1. Get to know MySQL
When I first started learning java last year, I saw the video of crazy teacher. Now I integrate the notes I made before and publish it for your reference
javaEE: Enterprise java Web Development
Front end (page: display, data)
Background (connection point: connect to database JDBC, connect to the front end (control attempts to jump, and transfer data to the front end)
Database (save data, Txt, Excel, word)
Can only knock the code, learn the database well, and basically make a living
Operating system, data structure algorithm, a good programmer
Discrete mathematics, digital circuit, architecture, compiling principle + practical experience
1.1 why learn database
1. Job requirements
2. Now is the era of big data ~, and we can gain the world from the data
3. Forced demand: save data
4. Database is the core DBA of all software systems
1.2. What is a database
Database (DB,DataBase)
Concept: data warehouse, software, installed on the operating system (window, linux, mac), can store a large amount of data
1.3 database classification
Relational database: SQL
- MySql ,Qracle,Sqlrver,DB2,SQLlite
- Through the relationship between tables and between rows and columns
Non relational database NOSQL Not Only
- Redis,MongDB
- Non relational database, object storage, is determined by the attributes of the object itself
DBMS (database management system)
- Database management software, scientific and effective management of data, maintenance and acquisition of data
- MySQL, database management system
1.4 introduction to MySQL
Relational database management system
Open source database software
Small size, fast speed, low cost and low recruitment cost
1.4. Connect to database
Command connection
mysql -uroot -p password --Connect database
updete mysql.user set authentication_string=password('password')where user='root'and Host='localost';--Modify user name and password
flush privileges--Refresh permissions
-----------------------
All statements";"ending
show databases ---View all databases
user Database name ---view the database
show tables ----Check the name in the database table
describe Table name----Display the information of the table in the database
create database Database name--Create a database
exit--Exit connection
#
--Single-Line Comments
/*
multiline comment
*/
DDL database definition language
DML database operation language
DQL database query language
DCL database control language
2. Operation database
2.1. Operation database
1. Create database
CREATE DATABASE [IF NOT EXISTS] znb;
2. Delete database
DROP DATABASE [IF EXISTS] znb;
3. Use database
USE school
4. View database
SHOW DATABASES ;View all databases
2.2. Column type of database
numerical value
- tinyint very small data one byte
- smallint smaller data, two bytes
- mediumint medium size data three bytes
- Four standard bytes of int
- big larger data is eight bytes
- float floating point number four bytes
- double floating point number eight bytes (precision problem)
- decimal floating point numbers in string form are generally used in financial calculation
character string
- char string fixed size 0 ~ 255
- varchar variable String 0~65535 common String
- tinytext microtext 2 ^ 8-1
- Text text 2 ^ 16-1
Time and date
java,util.Date
- Date yyyy MM DD, date
- time hh: mm: ss time format
- Datetime yyyy MM DD HH: mm: ss the most commonly used time format
- The number of milliseconds of timestamp timestamp from 1970.1.1 to now is relatively common
- Year means year
null
- No value, unknown
- Do not use null operation, the result is null
2.3. Field attributes of database (key points)
unsign
- Unsigned integer
- The column declared cannot be declared negative
zerofill
- 0 fill
- Insufficient mantissa fill int (3) with 0, 5········ 005
Self increasing
- Add one to the previous one
- Usually set a unique main keyboard, which must be an integer
- You can set the number yourself
Non NULL not null
- If the setting is not empty, an error will be reported if the value is not filled in
default
- Set default values
- The default value of sex is male. If the value of this column is not specified, it is the default
expand
/*Each table must have the following fields id Primary key version Optimistic lock is_delete Pseudo deletion gmt_create Creation time gmt_uodate Modification time */
2.4. Create database table (key)
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `student` ( `id`INT(4) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Student number', `pwd` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL DEFAULT '***' COMMENT'password', `name` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'Zhang San' COMMENT 'full name', `sex` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'male' COMMENT 'Gender', `birthday` VARCHAR (20) NOT NULL COMMENT 'birthday', `address` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT'address', `emill` VARCHAR (30) NOT NULL COMMENT'mailbox', PRIMARY KEY(`id`) )ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
format
CREATE TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS]`Table name`
(
`Field name` type [attribute] [Indexes] [notes],
`Field name` type [attribute] [Indexes] [notes],
`Field name` type [attribute] [Indexes] [notes],
)
`Field name` type [attribute] [Indexes] [notes]
)[table type] [character set setting] [comment]
Common commands ```sql SHOW CREATE TABLE student--View the statement that created the table SHOW CREATE DATABASE school--View the statement that created the database DESC student--Displays the structure of the table
2.5 type of data sheet
---database engine--- /* INNODB Default use MYISAM Used in earlier years */
| INNODB | MYISAM | |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction support | support | I won't support it |
| Data row locking | support | I won't support it |
| Foreign key constraint | support | I won't support it |
| Full text index | I won't support it | support |
| Table space size | Larger, twice as large as myisam | less |
General use and operation
- MYISAM saves space and is fast
- INNODB has high security, transaction processing, multi table and multi-user operation
Where it exists in physical space
All database files are in the data directory
The essence is the storage of files!
Differences between Mysql engine and physical engine files
innoDB has only one * fm file in the database table
2.6 modification and deletion
modify
--Modify table name ALTER TABLE student RENAME AS student1 --Modify constraints ALTER TABLE student MODIFY age1 FLOAT(10) --Modify the attribute name of the table ALTER TABLE student CHANGE age1 age INT(10) --Delete table fields ALTER TABLE student DROP age
delete
DROP TABLE [IF EXISTS] teacher
It is best to add judgment to all creation and deletion to avoid mistakes
3. MySQL data management
3.1. Foreign keys
Method 1: add constraints when creating tables
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `student` ( `id`INT(4) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Student number', `pwd` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL DEFAULT '***' COMMENT'password', `name` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'Zhang San' COMMENT 'full name', `sex` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'male' COMMENT 'Gender', `birthday` VARCHAR (20) NOT NULL COMMENT 'birthday', `address` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT'address', `emill` VARCHAR (30) NOT NULL COMMENT'mailbox', `gradeid` INT(4) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Student's grade', PRIMARY KEY(`id`), KEY `FK_gradeid`(`gradeid`) , CONSTRAINT `FK_gradeid` FOREIGN KEY(`gradeid`) REFERENCES `grade`(`gradeid`) )ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
Method 2: add the table after it is created successfully
ALTER TABLE student ADD CONSTRAINT `FK_gradeid` FOREIGN KEY(`gradeid`) REFERENCES `grade`(`gradeid`);
3.2. DML language
- Insert
- update
- delete
3.3 add
insert
--Insert a statement
INSERT INTO `student` (`name`) VALUES ('Liu Shuilong')
--Insert multiple statements separated by English commas
INSERT INTO `student` (`name`,`sex`,`pwd`) VALUES
('Li Si','female','123154') ,('Wang Wu','female','1232154') ,
('Liu San','female','123154') ,('Zhao Si','female','12355154')
matters needing attention:
1. Fields can be omitted, but the following values should correspond one by one
2. Multiple protective devices can be inserted at the same time, and the VALUES after VALUES need to be separated
3.4 modification
update modify who (condition) set original value = new value
---With conditions UPDATE `student` SET `name`='idiot' WHERE id=3; ----All values will be modified without conditions UPDATE `student` SET `name`='idiot' ; --Multiple attributes are separated by commas UPDATE `student` SET `name`='idiot',`pwd`='5201314' WHERE id=3;
| Operator | meaning | Range | result |
|---|---|---|---|
| = | be equal to | 1=2 | false |
| < > or= | Not equal to | 5<>6 | true |
| > | |||
| >= | |||
| < | |||
| <= | |||
| BETWEEN ...and... | Closed interval | ||
| AND | you and me | ||
| OR | Me or you |
3.5 deletion
delete
delete from table name where condition
DELETE FROM `student` WHERE id= '4'
TRUNCATE command
Delete a database table, and the structure and index of the table remain unchanged
The difference between delete and truncate
-
Same: the database can be deleted without deleting the table structure
-
Different:
Reset counter
truncate does not affect transactions
delete problem, restart the database
-
innoDB auto increment column will restart (if it exists in memory, it will be lost after power failure)
-
MySAM continues from the previous increment (those existing in the file will not be lost)
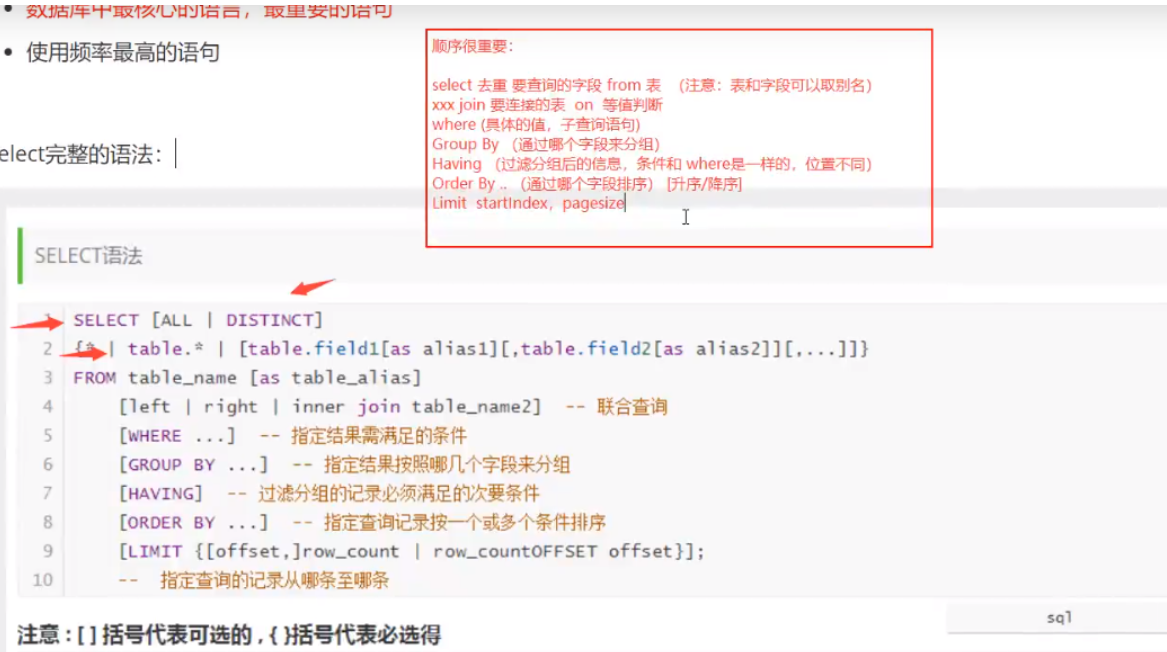
4. DQL query data (key)
4.1 DQL
(Data Query LANGUAGE)
- Most frequently used
select syntax
4.2 specifying query fields
--Change an alias to open, and the fields and table names can be changed SELECT `id` AS 'Student number',`name` AS 'full name',`9`AS 'Week 9',`10`AS 'Week 10',`11`AS 'Week 11',`12`AS 'Week 12',`13`AS 'Week Thirteen ', `14`AS 'week fourteen ',`15`AS 'Week 15',`16`AS 'Week 16' FROM `tykdk` --Query all people SELECT *FROM tykdk
De duplication distinct
Function: remove the duplicate data of the select result
select distinct `id`from student
Database columns (expressions)
SELECT VERSION()--View system version SELECT 100*3-1 AS Calculation results ---Used to calculate -----Ten points for all SELECT `studentno+1`AS After extra points FROM student
4.3 where conditional statement
Logical operation symbol
| operator | grammar | describe |
|---|---|---|
| and && | a and b a&&b | |
| or || | a or b a||b | |
| Not ! | not a !a |
Fuzzy query
| operator | grammar | describe |
|---|---|---|
| IS NULL | a is null | |
| IS NOT NULL | a is not null | |
| BETWEEN | a between b and c | |
| like | a like b | |
| in | a in (a1,a2...) |
--Between 0 and 1
SELECT *FROM tykdk WHERE daka BETWEEN 0 AND 1
--The last word is dragon. How many words are used“_",I don't know how to use it%
SELECT *FROM tykdk WHERE `name` LIKE ('%Loong')
--2018220111 And 2018220132
SELECT *FROM tykdk WHERE `id`IN('2018220111','2018220132')
4.4. Associated table query
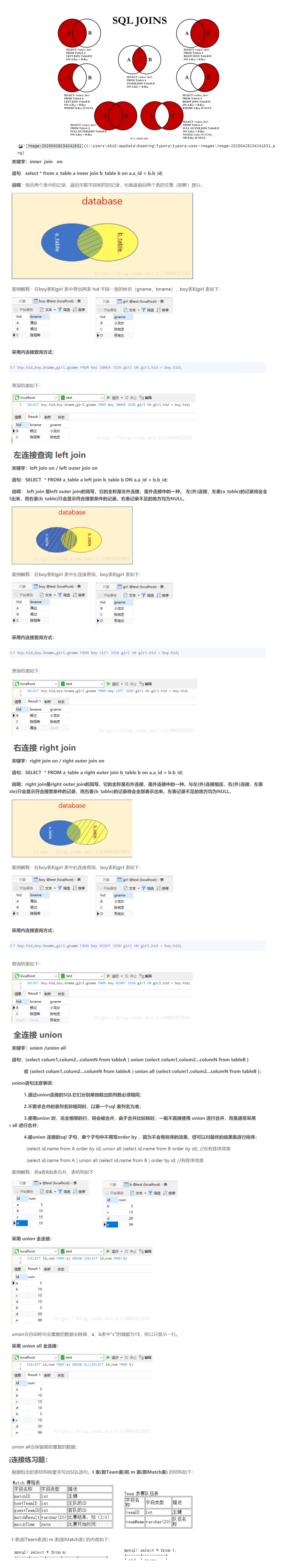
Self connection
As like as two peas, the table is connected to one's own table. The core is broken down into two identical tables.
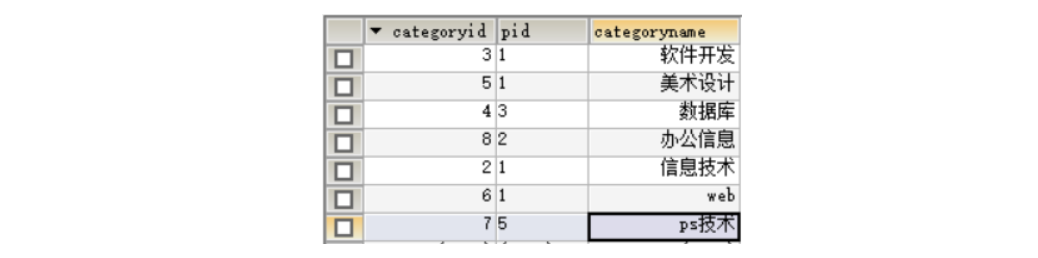
Parent class
| categoryid | categoryname |
|---|---|
| 2 | information technology |
| 3 | software development |
| 5 | Art design |
Subclass
| pid | categoryid | categoryname |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | database |
| 2 | 8 | Office information |
| 3 | 6 | web development |
| 5 | 7 | Art design |
Query the subclass corresponding to the parent class
| Parent class | Subclass |
|---|---|
| information technology | Office information |
| software development | database |
| software development | web development |
| Art design | ps Technology |
SELECT a.`categoryname` AS 'father',b.`categoryname`AS'son' FROM `test1`AS a,`test1`AS b WHERE a.`categoryid`=b.`pid`
4.5 paging and sorting
Sort:
SELECT *FROM `student` ORDER BY id DESC ----DESC In descending order, ASC sort----
paging
SELECT *FROM `tykdk` ORDER BY `id` DESC LIMIT 0,10
4.6 sub query
Where (this value is calculated)
Essence: nesting a query statement in a where statement)
SELECT `id`,`name`,`pwd` FROM `student` WHERE id=( SELECT `id` FROM `grade` WHERE `pwd`='***' )
4.7 grouping and filtering
[the external chain image transfer fails. The source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the image and upload it directly (img-jmiw02m4-1621309051592) (C: \ users \ ASUS \ appdata \ roaming \ typora user images \ image-20200429180334341. PNG)]
4.8. select section
5. MySQL function
5.1. Common functions
--mathematics
SELECT ABS(-55)
SELECT CEILING(22.995)
SELECT FLOOR(9.8)
SELECT RAND ()
SELECT SIGN(99)
--string
SELECT CHAR_LENGTH('Woge, you're paralyzed')
SELECT CONCAT('c','n','m')
SELECT INSERT ('I'm your father',1,2,'Fuck you')
SELECT LOWER('DSDDSADASF')
SELECT UPPER('sadasdasd')
SELECT INSTR ('zengnanbin','n')
SELECT REPLACE('You are a big fool','idiot','hybrid')
SELECT REPLACE(`name`,'Liu','cattle') FROM `student`
WHERE `name` LIKE ('Liu%')
---time
SELECT CURDATE()
SELECT NOW()
SELECT LOCALTIME()
SELECT SYSDATE()
SELECT YEAR(NOW())
SELECT USER()
SELECT VERSION()
5.2 aggregation function
[the external chain image transfer fails, and the source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the image and upload it directly (img-qrshglie-1621309051595) (C: \ users \ ASUS \ appdata \ roaming \ typora \ typora user images \ image-20200429174708478. PNG)]
SELECT COUNT(`name`)FROM `tykdk` SELECT SUM(`9`)AS 'the sum' FROM `tykdk` SELECT AVG (`9`)AS 'average'FROM `tykdk` SELECT MAX(`9`)AS 'Highest score'FROM `tykdk` SELECT MIN(`9`) AS 'Lowest score'FROM `tykdk`
5.3 MD5 encryption at database level
MD5 is irreversible. The specific MD5 password value is the same
The principle of MD5 cracking the website is that there is a dictionary behind it
UPDATE `testmd5` SET `pwd`='123456',`name`='Zhang San' WHERE id=1
INSERT INTO `testmd5` (`pwd`,`name`) VALUES ('123457','Li Si'),('1234557','Wang Wu')
UPDATE `testmd5` SET `pwd`=MD5(pwd) WHERE id=1
INSERT INTO `testmd5` VALUES ('4',MD5('123456'),'xm')
6. Business
Either all succeed or all fail
Transaction principle: ACID principle, atomicity, consistency, isolation and persistence (dirty reading, happy fantasy)
Reference blog: https://blog.csdn.net/dengjili/article/details/82468576
Atomicity
Either all succeed or all fail
Consistency
The data should be consistent before and after the transaction
Isolation
The isolation of transactions is that when multiple users access the database concurrently, the transactions opened by the database for each user cannot be disturbed by the operation data of other transactions, and multiple concurrent transactions should be isolated from each other.
Durability
Once the transaction is committed, it is irreversible and is persisted to the database
Isolation issues:

Execute transaction
---mysql Automatic transaction submission is enabled by default SET autocmmit=0--close SET autocommit=1--open ---Manual transaction processing SET autocommit =0--Turn off auto submit ---Transaction on START TRANSACTION --Mark the beginning of a transaction, starting from the beginning sql All in one transaction INSERT XX ---Commit: persistent (successful) commit --RollBACK -- ROLLBACK---Back to the way it was --End of transaction SET autocommit=1---Turn on auto submit --understand SAVEPOINT Save roll call---Set a transaction savepoint ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT Save roll call--Rollback to savepoint RELEASE SAVEPOINT Save roll call---Undo savepoint
SET autocommit =0;--Turn off auto submit START TRANSACTION --Start transaction UPDATE account1 SET money=money-2000 WHERE `id` = 1 UPDATE account1 SET money=money+2000 WHERE `id` = 2 COMMIT;--success ROLLBACK;--RollBACK SET autocommit=1;--Turn on auto submit
7. Index
7.1 classification of index
In a table, there can be only one primary key index and multiple unique indexes
-
Primary key (PRIMARY KEY)
Unique identifier. The primary key cannot be duplicate. There can only be one
-
Unique key
Avoid duplicate columns. Multiple columns can identify unique indexes
-
General index (FullText)
By default, it can be set with the keywords index and key
-
Full text index
Only in a specific database engine, mylsam
Fast positioning data
--Add a full-text index ALTER TABLE school.student ADD FULLTEXT INDEX `studentName` (`studentName`) ----EXPLAIN analysis sql Implementation of EXPLAIN SELECT *FROM student ---Non full text index EXPLAIN SELLCT * FROM student WHERE MATCH(studentName)AGAINST('Liu')
7.2 test index
---Insert 10 million pieces of data
DELIMITER $$
CREATE FUNCTION mock_data000()
RETURNS INT
BEGIN
DECLARE num INT DEFAULT 10000000;
DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;
WHILE i<num DO
INSERT INTO `app_user` (`name`,`phone`,`pwd`,`age`) VALUES
(CONCAT('user',i),FLOOR(CONCAT('18',RAND()*(999999999-100000000)+100000000)),UUID(),FLOOR(RAND()*100));
SET i=i+1;
END WHILE;
RETURN i;
END;
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM `app_user` WHERE `name`='User 854569'
----Insert Index
CREATE INDEX id_app_user_name ON `app_user`(`name`)
Before adding index
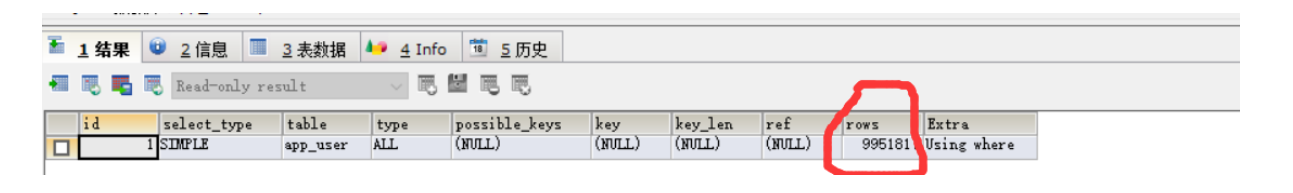
After adding index
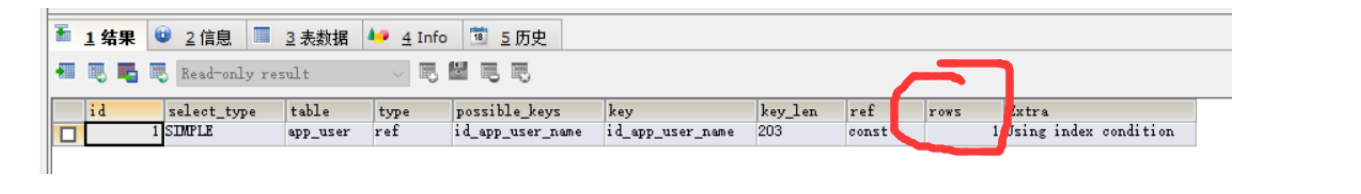
7.3 indexing principle
- The more indexes, the better
- Do not index data that changes frequently
- Don't add small data to the table
- It is usually added to the fields commonly used in query
Indexed data structure
Hash type index
Btree: the default data structure of InnoDB
reference material: https://blog.csdn.net/zq602316498/article/details/39323803
8. Database backup permissions and
8.1 user management
SQLyog visual management
User table: MySQL user
---Create user
CREATE USER kuangshen IDENTIFIED BY '123456'
---Change password (current account)
SET PASSWORD =PASSWORD('123456')
---Change password (specify account)
SET PASSWORD FOR kuangsheng =PASSWORD('123456')
---User authorization
GRANT ALL PRIVLEGES PN*.* TO kuangshen
--View permissions
SHOW GRANTS FOE kuangshen
--Revoke permission
REOMVE ALL PRIVILEGES OM*.* FROM kuangshen
8.2. Database backup
Why backup
- Ensure no data loss
- Data transfer
MySQL database backup method
- Copy physical files directly
- sqlyog visualization tool
- Command line export mysqldump command line use
--musqldummp -h Table name -u user name -p Password database table 1 database table 2.... >Import location --export mysqldump -hlocalhost -uroot -pehero000921 daka tykdk >D:a.sql --Import --In case of login, switch to the specified database --Import, login source D:/file.sql --No login mysql -u user -p Password database name<Backup files
Backup database to prevent data loss
Give the database to your friends and the sql file to bi people!
9. Standardize database design
9.1 why design
When the database is more complex, it needs to be designed
Poor database design:
- Lengthy data and waste of space
- Database insertion and deletion will be troublesome and abnormal
- Poor program performance
Good database design
- Save space
- Ensure integrity
- Convenient development
In software development, the design of database
- Analyze requirements
- Outline design
To design a database
-
Collect information and analyze requirements
User table (user login and logout, user's personal information, blogging, creating categories)
Classification table (article classification, who created it)
Article table (information of articles)
Comment form
Links (information)
User defined table (system information, a keyword)
Talk about the table (express your mood. id)
-
Identify the entity (implement the requirements to each field)
-
Identify relationships between entities
user ->blog
user->category
Attention: user - > User
Friend chain: links
Comment: user - > User blog
9.2 standardize database design
Why is there a paradigm
-
Duplicate information
-
Update exception
-
Insert exception
Unable to display information normally
-
Delete exception
Missing valid information
Three paradigms
First paradigm
Atomicity: ensure that each column cannot be further divided
Second norm paradigm
Premise: on the premise of meeting the first paradigm, each table represents only one information
Third paradigm
Premise: meet the first and second paradigm
Make sure that every column of data in the data table is directly related to the primary key, but not the primary key

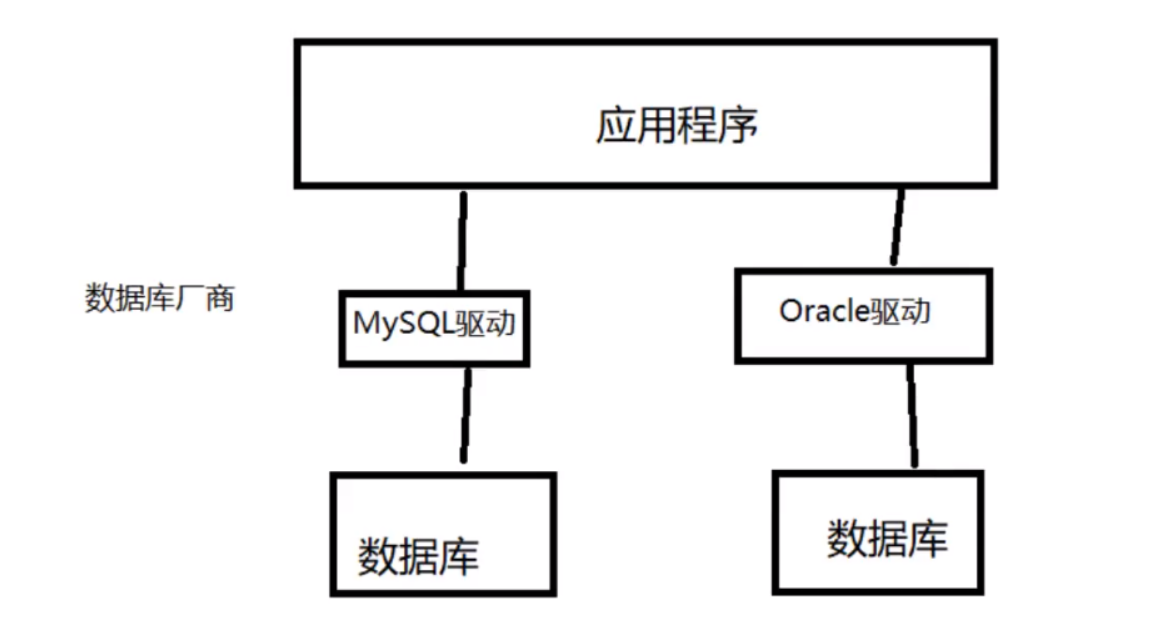
10,JDBC
10.1. Database driver
Driver: sound card, graphics card, database
10.2,JDBC
10.3. The first JDBC program
Create test database
1. Create a normal project
CREATE DATABASE `jdbcstudy`
CREATE TABLE users
(
`id` INT (4) PRIMARY KEY,
`name` VARCHAR(40),
`password` VARCHAR(40),
`birthday` DATE
);
INSERT INTO `users` (`id`,`name`,`password`,`birthday`)
VALUES ('1','Zhang San','123456','1999-02-02'),('2','Li Si','1234556','1999-08-02'),('3','Wang Wu','1288556','1998-02-15')
,('4','Zhao Liu','752156','1999-12-12')
2. Import database driver
package JDBC01;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//1. Load drive
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//fixed
//2. Connect user information and url
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true";
String username ="root";
String password="ehero000921";
//3. The Connection is successful, and the database object is Connection
Connection connection=DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//4. Execute sql object
Statement statement =connection.createStatement();
//5. The object executing sql executes sql
String sql="select * from users";
ResultSet rs=statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (rs.next())
{
System.out.print("id="+rs.getObject("id")+" ");
System.out.print("name="+rs.getObject("name")+" ");
System.out.print("password="+rs.getObject("password")+" ");
System.out.println("birthday="+rs.getObject("birthday"));
}
//6. Release the connection
rs.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
Step summary:
1. Load drive
2. Connect to the database DriverManager
3. Get the object Statement executing sql
4. Returned result set
5. Release the connection
DriverManager
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//Fixed writing
URL
String url ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true"
//mysql default 3306
//Protocol: / / host address: port number / database name? Parameter 1 & parameter 2 & parameter 3
Statement object executing SQL PrepareStatement object executing SQL
String sql="sekect * from users"; statement.executeQuery();//query statement.execute();//Execute any SQL statement.executeUpdate();//Update, insert, delete
ResultSet query result set: encapsulates all query results
Get the specified data type
resultset.getint();
resultset.getobject();
resultset.getDate();
...
//Pointer
resultset.beforFirst();//Move to first
resultset.afterLast();//Move to auto next
resultset.absolute(row)//Move to specified class
10.4 statement object
Configuration class
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true username=root password=ehero000921 ##It's best to write it in the src directory file. Pay attention to where it is written
Tool class
package JDBC01;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
public class jdbcutils {
private static String driver=null;
private static String url=null;
private static String username=null;
private static String password=null;
static{
try{
// InputStream in=jdbcutils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
InputStream in=jdbcutils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("JDBC01/db.properties");//That's good
Properties properties=new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driver =properties.getProperty("driver");
url =properties.getProperty("url");
username =properties.getProperty("username");
password =properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driver);
//The driver is loaded only once
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//Get connection
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException
{
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
}
//Release connection resources
public static void release(Connection conn,Statement st, ResultSet rs) throws SQLException
{
if(rs!=null)
{
rs.close();
}
if(st!=null)
{
st.close();
}
if(conn!=null)
{
conn.close();
}
}
}
code:
package JDBC01;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class testinsert {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection conn =null;
Statement st=null;
ResultSet rs=null;
try {
conn= jdbcutils.getConnection();
st=conn.createStatement();
String sql="INSERT INTO `users` (`id`,`name`,`password`,`birthday`)"
+ " VALUES ('9','Big fool 2','55201314','2000-12-11') ";
int i=st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(i>0)
{
System.out.println("Insert successful!");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
jdbcutils.release(conn, st, rs);
}
}
}
//Just change the sql
sql injection problem
There is a vulnerability in sql, which will cause it to be spliced
package JDBC01;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class sql {
public static void main(String[] args) {
sql.login(" 'or '1=1", "'or '1=1");
}
public static void login(String username,String password)
{
Connection conn=null;
Statement sta=null;
ResultSet re=null;
try {
conn= jdbcutils.getConnection();
sta=conn.createStatement();
String sql="SELECT * FROM `users` WHERE `name`='"+username+"' AND `password`='"+password+"'";
re=sta.executeQuery(sql);
while(re.next())
{
System.out.print(re.getString("name")+" ");
System.out.println(re.getString("password"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
10.5,PreparedStatement
increase
package JDBC01;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Date;
import com.mysql.fabric.xmlrpc.base.Data;
public class test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection con=null;
PreparedStatement pst=null;
try {
con=jdbcutils.getConnection();
String sql ="insert into users(id,name,password,birthday) values(?,?,?,?)";
pst=con.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setInt(1, 7);
pst.setString(2, "Fool");
pst.setString(3, "5201314888");
pst.setDate(4, new java.sql.Date(new Date().getTime()) );
int i=pst.executeUpdate();
if(i==1)
System.out.println("It's in");
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(pst!=null)
try {
pst.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(con!=null)
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
delete
package JDBC01;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection con=null;
PreparedStatement pst=null;
try {
con=jdbcutils.getConnection();
String sql="delete from users where id=? ";
pst=con.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setInt(1, 7);
int i=pst.executeUpdate();
if(i==1)
System.out.println("Deleted");
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
change
package JDBC01;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection con=null;
PreparedStatement pst=null;
try {
con=jdbcutils.getConnection();
String sql="update users set `name`='hybrid' where `id`=?";
pst=con.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setInt(1, 5);
int i=pst.executeUpdate();
if(i==1)
System.out.println("success");
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
delete
package JDBC01;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Date;
import com.mysql.fabric.xmlrpc.base.Data;
public class test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection con=null;
PreparedStatement pst=null;
ResultSet rs=null;
try {
con=jdbcutils.getConnection();
String sql="select * from `users` where id=?";
pst=con.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setInt(1, 2);
rs=pst.executeQuery();
while(rs.next())
{
System.out.println(rs.getInt("id"));
System.out.println(rs.getString("name"));
System.out.println(rs.getString("password"));
System.out.println(rs.getString("birthday"));
// System.out.println(rs.getDate(new java.sql.Date(new Date().getTime())));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
10.6. Use IDEA to connect to the database
10.7. Database connection pool
Database connection - execution complete - release
Connection is a waste of resources
Pooling Technology: prepare some resources in advance, and the connection is ready
----Open the door - salesman: wait - Service -
Number of common connections: 10
Minimum number of connections: 10
Minimum number of connections: 100 service maximum bearing limit
Waiting timeout: 100ms
Write a connection pool and implement an interface DateSource
Implementation of open source data source
DBCP
C3P0
Druid: Alibaba
After using these database connection pools, there is no need to write to the project connection pool in the project
DBCP