Although transformer has very strong learning and modeling ability in CV tasks, it lacks inductive bias like CNN, so transformer's generalization ability is relatively poor compared with CNN. Therefore, if only Transformer Models global information, Without pre training (JFT-300M), transformer is difficult to surpass CNN in performance (without pre training, VOLO's Outlook Attention partially perceives the feature information, which is equivalent to introducing inductive bias). Since CNN has stronger generalization ability and transformer has stronger learning ability, why can't transformer and CNN be combined?
CoAtNet, Google's latest model, integrates convolution + Transformer, and achieves 88.56% on ImageNet-1K data set. Today, we use CoAtNet to classify plant seedlings.
Thesis: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2106.04803v2.pdf
github replay: GitHub - chinhsuanwu/coatnet-pytorch: A PyTorch implementation of "CoAtNet: Marrying Convolution and Attention for All Data Sizes".
Project structure
CoAtNet_demo │ ├─data │ └─train │ ├─Black-grass │ ├─Charlock │ ├─Cleavers │ ├─Common Chickweed │ ├─Common wheat │ ├─Fat Hen │ ├─Loose Silky-bent │ ├─Maize │ ├─Scentless Mayweed │ ├─Shepherds Purse │ ├─Small-flowered Cranesbill │ └─Sugar beet ├─dataset │ └─dataset.py └─models │ └─coatnet.py │ └─train.py │ └─test.py
data set
The data set is classified by plant seedlings, with a total of 12 categories. The dataset connection is as follows:
Link: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1gYb-3XCZBhBoEFyj6d_kdw
Extraction code: q060
Create a new data folder in the root directory of the project. After obtaining the data set, unzip trian and test under the data folder, as shown in the following figure:

Install libraries and import the required libraries
After installation, import into the project.
import torch.optim as optim import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.parallel import torch.utils.data import torch.utils.data.distributed import torchvision.transforms as transforms from dataset.dataset import SeedlingData from torch.autograd import Variable from models.coatnet import coatnet_0
Set global parameters
Set GPU, set learning rate, BatchSize, epoch and other parameters
# Set global parameters
modellr = 1e-4
BATCH_SIZE = 16
EPOCHS = 50
DEVICE = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
Data preprocessing
The data processing is relatively simple without complex attempts. Those interested can add some processing.
# Data preprocessing
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5, 0.5, 0.5], [0.5, 0.5, 0.5])
])
transform_test = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5, 0.5, 0.5], [0.5, 0.5, 0.5])
])
data fetch
Then we will create init. Net under the dataset folder Py and dataset Py, in mydatasets Py folder write the following code:
Talk about the core logic of the code.
The first step is to establish a dictionary, define the ID corresponding to the category, and replace the category with numbers.
The second step is__ init__ Inside write the method to get the picture path. The test set has only one layer of path to read directly. The training set is the category folder under the train folder. First obtain the category, and then obtain the specific image path. Then, using the method of segmenting data set in sklearn, the training set and verification set are segmented according to the ratio of 7:3.
The third step is__ getitem__ Method defines the method of reading a single picture and category. Since the image has a bit depth of 32 bits, I made a conversion when reading the image.
The code is as follows:
# coding:utf8
import os
from PIL import Image
from torch.utils import data
from torchvision import transforms as T
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
Labels = {'Black-grass': 0, 'Charlock': 1, 'Cleavers': 2, 'Common Chickweed': 3,
'Common wheat': 4, 'Fat Hen': 5, 'Loose Silky-bent': 6, 'Maize': 7, 'Scentless Mayweed': 8,
'Shepherds Purse': 9, 'Small-flowered Cranesbill': 10, 'Sugar beet': 11}
class SeedlingData (data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, root, transforms=None, train=True, test=False):
"""
Main objective: to obtain the addresses of all pictures and divide the data according to training, verification and test
"""
self.test = test
self.transforms = transforms
if self.test:
imgs = [os.path.join(root, img) for img in os.listdir(root)]
self.imgs = imgs
else:
imgs_labels = [os.path.join(root, img) for img in os.listdir(root)]
imgs = []
for imglable in imgs_labels:
for imgname in os.listdir(imglable):
imgpath = os.path.join(imglable, imgname)
imgs.append(imgpath)
trainval_files, val_files = train_test_split(imgs, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
if train:
self.imgs = trainval_files
else:
self.imgs = val_files
def __getitem__(self, index):
"""
Returns the data of one picture at a time
"""
img_path = self.imgs[index]
img_path=img_path.replace("\\",'/')
if self.test:
label = -1
else:
labelname = img_path.split('/')[-2]
label = Labels[labelname]
data = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
data = self.transforms(data)
return data, label
def __len__(self):
return len(self.imgs)
Then we were in train Py calls seedlingdata to read the data and remember to import the dataset just written py(from mydatasets import SeedlingData)
# Read data
dataset_train = SeedlingData('data/train', transforms=transform, train=True)
dataset_test = SeedlingData("data/train", transforms=transform_test, train=False)
# Import data
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset_train, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset_test, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False)
Set model
- Set the loss function to NN CrossEntropyLoss().
- Set the model to coatnet_0, modify the last layer full connection output to 12.
- The optimizer is set to adam.
- The learning rate adjustment strategy is changed to cosine annealing
# Instantiate the model and move to the GPU criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() model_ft = coatnet_0() num_ftrs = model_ft.fc.in_features model_ft.fc = nn.Linear(num_ftrs, 12) model_ft.to(DEVICE) # Choose the simple and violent Adam optimizer to reduce the learning rate optimizer = optim.Adam(model_ft.parameters(), lr=modellr) cosine_schedule = optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer=optimizer,T_max=20,eta_min=1e-9)
# Define training process
def train(model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch):
model.train()
sum_loss = 0
total_num = len(train_loader.dataset)
print(total_num, len(train_loader))
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
data, target = Variable(data).to(device), Variable(target).to(device)
output = model(data)
loss = criterion(output, target)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print_loss = loss.data.item()
sum_loss += print_loss
if (batch_idx + 1) % 10 == 0:
print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, (batch_idx + 1) * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset),
100. * (batch_idx + 1) / len(train_loader), loss.item()))
ave_loss = sum_loss / len(train_loader)
print('epoch:{},loss:{}'.format(epoch, ave_loss))
# Verification process
def val(model, device, test_loader):
model.eval()
test_loss = 0
correct = 0
total_num = len(test_loader.dataset)
print(total_num, len(test_loader))
with torch.no_grad():
for data, target in test_loader:
data, target = Variable(data).to(device), Variable(target).to(device)
output = model(data)
loss = criterion(output, target)
_, pred = torch.max(output.data, 1)
correct += torch.sum(pred == target)
print_loss = loss.data.item()
test_loss += print_loss
correct = correct.data.item()
acc = correct / total_num
avgloss = test_loss / len(test_loader)
print('\nVal set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\n'.format(
avgloss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset), 100 * acc))
# train
for epoch in range(1, EPOCHS + 1):
train(model_ft, DEVICE, train_loader, optimizer, epoch)
cosine_schedule.step()
val(model_ft, DEVICE, test_loader)
torch.save(model_ft, 'model.pth')
test
The directory where the test set is stored is shown in the following figure:
The first step is to define the category. The order of this category corresponds to the category order during training. Do not change the order!!!!
classes = ('Black-grass', 'Charlock', 'Cleavers', 'Common Chickweed',
'Common wheat', 'Fat Hen', 'Loose Silky-bent',
'Maize', 'Scentless Mayweed', 'Shepherds Purse', 'Small-flowered Cranesbill', 'Sugar beet')
The second step is to define transforms, which is the same as the transforms of the validation set, without data enhancement.
transform_test = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5, 0.5, 0.5], [0.5, 0.5, 0.5])
])
Step 3: load the model and put the model in DEVICE.
DEVICE = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model = torch.load("model.pth")
model.eval()
model.to(DEVICE)
Step 4: read the picture and predict the category of the picture. Here, note that the Image of the PIL library is used to read the picture. Do not use cv2. transforms does not support it.
path = 'data/test/'
testList = os.listdir(path)
for file in testList:
img = Image.open(path + file)
img = transform_test(img)
img.unsqueeze_(0)
img = Variable(img).to(DEVICE)
out = model(img)
# Predict
_, pred = torch.max(out.data, 1)
print('Image Name:{},predict:{}'.format(file, classes[pred.data.item()]))
Test complete code:
import torch.utils.data.distributed
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from PIL import Image
from torch.autograd import Variable
import os
classes = ('Black-grass', 'Charlock', 'Cleavers', 'Common Chickweed',
'Common wheat', 'Fat Hen', 'Loose Silky-bent',
'Maize', 'Scentless Mayweed', 'Shepherds Purse', 'Small-flowered Cranesbill', 'Sugar beet')
transform_test = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5, 0.5, 0.5], [0.5, 0.5, 0.5])
])
DEVICE = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model = torch.load("model.pth")
model.eval()
model.to(DEVICE)
path = 'data/test/'
testList = os.listdir(path)
for file in testList:
img = Image.open(path + file)
img = transform_test(img)
img.unsqueeze_(0)
img = Variable(img).to(DEVICE)
out = model(img)
# Predict
_, pred = torch.max(out.data, 1)
print('Image Name:{},predict:{}'.format(file, classes[pred.data.item()]))
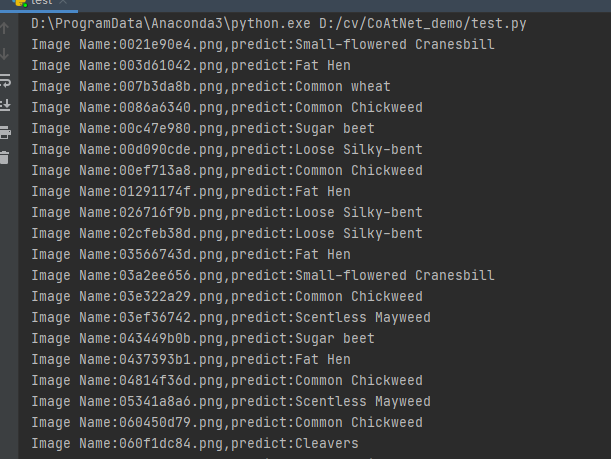
Operation results: