Case 1: Deployment redis colony Case 2: Management redis colony
- 1
- 2
1 case 1: deploying redis cluster
1.1 problems
Specific requirements are as follows: Prepare cluster environment install redis And create a cluster View cluster information
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
1.2 scheme
Build a redis cluster. The topology plan is shown in figure-1:
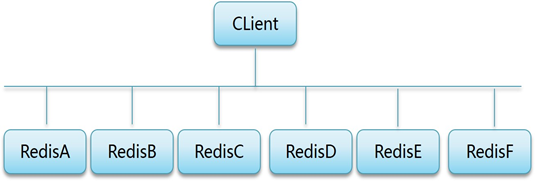
Figure-1
IP and port planning are shown in TABLE-1:
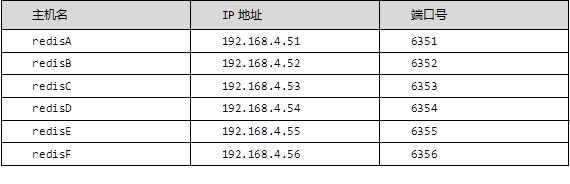
TABLE-1
1.3 steps
To realize this case, you need to follow the following steps.
Step 1: prepare the cluster environment
1) Configure the host name, ip address and yum source (system source) according to TABLE-1. There is no operation here
2) Transfer the redis software package to 6 database servers and install the redis server. The six servers operate in the same way (take 51 as an example)
[root@redisA ~]# yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ make
[root@redisA ~]# cd redis
redis/ redis-cluster/
[root@redisA ~]# cd redis/
[root@redisA redis]# ls
lnmp redis-4.0.8.tar.gz
[root@redisA redis]# tar -xf redis-4.0.8.tar.gz
[root@redisA redis]# cd redis-4.0.8/
[root@redisA redis-4.0.8]# make && make install
[root@redisA redis-4.0.8]# ./utils/install_server.sh
Welcome to the redis service installer
This script will help you easily set up a running redis server
Please select the redis port for this instance: [6379]
Selecting default: 6379
Please select the redis config file name [/etc/redis/6379.conf]
Selected default - /etc/redis/6379.conf
Please select the redis log file name [/var/log/redis_6379.log]
Selected default - /var/log/redis_6379.log
Please select the data directory for this instance [/var/lib/redis/6379]
Selected default - /var/lib/redis/6379
Please select the redis executable path [/usr/local/bin/redis-server]
Selected config:
Port : 6379
Config file : /etc/redis/6379.conf
Log file : /var/log/redis_6379.log
Data dir : /var/lib/redis/6379
Executable : /usr/local/bin/redis-server
Cli Executable : /usr/local/bin/redis-cli
Is this ok? Then press ENTER to go on or Ctrl-C to abort.
Copied /tmp/6379.conf => /etc/init.d/redis_6379
Installing service...
Successfully added to chkconfig!
Successfully added to runlevels 345!
Starting Redis server...
Installation successful! //Installation succeeded
[root@redisA redis-4.0.8]# ss -antlp | grep 6379 / / there are ports when viewing
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:6379 *:* users:(("redis-server",pid=10788,fd=6))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
2) Modify the configuration file for all 6 redis servers (take 51 as an example)
[root@redisA redis-4.0.8]# /etc/init.d/redis_6379 stop
//Stop the redis service that has been started
Stopping ...
Waiting for Redis to shutdown ...
Redis stopped
[root@redisA redis-4.0.8]# vim /etc/redis/6379.conf
...
bind 192.168.4.51 //Modify ip
port 6351 //The same is not allowed. Only the ip of the physical interface is specified
daemonize yes //Run as a daemon
pidfile /var/run/redis_6351.pid
cluster-enabled yes //Whether to enable the cluster, provided that it runs as a daemon
cluster-config-file nodes-6351.conf
//The configuration file for storing cluster information is automatically generated and cannot be the same
cluster-node-timeout 5000 //Cluster node communication timeout
...
[root@redisA redis-4.0.8]# /etc/init.d/redis_6379 start / / start the service
Starting Redis server...
[root@redisA redis-4.0.8]# ss -antlp | grep 6351 / / check whether there are ports
LISTEN 0 128 192.168.4.51:6351 *:* users:(("redis-server",pid=11092,fd=6))
LISTEN 0 128 192.168.4.51:16351 *:* users:(("redis-server",pid=11092,fd=8)) //16051: port used for host communication in the cluster
[root@redisA redis-4.0.8]# ps -C redis
PID TTY TIME CMD
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
Note: when modifying other hosts, please pay attention to the modification of ip and port, which should not be the same as that of 51 host
3) Close the firewall 51-56 host (take 51 as an example)
[root@redisA redis-4.0.8]# getenforce Permissive [root@redisA redis-4.0.8]# systemctl disable firewalld //Turn off the firewall without self starting
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
4) View cluster information
[root@redisA redis-4.0.8]# redis-cli -h 192.168.4.51 -p 6351 192.168.4.51:6351> ping PONG 192.168.4.51:6351> cluster info cluster_state:fail cluster_slots_assigned:0 cluster_slots_ok:0 cluster_slots_pfail:0 cluster_slots_fail:0 cluster_known_nodes:1 cluster_size:0 ... 192.168.4.51:6351> cluster nodes f81f997d5ed988ec1587558e78d5f7dbc96abcbf :6351@16351 myself,master - 0 0 0 connected
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
Step 2: create a cluster (you can execute the script to create a cluster on any computer) here, execute it on 51
1) Deploy ruby script running environment (execute on 51)
[root@redisA redis-4.0.8]# cd /root/redis-cluster/ [root@redisA redis-cluster]# ls redis-3.2.1.gem ruby-devel-2.0.0.648-30.el7.x86_64.rpm [root@redisA redis-cluster]# yum -y install ruby rubygems [root@redisA redis-cluster]# rpm -ivh –nodeps \ ruby-devel-2.0.0.648-30.el7.x86_64.rpm warning: ruby-devel-2.0.0.648-30.el7.x86_64.rpm: Header V3 RSA/SHA256 Signature, key ID f4a80eb5: NOKEY Preparing... ################################# [100%] Updating / installing... 1:ruby-devel-2.0.0.648-30.el7 ################################# [100%] [root@redisA redis-cluster]# which gem /usr/bin/gem [root@redisA redis-cluster]# gem install redis Successfully installed redis-3.2.1 Parsing documentation for redis-3.2.1 Installing ri documentation for redis-3.2.1 1 gem installed
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
2) Generate scripts for creating clusters
[root@redisA redis-cluster]# cd /root/redis/redis-4.0.8/src/ [root@redisA src]# cp redis-trib.rb /usr/local/bin/ [root@redisA src]# ll /usr/local/bin/redis-trib.rb -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 65991 Sep 27 16:12 /usr/local/bin/redis-trib.rb
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
3) Create cluster
[root@redisA src]# redis-trib.rb create --replicas 1 \ 192.168.4.51:6351 192.168.4.52:6352 \ 192.168.4.53:6353 192.168.4.54:6354 \ 192.168.4.55:6355 192.168.4.56:6356 //--Replica 1 configures a slave library for each master [root@redisA log]# redis-trib.rb create --replicas 1 192.168.4.51:6351 192.168.4.52:6352 192.168.4.53:6353 192.168.4.54:6354 192.168.4.55:6355 192.168.4.56:6356 >>> Creating cluster >>> Performing hash slots allocation on 6 nodes... Using 3 masters: 192.168.4.51:6351 192.168.4.52:6352 192.168.4.53:6353 Adding replica 192.168.4.55:6355 to 192.168.4.51:6351 Adding replica 192.168.4.56:6356 to 192.168.4.52:6352 Adding replica 192.168.4.54:6354 to 192.168.4.53:6353 ... ... ... [OK] All nodes agree about slots configuration. >>> Check for open slots... >>> Check slots coverage... [OK] All 16384 slots covered.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
4) To view the cluster information, any host can access the local redis service to view it
cluster info view cluster information
cluster nodes view cluster node information
[root@redisA log]# redis-cli -h 192.168.4.52 -p 6352 192.168.4.52:6352> CLUSTER INFO cluster_state:ok //state cluster_slots_assigned:16384 cluster_slots_ok:16384 cluster_slots_pfail:0 cluster_slots_fail:0 cluster_known_nodes:6 cluster_size:3 cluster_current_epoch:6 cluster_my_epoch:2 cluster_stats_messages_ping_sent:367 cluster_stats_messages_pong_sent:327 cluster_stats_messages_meet_sent:5 cluster_stats_messages_sent:699 cluster_stats_messages_ping_received:327 cluster_stats_messages_pong_received:372 cluster_stats_messages_received:699 192.168.4.52:6352> CLUSTER NODES //View cluster node information 63afbb5e7d63b1f142358634578a3488e3c9e634 192.168.4.54:6354@16354 slave bc5c4e082a5a3391b634cf433a6486c867cfc44b 0 1538039278871 4 connected bc5c4e082a5a3391b634cf433a6486c867cfc44b 192.168.4.53:6353@16353 master - 0 1538039278571 3 connected 10923-16383 28e06c5f24a2b6c6412f81369e09bc9653cc51ff 192.168.4.56:6356@16356 slave 8568fbd73cb296cad6915d524e34761b2114af47 0 1538039278069 6 connected 7e8d9121f44d8331ff55b45c218b87df9bda1b70 192.168.4.55:6355@16355 slave a3083123bc5c87a76aab2655171634d4ee84f418 0 1538039278000 5 connected 8568fbd73cb296cad6915d524e34761b2114af47 192.168.4.52:6352@16352 myself,master - 0 1538039277000 2 connected 5461-10922 a3083123bc5c87a76aab2655171634d4ee84f418 192.168.4.51:6351@16351 master - 0 1538039277869 1 connected 0-5460 192.168.4.52:6352>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
5) Test cluster
Command:
Redis cli - C - H IP address - p port
[root@redisA log]# redis-cli -c -h 192.168.4.51 -p 6351 192.168.4.51:6351> set name jim -> Redirected to slot [5798] located at 192.168.4.52:6352 OK 192.168.4.52:6352> get name "jim" 192.168.4.52:6352> set class linux OK 192.168.4.52:6352> get class "linux" 192.168.4.52:6352> set pay 26800 -> Redirected to slot [4013] located at 192.168.4.51:6351 OK 192.168.4.51:6351> get pay "26800"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
The cluster cannot be used:
If half or more of the main database machines hang up, the cluster cannot be used
Upgrade a slave database to a master database. Without a slave database, the cluster cannot be used (provided that half or more of the master database machines hang up)
When a master database is suspended, its slave database will automatically replace the master database and be used normally (provided that half or more than half of the master database machines can be used). After the suspended master database is repaired, it will become a slave database and will not seize the master database
6) Cluster node election strategy (three master and three slave)
Stop the redis service of a master database, and the corresponding slave database will be automatically upgraded to the master database
First check the master-slave status of node information
[root@redisA log]# redis-cli -c -h 192.168.4.51 -p 6351 192.168.4.51:6351> CLUSTER nodes ... 8568fbd73cb296cad6915d524e34761b2114af47 192.168.4.52:6352@16352 master - 0 1538040400840 2 connected 5461-10922 28e06c5f24a2b6c6412f81369e09bc9653cc51ff 192.168.4.56:6356@16356 slave 8568fbd73cb296cad6915d524e34761b2114af47 0 1538040400000 6 connected ... 192.168.4.51:6351>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
See who is whose slave library, such as:
Check whether the number id before and after the node is the same
For example: 8568fbd73cb296cad6915d524e34761b2114af47
The slave Library of discovery 52 is 56
Stop main library 52
[root@redisA log]# redis-cli -h 192.168.4.52 -p 6352 shutdown [root@redisA log]# redis-cli -c -h 192.168.4.51 -p 6351 192.168.4.51:6351> CLUSTER NODES ... 8568fbd73cb296cad6915d524e34761b2114af47 192.168.4.52:6352@16352 master,fail - 1538041052349 1538041051000 2 disconnected //The main library of 52 is broken 28e06c5f24a2b6c6412f81369e09bc9653cc51ff 192.168.4.56:6356@16356 master - 0 1538041066000 7 connected 5461-10922 //56 become the main library ...
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
Open 52 and find that 52 becomes slave library
[root@redisB redis-4.0.8]# /etc/init.d/redis_6352 start Starting Redis server... [root@redisA log]# redis-cli -c -h 192.168.4.51 -p 6351 192.168.4.51:6351> CLUSTER NODES 8568fbd73cb296cad6915d524e34761b2114af47 192.168.4.52:6352@16352 slave 28e06c5f24a2b6c6412f81369e09bc9653cc51ff 0 1538041254000 7 connected
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
2 case 2: managing redis clusters
2.1 problems
Specific requirements are as follows: Practice adding hosts Practice deleting hosts
- 1
- 2
- 3
2.2 steps
To realize this case, you need to follow the following steps.
Step 1: add host
1) Deploy a new redis server with ip 192.168.4.58, package, initialize, enable cluster configuration, and restart the service (this has been done before, and if not, please refer to case 1)
2) Add cluster 4.58 (add master node)
Format: redis trib RB option parameters
Option: add nade add host (no role specified)
Because the ruby script was created on 51 before, only 51 has redis trib RB command, executed on 51
[root@redisA ~]# redis-trib.rb add-node 192.168.4.58:6358 192.168.4.51:6351 >>> Adding node 192.168.4.58:6358 to cluster 192.168.4.51:6351 >>> Performing Cluster Check (using node 192.168.4.51:6351) S: a3083123bc5c87a76aab2655171634d4ee84f418 192.168.4.51:6351 slots: (0 slots) slave replicates 7e8d9121f44d8331ff55b45c218b87df9bda1b70 M: 7e8d9121f44d8331ff55b45c218b87df9bda1b70 192.168.4.55:6355 slots:0-5460 (5461 slots) master 1 additional replica(s) S: 8568fbd73cb296cad6915d524e34761b2114af47 192.168.4.52:6352 slots: (0 slots) slave replicates 28e06c5f24a2b6c6412f81369e09bc9653cc51ff M: bc5c4e082a5a3391b634cf433a6486c867cfc44b 192.168.4.53:6353 slots:10923-16383 (5461 slots) master 1 additional replica(s) S: 63afbb5e7d63b1f142358634578a3488e3c9e634 192.168.4.54:6354 slots: (0 slots) slave replicates bc5c4e082a5a3391b634cf433a6486c867cfc44b M: 28e06c5f24a2b6c6412f81369e09bc9653cc51ff 192.168.4.56:6356 slots:5461-10922 (5462 slots) master 1 additional replica(s) [OK] All nodes agree about slots configuration. >>> Check for open slots... >>> Check slots coverage... [OK] All 16384 slots covered. >>> Send CLUSTER MEET to node 192.168.4.58:6358 to make it join the cluster. [OK] New node added correctly.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
3) Check the status information of the cluster host
Option: check permission
[root@redisA ~]# redis-trib. RB check 192.168.4.58:6358 / / check the status >>> Performing Cluster Check (using node 192.168.4.58:6358) M: c5e0da48f335c46a2ec199faa99b830f537dd8a0 192.168.4.58:6358 slots: (0 slots) master //No hash slot found 0 additional replica(s) M: 7e8d9121f44d8331ff55b45c218b87df9bda1b70 192.168.4.55:6355 slots:0-5460 (5461 slots) master 1 additional replica(s) ... S: a3083123bc5c87a76aab2655171634d4ee84f418 192.168.4.51:6351 slots: (0 slots) slave replicates 7e8d9121f44d8331ff55b45c218b87df9bda1b70 [OK] All nodes agree about slots configuration. >>> Check for open slots... >>> Check slots coverage... [OK] All 16384 slots covered.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
4) Manually migrate the cluster in pieces
Option: reshard reassign hash slot
[root@redisA ~]# redis-trib.rb reshard 192.168.4.58:6358 How many slots do you want to move (from 1 to 16384)?4096 //How many hash slots are taken out to the host 192.168.4.58 What is the receiving node ID? c5e0da48f335c46a2ec199faa99b830f537dd8a0 //id value of host 192.168.4.58 Source node #1:all / / get the hash slot from all current primary Do you want to proceed with the proposed reshard plan (yes/no)?yes ... Moving slot 12283 from 192.168.4.53:6353 to 192.168.4.58:6358: Moving slot 12284 from 192.168.4.53:6353 to 192.168.4.58:6358: Moving slot 12285 from 192.168.4.53:6353 to 192.168.4.58:6358: Moving slot 12286 from 192.168.4.53:6353 to 192.168.4.58:6358: Moving slot 12287 from 192.168.4.53:6353 to 192.168.4.58:6358:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
Check again and find 4096 hash slot s in 4.58
[root@redisA ~]# redis-trib.rb check 192.168.4.58:6358 >>> Performing Cluster Check (using node 192.168.4.58:6358) M: c5e0da48f335c46a2ec199faa99b830f537dd8a0 192.168.4.58:6358 slots:0-1364,5461-6826,10923-12287 (4096 slots) master 0 additional replica(s)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
5) Delete the host of master role
Delete the hash slot occupied by the host first
[root@redisA ~]# redis-trib.rb reshard 192.168.4.58:6358
How many slots do you want to move (from 1 to 16384)?4096
//Number of hash slots removed
What is the receiving node ID? bc5c4e082a5a3391b634cf433a6486c867cfc44b
//The ID to which you want to move is the target host (you can write the ID of a master randomly here)
Source node #1: c5e0da48f335c46a2ec199faa99b830f537dd8a0
//From whom to move is the source host (write the ID of 4.58 here)
Source node #2:done / / setting is complete
...
Moving slot 12282 from c5e0da48f335c46a2ec199faa99b830f537dd8a0
Moving slot 12283 from c5e0da48f335c46a2ec199faa99b830f537dd8a0
Moving slot 12284 from c5e0da48f335c46a2ec199faa99b830f537dd8a0
Moving slot 12285 from c5e0da48f335c46a2ec199faa99b830f537dd8a0
Moving slot 12286 from c5e0da48f335c46a2ec199faa99b830f537dd8a0
Moving slot 12287 from c5e0da48f335c46a2ec199faa99b830f537dd8a0
Do you want to proceed with the proposed reshard plan (yes/no)?yes //Submit
...
Moving slot 12282 from 192.168.4.58:6358 to 192.168.4.53:6353:
Moving slot 12283 from 192.168.4.58:6358 to 192.168.4.53:6353:
Moving slot 12284 from 192.168.4.58:6358 to 192.168.4.53:6353:
Moving slot 12285 from 192.168.4.58:6358 to 192.168.4.53:6353:
Moving slot 12286 from 192.168.4.58:6358 to 192.168.4.53:6353:
Moving slot 12287 from 192.168.4.58:6358 to 192.168.4.53:6353:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
Delete cluster host 4.58 (redis service will be automatically shut down after deletion)
[root@redisA ~]# redis-trib.rb del-node 192.168.4.58:6358 \ c5e0da48f335c46a2ec199faa99b830f537dd8a0 //Delete who + deleted id >>> Removing node c5e0da48f335c46a2ec199faa99b830f537dd8a0 from cluster 192.168.4.58:6358 >>> Sending CLUSTER FORGET messages to the cluster... >>> SHUTDOWN the node.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
6) Add slave node host, add randomly
[root@redisA ~]# redis-trib.rb add-node --slave \ 192.168.4.57:6357 192.168.4.51:6351 >>> Adding node 192.168.4.57:6357 to cluster 192.168.4.51:6351 >>> Performing Cluster Check (using node 192.168.4.51:6351) ...... ...... [OK] All 16384 slots covered. Automatically selected master 192.168.4.51:6351 >>> Send CLUSTER MEET to node 192.168.4.57:6357 to make it join the cluster. Waiting for the cluster to join. >>> Configure node as replica of 192.168.4.51:6351. [OK] New node added correctly.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
7) Remove the slave node. The slave node host has no slot range. You can remove it directly
Command format:
redis-trib. RB del node 192.168.4.57: 6357 host id value
[root@redisA ~]# redis-trib.rb del-node 192.168.4.57:6357 \
f6649ea99b2f01faca26217691222c17a3854381
>>> Removing node f6649ea99b2f01faca26217691222c17a3854381
from cluster 192.168.4.57:6351
>>> Sending CLUSTER FORGET messages to the cluster...
>>> SHUTDOWN the node.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6