head node). When adding nodes to the header, we need to discuss separately the first insertion of nodes, head.next = head.
Deletion nodes are divided into two types: head deletion and general case (tail does not need special treatment because tail has a pointer to head node). When deleting the last node of the header, special processing is also required.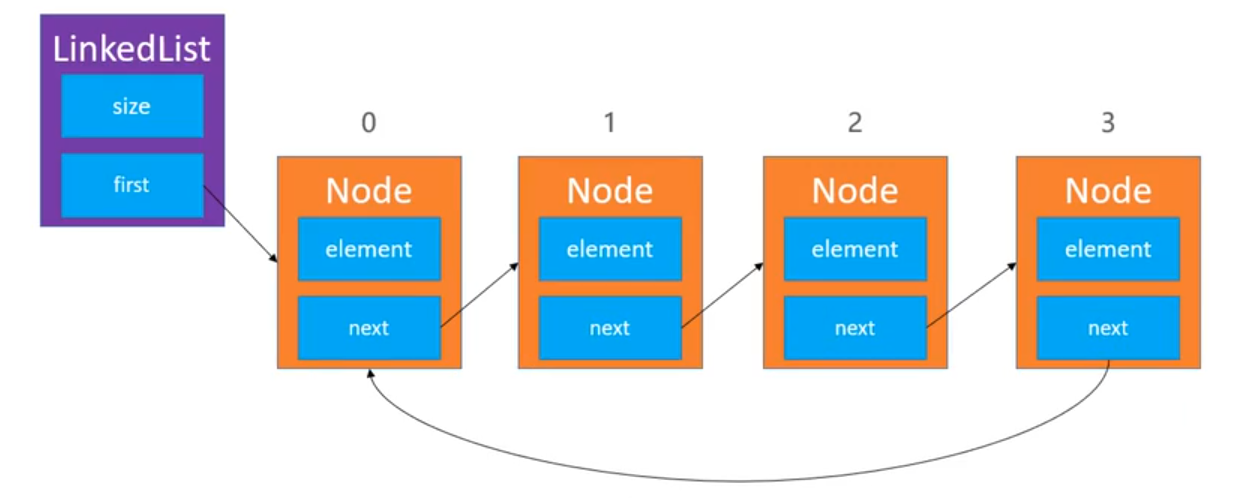
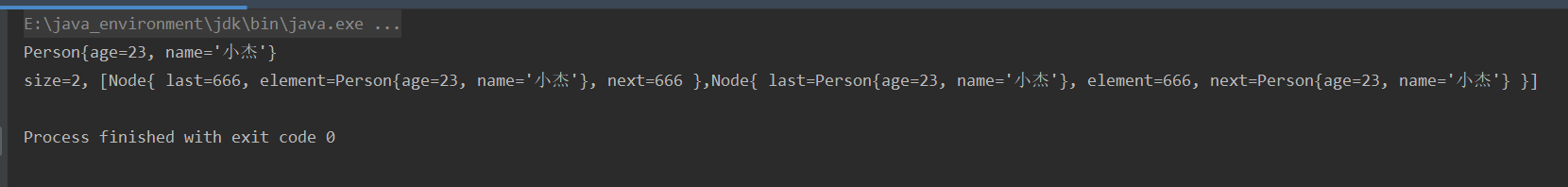
public class CircleLinkedList<E> extends AbstractList<E> { private Node<E> head; private Node<E> current; public static class Node<E> { E element; Node<E> next; public Node(E element, Node<E> next) { this.element = element; this.next = next; } @Override public String toString() { return "Node{" + "element=" + element + ", next=" + next.element + '}'; } } @Override public void clear() { this.size = 0; head = null; //Clear memory space of all nodes } @Override public void add(int index, E element) { //Watch the head and tail of the list if (index == 0) { //Head insertion Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(element, head); if (size == 0 || head == null) { //When inserting the first node head = newNode; head.next = head; } else { Node<E> tail = getNode(size - 1); head = newNode; tail.next = head; } } else { //In general, tail insertion is the same as in general, because the tail has a pointer to the head node rangeCheckForAdd(index); Node<E> preNode = getNode(index - 1); Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(element, preNode.next); preNode.next = newNode; } size++; } @Override public void remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); Node<E> preNode = head; if (index == 0) { //Head deletion if (size == 1) { head = null; } else { head = head.next; Node<E> tail = getNode(size - 1 - 1); //If the head is changed, the parameters for finding the tail node also need to be changed, or check before changing the head tail.next = head; //Equivalent 1 // Node<E> tail = getNode(size - 1); head = head.next; tail.next = head; //Equivalent writing 2 // preNode=preNode.next; Node<E> tail = getNode(size - 1); tail.next=preNode; head=preNode; } } else { //In general, tail deletion is the same as in general, because the tail has a pointer to the head node preNode = getNode(index - 1); preNode.next = preNode.next.next; } size--; } public void reset() { current = head; } public void next() { if (current == null) return; current = current.next; } /** * Delete the current node and return the data of the deleted node. At the same time, move the current node backward * * @return */ public E remove() { if (current == null) return null; E element = current.element; int index = indexOf(element); rangeCheck(index); Node<E> preNode = head; if (index == 0) { //Head deletion if (size == 1) { head = null; } else { Node<E> tail = getNode(size - 1); head = head.next; tail.next = head; } } else { //In general, tail deletion is the same as in general, because the tail has a pointer to the head node preNode = getNode(index - 1); preNode.next = preNode.next.next; } size--; current = current.next; return element; } @Override public E set(int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); Node<E> temp = getNode(index); E old = temp.element; temp.element = element; return old; } @Override public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); Node<E> temp = getNode(index); return temp.element; } public Node<E> getNode(int index) { Node<E> temp = head; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) { temp = temp.next; } return temp; } @Override public int indexOf(E element) { Node<E> temp = head; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (temp.element.equals(element)) return i; temp = temp.next; } return ELEMENT_NOT_FOUND; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(); str.append("size=").append(size); if (size != 0) { Node temp = head; str.append(", ["); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { str.append(temp); if (i != size - 1) { str.append(","); } temp = temp.next; } str.append("]"); } return str.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { CircleLinkedList<Object> list = new CircleLinkedList<>(); //Polymorphism, member method compilation on the left, operation on the right list.add(new Person(23, "Gon Freecss")); list.add(0, 66); list.add(99.9); list.add(list.size(), 100); list.remove(0); list.remove(list.size() - 1); list.set(1, 666); System.out.println(list.get(0)); System.out.println(list); } }
2. Test results
2, Two way circular list
1. Two way circular list details
In fact, the two-way circular list is a two-way list, but the special thing is that the tail node has a pointer to the head node, and the head node also has a pointer to the tail node.
When adding and deleting nodes, it is similar to the case of unidirectional circular list division, except that when adding and deleting the head, the head and tail will change.
A group of people...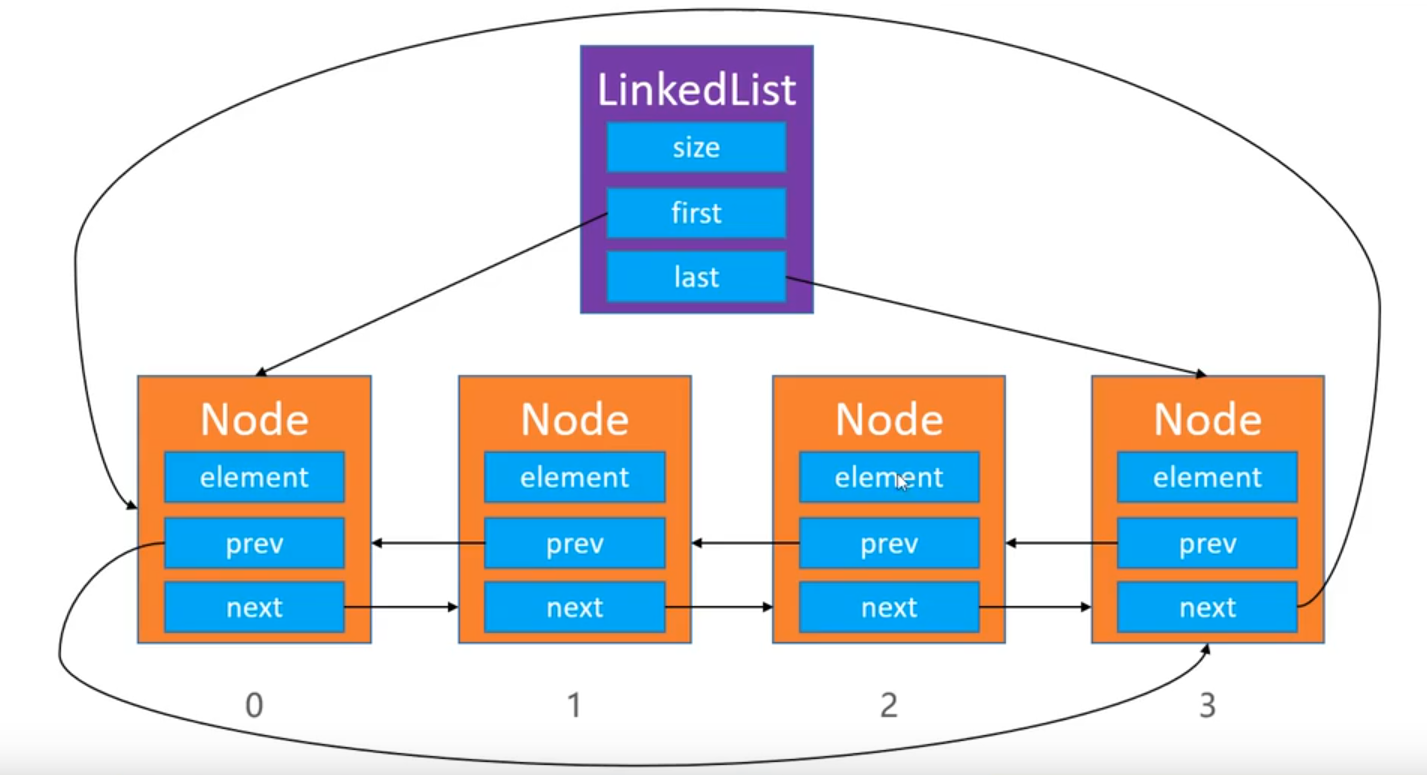
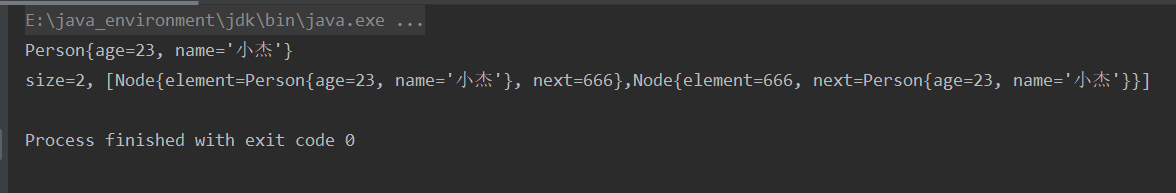
public class DoubleCircleLinkedList<E> extends AbstractList<E> { private Node<E> head; private Node<E> tail; private Node<E> current; public static class Node<E> { Node<E> last; E element; Node<E> next; public Node(Node<E> last, E element, Node<E> next) { this.last = last; this.element = element; this.next = next; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(); str.append("Node{ last="); if (last != null) str.append(last.element); else str.append("null"); str.append(", element="); str.append(element); str.append(", "); str.append("next="); if (next != null) str.append(next.element); else str.append("null"); str.append(" }"); return str.toString(); } @Override protected void finalize() throws Throwable { System.out.println("Node Hang up"); } } @Override public void clear() { this.size = 0; //As long as any space in the JVM is not pointed to by the GC Roots object, it will be destroyed head = null; tail = null; } @Override public void add(int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); Node<E> node = getNode(index); if (index == 0) { //Insert in the head Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(tail, element, node); //The head node of two-way circular chain should point to the tail node if (node == null || size == 0) { //When inserting the first node head = newNode; tail = newNode; head.last = tail; tail.next = head; //After the head is inserted, modify the tail node to point to the new head node } else { head.last = newNode; head = newNode; tail.next = head; //After the head is inserted, modify the tail node to point to the new head node } } else if (index == size) { //Tail insertion Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(tail, element, head); //The tail node of two-way circular list should point to the head node tail.next = newNode; tail = newNode; head.last = tail; //After the tail is inserted, modify the head node to point to the new tail node } else { //Ordinary circumstances Node<E> former = node.last; Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(former, element, node); former.next = newNode; node.last = newNode; } size++; } @Override public void remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); Node<E> node = getNode(index); Node<E> former = node.last; Node<E> latter = node.next; if (index == 0) { //Head deletion latter.last = tail; //The head node of two-way circular chain should point to the tail node head = latter; tail.next = head; //The tail node of two-way circular list should point to the head node } else if (index == size - 1) { //Tail deletion former.next = head; //The tail node of two-way circular list should point to the head node tail = former; head.last = tail; //The head node of two-way circular chain should point to the tail node } else { //Ordinary circumstances former.next = latter; latter.last = former; } size--; } public void reset() { current = head; } public void next() { if (current == null) return; current = current.next; } /** * Delete the current node and return the data of the deleted node. At the same time, move the current node backward * * @return */ public E remove() { if (current == null) return null; E element = current.element; int index = indexOf(element); rangeCheck(index); Node<E> node = getNode(index); Node<E> former = node.last; Node<E> latter = node.next; if (index == 0) { //Head deletion latter.last = tail; //The head node of two-way circular chain should point to the tail node head = latter; tail.next = head; //The tail node of two-way circular list should point to the head node } else if (index == size - 1) { //Tail deletion former.next = head; //The tail node of two-way circular list should point to the head node tail = former; head.last = tail; //The head node of two-way circular chain should point to the tail node } else { //Ordinary circumstances former.next = latter; latter.last = former; } size--; current = current.next; return element; } @Override public E set(int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); Node<E> temp = getNode(index); E old = temp.element; temp.element = element; return old; } @Override public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); return getNode(index).element; } public Node<E> getNode(int index) { Node<E> temp = null; if (index < this.size >> 1) { temp = head; //Ab initio traversal for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) { temp = temp.next; } } else { temp = tail; //Traversal from tail for (int i = 0; i < size - 1 - index; i++) { temp = temp.last; } } return temp; } @Override public int indexOf(E element) { Node<E> temp = head; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (temp.element.equals(element)) return i; temp = temp.next; } return ELEMENT_NOT_FOUND; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(); str.append("size=").append(size); if (size != 0) { Node temp = head; str.append(", ["); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { str.append(temp.toString()); if (i != size - 1) { str.append(","); } temp = temp.next; } str.append("]"); } return str.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { DoubleCircleLinkedList<Object> list = new DoubleCircleLinkedList<>(); //Polymorphism, member method compilation on the left, operation on the right list.add(new Person(23, "Gon Freecss")); list.add(0, 66); list.add(99.9); list.add(list.size(), 100); list.remove(0); list.remove(list.size() - 1); list.set(1, 666); System.out.println(list.get(0)); System.out.println(list); } }
2. Test results