create object
ECMA variable
- Define variables with the'var'keyword and initialize them to arbitrary values
- Values stored in variables can be changed
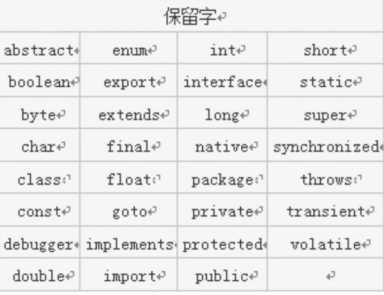
Keyword and Retained Word
Keyword

Retention words
ECMAJscript operator
- Operators are a series of symbols that complete operations, also known as operators.
- Operators are used to perform operations on one or more fingers of a river and return results.
- The value of an operator is called an operand.
- The combination of operators and operands is called an expression.
Operator type
1 arithmetic operator
They are: + - * /%+ -.
2 Compare (Relational) Operators
They are: > <= >===========!=
!==
The comparison operator must return a Boolean value (true,false)
3 logical operators
They are & & & | |!
The result of a logical operator must be a Boolean value
In logical operators, logic is not (!) In a certain proportion, it will reduce the amount of code development to a certain extent.
Logical nonsense
In the expression, the values of logically non-representational true are
'!''Non-String - Notice the difference between a space character and a space character. Because a space character has space occupancy, it is counted as a non-empty string!!!!! null! NaN! undefined;
Conjecture: From the above five special return values true, can we think so?
As long as it means that there is nothing or that it does not occupy any place except the object, the return is true.
Or as long as the five exceptions mentioned above are true
console.log(!{}); //false
console.log(!' ') //false
console.log('Arbitrary non-character'); //false
console.log(!'') //true
console.log(!1) //false
console.log(!0) //true
console.log(!null); //true
console.log(!NaN); //true
console.log(!undefined) //true
Logic and&&
[External Link Picture Transfer Failure (img-XBYhXmAW-15661347139) (C: Users Don AppData Roaming Typora typora-user-images 1592;850.png)]
4 assignment operator
= += -= *= /= %=
5 join operator
- As long as the number of operations on either side of "+" is string data, the addition operation is no longer performed.
- The result of the connection is string data
console.log(12 + '12'); //1212 console.log(12 - '12') //0
Particular attention
Only + can be used for default character splicing, and Number type conversion between deleted numbers by default
Number implicit conversion occurs by default in * - /% arithmetic operators.
Operator priority
Parentheses > arithmetic operators > comparison operators > logical operators > assignment operators
Method of creating objects
Create ordinary objects through the constructor Object()
new role: instantiating objects
new constructor () --> instantiate object
The constructor can be built-in by js or customized by us
var student = new Object();
var liuMing = "Liu Ming",
var liuJuan = "Liu Juan",
Object Addendum and Access
Create ordinary objects through the constructor Object()
new role: instantiating objects
new constructor () --> instantiate object
The constructor can be built-in by js or customized by us
Object takes value, object adds key:value
1. Object adds key:value
If an object is created by a constructor, key:value can be added as a parameter.
//Method 1. Adding key:value to the data transmission
var person = new Object({
'a':'Liu Ming',
'b':'Liu Ming1',
'c':'Liu Ming 2',
});
// Mode 2: Add key:value to the dot.
// Grammar: object.key = value
person.d = "Liu Ming 3";
var liuMing4 = "Liu Ming 4";
person.e = liuMing4;
Obtain
Value selection method 1. Punctuation and acceptance of the results by variables
var one = person.a
console.log(person.d)
//Value selection method II
// Grammar: object ['attribute'], functions with and only with left and right values
// How to process the acquired value is either used directly or output directly
var d1 = person['d'];
console.log(d1,'wer');
var a = {
e:"sd",
b:{
}
}
Summary: The last point is always the object on the left and the arbitrary data type on the right.
Boolean
var bool = new Boolean({
a :false,
//Boolean() function: converting other types of data into Boolean types
// Create (construct) Boolean objects,
// A bool attribute has been added, which changes the built-in value from empty to structured, so it is true
});
//Example
var boolstr1 = new Boolean('aaa'); //true
var boolstr2 = new Boolean('true'); //true
var boolstr3 = new Boolean('false'); //true
var boolstr4 = new Boolean(true); //true
var boolstr5 = new Boolean(0); //false
var boolstr6 = new Boolean(NaN); //false
var boolstr7 = new Boolean(null); //false
var boolstr8 = new Boolean(23); //true
var boolstr9 = new Boolean([]); //true
var boolstr10 = new Boolean(' '); //true
var boolstr11 = new Boolean(''); //false
var boolstr12 = new Boolean(false);
Summary: Converting in Boolean(), if null''0 represents a value that does not exist, the input result is false, except for [] empty arrays.
If there is a real value in it, it is converted to true. Except for false
String object
Strings use the base class String to construct objects.
var str = 'Hong Kong is part of China';
console.log(str); //Hong Kong is part of China
var str2 = 'Transferred meaning\'character\'';
console.log(str2) //Escape'character'
var str3 = "123.13.23";
console.log(Number(str3)) //NaN
console.log(Number('')) //0
console.log(parseInt(true)) //true
console.log(parseInt("")) //NaN
console.log(parseInt('')) //NaN
console.log(parseFloat('13.123 Hong Kong')) //13.123
console.log(parseFloat('')) //NaN
console.log(Math.round('123.343 Hong Kong') ) //NaN
console.log(Math.round(true) ) //1
console.log(Math.round(false) ) //0
console.log(Math.round("12321.943") ) //12322
console.log( Math.round("true") ) //NaN
console.log(Number("12321.Hong Kong") ) //NaN
console.log(Number("true") ) //NaN
The string is converted to Number(), with a value of NaN and no value of 0.
Digital Object

Date object
Use Date();
GetTime () 1565766812786 timestamp timestamp, unique, timestamp is the total time milliseconds of the current time
One second equals 1000 milliseconds
When using time, be sure to pay attention to the api of time.
Create the date object new Date(), which can be abbreviated as new Date().getTime();
One day of the week, use local time. The return value is an integer between 0 (Sunday) and 6 (Saturday).
var date = new Date(); var year = date.getFullYear(); var month = date.getMonth() + 1; var day = date.getDate(); var hours = date.getHours(); var m = date.getMinutes(); var s = date.getSeconds(); var ms = date.getMilliseconds(); var timeX = date.getTime(); var a = new Date().getTime(); console.log(date)
1. Create a date object, Date();
Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Sunday
The week system established by the Babylonians first spread to ancient Greece and Rome. Ancient Romans named a week and seven day s after their own gods: Sun's-day, Moon's-day, Mars's-day, Mercury's-day, Jupiter's-day, Venus'-day, Saturn's-day. Day).
After the seven names came to Britain, the Anglo-Saxons changed four of them with the names of their own gods of faith, replacing Mars's-day, Mercury's-day, Jupiter's-day and Venus'-day with Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday, respectively. Tuesday comes from Tiu, the Anglo-Saxon God of war; Wednesday comes from Woden, the highest god, also known as the Lord God; Thursday comes from Thor, the God of thunder; Friday comes from Frigg, the goddess of love. This gives us the name of seven days a week in today's English.
Array object
-
Array characteristics
-
Ordered index values, which can start at [0] and end at [length-1].
-
Array data: can be any data type, data repeatable
-
Future data structures, arrays are i objects, objects have arrays
-
-
Values in arrays
- Array name [index value]
- Get the most data array[array.length -1]
-
Array length
- Represents the total number of data in an array
- Get var len = array.length
-
Create arrays
Way 1. Constructor Way - Array Array Array Array's Constructor Function, Create Array
Array, data in an array with no parameters
Array characteristics
1. Orderly, starting from 0.
2. 0~n is the [index value] of an array
Note: Index values are unique and orderly
3. Data in an array can be of any data type
4. Data repeatability in arrays
Note: The data structures we will encounter later are all objects in the array and arrays in the object.
var arr = new Array(1,'Hello',true,{name:'Huang Shunfei'},'');
console.log(arr)
/**
Array Creation Mode II
*/
var arr1 = [1,2,3,4,5,{name:'Huang Shunfei'},[1,2,3[245,465,7632,432,657,6,53,42],4,5]];
console.log(arr1)
/*
Array value, syntax array[index] array - array name index value
Get the last element length - 1 of the array
*/
var arr2 = arr1[arr1.length - 1];
console.log(arr2)
/*
Change the contents of array elements
*/
arr1[2] = {mes:'I love China'};
console.log(arr1[2])
- Create Array 2
API s inside arrays
slice
Returns a part of the array and composes a new array without affecting the original array object.
Reference 1: Starting with the number of index values
Reference 2: End with the number of index values, excluding this index value
Interception data interval: start <= x < end
var arr = [1,2,3,'Liu Ming','Liu Ming 2',4];
var res = arr.slice(3,5);
console.log(res); //(2) ["Liu Ming", "Liu Ming 2"]
console.log(arr); //(6) 1, 2, 3,'Liu Ming','Liu Ming 2','Liu Ming 2', 4]
Roll caller
Finding Random Index Value
var arr = ['Liu Ming','king','Liu Yi','woqu','snow peak'];
/*
Finding Random Index Value
*/
var i = Math.round(Math.random()*4);
// Requirement: Output is pointed to in the page
// document.write(arr[i]);
document.write("<h1>" + "Call the roll."+ arr[i] + "</h1>");
split
split() cuts the string into arrays and returns a new array
Converting arrays to strings
var className = 'icon,icon2';
var arr = className.split(',');
console.log(className); // icon,icon2
console.log(arr); // (2) ["icon", "icon2"]
/*
Array content addition
*/
arr[2] = 'icon3';
arr[3] = 'icon4';
arr[4] = 'icon5';
console.log(arr); //(5) ["icon", "icon2", "icon3", "icon4", "icon5"]
var str = arr.toString();
console.log(str) //icon,icon2,icon3,icon4,icon5
var str1 = arr.join(' ');
/*
Spaces separate each data into strings
*/
console.log(str1) //icon icon2 icon3 icon4 icon5
document.write(' <div class=" '+ str1+' "> '+ 'I am the addition of array classes'+' </div>');
Class addition involves adding sections to arrays, where arrays are spliced into join s and arrays are converted into strings to String.
Array deletion
Array element content deletion
delete deletes the contents of an array, which is equivalent to resetting the contents, but the length of the array remains unchanged, which means that the data is in a negative state until then.
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6];
var arr1 = delete arr[2];
console.log(arr1) //true
console.log(arr); //(6) [1, 2, empty, 4, 5, 6]
console.log(arr.constructor); //ƒ Array() { [native code] }
pop
Deleting the last element of the array will delete and modify the original array.
Grammar: arr.pop()
Interpretation: arr represents the target array of elements to be deleted.
There are no parameters, the parameters are invalid, only one array element can be deleted at a time, and it is the last element in the list.
There is a default return value, which returns deleted elements
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,'Be gone']; var arr1 = arr.pop(2); console.log(arr1); //Be gone console.log(arr); //(7) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] console.log(arr.pop()); //7 console.log(arr); //(6) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
shift
Delete the first element of the target array and change the contents of the original array.
Grammar: arr.shift();
Array represents a modified target arr ay.
There are no parameters and the parameters are invalid.
There is a default return value, which returns the deletion of the original first element in the target array.
var arr = ['I'm in the front position.',1,2,3,4,5,6,7]; var arr1 = arr.shift(2); console.log(arr1); //I'm in the front position. console.log(arr); //(7) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] console.log(arr.shift()); // 1 console.log(arr); //(6) [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
splice
Deleting an array changes the contents of the original array
Grammar: arr. splice (parameter 1, parameter 2);
// Syntax: arr. splice (parameter 1, parameter 2, parameter 3,...). It does not take into account parameter 3 and redundant parameters, if any, it will be replaced, which is not consistent with the theme.
Interpretation: arr is the target array of deletion operations.
Parametric 1 represents the element index value of arr array, [index value]
Parametric 2 denotes the number of intercepted elements
With a return value, the default return is an intercepted array
var arr = ['I'm in the front position.',1,2,3,4,5,6,7]; var arr1 = arr.splice(1,2); console.log(arr1); //(2) [1, 2] console.log(arr); //(6) ["I'm in the front position", 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] console.log(arr.splice(1,2)); //(2) [3, 4] console.log(arr); //(4) ["I'm in the front position", 5, 6, 7]
Array addition
In practice, adding selectors to build style cascades can be accomplished by adding arrays. Refer to the split section
push
Adding elements at the end of the array modifies the original array.
*** Grammar: *** arr. push (parameter 1, parameter 2,...). )
Interpretation: push is the API for arrays
Where arr represents the target parameter added to the array,
Parameter 1, parameter 2,.... Represents the target element that needs to be added, and can be of any type value.
Returns the default value, which is the modified array length
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7];
var arr1 = arr.push('I am the first push','I am the second push');
console.log(arr1); //9
console.log(arr.push('I'm the third push')) // 10
console.log(arr); //(10) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7,'I'm the first push','I'm the second push','I'm the third push']
unshift
In front of the first element of the array, adding n elements will modify the original array.
Characteristic
Before adding an element to the first element of an array, it occupies the position of the first element, and the position of the original element moves one bit backward in turn.
Syntax: arr. unshift (parameter 1, parameter 2,...). );
Interpretation: unshift is an API for arrays.
Where arr indicates that the target parameter is added to the ARR array;
The parameter n denotes the element to be added. If the number of parameters to be added is greater than 1, an orderly arrangement is added after the last addition of the array element.
The parameters can be arbitrary values.
There is a default return value, which is the length of the added array
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7];
var arr1 = arr.unshift('I am the first','I am the second',{},[''],null,undefined,);
console.log(arr1) //8
console.log(arr) //(8) ["I am the first", [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
concat
Merge one or more arrays and [return] a new array.
Characteristic:
Splicing between concat arrays does not affect the value of array parameters, and returns a new array after completing the method.
Syntax: Array 1. concat (Array parameter 2 for stitching, Array parameter 2 for stitching). )
Interpretation: This API will be array 1 and splicing array parameter 2, splicing array parameter 3. Wait for stitching, will not change any of the original array, and return a stitched array.
The principle is to copy array 1 by default, then splice the array, and finally return the new array.
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]; var arr1 = ['I am arr1',2,33,44,55,77]; var arr2 = ['arr2',3,4,5,1]; var arr3 = arr1.concat(arr,arr2); console.log(arr3) //(18) ["I am arr1", 2, 33, 44, 55, 77, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, arr2, 3, 4, 5, 1] console.log(arr1.concat(arr,arr2)) //(18) ["I am arr1", 2, 33, 44, 55, 77, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, arr2, 3, 4, 5, 1] console.log(arr1) //(6) ["I am arr1", 2, 33, 44, 55, 77]
Array modification
splice
Deleting an array changes the contents of the original array
Syntax: arr. splice (parameter 1, parameter 2, parameter 3,...). It does not take into account that there are only two parameters, if any, they will be replaced, which is not consistent with the theme.
Interpretation: arr is the target array of deletion operations.
Parametric 1 represents the element index value of arr array, [index value]
Parametric 2 denotes the number of intercepted elements
Parametric 3 and subsequent parameters represent elements that are replaced at that location.
With a return value, the default return is an intercepted array
var arr = ['I'm in the front position.',1,2,3,4,5,6,7];
var arr1 = arr.splice(1,2,'I am a replacement. splice',{},'I am Replacement 2');
console.log(arr1); //(2) [1, 2]
console.log(arr); //(9) ["I'm in the front position," "I'm replacing splice," { } "I am Replacement 2", 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
console.log(arr.splice(1,2)); //(2) ["I am replacing splice", { ]
console.log(arr); //(7) ["I'm in the front position", "I'm replacing 2", 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
Summary:
Spice () function: delete, add, replace
There may be many parameters, but note the parameter representation:
Reference 1: Indicates that the index value of the array begins with the index value of the array.
Reference 2: Represents deleting parameter elements from the position of [index]
Reference 3 and subsequent parameters: Indicates the number of elements added to the index that occupies the index.
Array sorting
sort
sort() sort step
ASCII Code Sorting
1. Convert each element to a string type.
2. Retrieve the first character and convert it to pseudo-ASCII code value
3. Use the converted ASCII code value to sort the size and ascend the order by ASCII code.
Note: The function has a return value. It returns an array after changing the order of the array, which will change the original order of the array.
Some commonly used ASCII codes and Unicode codes can be recited when necessary.
var arr = [1,3,6,2,7,44,11]; arr.sort(); console.log(arr.sort()) //(7) [1, 11, 2, 3, 44, 6, 7] console.log(arr) // [1, 11, 2, 3, 44, 6, 7] // Note: 1 11 111 2 23 2444 5 516
reverse
To reverse the order of elements in an array, from the previous order to reverse order
Note: Functions have return values, returning an array after operation, which will affect the order of the original array.
var arr = [1,3,6,2,7,44,11]; arr.reverse(); console.log(arr.reverse()) // [1, 3, 6, 2, 7, 44, 11] console.log(arr) //[1, 3, 6, 2, 7, 44, 11]
Conversion between Arrays and Strings
Converting arrays to strings
toString
* toString converts all fields in an array into strings and returns a new string,* without changing the contents of the original array.
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5];
var str1 = arr.toString(); //1,2,3,4,5 strings
console.log(arr1) //(5) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
join
join: Stitching the contents of an array into strings does not change the original contents of the original array and returns a new string
If the content is empty, the effect is the same as toString
If the content is a space string, it means splicing all fields in the array into a new string.
Parameters: Characters used to replace commas, default commas
console.log(str1);
var str2 = arr.join();
console.log(str2);
var str3 = arr.join("");
console.log(str3) //12345
var str4 = arr.join(" ");
console.log(str4) //12345