1, Help command
docker --help
2, Process related commands
-
Start Docker service
systemctl start docker
-
Stop docker service
systemctl stop docker
-
Restart docker service
systemctl restart docker
-
View docker service status
systemctl status docker
-
Start the docker service
systemctl enable docker
3, Mirror related commands
-
View mirror
# View all information about the mirror docker images # View the id of the image used docker images –q
-
Search image
# Search image docker search Image name # For example, search for redis images docker search redis
-
Pull image
# Pull the latest image docker pull Image name # Pull the image of the specified version docker pull Image name:Version number
If you don't know the image version, you can go docker hub Search to view the version.
-
delete mirror
# Deletes the specified local mirror docker rmi image id # Delete all local images (generally do not need to change the command) docker rmi `docker images -q`
4, Container related commands
-
View container
# View running containers docker ps # View all containers docker ps -a
-
Create container
# Create container docker run parameter # For example, after creating a centos container, it automatically enters the container. When exiting the container, the container automatically closes docker run -it --name=c2 centos:8 # For example, create a centos container in background guard mode docker run -id --name=c3 centos:8
Parameter Description:
- -i: Keep the container running. Usually used with - t.
- -t: Reassign a pseudo input terminal to the container, usually in conjunction with - i.
- -d: Run the container in daemon (background) mode.
- -The container created by it is generally called interactive container. After the container is created, it automatically enters the container. After exiting the container, the container automatically closes.
- -The container created by id is generally called a guard container.
- – Name: name the created container.
-
Enter container
# Exit the container and the container will not close docker exec parameter # For example, enter a container named c3 docker exec -it c3 /bin/bash
-
Start container
# Start container docker start Container name # For example, start a container named c3 docker start c3
-
Stop container
# Stop container docker stop Container name # For example, stop a container named c3 docker stop c3
-
Delete container
# Delete container docker rm Container name # For example, delete a container named c3 docker rm c3
Note: you need to stop the container to delete it.
-
View container information
# View container information docker inspect Container name # For example, view the information of a container named c3 docker inspect c3
-
Copy container files to host
docker cp container id Or container name:The file path to be copied by the container is copied to the file path belonging to the master
5, Container's data volume
-
Data volume
- Data volume
- A data volume is a directory or file in the host
- When the container directory and the data volume directory are bound, the other party's modifications will be synchronized immediately
- A data volume can be mounted by multiple containers at the same time
- A container can also mount multiple data volumes
- Data volume function:
- Container data persistence
- Indirect communication between external machine and container
- Data exchange between containers
- Data volume
# When creating a boot container, use the – v parameter to set the data volume docker run ... –v Host Directory(file):In container directory(file) [–v Host Directory(file):In container directory(file)...] # For example, create centos8 c1 container and / root / Tata of the container_ Mount the container to / root/data of the system docker run -it --name=c1 -v /root/data:/root/tata_container centos:8 /bin/bash
[note]:
- The directory of the container must be an absolute path.
- If the directory does not exist, it is created automatically.
- Multiple data volumes can be mounted.
- The following / bin/bash can be ignored.
-
Data volume container
- Concept: a directory or file of the host
- effect:
- Container data persistence
- Client and container data exchange
- Data exchange between containers
- Data volume container:
- Create a container, mount a directory, and let other containers inherit from the container (– volume from).
- Data volume configuration in a simple way
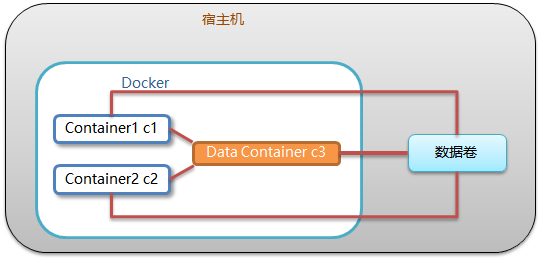
# Create a boot c3 data volume container and set the data volume using the – v parameter docker run –it --name=c3 –v /volume centos:8 /bin/bash # Create the boot c1 c2 container and set the data volume with the – - volumes from parameter docker run –it --name=c1 --volumes-from c3 centos:8 /bin/bash docker run –it --name=c2 --volumes-from c3 centos:8 /bin/bash