preface
The Java class library provides many common classes that can be called directly in programming. This section focuses on the Arrays, StringBuilder, Calendar, Date, Math, System, Random classes and common methods of classes.
Tip: the following is the main content of this article. The following cases can be used for reference
1, Arrays
The Arrays class contains various methods for manipulating Arrays, such as sorting and searching. It also contains a static factory that allows you to turn Arrays into lists.
Common methods:
| method | describe |
|---|---|
| List asList(T... a) | Returns a List constructed from the specified array |
| void sort(Object[] a) | Sort arrays |
| void fill(Object[] a, Object val) | Assign the same value to all elements of the array |
| boolean equals(Object[] a, Object[] a2) | Check whether the two arrays are equal |
| int binarySearch(Object[] a, Object key) | Use dichotomy to find data for the sorted array |
2, StringBuilder
The StringBuilder class is mutable. It is the equivalent class of String. It can add and write variable sequences of characters, and insert characters into the middle of the String or append them to the end of the String (of course, there is no need to create other objects).
Construction method of StringBuilder:
| Construction method | explain |
|---|---|
| StringBuilder() | Construct a StringBuilder without characters, with an initial capacity of 16 characters |
| StringBuilder(CharSequence seq) | Construct a StringBuilder that contains the same characters as the specified CharSequence |
| StringBuilder(int capacity) | Construct a StringBuilder with the specified initial capacity |
| StringBuilder(String str) | And initializes its contents to the specified string contents |
Common methods of StringBuilder class:
| method | Return value | Function description |
|---|---|---|
| insert(int offsetm,Object obj) | StringBuilder | Insert the string obj at offset M |
| append(Object obj) | StringBuilder | Append the string obj to the end of the string |
| length() | int | Determines the length of the StringBuilder object |
| setCharAt(int index,char ch) | void | Sets the character at the position specified by index using the new value specified by ch |
| toString() | String | Convert to string form |
| reverse() | StringBuilder | Reverse string |
| delete(int start, int end) | StringBuilder | Deletes the character sequence from the start position to the index (end-1) position specified by end in the calling object |
| replace(int start, int end, String str) | StringBuilder | Replace one set of characters with another. The replacement string starts at the position specified by start and ends at the position specified by end |
The code is as follows (example):
public class StringBuilderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder("I");
s.append(" java");
s.insert(1," love");
String t = s.toString();
System.out.println(t);
s.reverse();
String x= s.toString();
System.out.println(x);
s.delete(1,4);
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
}
Operation results:

3, Calendar
Calendar class is an abstract class, which completes the conversion between Date class and ordinary Date notation. We mostly use GregorianCalendar class, a subclass of calendar class. It realizes the Gregorian calendar system widely used in the world. Of course, we can also inherit the calendar class, and then define and implement the calendar method ourselves.
| Construction method | function |
|---|---|
| GregorianCalendar() | The relevant values in the created object are set to the specified time zone, and the current time of the default location, that is, the time zone in which the program runs and the current time of the location |
| GregorianCalendar(TimeZone zone) | The relevant values in the created object are set to the specified time zone, the current time of the default location |
| GregorianCalendar(Locale aLocale) | The relevant values in the created object are set to the default time zone, specifying the current time of the location a locale |
| GregorianCalendar(TimeZone zone,Locale aLocale) | The relevant values in the created object are set to the specified time zone and the current time of the specified place |
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class CalendarDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Full display date and time:");
// String conversion date format
DateFormat fdate = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String str = fdate.format(new Date());
System.out.println(str);
// Create Calendar object
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
// Initialize the Calendar object, but it is not necessary unless you need to reset the time
calendar.setTime(new Date());
// Show year
System.out.println("Year: " + calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR));
// Display month (starting from 0, the actual display needs to be increased by one)
System.out.println("Month: " + calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH));
// Current minutes
System.out.println("minute: " + calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE));
// The nth day of this year
System.out.println("This year's third " + calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR) + "day");
// The nth day of this month
System.out.println("The third day of this month " + calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH) + "day");
// After 3 hours
calendar.add(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, 3);
System.out.println("Time after three hours: " + calendar.getTime());
// Format display
str = (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SS")).format(calendar.getTime());
System.out.println(str);
// Reset Calendar to display the current time
calendar.setTime(new Date());
str = (new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SS")).format(calendar.getTime());
System.out.println(str);
// Create a Calendar to compare time
Calendar calendarNew = Calendar.getInstance();
// Set to 5 hours ago, the latter is large and displays - 1
calendarNew.add(Calendar.HOUR, -5);
System.out.println("Time comparison:" + calendarNew.compareTo(calendar));
// After setting for 7 hours, the former is large and displays 1
calendarNew.add(Calendar.HOUR, +7);
System.out.println("Time comparison:" + calendarNew.compareTo(calendar));
// Return for 2 hours, the time is the same, and 0 is displayed
calendarNew.add(Calendar.HOUR, -2);
System.out.println("Time comparison:" + calendarNew.compareTo(calendar));
// calendarNew creation time point
System.out.println((new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SS")).format(calendarNew.getTime()));
// calendar creation time point
System.out.println((new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SS")).format(calendar.getTime()));
System.out.println("Time comparison:" + calendarNew.compareTo(calendar));
}
}
Operation results:
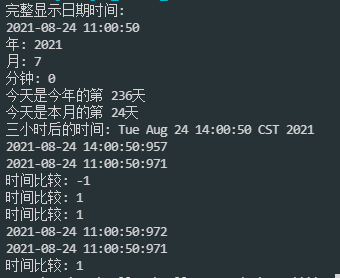
Note: the meaning of month is the same as that of Date class. 0 represents January and 11 represents December.
4, Date
The Date class represents Date and time, which encapsulates the methods of operating Date and time. The Date class is often used to get the current time of the system.
Take a look at the non obsolete constructor defined in class Date:
| Construction method | explain |
|---|---|
| Date() | Construct a Date object and initialize it to reflect the current time |
| Date(long date) | Construct a Date object and initialize it according to the number of milliseconds relative to GMT January 1, 1970 00:00:00 |
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class DateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String strDate, strTime;
Date objDate = new Date();
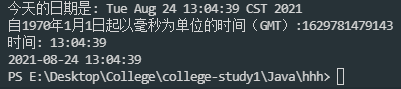
System.out.println("Today's date is:" + objDate);
long time = objDate.getTime();
System.out.println("Time in milliseconds since January 1, 1970( GMT): " + time);
strDate = objDate.toString();
//Extract GMT time
strTime = strDate.substring(11, (strDate.length() - 4));
//Extract time by hour, minute, and second
strTime = "Time:" + strTime.substring(0, 8);
System.out.println(strTime);
//Format time
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(formatter.format(objDate));
}
}
Operation results
5, Math
Math class in Java Lang package contains methods for performing basic mathematical operations, such as elementary exponent, logarithm, square root and trigonometric function.
Common methods:
| method | Return value | Function description |
|---|---|---|
| sin(double numvalue) | double | Calculate the sine of the angle numvalue |
| cos(double numvalue) | double | Calculates the cosine of the angle numvalue |
| acos(double numvalue) | double | Calculates the arccosine of numvalue |
| asin(double numvalue) | double | Calculate the inverse sine of numvalue |
| atan(double numvalue) | double | Calculate the arctangent of numvalue |
| pow(double a, double b) | double | Calculate the power b of a |
| sqrt(double numvalue) | double | Calculates the positive square root of a given value |
| abs(int numvalue) | int | Calculates the absolute value of the int type value numvalue, and also receives parameters of types long, float, and double |
| ceil(double numvalue) | double | Returns the smallest integer value greater than or equal to numvalue |
| floor(double numvalue) | double | Returns the maximum integer value less than or equal to numvalue |
| max(int a, int b) | int | Returns the larger value of int type a and b, and also receives parameters of type long, float and double |
| min(int a, int b) | int | Returns the smaller of a and b, and can also accept parameters of type long, float, and double |
| rint(double numvalue) | double | Returns the integer value closest to numvalue |
| round(T arg) | long is returned when arg is double and int is returned when arg is float | Returns the integer value closest to arg |
| random() | double | Returns a double value with a positive sign, which is greater than or equal to 0.0 and less than 1.0 |
public class MathDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
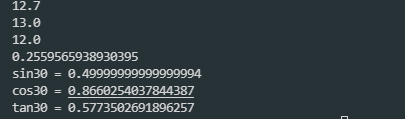
System.out.println(Math.abs(-12.7));
System.out.println(Math.ceil(12.7));
System.out.println(Math.rint(12.4));
System.out.println(Math.random());
System.out.println("sin30 = " + Math.sin(Math.PI / 6));
// Calculate the sine value of 30 °, and the parameter is the angle expressed in radians, i.e. one sixth of π
System.out.println("cos30 = " + Math.cos(Math.PI / 6));
// Calculate the cosine value of 30 °. The parameters and return values of these methods for calculating trigonometric functions are double
System.out.println("tan30 = " + Math.tan(Math.PI / 6));
// Calculate the tangent of 30 °
}
}
Operation results:
- Using math Random () generates two random numbers a and b.
- Find the larger of the two random numbers.
- Only methods in the Math class can be used.
import java.lang.Math;
public class MathTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double a = Math.random();
double b = Math.random();
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(Math.max(a, b));
}
}
Operation results:

6, Random
Random class is used to generate pseudo-random number stream in Java Util package.
import java.util.Random;
public class RandomDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
//Randomly generate an integer int range
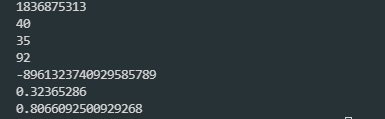
System.out.println(random.nextInt());
//Generate an integer in the range of [0,n], and set n=100
System.out.println(random.nextInt(100 + 1));
//Generate an integer in the [0,n) range, and set n=100
System.out.println(random.nextInt(100));
//Generate an integer in the range of [m,n], set n = 100, M = 40
System.out.println((random.nextInt(100 - 40 + 1) + 40));
//Randomly generate an integer long range
System.out.println(random.nextLong());
//Generate float type decimal in [0,1.0) range
System.out.println(random.nextFloat());
//Generate double type decimals in the [0,1.0) range
System.out.println(random.nextDouble());
}
}
Operation results:
summary
Tip: here is a summary of the article:
For example, the above is what we are going to talk about today. The Java class library also has many classes. This section only explains the commonly used categories.