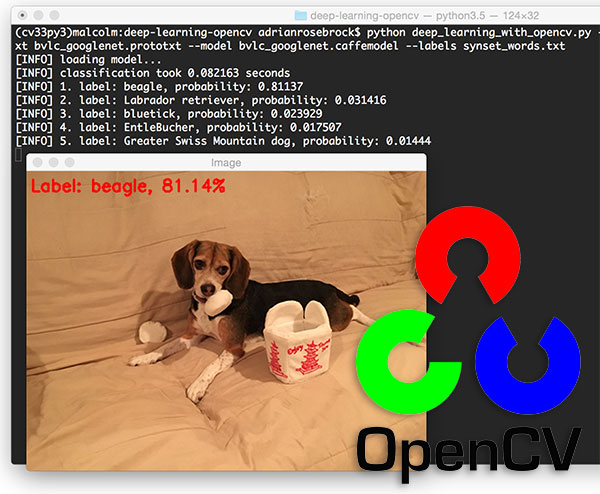
Using the pre trained deep learning face detector model provided by OpenCV, face recognition can be carried out quickly and accurately.
In August 2017, OpenCV 3.3 was officially released, bringing a highly improved "DNN deep neural networks" module. The module supports many deep learning frameworks, including Caffe, TensorFlow and Torch / PyTorch.
Caffe based face detector in Here.
Two sets of files are required:
- . prototype file defining the model architecture
- . caffemodel file containing the weight of the actual layer
The weight file is not included in the OpenCV sample directory.
How does OpenCV deep learning face detector work?
# USAGE # python detect_faces.py --image rooster.jpg --prototxt deploy.prototxt.txt --model res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000.caffemodel # import the necessary packages import numpy as np import argparse import cv2 # construct the argument parse and parse the arguments ap = argparse.ArgumentParser() ap.add_argument("-i", "--image", required=True, help="path to input image") ap.add_argument("-p", "--prototxt", required=True, help="path to Caffe 'deploy' prototxt file") ap.add_argument("-m", "--model", required=True, help="path to Caffe pre-trained model") ap.add_argument("-c", "--confidence", type=float, default=0.5, help="minimum probability to filter weak detections") args = vars(ap.parse_args()) # load our serialized model from disk print("[INFO] loading model...") net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(args["prototxt"], args["model"]) # load the input image and construct an input blob for the image # by resizing to a fixed 300x300 pixels and then normalizing it image = cv2.imread(args["image"]) (h, w) = image.shape[:2] blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(cv2.resize(image, (300, 300)), 1.0, (300, 300), (104.0, 177.0, 123.0)) # pass the blob through the network and obtain the detections and # predictions print("[INFO] computing object detections...") net.setInput(blob) detections = net.forward() # loop over the detections for i in range(0, detections.shape[2]): # extract the confidence (i.e., probability) associated with the # prediction confidence = detections[0, 0, i, 2] # filter out weak detections by ensuring the `confidence` is # greater than the minimum confidence if confidence > args["confidence"]: # compute the (x, y)-coordinates of the bounding box for the # object box = detections[0, 0, i, 3:7] * np.array([w, h, w, h]) (startX, startY, endX, endY) = box.astype("int") # draw the bounding box of the face along with the associated # probability text = "{:.2f}%".format(confidence * 100) y = startY - 10 if startY - 10 > 10 else startY + 10 cv2.rectangle(image, (startX, startY), (endX, endY), (0, 0, 255), 2) cv2.putText(image, text, (startX, y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.45, (0, 0, 255), 2) # show the output image cv2.imshow("Output", image) cv2.waitKey(0)
Implementation:
$ python detect_faces.py --image rooster.jpg --prototxt deploy.prototxt.txt --model res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000.caffemodel
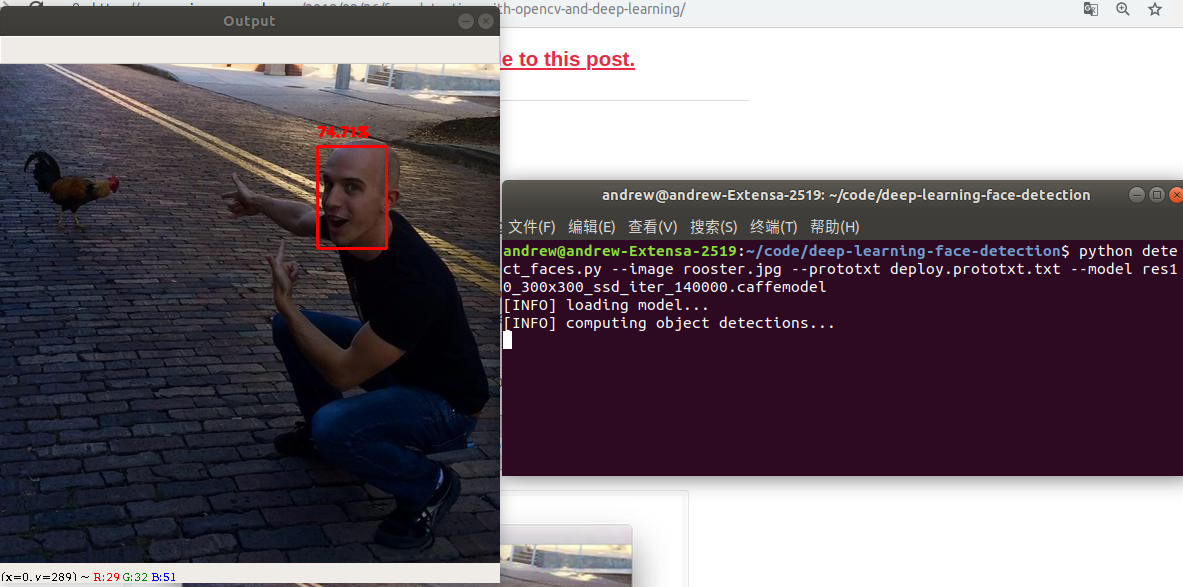
The upper face has a 74.30% confidence level. Although opencv's Haar cascade lacks "direct" angle faces, it can still detect faces by using OpenCV's deep learning face detector.
Here are three examples of faces:
python detect_faces.py --image iron_chic.jpg --prototxt deploy.prototxt.txt --model res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000.caffemodel

Face detection in video, video stream and webcam applications
# USAGE # python detect_faces_video.py --prototxt deploy.prototxt.txt --model res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000.caffemodel # import the necessary packages from imutils.video import VideoStream import numpy as np import argparse import imutils import time import cv2 # construct the argument parse and parse the arguments ap = argparse.ArgumentParser() ap.add_argument("-p", "--prototxt", required=True, help="path to Caffe 'deploy' prototxt file") ap.add_argument("-m", "--model", required=True, help="path to Caffe pre-trained model") ap.add_argument("-c", "--confidence", type=float, default=0.5, help="minimum probability to filter weak detections") args = vars(ap.parse_args()) # load our serialized model from disk print("[INFO] loading model...") net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(args["prototxt"], args["model"]) # initialize the video stream and allow the cammera sensor to warmup print("[INFO] starting video stream...") vs = VideoStream(src=0).start() time.sleep(2.0) # loop over the frames from the video stream while True: # grab the frame from the threaded video stream and resize it # to have a maximum width of 400 pixels frame = vs.read() frame = imutils.resize(frame, width=400) # grab the frame dimensions and convert it to a blob (h, w) = frame.shape[:2] blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(cv2.resize(frame, (300, 300)), 1.0, (300, 300), (104.0, 177.0, 123.0)) # pass the blob through the network and obtain the detections and # predictions net.setInput(blob) detections = net.forward() # loop over the detections for i in range(0, detections.shape[2]): # extract the confidence (i.e., probability) associated with the # prediction confidence = detections[0, 0, i, 2] # filter out weak detections by ensuring the `confidence` is # greater than the minimum confidence if confidence < args["confidence"]: continue # compute the (x, y)-coordinates of the bounding box for the # object box = detections[0, 0, i, 3:7] * np.array([w, h, w, h]) (startX, startY, endX, endY) = box.astype("int") # draw the bounding box of the face along with the associated # probability text = "{:.2f}%".format(confidence * 100) y = startY - 10 if startY - 10 > 10 else startY + 10 cv2.rectangle(frame, (startX, startY), (endX, endY), (0, 0, 255), 2) cv2.putText(frame, text, (startX, y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.45, (0, 0, 255), 2) # show the output frame cv2.imshow("Frame", frame) key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF # if the `q` key was pressed, break from the loop if key == ord("q"): break # do a bit of cleanup cv2.destroyAllWindows() vs.stop()
Implementation:
python detect_faces_video.py --prototxt deploy.prototxt.txt --model res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000.caffemodel
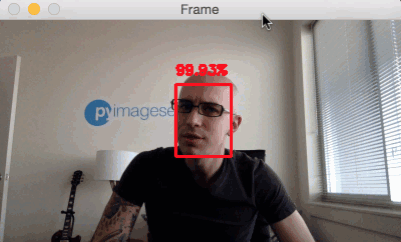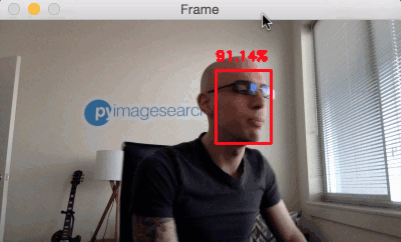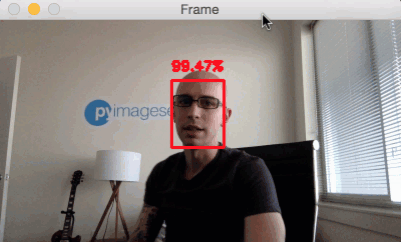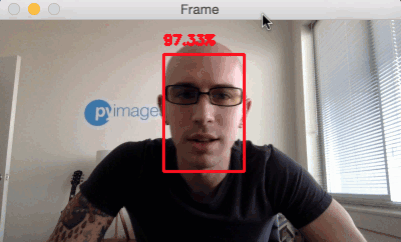
Reference material
- Technical support qq group 144081101 (code and model storage)
- Address of the latest version of this article
- python test development library involved in this article Thanks a lot!
- This article related massive books Download
- 2018 best artificial intelligence machine learning tool book and download (continuous update)