Codeforces Round #761 (Div. 2)
A. Forbidden Subsequence
subject

Knowledge points
sort
Problem solving ideas
According to the meaning of the topic, it is easy for us to know when T = a b c T = abc When T=abc and we S S S medium a , b , c a,b,c a. B and C all appear, our youngest S ′ S' S' should be in accordance with a c b d e f g . . . z acbdefg...z acbdefg...z, otherwise it is in dictionary order a b c d e . . . z abcde...z abcde...z .
So we just have to judge T T Whether T is a b c abc abc, S S S medium a , b , c a,b,c a. Whether B and C all appear, and then write the cmp function.
(see code for details)
code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(x) cerr << #x << " = " << x << '\n'
#define between(x, l, r) (x >= l && x <= r)
#define point(a, b, m) ((a - 1) * m + b)
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define SUM(a) accumulate(all(a), 0LL)
#define MIN(a) (*min_element(all(a)))
#define MAX(a) (*max_element(all(a)))
#define np next_permutation
#define lb lower_bound
#define ub upper_bound
#define eb emplace_back
#define pb push_back
#define y second
#define x first
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<double, double> PDD;
const int N = 3e5 + 10, M = 2 * N, mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
bool cmp(char a, char b)
{
if(a == 'b' && b == 'c') return 0;
if(b == 'b' && a == 'c') return 1;
return a < b;
}
void solve()
{
string s, t;
cin >> s >> t;
int num[100] = {0};
for (auto &it : s) num[it - 'a'] ++ ;
if(t == "abc" && num[0] && num[1] && num[2]) sort(all(s), cmp);
else sort(all(s));
cout << s << '\n';
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0);
cout.precision(2), cout.setf(ios::fixed);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t -- )
solve();
return 0;
}
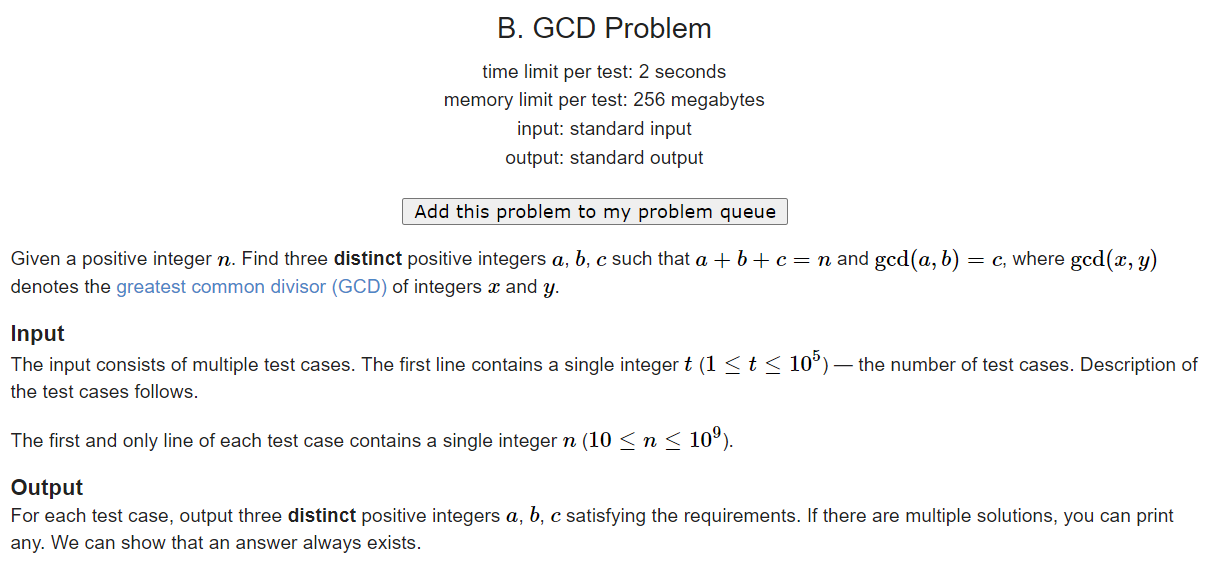
B. GCD Problem
subject
Knowledge points
number theory
Problem solving ideas
If n n n is an even number
We can construct c = 1 c = 1 c=1, a = ( n − 1 ) / 2 a = (n - 1) / 2 a=(n−1)/2 , b = n − 1 − a b = n - 1 - a b=n−1−a
Because ∣ a − b ∣ = 1 |a - b| = 1 ∣ a − b ∣ = 1, so g c d ( a , b ) = 1 gcd(a, b) = 1 gcd(a,b)=1
If n n n is an even number
We order c = 1 c = 1 c=1, and then the traversal of violence a , b a, b a. B. find satisfaction g c d ( a , b ) = 1 , a + b = n − 1 gcd(a, b) = 1, a+b=n - 1 A pair of gcd(a,b)=1,a+b=n − 1 ( a , b ) (a, b) (a,b)
We can find out by typing the watch g c d ( a , n − 1 − a ) = 1 gcd(a, n - 1 - a) = 1 The interval between gcd(a,n − 1 − a)=1 will not be too large, so the violence will not timeout.
(see code for details)
code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(x) cerr << #x << " = " << x << '\n'
#define between(x, l, r) (x >= l && x <= r)
#define point(a, b, m) ((a - 1) * m + b)
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define SUM(a) accumulate(all(a), 0LL)
#define MIN(a) (*min_element(all(a)))
#define MAX(a) (*max_element(all(a)))
#define np next_permutation
#define lb lower_bound
#define ub upper_bound
#define eb emplace_back
#define pb push_back
#define y second
#define x first
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<double, double> PDD;
const int N = 3e5 + 10, M = 2 * N, mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
/*
gcd(a, b) = c
a + b + c = n
(k + 1) * c == n
c =
If n is even
c = 1
a = (n - 1) / 2
b = n - 1 - a
*/
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
if(n % 2 == 0)
{
int a = (n - 1) / 2, b = n - 1 - a;
int c = 1;
cout << a << ' ' << b << ' ' << c << '\n';
}
else
{
for (int i = 3; i * 2 <= n; i += 2)
{
if(__gcd(i, n - 1 - i) != 1 || i == n - 1 - i) continue;
cout << i << ' ' << n - (1 + i) << ' ' << 1 << '\n';
return;
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0);
cout.precision(2), cout.setf(ios::fixed);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t -- )
solve();
return 0;
}
C. Paprika and Permutation
subject

Knowledge points
Thinking, greed
Problem solving ideas
This problem requires us to find the minimum number of modular operations so that the array a a A become a [ 1 , n ] [1, n] Arrangement of [1,n].
Our analysis shows that a number X X X is the number that can be obtained by modulus operation X ′ ∈ [ 0 , ⌊ X − 1 2 ⌋ ] X' ∈[0, \lfloor \frac{X - 1}{2} \rfloor] X ′∈ [0, ⌊ 2X − 1 ⌋] (modulus greater than X X X (meaningless, not considered).
Then we first put the array a a Which has already appeared in a [ 1 , n ] [1, n] Remove the number in [1,n], for example a : [ 1 , 100 , 5 , 2 , 24 , 8 , 5 ] → a : [ 100 , 24 , 8 , 5 ] a:[1, 100, 5, 2, 24,8, 5] → a:[100,24,8,5] a: [1100,5,2,24,8,5] → a:[100,24,8,5], and then an array of numbers that have not been matched b : [ 7 , 6 , 4 , 3 ] b:[7,6,4,3] b:[7,6,4,3] match from large to small, and let the remaining unmatched numbers have m m m, judge whether it meets the requirements for ∀ i ∈ [ 1 , m ] , a [ i ] ≤ ⌊ b [ i ] − 1 2 ⌋ ∀i∈[1, m], a[i]≤\lfloor \frac{b[i] - 1}{2} \rfloor ∀ I ∈ [1,m],a[i] ≤ ⌊ 2b[i] − 1 ⌋, output if not satisfied − 1 -1 − 1, output when satisfied m m m . (among the remaining unmatched numbers, the large and large matching must be the best)
(see code for details)
code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(x) cerr << #x << " = " << x << '\n'
#define between(x, l, r) (x >= l && x <= r)
#define point(a, b, m) ((a - 1) * m + b)
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define SUM(a) accumulate(all(a), 0LL)
#define MIN(a) (*min_element(all(a)))
#define MAX(a) (*max_element(all(a)))
#define np next_permutation
#define lb lower_bound
#define ub upper_bound
#define eb emplace_back
#define pb push_back
#define y second
#define x first
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<double, double> PDD;
const int N = 3e5 + 10, M = 2 * N, mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int a[N];
int st[N];
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) st[i] = 0; // Has the number been matched
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
int res = n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
if(a[i] <= n && !st[a[i]])
{
st[a[i]] = 1;
res -- ;
a[i] = 0; // Delete directly
}
}
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1, greater<int>());
//Traverse the number to be matched from large to small
for (int i = n, j = 1; i >= 1; i -- )
{
if(st[i]) continue;
int t = a[j] / 2 + 1, r = a[j] % t; //r is the maximum value of a[j] that can be obtained by taking the mold
if(r < i) // Can't get
{
cout << -1 << '\n';
return;
}
j ++ ;
}
cout << res << '\n';
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0);
cout.precision(2), cout.setf(ios::fixed);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t -- )
solve();
return 0;
}
D. Too Many Impostors
subject

Knowledge points
thinking
Problem solving ideas
easy:
We set q u e r y ( a , b , c ) query(a,b,c) query(a,b,c) represents triples ( a , b , c ) (a, b, c) Which of (a,b,c) has more people.
Let's go through traversal to find satisfaction q u e r y ( i , i + 1 , i + 2 ) ! = q u e r y ( i + 1 , i + 2 , i + 3 ) query(i, i+1,i+2) != query(i+1,i+2,i+3) query(i,i+1,i+2)!= A of query (I + 1, I + 2, I + 3) i i The position of i can be obtained i , i + 3 i, i+3 i. I + 3 are two different people, and then we pass q u e r y ( i , i + 3 , x ) query(i, i+3, x) query(i,i+3,x) can get x x What kind of person is in position x.
Upper limit times: 2 ∗ n 2 * n 2∗n
hard:
Let's divide people first n 3 \frac{n}{3} 3n # blocks, i.e [ 1 , 2 , 3 ] , [ 4 , 5 , 6 ] , . . . , [ n − 2 , n − 1 , n ] [1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6],...,[n - 2, n - 1, n] [1,2,3],[4,5,6],...,[n − 2,n − 1,n] blocks, and the of each block is obtained q u e r y query query value
Because n 3 < k < 2 n 3 \frac{n}{3}<k<\frac{2n}{3} 3n < K < 32n, so there will be at least one block q u e r y query The query value is 1 1 1. One is 0 0 0.
We choose one q u e r y query The query value is 0 0 The first subscript of the block of 0 x x x , q u e r y query The query value is 1 1 The first subscript of the block of 1 y y y .
We can ask twice q 1 = q u e r y ( x , x + 1 , y ) q_1 = query(x, x+1, y) q1=query(x,x+1,y) , q 2 = q u e r y ( x , x + 1 , y + 1 ) q_2 = query(x, x+1, y + 1) q2 = query(x,x+1,y+1) to get a 0 0 Location of 0( 1 1 Position of 1 (the same is true)
Because q u e r y ( y , y + 1 , y + 2 ) = 1 query(y, y + 1, y + 2) = 1 query(y,y+1,y+2)=1, so y , y + 1 y, y+1 y. At least one of Y + 1 is 1 1 1, so if q 1 , q 2 q_1,q_2 q1, q2 , are all 0, then it means x , x + 1 x, x+1 x. X + 1 is all 0 0 0, otherwise description x , x + 1 x,x+1 x. One of X + 1 is 1 1 1. Due to q u e r y ( x , x + 1 , x + 2 ) = 0 query(x,x+1,x+2) = 0 query(x,x+1,x+2)=0, then x + 2 x+2 x+2 must be 0 0 0.
Finding one 1 , 0 1, 0 After the position of 1,0, we make a a a is 0 0 Location of 0, b b b is 1 1 1 position.
We traverse each block, and each block we can pass twice q u e r y query query gets the types of the three elements, as shown below q u e r y query The query value is 1 1 1 as an example.
[ 1 , 1 , 0 ] [1, 1, 0] [1,1,0] Yes q u e r y ( i , i + 1 , a ) = 1 , q u e r y ( i + 1 , i + 2 , a ) = 0 query(i,i+1,a) = 1, query(i+1, i+2,a) = 0 query(i,i+1,a)=1,query(i+1,i+2,a)=0
[ 1 , 0 , 1 ] [1, 0, 1] [1,0,1] Yes q u e r y ( i , i + 1 , a ) = 0 , q u e r y ( i + 1 , i + 2 , a ) = 0 query(i,i+1,a) = 0, query(i+1, i+2,a) = 0 query(i,i+1,a)=0,query(i+1,i+2,a)=0
[ 0 , 1 , 1 ] [0, 1, 1] [0,1,1] Yes q u e r y ( i , i + 1 , a ) = 0 , q u e r y ( i + 1 , i + 2 , a ) = 1 query(i,i+1,a) = 0, query(i+1, i+2,a) = 1 query(i,i+1,a)=0,query(i+1,i+2,a)=1
[ 1 , 1 , 1 ] [1, 1, 1] [1,1,1] Yes q u e r y ( i , i + 1 , a ) = 1 , q u e r y ( i + 1 , i + 2 , a ) = 1 query(i,i+1,a) = 1, query(i+1, i+2,a) = 1 query(i,i+1,a)=1,query(i+1,i+2,a)=1
At this point, we can distinguish all kinds of numbers.
Upper limit times: n + 4 n + 4 n+4
(see code for details)
code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(x) cerr << #x << " = " << x << '\n'
#define between(x, l, r) (x >= l && x <= r)
#define point(a, b, m) ((a - 1) * m + b)
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define SUM(a) accumulate(all(a), 0LL)
#define MIN(a) (*min_element(all(a)))
#define MAX(a) (*max_element(all(a)))
#define np next_permutation
#define lb lower_bound
#define ub upper_bound
#define eb emplace_back
#define pb push_back
#define y second
#define x first
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<double, double> PDD;
const int N = 3e5 + 10, M = 2 * N, mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
/*
*/
vector<int> g[2];
int p[N], ans[N];
int query(int a, int b, int c)
{
int res;
cout << "? " << a << ' ' << b << ' ' << c << endl;
cin >> res;
return res;
}
void EasySolve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int last = -1, ans, a, b;
g[0].clear(), g[1].clear();
/*
You can get different numbers a, b
Then we can use this to determine other numbers
Then we choose the other two different ones to judge a and b
*/
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 2; i ++ )
{
ans = query(i, i + 1, i + 2);
if(last != -1 && ans != last)
{
a = i - 1, b = i + 2;
g[ans].push_back(i + 2);
g[!ans].push_back(i - 1);
break;
}
last = ans;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
if(i == a || i == b) continue;
ans = query(a, b, i);
g[ans].push_back(i);
}
sort(all(g[0]));
cout << "! " << g[0].size();
for (auto &it : g[0]) cout << ' ' << it;
cout << endl;
}
void HardSolve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int x, y; // More liars, more good people
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) ans[i] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i += 3)
{
p[i] = query(i, i + 1, i + 2);
if (p[i] == 0) x = i;
else y = i;
}
int a, b;// Liar, good man
if (query(x, x + 1, y) || query(x, x + 1, y + 1)) a = x + 2;
else a = x;
if (query(y, y + 1, x) && query(y, y + 1, x + 1)) b = y;
else b = y + 2;
// Traversal block
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i += 3)
{
if (p[i] == 1)//Bad < good
{
ans[i] = ans[i + 1] = ans[i + 2] = 1;
int t1 = query(a, i, i + 1), t2 = query(a, i + 1, i + 2);
if (t1 == 0 && t2 == 0) ans[i + 1] = 0;
else if (t1 == 0) ans[i] = 0;
else if (t2 == 0) ans[i + 2] = 0;
}
else //Good < bad
{
int t1 = query(b, i, i + 1), t2 = query(b, i + 1, i + 2);
if(t1 == 1 && t2 == 1) ans[i + 1] = 1;
else if (t1 == 1 && t2 == 0) ans[i] = 1;
else if (t2 == 1 && t1 == 0) ans[i + 2] = 1;
}
}
// Statistical answer
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cnt += 1 - ans[i];
// Output answer
cout << "! " << cnt;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
if(ans[i] == 0) cout << " " << i;
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0);
cout.precision(2), cout.setf(ios::fixed);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t -- ) HardSolve();
return 0;
}