directory structure
- dist packaged vue version
- flow type detection, typeScript changed in 3.0
- script build related configurations of different versions of vue
- src source code
Compiler compiler
Core does not distinguish the core code of the platform
Global API global API
Constructor and prototype method of instance
observer data response
util common tools and methods
vdom virtual dom related - Tfplatforms are implemented on different platforms
- Server server rendering
- sfc .vue single file component analysis
- shared global general tools and methods
- Test test
We mainly focus on src

1, What happens to new vue
index.html
debugger
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
name: 233
},
})
After entering breakpoint debugging, you can see that new Vue has entered / SRC / core / install / index js
function Vue(options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)//Perform a series of initialization and mount
}
/*
*Here are some initialization functions, such as_ init et al
*/
initMixin(Vue)//Definition_ init method
stateMixin(Vue)//Define responsive method $set $delete $watch
eventsMixin(Vue)//Method of defining event $--- on once off emit
lifecycleMixin(Vue)//Method of defining life cycle_ update $forceUpdate $destroy
renderMixin(Vue)//Define rendering related methods $nexttick_ render
export default Vue
Mixin: the main initialization methods are to mount these methods to Vue's prototype.
Note: why not use ES6 class?
in my submission:
1. Compatibility
2. Use the prototype design structure of function, different functions and different files, which is convenient for separation and maintenance, which is an ingenious place of vue.
2, Enter this_ init(options)
src\core\instance\init.js
It is suggested to combine with the official website:
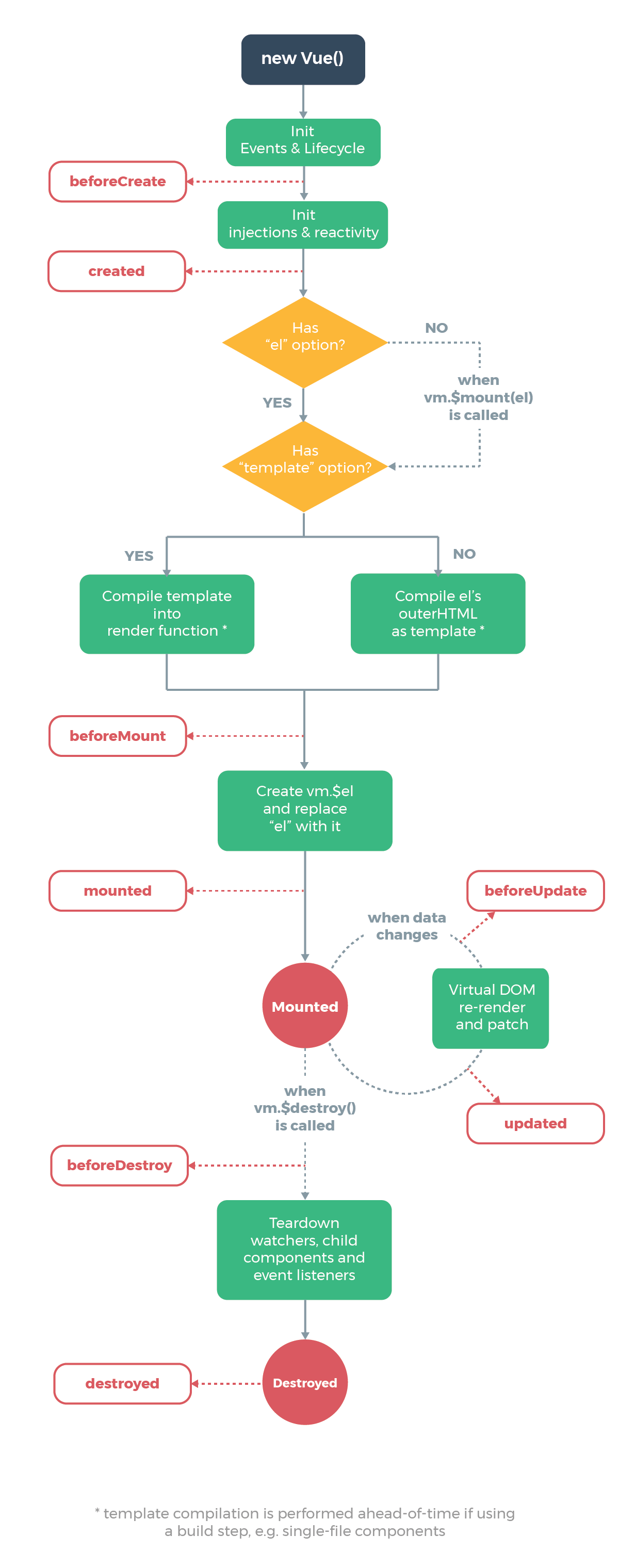
1. Structure (omit unnecessary)
Note that the mark s are performance buried points, which can be skipped, and are based on flow syntax, so your vscode will be popular
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
const vm: Component = this
// a uid
vm._uid = uid++
//slightly
// a flag to avoid this being observed
vm._isVue = true
// merge options
if (options && options._isComponent) {
initInternalComponent(vm, options)//If options is an internal component, the internal component is instantiated
} else {
vm.$options = mergeOptions(//Merge parameters: merge the parameters passed in by the user with the default parameters defined on the prototype
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
)
}
// expose real self
vm._self = vm
initLifecycle(vm)//Confirm the parent-child relationship of the component and initialize some instance properties.
initEvents(vm)//Initialization event
initRender(vm)//Initialize rendering and mount the method that can convert the render function to vnode
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')//implement
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm)//Initialization data
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created')
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)//Mount to dom
}
}
2. Enter entry runtime with compiler This$ mount
src\platforms\web\entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
Code structure:
const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && query(el)
//slightly
// resolve template/el and convert to render function
if (!options.render) {
let template = options.template
if (template) {
template = idToTemplate(template)
} else if (template.nodeType) {
template = template.innerHTML
} else {
return this
}
} else if (el) {
template = getOuterHTML(el)
}
if (template) {
const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, {...}, this)
options.render = render
options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns
}
}
return mount.call(this, el, hydrating)
}
- const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount
What is this business?
- vue has two versions, with and without compiler. We run vue JS with compiler
- If it is runtime only, the render function must be provided. Obviously, we enter entry runtime with compiler js,
- The of this document$ Mount is used to generate the render function from el or template and provide it to runtime only $mount() of JS
- runtime-only. Vue. JS prototype.$ Mount() in SRC \ platforms \ web \ runtime \ index js
-
So the real mount function is SRC \ platforms \ web \ runtime \ index js
-
entry-runtime-with-compiler. Vue. JS prototype.$ Detailed explanation of Mount function
- Get el dom element (finally replace dom, so el cannot be body or html)
- The priority of template is higher than el. If there is a template string = > element, then El will be used instead
- compileToFunctions template = > render function
3. Enter Vue in runtime prototype.$ mount()
The function is: render = > vdom = > Dom and collect the dependencies of the subscription system
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
}
Continue to:
src\core\instance\lifecycle.js
export function mountComponent(
vm: Component,
el: ? Element,
hydrating ? : boolean
): Component {
vm.$el = el
if (!vm.$options.render) {
vm.$options.render = createEmptyVNode
....
}
callHook(vm, 'beforeMount')
let updateComponent
/* istanbul ignore if */
updateComponent = () => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before() {
if (vm._isMounted && !vm._isDestroyed) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */ )
if (vm.$vnode == null) {
vm._isMounted = true
callHook(vm, 'mounted')
}
return vm
}
- explain
In other words, beforeMount template/el has been compiled into the render function, and the virtual dom has not been generated yet
_render render()=>vdom,_update vdom => dom
updateComponent is wrapped in functions_ render(),_ update, and then new Watcher collects the updateComponent
When_ The in render() uses responsive data, adds dependency collection, and executes updateComponent again when the update is triggered
This is data-driven.
At this point, the basic logic has been completed. Go to the debugger to see which part you want to see
4. Process summary
new Vue(op)
- Xxxmixin first defines various methods on the prototype of Vue
- Enter_ init
- If options is a component, the component is instantiated. If not, the parameters are merged
- Confirm the parent-child relationship of components, and events, Render
- beforeCreate
- Injections, responsive data, Provide
- created
- compile-$mount template/el=>render
- runtime-$mount render =>vdom=>dom
summary
Don't stick to details, step by step.