First issue of this article: https://www.cnblogs.com/somata/p/LinuxLDAPUserAuthentication.html
I use the LDAP user management completed by CentOS, which may be different from most of the online tutorials, but if I write it out, it will certainly be useful, but there will be some files, forget to teach.
The OPENLdap used here cooperates with the user management completed by CentOS 7. It needs to configure three services: nssswitch, pam and sssd. It needs some understanding before the configuration of this paper can be completed.
Basic configuration
- Complete the configuration of yum source
mkdir /root/back tar -Jcvf /root/back/yum.repos.d-`date '+(%Y.%m.%d_%H:%M:%S)'`.tar.xz /etc/yum.repos.d/ rm -rf /etc/yum.repos.d/* curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo curl -o /etc/yum,repos.d/CentOS-epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo yum makecache
- Install necessary software
yum -y install vim bash-completion openldap-servers openldap-clients nss-pam-ldapd sssd
OPENLdap service initialization
Initialization process will not go into too much detail, detailed queries< OPENLDAP Service Construction and Post-management>.
- First stop the database service:
systemctl stop slapd
- Then edit the file:
# Back up the file first so that it won't be restored mkdir /root/back tar -Jcvf /root/back/slapd.config-`date '+(%Y.%m.%d_%H:%M:%S)'`.tar.xz /etc/openldap/slapd.d/ tar -Jcvf /root/back/slapd.data-`date '+(%Y.%m.%d_%H:%M:%S)'`.tar.xz /var/lib/ldap/ # Then delete the configuration file rm -rf /etc/openldap/slapd.d/* rm -rf /var/lib/ldap/* # Copy configuration files to temporary directories mkdir /root/ldap cd /root/ldap
- Write the configuration file of slapd. The configuration file here evolved from / usr/share/openldap-servers/slapd.ldif, mainly modifying baseDN(suffix), OPENLDAPTLS, olcRootPW (password generated by slappasswd, password in this article is 123456) and include.
# file: /root/ldap/slapd.ldif
dn: cn=config
objectClass: olcGlobal
cn: config
olcArgsFile: /var/run/openldap/slapd.args
olcPidFile: /var/run/openldap/slapd.pid
olcTLSCertificateFile: /etc/openldap/certs/server.crt
olcTLSCertificateKeyFile: /etc/openldap/certs/server.key
olcTLSCACertificateFile: /etc/openldap/cacerts/cacert.pem
dn: cn=schema,cn=config
objectClass: olcSchemaConfig
cn: schema
include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/core.ldif
include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/cosine.ldif
include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/nis.ldif
include: file:///etc/openldap/schema/inetorgperson.ldif
dn: olcDatabase=frontend,cn=config
objectClass: olcDatabaseConfig
objectClass: olcFrontendConfig
olcDatabase: frontend
dn: olcDatabase=config,cn=config
objectClass: olcDatabaseConfig
olcDatabase: config
olcAccess: to *
by dn.base="gidNumber=0+uidNumber=0,cn=peercred,cn=external,cn=auth" manage
by * none
dn: olcDatabase=monitor,cn=config
objectClass: olcDatabaseConfig
olcDatabase: monitor
olcAccess: to *
by dn.base="gidNumber=0+uidNumber=0,cn=peercred,cn=external,cn=auth" read
by dn.base="cn=Manager,dc=black,dc=com" read
by * none
dn: olcDatabase=hdb,cn=config
objectClass: olcDatabaseConfig
objectClass: olcHdbConfig
olcDatabase: hdb
olcSuffix: dc=black,dc=com
olcRootDN: cn=Manager,dc=black,dc=com
olcRootPW: {SSHA}l1vBI/HOMKLEiQZgcm3Co+hFQI68rH1Q
olcDbDirectory: /var/lib/ldap
olcDbIndex: objectClass eq,pres
olcDbIndex: ou,cn,mail,surname,givenname eq,pres,sub- Configure OPENSSL certificates. Encrypted tunnel for openldap server.
# First, create the certificate file for the CA service cd /etc/pki/CA openssl genrsa -out private/cakey.pem 2048 openssl req -new -x509 -key private/cakey.pem -out cacert.pem # The Certificate creation process here is omitted. # However, it should be noted that it is necessary to ensure that the beginning of the application for server certificate must be the same as the beginning of the certificate, otherwise the certificate can not be issued through CA. touch index.txt echo "01" > serial # Then apply for the issuance of server certificates cd /etc/openldap/certs/ openssl genrsa -out server.key 2048 openssl ca -in server.csr -out server.crt -days 365 # Copy CA certificate to specified location mkdir /etc/openldap/cacerts cp /etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem /etc/openldap/cacerts/
- Generate server configuration files based on configuration
slapadd -F "/etc/openldap/slapd.d/" -b "cn=config" -l slapd.ldif # You also need to pay attention to whether the file belongs to the owner or root, and you need to change it back to openldap. chown -R ldap:ldap /etc/openldap/slapd.d/* # Then open the service. systemctl start slapd
_#################### 100.00% eta none elapsed none fast!
Closing DB...
- Initialize the database
dn: dc=black,dc=com dc: black objectClass: top objectClass: domain dn: cn=Manager,dc=black,dc=com objectClass: organizationalRole cn: Manager description: LDAP Manager dn: ou=People,dc=black,dc=com ou: People objectClass: top objectClass: organizationalUnit objectClass: domainRelatedObject associatedDomain: black.com dn: ou=Group,dc=black,dc=com ou: Group objectClass: top objectClass: organizationalUnit objectClass: domainRelatedObject associatedDomain: black.com
- Import to database
ldapadd -x -D "cn=Manager,dc=black,dc=com" -w 123456 -f base.ldif # Import basic information into the database.
adding new entry "dc=black,dc=com"
adding new entry "cn=root,dc=black,dc=com"
adding new entry "ou=People,dc=black,dc=com"
adding new entry "ou=Group,dc=black,dc=com"
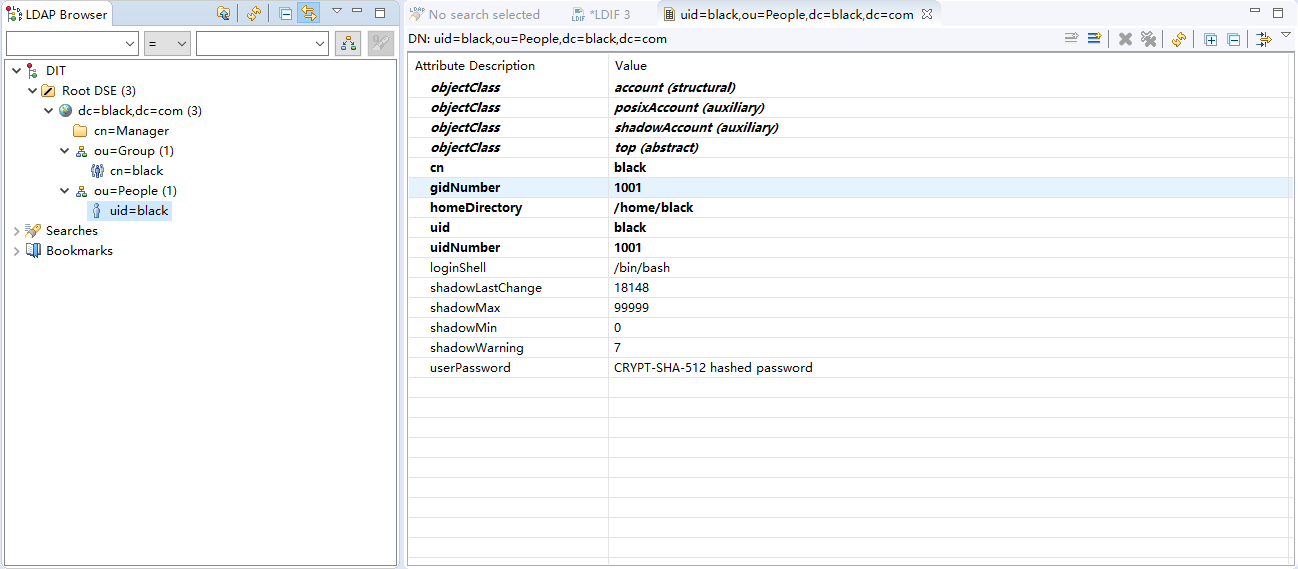
- Then use apache directory studio to see if the server has been successfully configured.
First, open the firewall.
firewall-cmd --add-service=ldap
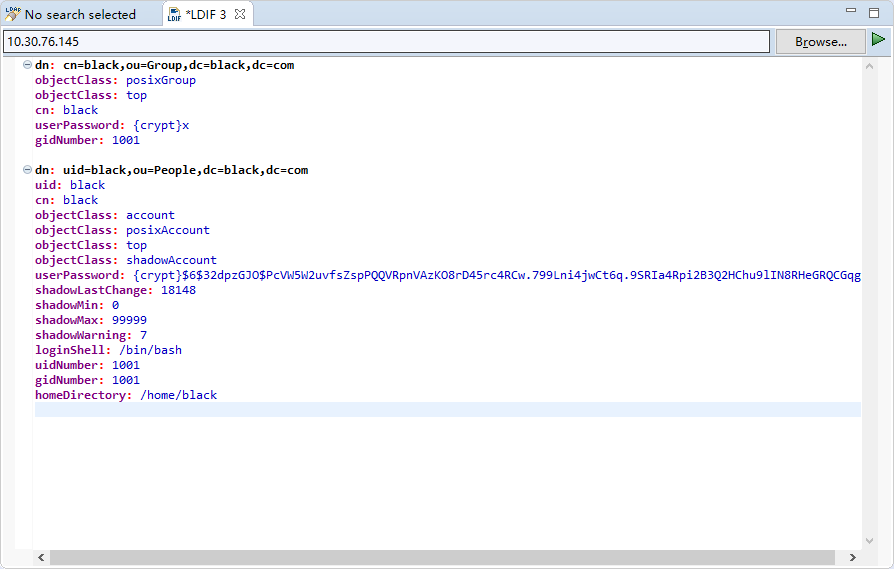
- Let's import a user here for later test usage
NSS, PAM and SSD configuration
NSS Service Configuration
If you want nss to query ldap, you first need to enable a service called nslcd. Here is the configuration file for that service.
# file: /etc/nslcd.conf uid nslcd gid ldap uri ldap://127.0.0.1/ base dc=black,dc=com binddn cn=Manager,dc=black,dc=com bindpw 123456 ssl no tls_cacertdir /etc/openldap/cacerts
Startup service
chmod 600 /etc/nslcd.conf systemctl start nslcd systemctl enable nslcd
Configure nss
# file: /etc/nsswitch.conf passwd: files ldap # The main thing is that passwd, shadow and group need to add ldap later. shadow: files ldap group: files ldap hosts: files dns myhostname bootparams: nisplus [NOTFOUND=return] files ethers: files netmasks: files networks: files protocols: files rpc: files services: files sss netgroup: nisplus sss publickey: nisplus automount: files nisplus sss aliases: files nisplus
Test for availability:
getent passwd | grep black
black❌1001:1001:black:/home/black:/bin/bash
PAM Service Configuration
Here I copied the PAM configuration file from another one using authconfig-tui configuration content.
# file: /etc/pam.d/system-auth auth required pam_env.so auth required pam_faildelay.so delay=2000000 auth [default=1 ignore=ignore success=ok] pam_succeed_if.so uid >= 1000 quiet auth [default=1 ignore=ignore success=ok] pam_localuser.so auth sufficient pam_unix.so nullok try_first_pass auth requisite pam_succeed_if.so uid >= 1000 quiet_success auth sufficient pam_sss.so forward_pass auth required pam_deny.so account required pam_unix.so broken_shadow account sufficient pam_localuser.so account sufficient pam_succeed_if.so uid < 1000 quiet account [default=bad success=ok user_unknown=ignore] pam_sss.so account required pam_permit.so password requisite pam_pwquality.so try_first_pass local_users_only retry=3 authtok_type= password sufficient pam_unix.so sha512 shadow nullok try_first_pass use_authtok password sufficient pam_sss.so use_authtok password required pam_deny.so session optional pam_keyinit.so revoke session required pam_limits.so -session optional pam_systemd.so session [success=1 default=ignore] pam_succeed_if.so service in crond quiet use_uid session required pam_unix.so session optional pam_sss.so
PAM can be used directly without service restart
sssd service configuration
For LDAP user login, the PAM configuration forwards it to SSSD, which authenticates the user.
# file: /etc/sssd/sssd.conf [domain/black.com] autofs_provider = ldap cache_credentials = True ldap_search_base = dc=black,dc=com id_provider = ldap auth_provider = ldap chpass_provider = ldap ldap_uri = ldap://127.0.0.1/ ldap_id_use_start_tls = True ldap_tls_reqcert = never ldap_tls_cacertdir = /etc/openldap/cacerts [sssd] services = nss, pam, autofs domains = black.com [nss] homedir_substring = /home [pam] [sudo] [autofs] [ssh] [pac] [ifp] [secrets] [session_recording]
Configure the startup service and set the startup self-startup.
chmod 600 /etc/sssd/sssd.conf # Pay attention to the configuration of permissions, otherwise it will not start. systemctl start sssd systmctl enable sssd
test
Then the user authentication part is made. Now let's test it.
Because the system-auth file is configured and no ssh file is configured, ssh is not connected. So login is used here to test the feasibility.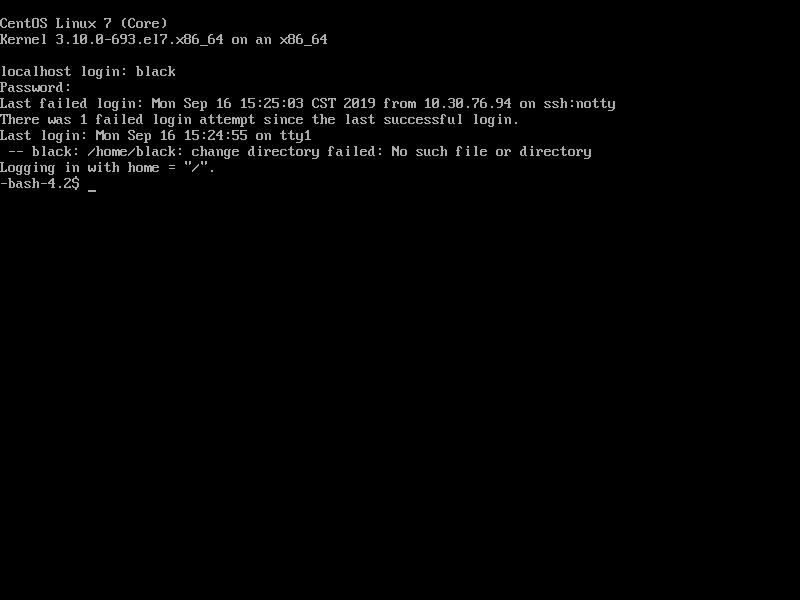
Script
I wrote a script for this LDAP user authentication to facilitate adding users. I would like to emphasize that although CentOS provides migration tools to store users in LDAP databases, if you mention all local users to LDAP databases without retaining local users, then you will find that the computer will not be able to restart, so it is recommended that users with UID s less than 1000 not be restarted. Store it on the LDAP server.
The script is on gitee. https://gitee.com/somata/script/blob/master/ldap_adduser.sh
It's easy to use.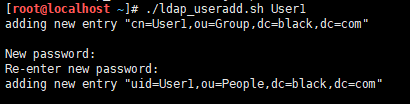
Then test whether the added user can log in: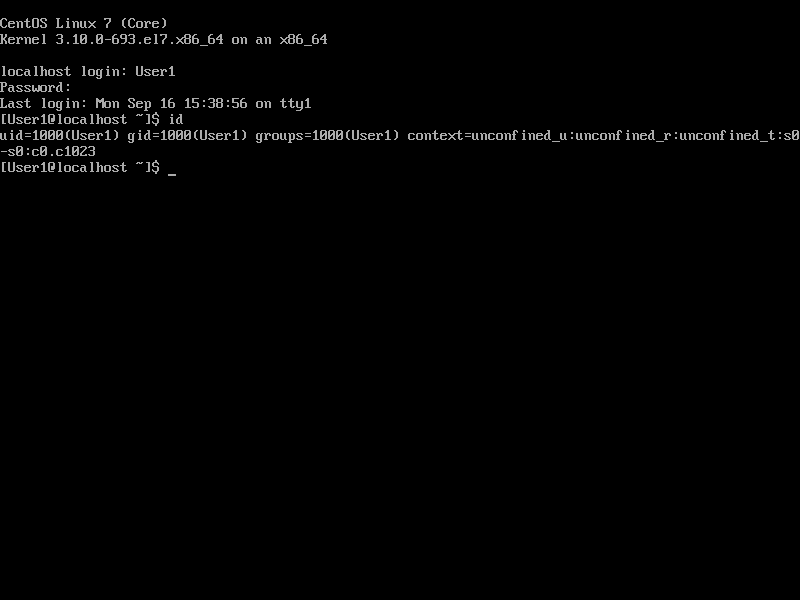
This article is authenticated by the original. The author visited yuanben.io to get authorization information.