After genome assembly or transcriptome differential gene expression analysis, annotation of the results is an important step. How to annotate and how to obtain accurate annotation results?
Nr database, fully known as non redundantprotein sequence database, refers to the protein database containing the sequences in GenPept, Swissprot, PIR, PDF, PDB and RefSeq Database.
(1) Database download
Personal download methods are divided into graphical interface download and command line download.
Software installation required:
# blast wget https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/executables/blast+/LATEST/ncbi-blast-2.12.0+-x64-linux.tar.gz tar -zxvf ncbi-blast-2.12.0+-x64-linux.tar.gz echo 'PATH=your_path/blast/ncbi-blast-2.12.0+/bin:$PATH' >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc # aspera wget -c https://d3gcli72yxqn2z.cloudfront.net/connect_latest/v4/bin/ibm-aspera-connect_4.1.0.46-linux_x86_64.tar.gz tar -zxvf ibm-aspera-connect_4.1.0.46-linux_x86_64.tar.gz # Automatic installation sh ibm-aspera-connect_4.1.0.46-linux_x86_64.tar.gz echo 'PATH=~/.aspera/connect/bin/:$PATH' >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc
1. Manual download, that is, download under the graphical interface
[note] the data downloaded here is in fasta format, not pre formatted (i.e. Nr database built in advance)
The steps are:
(1) Log in NCBI official website
(2) Click Download
(3) Click FTP

(4) Enter the corresponding path: https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/db/FASTA/
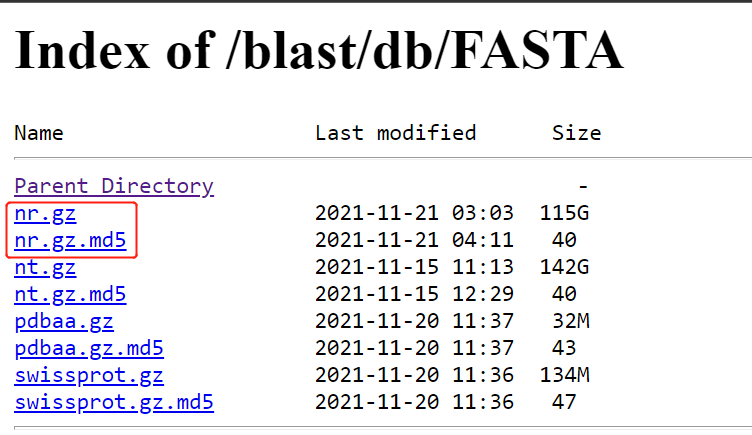
(5) Right click to copy nr.gz and nr.gz Link to MD5
(6) Select Xunlei and other tools to download
2. Command line interface download
1. aspera
1.1 download nr.gz
ascp -i ~/.aspera/connect/etc/asperaweb_id_dsa.openssh -l 200M -k 1 --overwrite=diff -QT anonftp@ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:blast/db/FASTA/nr.gz ./
# Description of parameters used:
-i # Use public key authentication and specify the private key file.
# The storage location of the key is generally ~ / aspera/connect/etc/
-l # Set the target transfer rate in Kbps. Default: 10000
# That is, set the maximum transmission rate
-k # The optional parameter is {0 | 1 | 2 | 3}, that is, breakpoint continuation, which is generally set to 1
# Enable resuming partially transferred files. (Default: 0). Please note that this must be specified for your first transfer; otherwise, it will not work for subsequent transfers.
# "- k 1 specific description": - k 1 if the transfer stops because of connection loss or other issues the K option calls the transfer to resume from where it left off her than restarting the entire transfer over
### Description of other parameters:
# 0 Always retransfer the entire file.
# 1 Check file attributes and resume if the current and original attributes match.
# 2 Check file attributes and do a sparse file checksum; resume if the current and original attributes/checksums match.
# 3 Check file attributes and do a full file checksum; resume if the current and original attributes/checksums match.
--overwrite=diff # The default setting is diff, which means that if the currently downloaded file is inconsistent with the previously downloaded file, it will be overwritten
-Q # Enable fair (-Q) or trickle (-QQ) transfer policy. Use the -l and -m to set the target and minimum rates.
-T # Disable encryption for maximum throughput.1.2 download the preformatted version
for i in {00..55}
do
echo "ascp -i ~/.aspera/connect/etc/asperaweb_id_dsa.openssh -l 200M -k 1 --overwrite=diff -QT anonftp@ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:/blast/db/nr.${i}.tar.gz ./" >> aspera.preformatted.nr.sh
echo "ascp -i ~/.aspera/connect/etc/asperaweb_id_dsa.openssh -l 200M -k 1 --overwrite=diff -QT anonftp@ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:/blast/db/nr.${i}.tar.gz.md5 ./" >> aspera.preformatted.nr.sh
done
ParaFly -c aspera.preformatted.nr.sh -CPU 1 &
# Check whether the downloaded database is complete
for i in {00..55};do md5sum -c nr.${i}.tar.gz.md5;done2. Download the built-in script of blast +
Version: version 2.12.0+
Download object: preformatted database
perl ~/biosoft/blast/ncbi-blast-2.12.0+/bin/update_blastdb.pl --blastdb_version 5 --decompress nr --source gcp --passive
# Description of parameters used:
--blastdb_version # Specify which BLAST database version to download (default: 5).
# Supported values: 4, 5
--decompress # Downloads, decompresses the archives in the current working directory, and deletes the downloaded archive to save disk space, while preserving the archive checksum files (default: false).
--source # to download BLAST databases from (default: auto-detect closest location). Supported values: ncbi, aws, or gcp.
--passive # Use passive FTP, useful when behind a firewall or working in the cloud (default: true).
# To disable passive FTP, configure this option as follows: --passive no3.wget Download
Download object: preformatted database
# website: https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/db/
# Write your own shell script to download
for i in {00..55}
do
echo "wget -c https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/db/v5/nr.${i}.tar.gz ./" >> preformatted.wget.nr.sh
echo "wget -c https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/db/v5/nr.${i}.tar.gz.md5 ./" >> preformatted.wget.nr.sh
done
ParaFly -c preformatted.wget.nr.sh -CPU 10 2>err &(2) Extracting taxid from corresponding species: Taking plants as an example
Software installation required:
# taxonkit conda install -c bioconda taxonkit # csvtk conda install csvtk
NCBI uses taxid to divide species, which forms the database NCBI Taxonomy.
1. Query the taxid of the corresponding species and groups
A. NCBI official website manual query method
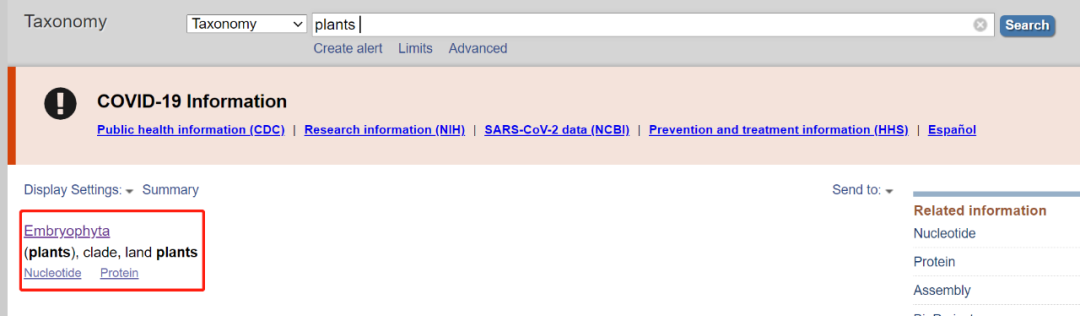
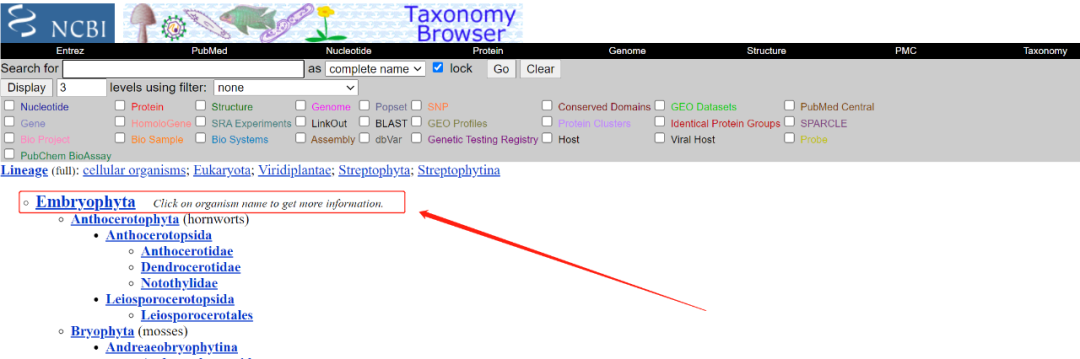
1. Enter the NCBI official website and select "Taxonomy" in the database

2. Enter "Plants" to get the corresponding query results (specifically land plants, i.e. terrestrial Plants. The green plant community covers a wider range)

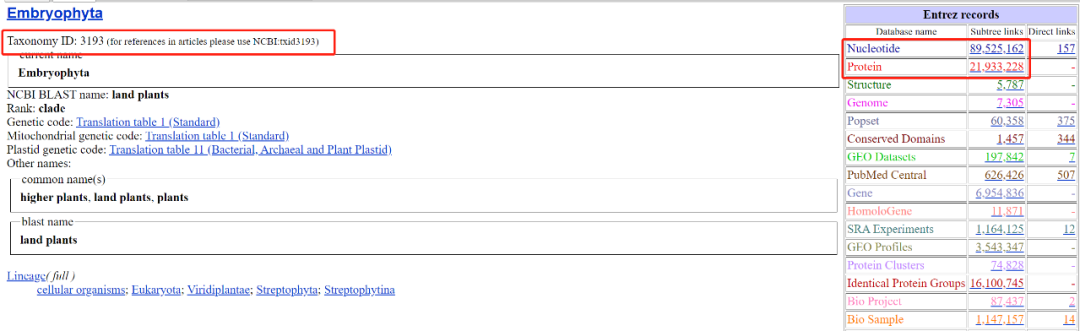
B. taxdump.tar.gz query
grep -P "\|\s+[pP]lant\w*\s*\|" ~/.taxonkit/names.dmp
C. taxonkit query
echo Embryophyta | taxonkit name2taxid --show-rank
2. Obtain the sequence contained in the corresponding species group (accessionID acquisition)
1. Manually download from NCBI official website
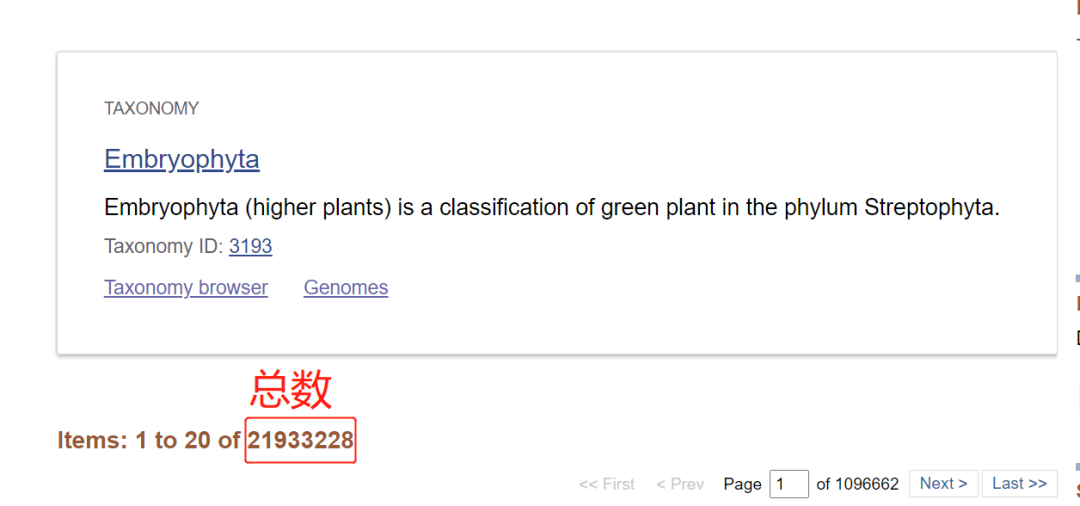
(1) Select "Protein" for the database. The query format is txidxxxxx [organization] or txidxxxxx [org].
[annotation] add "[]" to represent the whole to which the corresponding taxid belongs.
(2) The query results are as follows:
2. Use taxonkit to obtain the access ID of the corresponding species
NCBI classification data & taxi access ID conversion file needs to be downloaded
wget -c https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/taxonomy/taxdump.tar.gz wget -c https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/taxonomy/taxdump.tar.gz.md5 md5sum -c taxdump.tar.gz.md5 # Check whether the downloaded database is complete mkdir ~/.taxonkit tar zxf taxdump.tar.gz -C ~/.taxonkit wget -c https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/taxonomy/accession2taxid/prot.accession2taxid.gz wget -c https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/taxonomy/accession2taxid/prot.accession2taxid.gz.md5 md5sum -c prot.accession2taxid.gz.md5
# Get the taxids of the corresponding class group taxonkit list --ids 3193 --indent "" > plants.taxid.txt # Get the access ID of the corresponding class group pigz -dc prot.accession2taxid.gz | csvtk grep -t -f taxid -P plants.taxid.txt | csvtk cut -t -f accession.version,taxid | sed 1d > plant.acc2taxid.txt && cut -f 1 plant.acc2taxid.txt > plant.acc.txt &
3. Use the blast related script to obtain the access ID
To use blast's own script get_species_taxids.sh, to obtain the access ID of the corresponding species, you need to install the program edirect command lineutility in advance. The link to install manual is: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK179288/
get_species_taxids.sh -t 3193 > plants.blast.taxids.txt # After the above taxids list is obtained, the access ID can be obtained by combining csvtk
3. Construction of nr sub Library of corresponding species group
[annotation] the sub database is constructed here. Take the preformed NR database as an example
# Unzip the downloaded preformed NR database
for i in {00..55}
do
tar -zxvf nr.${i}.tar.gz -C ../nr_preformatted_20211122_decompress
done1.blastdb_ Building blast sub library with alias tool
blastdb_aliastool -seqidlist sequence.seq -db nr -out nr_plant -title nr_plant # sequence.seq is the access list of the corresponding class group
The result is an index file: nr_plant.pal.
2. Extract the corresponding group sequence and construct the local nr database sub database by ourselves
Method 1:
blastdbcmd -db nr -entry_batch sequence.seq -out - | pigz -c > blastdbcmd.nr.3193.fa.gz
Method 2:
# Extract all sequences in the preformed NR database
blastdbcmd -db nr -dbtype prot -entry all -outfmt "%f" -out - | pigz -c > nr.fa.gz
time cat <(echo) <(pigz -dc nr.fa.gz) \
| perl -e 'BEGIN{ $/ = "\n>"; <>; } while(<>){s/>$//; $i = index $_, "\n"; $h = substr $_, 0, $i; $s = substr $_, $i+1; if ($h !~ />/) { print ">$_"; next; }; $h = ">$h"; while($h =~ />([^ ]+ .+?) ?(?=>|$)/g){ $h1 = $1; $h1 =~ s/^\W+//; print ">$h1\n$s";} } ' \
| seqkit grep -f 3193.acc.txt -o nr.3193.fa.gz[interesting phenomenon]
After the extraction is completed, blastdbcmd. Is found nr.3193.fa.gz and nr.3193 fa. GZ has different file sizes (first 13G, last 4G). After checking the number of sequences, it is found that the number of sequences contained in the two result files is the same. The reason for the above results is the result extracted by the official software and there is too much redundant information in the sequence header.
seqkit stats blastdbcmd.nr.3193.fa.gz file format type num_seqs sum_len min_len avg_len max_len blastdbcmd.nr.3193.fa.gz FASTA Protein 19,326,820 7,670,152,256 6 396.9 23,040 seqkit stats nr.3193.fa.gz file format type num_seqs sum_len min_len avg_len max_len nr.3193.fa.gz FASTA Protein 19,326,820 7,670,152,256 6 396.9 23,040
If the downloaded nr.gz (fasta format), that is, the NR database is not built in advance, you need to use makeblastdb or diamond makedb locally to build the local database
reference material
[1] http://www.chenlianfu.com/?p=2691
[2] https://bioinf.shenwei.me/taxonkit/tutorial/
[2] https://www.burning.net.cn/article/article-59