Continuous check-in and receive gold coins
describe
User behavior log table tb_user_log
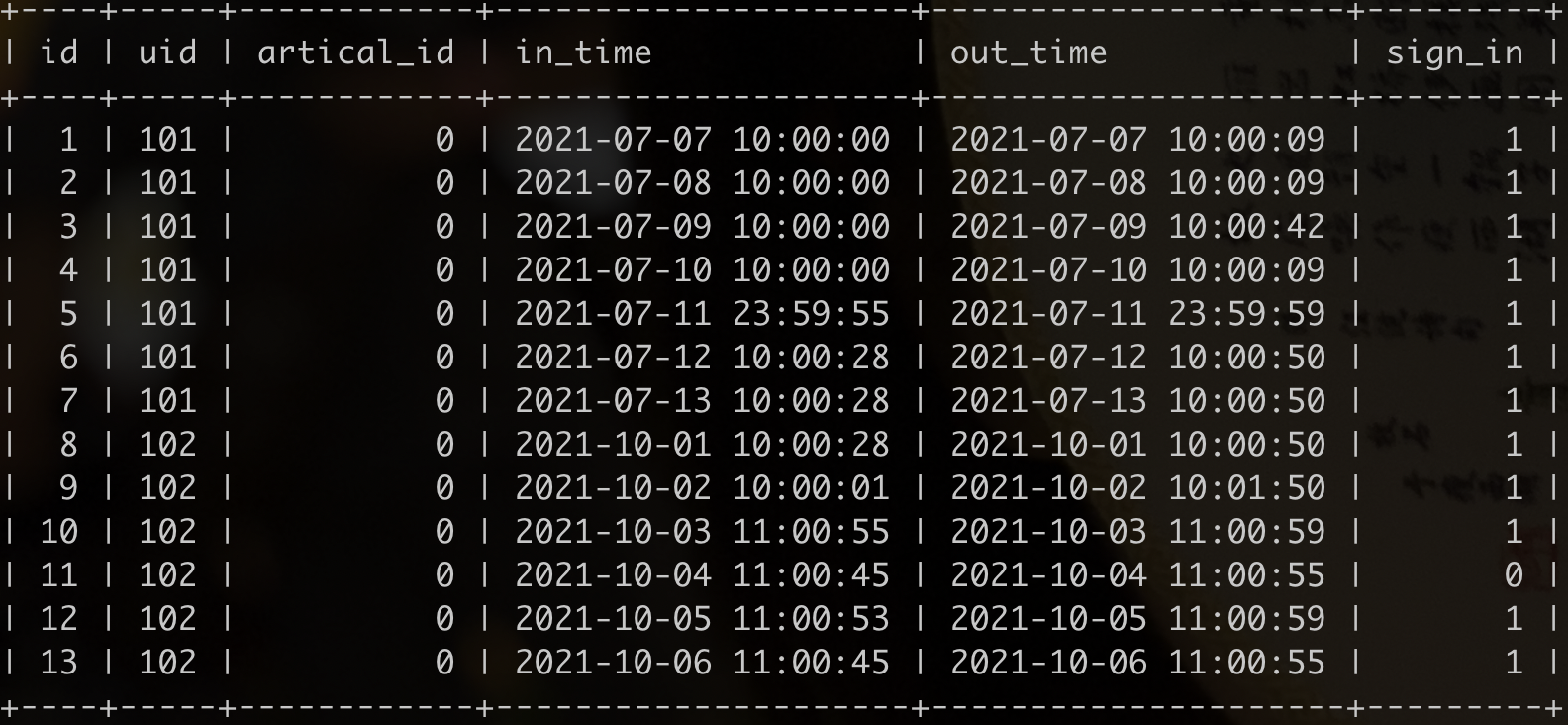
(uid - user ID, artistic_id - article ID, in_time - entry time, out_time - departure time, sign_in - check in or not)
Scenario Logic Description:
artical_id - article ID represents the ID of the article the user browses. In special cases, it is artistic_ ID - if the article ID is 0, it means that the user is on the non article content page (such as the list page, activity page, etc. in the App). Note: only artistic_ Sign when ID is 0_ In value is valid.
From 0:00 on July 7, 2021, users can receive 1 gold coin every day, and can start accumulating the number of check-in days. On the third and seventh days of continuous check-in, they can receive 2 and 6 additional gold coins respectively.
Every 7 consecutive days of check-in, the number of check-in days will be accumulated again (i.e. reset the number of check-in days: the eighth consecutive day of check-in will be recorded as the first day of a new round of check-in, and 1 gold coin will be received)
Question: calculate the number of gold coins each user has received each month since July 2021 (the activity ends at the end of October, and the check-in starting on November 1 will no longer receive gold coins). The results are sorted in ascending order by month and ID.
Note: if the check-in record is in_time - enter time and out_time - it's time to leave. It's only recorded as in_ The date corresponding to time has been signed in.
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS tb_user_log;
CREATE TABLE tb_user_log (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Self increasing ID',
uid INT NOT NULL COMMENT 'user ID',
artical_id INT NOT NULL COMMENT 'video ID',
in_time datetime COMMENT 'Entry time',
out_time datetime COMMENT 'Departure time',
sign_in TINYINT DEFAULT 0 COMMENT 'Check in'
) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_bin;
INSERT INTO tb_user_log(uid, artical_id, in_time, out_time, sign_in) VALUES
(101, 0, '2021-07-07 10:00:00', '2021-07-07 10:00:09', 1),
(101, 0, '2021-07-08 10:00:00', '2021-07-08 10:00:09', 1),
(101, 0, '2021-07-09 10:00:00', '2021-07-09 10:00:42', 1),
(101, 0, '2021-07-10 10:00:00', '2021-07-10 10:00:09', 1),
(101, 0, '2021-07-11 23:59:55', '2021-07-11 23:59:59', 1),
(101, 0, '2021-07-12 10:00:28', '2021-07-12 10:00:50', 1),
(101, 0, '2021-07-13 10:00:28', '2021-07-13 10:00:50', 1),
(102, 0, '2021-10-01 10:00:28', '2021-10-01 10:00:50', 1),
(102, 0, '2021-10-02 10:00:01', '2021-10-02 10:01:50', 1),
(102, 0, '2021-10-03 11:00:55', '2021-10-03 11:00:59', 1),
(102, 0, '2021-10-04 11:00:45', '2021-10-04 11:00:55', 0),
(102, 0, '2021-10-05 11:00:53', '2021-10-05 11:00:59', 1),
(102, 0, '2021-10-06 11:00:45', '2021-10-06 11:00:55', 1);
Topic analysis
A better way to think is to deduce the format of data you need step by step according to the results you need
- Ask for the total number of gold coins obtained during the check-in period of the activity. What I hope most is to obtain the number of gold coins obtained during the user's check-in every day, and then just group them according to ID and month, and sum them once, as shown in the figure
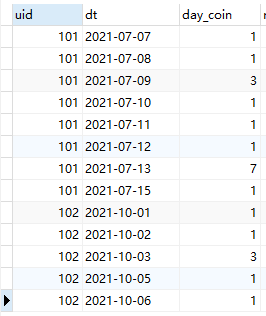
- If you want to get the number of gold coins you get when you check in every day, I must know that the user's check-in on that day is the first day of continuous check-in. After you get the number of days, it's very simple. Use case when to% 7 the number of days and see the remainder. The remainder is 3, and 3 were obtained on the same day. The remainder is 0, and 7 were obtained on the same day. The other is 1. As shown in the figure
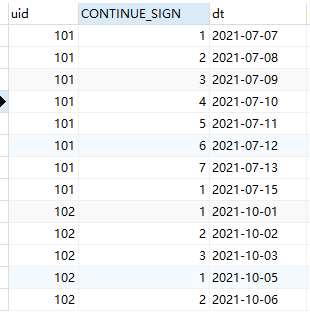
-
In fact, the train of thought has been clear. Seeking the number of consecutive check-in days is nothing more than a continuous problem
-
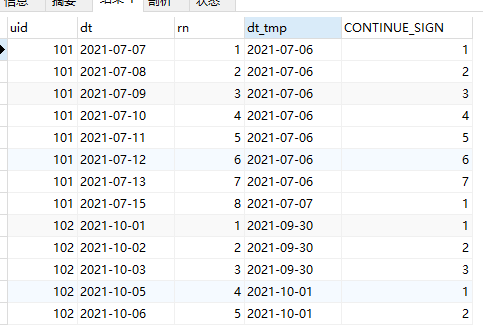
The core of the continuous problem is to use that the difference between the sorting number and the check-in date is equal. Because if it is continuous, the number is also increased by 1, and the date is also increased by 1.
-
As shown in the figure, * * * dt * * * is the sign in date, * * * dt_tmp * * * is the difference between the number and the check-in date. It can be found that No. 8 is disconnected from continuous check-in, so * * * dt_tmp * * * is different from the previous one
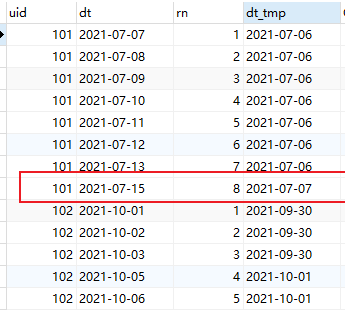
-
-
Then take dt_tmp and uid are grouped, and then * * * deny_ Rank * * * once, you can get the number of consecutive check-in days. Then the problem is solved.
Full SQL
WITH t1 AS( -- t1 The table filters out the data during the activity period, and in order to prevent multiple check-in activities in a day, distinct duplicate removal SELECT DISTINCT uid, DATE(in_time) dt, DENSE_RANK() over(PARTITION BY uid ORDER BY DATE(in_time)) rn -- number FROM tb_user_log WHERE DATE(in_time) BETWEEN '2021-07-07' AND '2021-10-31' AND artical_id = 0 AND sign_in = 1 ), t2 AS ( SELECT *, DATE_SUB(dt,INTERVAL rn day) dt_tmp, case DENSE_RANK() over(PARTITION BY DATE_SUB(dt,INTERVAL rn day),uid ORDER BY dt )%7 -- Renumber WHEN 3 THEN 3 WHEN 0 THEN 7 ELSE 1 END as day_coin -- The number of gold coins that the user should get when signing in that day FROM t1 ) SELECT uid,DATE_FORMAT(dt,'%Y%m') `month`, sum(day_coin) coin -- Total gold coins FROM t2 GROUP BY uid,DATE_FORMAT(dt,'%Y%m') ORDER BY DATE_FORMAT(dt,'%Y%m'),uid;