Mybatis-7.9
1. Introduction
1.1. What is Mybatis
- MyBatis is an excellent persistence layer framework
- It supports custom SQL, stored procedures, and advanced mapping
- MyBatis eliminates almost all JDBC code and the work of setting parameters and obtaining result sets
- MyBatis can configure and map primitive types, interfaces and Java POJO s (Plain Old Java Objects) to records in the database through simple XML or annotations
- Moved to Github in November 2013
How do I get Mybatis?
-
maven warehouse:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.2</version> </dependency> -
Github:
-
Chinese documents: https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html
1.2. Durable layer
Data persistence
-
Persistence is the process of transforming program data in persistent state and transient state
-
Memory: loss upon power failure
-
Database (jdbc), io file persistence
-
Life: refrigerate can.
Why persistence?
-
There are some objects that he can't lose.
-
Memory is too expensive
1.3. Durable layer
Dao layer, Service layer, Controller layer
- Code block that completes the persistence work
- The layer boundary is very obvious
1.4 why do you need Mybatis?
-
The helper program stores the data into the database.
-
convenient
-
Traditional JDBC code is too complex. simplify. Frame. Automation.
-
Not Mybatis. Easier to use. There is no distinction between high and low technology
-
advantage:
- Easy to learn
- flexible
- The separation of sql and code improves maintainability.
- Provide mapping labels to support the mapping of orm fields between objects and databases
- Provide object relationship mapping labels to support object relationship construction and maintenance
- Provide xml tags to support writing dynamic sql.
The most important point: many people use it!
Spring SpringMVC SpringBoot
2. The first Mybatis program
Idea: build environment – > Import Mybatis – > write code – > test!
2.1 construction environment
Build database
CREATE DATABASE `mybatis`;
USE `mybatis`;
CREATE TABLE `user`(
`id` INT(20) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
`name` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
`pwd` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL
)ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `user`(`id`,`name`,`pwd`) VALUES
(1,'Anan','123456'),
(2,'Zhang San','123456'),
(3,'Li Si','123456')
New project
-
Create a normal maven project
-
Delete src directory
-
Import maven dependencies
<!--Import dependency--> <dependencies> <!--mysql drive--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.47</version> </dependency> <!--mybatis--> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.2</version> </dependency> <!--junit--> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>
2.2. Create a module
- Write the core configuration file of mybatis
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!--configuration Core profile-->
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=true&userUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="20010223"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
</configuration>
- Write mybatis tool class
public class MybatisUtils {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
static {
try {
//The first step in using Mybotis: get the sqlsessionfactory object
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//Now that we have SqlSessionFactory, as the name suggests, we can get an instance of SqlSession from it.
//SqlSession provides all the methods required to execute SQL commands in the database.
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(){
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
}
2.3. Code writing
- Entity class
package com.Ananhyle.pojo;
//Entity class
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String pwd;
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String name, String pwd) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.pwd = pwd;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", pwd='" + pwd + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
- Dao interface
public interface UserDao {
List<User> getUserList();
}
- The interface implementation class is transformed from the original UserDaoImpl without a Mapper configuration file
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namespace=Bind a corresponding Dao/Mapper Interface-->
<mapper namespace="com.Ananhyle.dao.UserDao">
<!--select Query statement-->
<select id="getUserList" resultType="com.Ananhyle.pojo.User">
select * from mybatis.user
</select>
</mapper>
2.4 test
<!--stay build Medium configuration resources,To prevent the failure of resource export -->
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
Note:
org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException: Type interface com.Ananhyle.dao.UserDao is not known to the MapperRegistry.
What is Mapper Registry?
Register mappers in the core configuration file
- junit test
public class UserDaoTest {
@Test
public void test(){
//Step 1: get SqlSession object
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//Execute SQL
//Method 1: getMapper
UserDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);
List<User> userList = mapper.getUserList();
for (User user : userList){
System.out.println(user);
}
//Close SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
}
2.5 problems we may encounter:
1. The configuration file is not registered
2. Binding interface error
3. Wrong method name
4. Incorrect return type
5.Maven export resources
3,CRUD
3.1,namespace
The package name in the namespace should be consistent with the package name of Dao/mapper interface!
3.2,select
Select, query statement
- id: is the method name in the corresponding namespace;
- Resulttype: return value of SQL statement execution!
- parameterType: parameter type!
1. Write interface
//Query user by ID User getUserById(int id);
2. Write the sql statement in the corresponding mapper
<select id="getUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.Ananhyle.pojo.User">
select * from mybatis.user where id = #{id}
</select>
3. Test
@Test
public void getUserById(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = mapper.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
sqlSession.close();
}
3.3,Insert
<!--Properties in object,You can take it out directly-->
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="com.Ananhyle.pojo.User">
insert into mybatis.user (id, name, pwd) values (#{id},#{name},#{pwd});
</insert>
3.4,update
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="com.Ananhyle.pojo.User">
update mybatis.user set name=#{name},pwd=#{pwd} where id = #{id};
</update>
3.5,Delete
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="int">
delete from mybatis.user where id = #{id};
</delete>
3.6. Precautions
- Add, delete and modify transactions need to be submitted!
- Don't match the labels incorrectly
- resource binding mapper requires a path
- The program configuration file must conform to the specification
- NullPointerException, not registered with resource
- There is Chinese garbled code in the output xml file
- There is no export problem with maven resources
3.7 universal Map
Assuming that there are too many entity classes or tables, fields or parameters in the database, we should consider using Map!
//Omnipotent map int addUser2(Map<String,Object> map);
<!--Properties in object,You can take it out directly
transmit map of key
-->
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="map">
insert into mybatis.user (id, name, pwd) values (#{userid},#{userName},#{password});
</insert>
@Test
public void addUser2(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
Map<String ,Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("userid",5);
map.put("userName","Hello");
map.put("userWord","123456");
mapper.addUser2(map);
sqlSession.close();
}
Pass parameters from map and directly get the key from sql! [parameterType=“map”]
Object transfer parameters, you can directly get the attribute of the object in sql! [parameterType=“Object”]
If there is only one basic type parameter, you can get it directly in sql!
Use Map or annotation for multiple parameters!
3.8 thinking questions
How to write fuzzy query?
1. When executing java code, pass wildcard%%
List<User> userList = mapper.getUserLike("%Lee%");
2. Use wildcards in sql splicing!
select * from user where name like "%"#{value}"%"
4. Configuration resolution
4.1. Core configuration file
- mybatis-config.xml
- The MyBatis configuration file contains settings and attribute information that deeply affect MyBatis behavior.
-
configuration(Configuration) properties(Properties) settings(Settings) typeAliases(Type alias) typeHandlers(Type (processor) objectFactory(Object factory) plugins(Plug in) environments(Environment configuration) environment(Environment variables) transactionManager(Transaction manager) dataSource((data source) databaseIdProvider(Database (vendor ID) mappers(Mapper)
4.2. Environment variables
MyBatis can be configured to adapt to a variety of environments
However, remember that although multiple environments can be configured, only one environment can be selected for each SqlSessionFactory instance.
Learn to use configuration to adapt to a variety of environments
The default transaction manager of Mybatis is JDBC, and the connection pool is POOLED
4.3. Properties
These properties can be configured externally and can be replaced dynamically.
These properties can be configured either in a typical Java properties file or in a child element of the properties element. [db.properties]
Write a configuration file
db.properties
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=false&userUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8 username=root password=20010223
Import in core configuration file
<!--Import external profile-->
<properties resource="db.properties">
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="20010223"/>
</properties>
- External configuration files can be imported directly
- You can add some attribute configurations
- If two files have the same field, the external configuration file is preferred!
4.4 type aliases
- A type alias is a short name for a java type
- The meaning of existence is only to reduce the redundancy of class fully qualified names
<!--You can alias an entity class-->
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="com.Ananhyle.pojo.User" alias="User"/>
</typeAliases>
You can also specify a package name. MyBatis will search for the required Java beans under the package name, such as:
Scan the package of an entity class, and its default alias is the package name of this class, with the first letter in lowercase!
<!--You can alias an entity class-->
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.Ananhyle.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
The first method is used when there are few entity classes.
If there are many entity classes, the second one is recommended.
The first can be a DIY alias, but the second can't. If you have to change it, you need to add notes on the entity
@Alias("user")
public class User {}
4.5. Settings
These are extremely important tuning settings in MyBatis, which change the runtime behavior of MyBatis


4.6 other configurations
- Typehandlers
- Objectfactory (object factory)
- [plugins]
4.7 mappers
MapperRegistry: register and bind our Mapper file;
Mode 1:
<!--every last Mapper.XML All need to be in Mybotis Register in core profile!-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/Ananhyle/dao/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
Method 2: register with class file binding
<!--every last Mapper.XML All need to be in Mybotis Register in core profile!-->
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.Ananhyle.dao.UserMapper"/>
</mappers>
Note:
- Interface and its Mapper configuration file must have the same name!
- Interface and its Mapper configuration file must be in the same package!
Method 3: use scan package for injection binding
<!--every last Mapper.XML All need to be in Mybotis Register in core profile!-->
<mappers>
<package name="com.Ananhyle.dao"/>
</mappers>
Note:
- Interface and its Mapper configuration file must have the same name!
- Interface and its Mapper configuration file must be in the same package!
practice:
- Bringing a database configuration file into an external database
- Entity class alias
- Ensure the UserMapper interface and UserMapper XML changed to consistent! And put it under the same bag!
4.8 life cycle and scope
Life cycle, and scope, are crucial, thinking that incorrect use can lead to very serious concurrency problems.
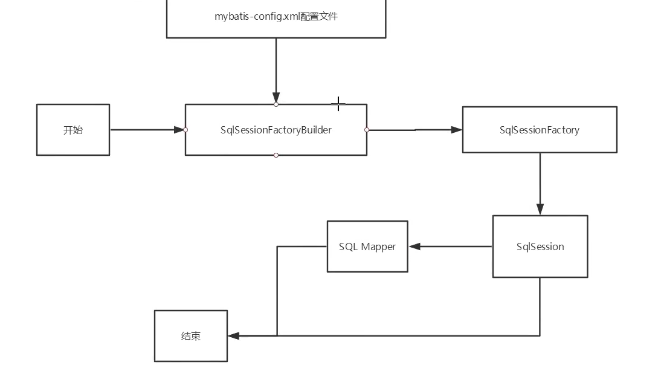
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder:
- Once SqlSessionFactory is created, it is no longer needed
- local variable
SqlSessionFactory:
-
To put it bluntly, it can be imagined that there is nothing in the database connection pool to discard it or recreate another instance.
-
Therefore, the best scope of SqlSessionFactory is the application scope.
-
The simplest is to use singleton mode or static singleton mode.
SqlSession
- A request to connect to the connection pool!
- The instance of SqlSession is not thread safe, so it cannot be shared, so its best scope is the request or method scope.
- You need to close it immediately after use, otherwise the resources will be occupied!
Each Mapper in this represents a specific business!
5. Solve the problem of inconsistency between attribute name and field name
5.1 problems
Fields in the database
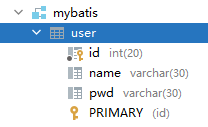
Create a new project and test the inconsistency of entity class fields before copying
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String password;
}
There is a problem with the test
//select * from mybatis.user where id = #{id}
//Type processor
//select id,name,pwd from mybatis.user where id = #{id}
resolvent:
- Alias
<select id="getUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.Ananhyle.pojo.User">
select id,name,pwd as password from mybatis.user where id = #{id}
</select>
5.2,resultMap
Result set mapping
id name pwd id name password
<!--Result set mapping-->
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<!--column Fields in the database, property Properties in entity classes-->
<result column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="pwd" property="password"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getUserById" resultMap="UserMap">
select * from mybatis.user where id = #{id}
</select>
- The resultMap element is the most important and powerful element in MyBatis
- The design idea of ResultMap is that there is no need to configure explicit result mapping for simple statements, but only need to describe their relationship for more complex statements.
- The best thing about ResultMap is that although you already know it well, you don't need to use it explicitly at all.
- If only the world were always that simple
6. Log
6.1 log factory
If an exception occurs in a database operation, we need to troubleshoot it. Log is the best assistant!
Once: South, debug
Now: log factory!
If a database appears

- SLF4J
- LOG4J [Master]
- LOG4J2
- JDK_LOGGING
- COMMONS_LOGGING
- STDOUT_LOGGING [mastering]
- NO_LOGGING
The specific log implementation used in Mybatis is set in settings!
STDOUT_LOGGING standard log output
In the mybatis core file, configure our logs!
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
</settings>
6.2,Log4j
What is Log4j?
- Log4j yes Apache By using Log4j, we can control the destination of log information delivery Console , documents GUI assembly
- We can also control the output format of each log;
- By defining the level of each log information, we can control the log generation process in more detail
- adopt configuration file To flexibly configure without modifying the application code
1. Import the package of log4j first
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
2,log4j.properties
log4j.properties
#Output the log information with the level of DEBUG to the console and file destinations
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG,console,file
#Settings related to console output
log4j.appender.console=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.console.Target=System.out
log4j.appender.console.Threshold=DEBUG
log4j.appender.console.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern=[%c]-%m%n
#Configuration related to file output
log4j.appender.file=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.file.File=./log/Ananhyle.log
log4j.appender.file.MaxFileSize=10mb
log4j.appender.file.Threshold=DEBUG
log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=[%p][%d{yy-MM-dd}[%c]%m%n
#Log output level
log4j.logger.org.mybatis=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.Statement=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.ResultSet=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.PreparedStatement=DEBUG
3. Configure log4j as the implementation of log
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value=""/>
</settings>
4. Use of log4j!, Run the query directly
Simple use
1. In the class to use Log4j, import the package import org apache. Log4j. Logger;
2. Log object. The parameter is the class of the current class
static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(UserDaoTest.class);
3. Log level
logger.info("info:Entered testLog4j");
logger.debug("debug:Entered testLog4j");
logger.error("error:Entered testLog4j");
7. Pagination
Think: why pagination?
- Reduce data processing
7.1. Use Limit paging
Paging with Limit
grammar:SELECT * from user limit startIndex.pageSize;
Pagination using Mybatis, core SQL
1. Interface
//paging List<User> getUserByLimit(Map<String,Integer> map);
2.Mapper.XML
<!--paging-->
<select id="getUserByLimit" parameterType="map" resultMap="UserMap">
select * from mybatis.user limit #{startIndex},#{pageSize}
</select>
3. Test
@Test
public void getUserByLimit(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("startIndex",1);
map.put("pageSize",2);
List<User> userList = mapper.getUserByLimit(map);
for (User user : userList){
System.out.println(user);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
7.2 rowboundaries paging
No longer use SQL for paging
1. Interface
//Pagination 2 List<User> getUserByRowBounds();
2.mapper.xml
<!--Pagination 2-->
<select id="getUserByRowBounds" resultMap="UserMap">
select * from mybatis.user
</select>
3. test
@Test
public void getUserByRowBounds(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//RowBounds implementation
RowBounds rowBounds = new RowBounds(1, 2);
//Paging through Java code level
List<User> userList = sqlSession.selectList("com.Ananhyle.dao.UserMapper.getUserByRowBounds",null,rowBounds);
for (User user : userList) {
System.out.println(user);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
7.3 paging plug-in
Just understand. If the company's architects say they want to use it in the future, you need to know what it is!
8. Using annotation development
8.1 interface oriented programming
·Everyone has studied object-oriented programming and interface before, but in real development, we often choose interface oriented programming
-Root cause: decoupling, expandable, improved reuse. In layered development, the upper layer does not care about the specific implementation. Everyone abides by common standards, making the development easier and more standardized
-In an object-oriented system, various functions of the system are completed by many different objects. In this case, how each object implements itself is not so important to system designers;
-The cooperative relationship between various objects has become the key of system design. From the communication between different classes to the interaction between modules, we should focus on it at the beginning of system design, which is also the main work of system design. Interface oriented programming means programming according to this idea.
Understanding of interfaces
·From the level of understanding, the interface should be the separation of definition (specification, constraint) and Implementation (the principle of separation of name and reality).
·The interface itself reflects the system designer's abstract understanding of the system.
-There shall be two types of interfaces
- the first type is the abstraction of an individual, which can correspond to an abstract class;
- the second type is the abstraction of an aspect of an individual, that is, forming an abstract interface;
·An individual may have multiple Abstract faces. Abstract body and abstract surface are different.
Three oriented differences
-Object - oriented means that when we need to consider a problem, we take the object as the unit and consider its attributes and methods
-Process oriented means that when we consider a problem, we consider its implementation in a specific process (transaction process)
-Interface design and non interface design are aimed at reuse technology, and object-oriented (process) is not a problem It is more reflected in the overall architecture of the system
8.2 development using annotations
1. Annotation is implemented on the interface
@Select("select * from user")
List<User> getUsers();
2. You need to bind the interface in the core configuration file again!
<!--Binding interface-->
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.Ananhyle.dao.UserMapper"/>
</mappers>
3. Test
Essence: reflection mechanism implementation
Bottom layer: dynamic agent!
Mybatis detailed execution process!
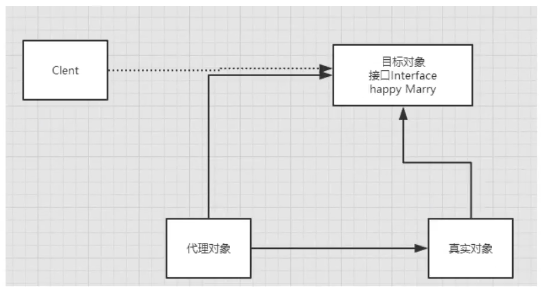
8.3,CRUD
We can automatically commit transactions when the tool class is created!
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(){
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
}
Write the interface and add comments
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user")
List<User> getUsers();
//Method has multiple parameters. All parameters must be preceded by @ Param("id") annotation
@Select("select * from user where id = #{id}")
User getUserByID(@Param("id") int id);
@Insert("insert into user(id,name,pwd) values (#{id},#{name},#{password})")
int addUser(User user);
@Update("update user set name=#{name},pwd=#{password} where id = #{id}")
int updateUser(User user);
@Delete("delete from user where id = #{id}")
int deleteUser(@Param("id") int id);
}
Test class
[Note: we must bind the interface registration to our core configuration file!]
8.4 notes on @ Param()
- Parameters of basic type or String type need to be added
- Reference types do not need to be added
- If there is only one basic type, it can be ignored, but it is recommended that everyone add it
- What we refer to in SQL is the attribute name set in @ Param()!
#{} ${} difference
9,Lombok
Project Lombok is a java library that automatically plugs into your editor and build tools, spicing up your java. Never write another getter or equals method again, with one annotation your class has a fully featured builder, Automate your logging variables, and much more.
- java library
- plugs
- build tools
- with one annotation your class
Use steps:
1. Install Lombok plug-in in IDEA!
2. Import the jar package of lombok in the project
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.projectlombok/lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.10</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
3. Annotate the entity class!
@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor
@Getter and @Setter *** @FieldNameConstants @ToString *** @EqualsAndHashCode *** @AllArgsConstructor *** , @RequiredArgsConstructor and @NoArgsConstructor *** @Log, @Log4j, @Log4j2, @Slf4j, @XSlf4j, @CommonsLog, @JBossLog, @Flogger, @CustomLog @Data *** @Builder @SuperBuilder @Singular @Delegate @Value @Accessors *** @Wither @With @SneakyThrows
explain:
@Data: Nonparametric structure, get,set,tostring,hashcode, equals @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor
10. Many to one processing
-
Multiple students correspond to one teacher
-
For the students, associate... Multiple students, associate a teacher [many to one]
-
For teachers, a collection, a teacher, has many students [one to many]
SQL
CREATE TABLE `teacher` (
`id` INT(10) NOT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
INSERT INTO teacher(`id`, `name`) VALUES (1, 'Miss Qin');
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` INT(10) NOT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
`tid` INT(10) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `fktid` (`tid`),
CONSTRAINT `fktid` FOREIGN KEY (`tid`) REFERENCES `teacher` (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
INSERT INTO `student` (`id`, `name`, `tid`) VALUES (1, 'Xiao Ming', 1);
INSERT INTO `student` (`id`, `name`, `tid`) VALUES (2, 'Xiao Hong', 1);
INSERT INTO `student` (`id`, `name`, `tid`) VALUES (3, 'Xiao Zhang', 1);
INSERT INTO `student` (`id`, `name`, `tid`) VALUES (4, 'petty thief', 1);
INSERT INTO `student` (`id`, `name`, `tid`) VALUES (5, 'Xiao Wang', 1);
Test environment construction
- Import lombok
- New entity class Teacher,Student
- Establish Mapper interface
- Create Mapper,XML file
- Bind and register our Mapper interface or file in the core configuration file! [there are many ways to choose]
- Test whether the query is successful!
Nested processing by query
<!--
thinking:
1.Query all student information
2.According to the student's tid, Find the corresponding teacher!
-->
<select id="getStudent" resultMap="StudentTeacher">
select * from student;
</select>
<resultMap id="StudentTeacher" type="Student">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<!--Complex properties,We need to deal with it separately
object: association
aggregate: collection
-->
<association property="teacher" column="tid" javaType="Teacher" select="getTeacher"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getTeacher" resultType="Teacher">
select * from teacher where id = #{id};
</select>
Nested processing according to results
<!--Nested processing according to results-->
<select id="getStudent2" resultMap="StudentTeacher2">
select s.id sid,s.name sname,t.name tname
from student s,teacher t
where s.tid = t.id;
</select>
<resultMap id="StudentTeacher2" type="Student">
<result property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<association property="teacher" javaType="Teacher">
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
Review the Mysql many to one query method:
- Subquery
- Join table query
11. One to many processing
For example: a teacher has multiple students!
For teachers, it is a one to many relationship!
Environment construction
1. The environment construction is the same as just now
Entity class
@Data
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private int tid;
}
@Data
public class Teacher {
private int id;
private String name;
//A teacher has more than one student
private List<Student> students;
}
Nested processing according to results
<!--Nested query by result-->
<select id="getTeacher" resultMap="TeacherStudent">
select s.id sid, s.name sname, t.name tname, t.id tid
from student s,teacher t
where s.tid = t.id and t.id = #{tid}
</select>
<resultMap id="TeacherStudent" type="Teacher">
<result property="id" column="tid"/>
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
<!--Complex properties,We need to deal with it separately
object: association
aggregate: collection
javaType="" Specifies the type of the property;
Generic information in the collection,We use ofType obtain
-->
<collection property="students" ofType="Student">
<result property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<result property="tid" column="tid"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
Nested processing by query
<select id="getTeacher2" resultMap="TeacherStudent2">
select * from mybatis.teacher where id = #{tid}
</select>
<resultMap id="TeacherStudent2" type="Teacher">
<collection property="students" javaType="ArrayList" ofType="Student" select="getStudentByTeacherId" column="id"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getStudentByTeacherId" resultType="Student">
select * from mybatis.student where tid = #{tid}
</select>
Summary
- association - association [many to one]
- Set - collection [one to many]
- javaType & ofType
- JavaType is used to specify the type of attribute in the entity class
- ofType is used to specify the pojo type mapped to List or collection, and the constraint type in generic type!
Note:
- Ensure the readability of SQL and make it easy to understand as much as possible
- Note the problem of attribute names and fields in one to many and many to one!
- If the problem is difficult to troubleshoot, log can be used. Log4j is recommended
Interview frequency
- Mysql engine
- InnoDB underlying principle
- Indexes
- Index optimization!
12. Dynamic SQL
What is dynamic SQL: dynamic SQL refers to generating different SQL statements according to different conditions
MyBatis 3 Most of the previous elements have been replaced, and the element types have been greatly simplified. Now there are fewer element types to learn than half of the original ones. if choose (when, otherwise) trim (where, set) foreach
Build environment
CREATE TABLE `blog`(
`id` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Blog id',
`title` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Blog title',
`author` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Blogger',
`create_time` DATETIME NOT NULL COMMENT 'Creation time',
`views` INT(30) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Views'
)ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
Create a basic project
1. Guide Package
2. Prepare configuration file
3. Write entity class
@Data
public class Blog {
private int id;
private String title;
private String author;
private Date date;
private int views;
}
4. Write entity classes corresponding to Mapper interface and Mapper XML file
IF
<select id="queryBlogIF" parameterType="map" resultType="blog">
select * from mybatis.blog where 1=1
<if test="title != null">
and title = #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
</if>
</select>
choose(when,otherwise)
<select id="queryBlogChoose" parameterType="map" resultType="blog">
select * from mybatis.blog
<where>
<choose>
<when test="title != null">
title = #{title}
</when>
<when test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
</when>
<otherwise>
and views = #{views}
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
time(where,set)
select * from mybatis.blog
<where>
<if test="title != null">
title = #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
</if>
</where>
<update id="updateBlog" parameterType="map">
update mybatis.blog
<set>
<if test="title != null">
title = #{title},
</if>
<if test="author != null">
author = #{author}
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>
The so-called dynamic SQL is still an SQL statement in essence, but we can execute a logical code at the SQL level
if
where , set , choose , when
SQL fragment
Sometimes, we may extract some functions for reuse!
1. Extract common parts using SQL Tags
<sql id="if-title-author">
<if test="title != null">
title = #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
</if>
</sql>
2. Use the Include tag reference where necessary
<select id="queryBlogIF" parameterType="map" resultType="blog">
select * from mybatis.blog
<where>
<include refid="if-title-author"></include>
</where>
</select>
matters needing attention:
- It is best to define SQL fragments based on a single table
- Do not have a where tag
Foreach
select * from user where 1=1 and
<foreach item="id" collection="ids" open="(" separator="or" close=")">
#{item}
</foreach>
(id=1 or id=2 or id=3)
<!--
select * from mybatis.blog where 1=1 and (id=1 or id=2 or id=3)
We are now passing on a universal message map,this map A collection can exist in!
-->
<select id="queryBlogForeach" parameterType="map" resultType="blog">
select * from mybatis.blog
<where>
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="and (" close=")" separator="or">
id = #{id}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
Dynamic SQL is splicing SQL statements. We just need to ensure the correctness of SQL and arrange and combine them according to the SQL format
Recommendations:
- Now write a complete SQL in Mysql, and then modify it accordingly to become our dynamic SQL, which can be used for general purpose!
13. Cache
13.1 introduction
query : Connect to database , Resource consumption! Results of a query,Give him a temporary place where he can get it directly! -->Memory : cache When we query the same data again, we directly go to the cache instead of the database
1. What is Cache?
-
There is temporary data in memory.
-
Put the data frequently queried by users in the cache (memory), and users do not need to query from the disk (relational database data file) but from the cache to query the data, so as to improve the query efficiency and solve the performance problem of high concurrency system.
2. Why cache?.
Reduce the number of interactions with the database, reduce system overhead and improve system efficiency.
3. What kind of data can be cached?.
Frequently queried and infrequently changed data. [cache can be used]
13.2. Mybatis cache
-
MyBatis includes a very powerful query caching feature, which can easily customize and configure the cache. Caching can greatly improve query efficiency.
-
Two levels of cache are defined by default in MyBatis system: L1 cache and L2 cache
- By default, only L1 cache is on. (SqlSession level cache, also known as local cache)
- L2 caching needs to be manually enabled and configured, he said, based on namespace level caching
- In order to improve scalability, MyBatis defines the Cache interface Cache. We can customize the L2 Cache by implementing the Cache interface
13.3. L1 cache
- The first level cache is also called local cache. sqlSession
- The data queried during the same session with the database will be placed in the local cache.
- In the future, if you need the same data, you can get it directly from the cache. You don't have to query the database again;
Test steps:
1. Open log!
2. The test queries the same record twice in a session
3. View log output
Cache invalidation:
1. Adding, deleting and modifying may change the original data, so the cache will be refreshed!
2. Query different mapper xml
3. Query different things
4. Manually clean up the cache!
Summary: the L1 cache is enabled by default and is only valid in one sqlSession, that is, the interval from getting the connection to closing the connection!
The first level cache is equivalent to a Map.
13.4 L2 cache
- L2 cache is also called global cache. The scope of L1 cache is too low, so L2 cache was born
- Based on the namespace level cache, a namespace corresponds to a L2 cache;
- Working mechanism
- When a session queries a piece of data, the data will be placed in the first level cache of the current session;
- If the current session is closed, the L1 cache corresponding to the session is gone; But what we want is that the session is closed and the data in the L1 cache is saved to the L2 cache
- The new session query information can get the content from the L2 cache;
- The data found by different mapper s will be placed in their corresponding cache (map);
Steps:
1. Turn on global cache
<!--Explicitly turn on global cache--> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
2. Where you want to use L2 cache Mapper Middle opening
<!--At present Mapper.xml Using L2 cache in-->
<cache/>
You can also customize parameters
<!--At present Mapper.xml Using L2 cache in-->
<cache eviction="FIFO"
flushInterval="60000"
size="512"
readOnly="true"/>
3. test
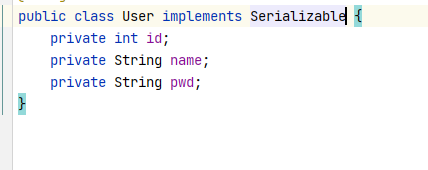
1. Problem: we need to serialize the entity class! Otherwise, an error will be reported!
Caused by: java.io.NotSerializableException: com.Ananhyle.pojo.User
Open in app
<!--At present Mapper.xml Using L2 cache in-->
<cache/>
You can also customize parameters
<!--At present Mapper.xml Using L2 cache in-->
<cache eviction="FIFO"
flushInterval="60000"
size="512"
readOnly="true"/>
3. test
1. Problem: we need to serialize the entity class! Otherwise, an error will be reported!
Caused by: java.io.NotSerializableException: com.Ananhyle.pojo.User
13.5 summary:
- As long as the L2 cache is enabled, it is valid under the same Mapper
- All data will be put in the first level cache first;
- Only when the session is submitted or closed will it be submitted to the L2 cache!
13.6 cache principle:
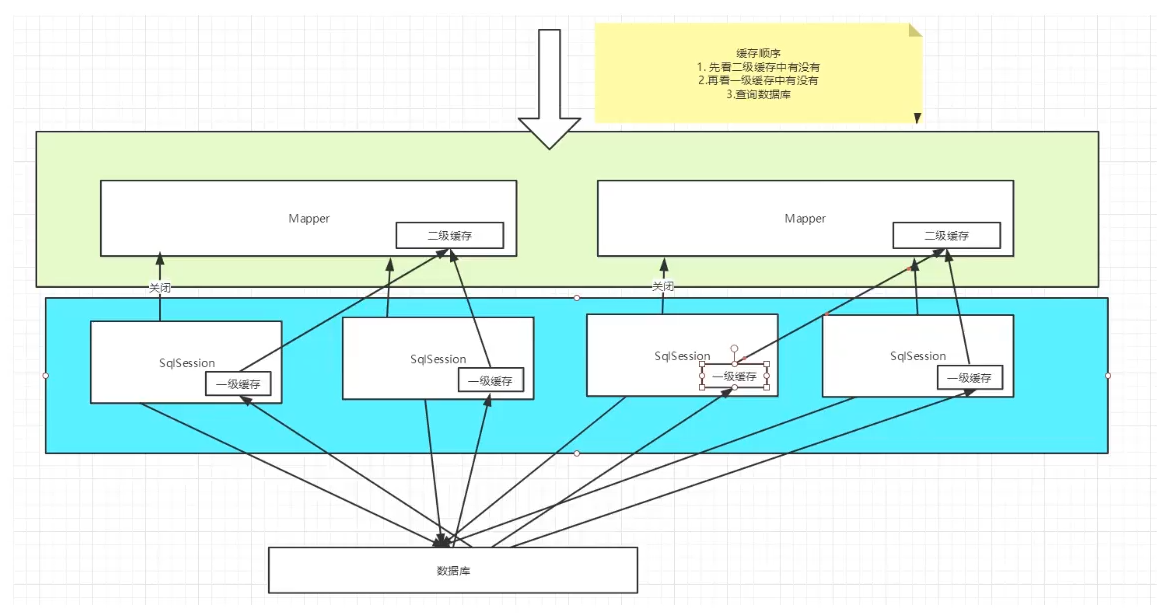
13.7 user defined cache ehcache
Ehcache Is a widely used open source Java Distributed cache. Mainly for general cache
To use ehcache in the program, you must first import the package!
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis.caches/mybatis-ehcache -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.caches</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</dependency>
Specify our ehcache cache implementation in mapper!
<!--At present Mapper.xml Using L2 cache in--> <cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
ehcache.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd"
updateCheck="false">
<diskStore path="./tmpdir/Tmp_EhCache"/>
<defaultCache
eternal="false"
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
overflowToDisk="false"
diskPersistent="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="1800"
timeToLiveSeconds="259200"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
<cache
name="cloud_user"
eternal="false"
maxElementsInMemory="5000"
overflowToDisk="false"
diskPersistent="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="1800"
timeToLiveSeconds="1800"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
</ehcache>